APHG Unit 1: Thinking Geographically
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Situation (or relative location)
The location of a place in relation to other places or objects
“It’s down past the courthouse, on Locust Street, after the third traffic light..”
Absolute Location
Description of the position of a place in a way that never changes. such as geographic coordinates of latitude and longitude
Assimilation
The process by which a group’s cultural features are altered to resemble those of another group
Acculturation
The process of changes in culture that result from the meeting of two groups, each of which retains distinct cultural features
Taking small pieces from one culture while keeping the original one
Syncretism
The combing of elements of two groups into a new cultural feature
Behavioral geography
An approach to human geography that emphasizes the importance of understanding the psychological basis for individual human actions in space
Focus on human behavior and decision-making in relation to the amount of space
Cartogram
A map in which the projection and scale are distorted in order to convey the information of a variable
Cartography
The science of making maps
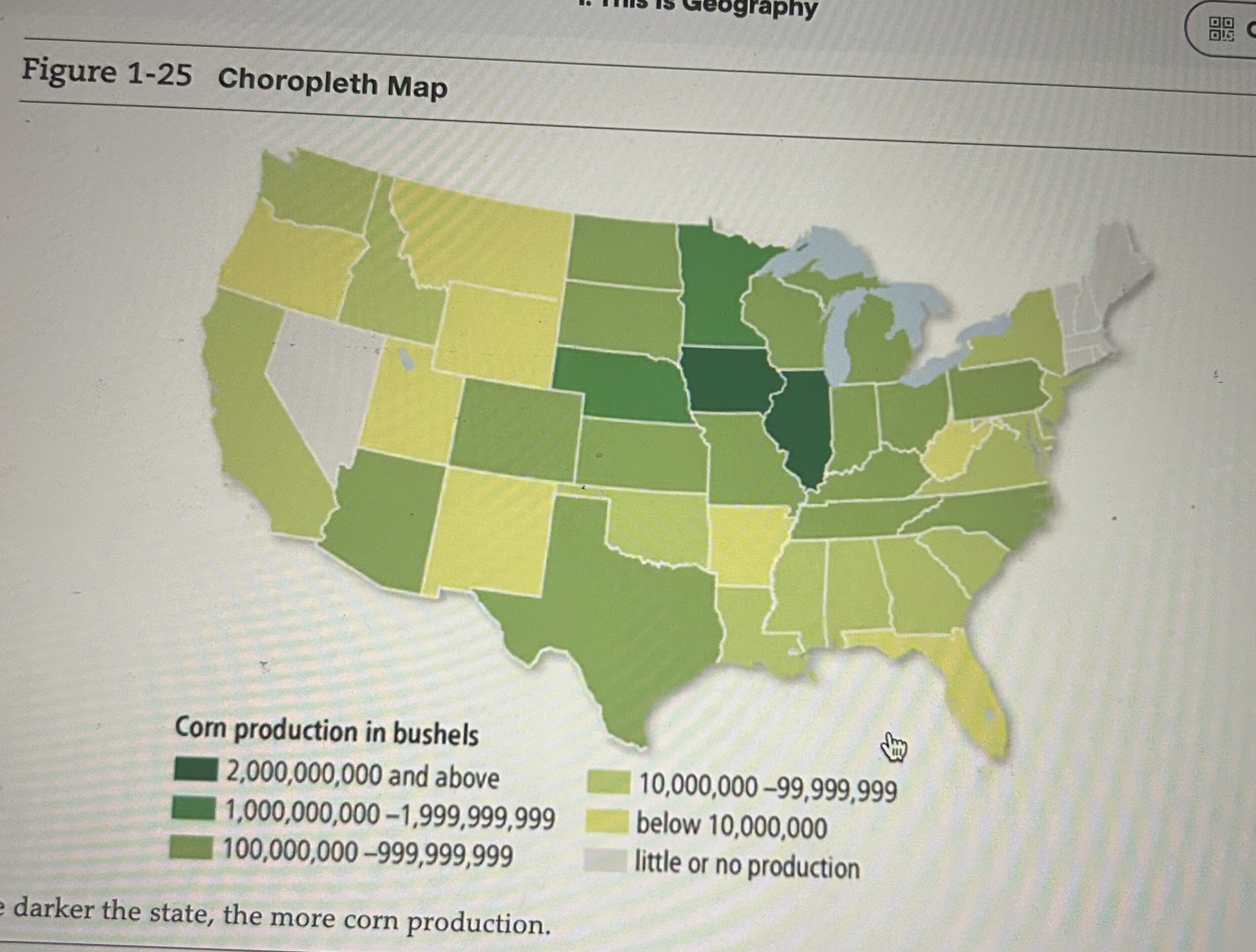
Choropleth Map
A map in which areas are shaded or patterned in proportion to the measurement of the variable
Graduated symbol map
A map that displays symbols that change in size according to the value of the variable
Bigger circles over areas with bigger values of something
Volunteered geographic information (VGI)
Creation of dissemination of geographic data contributed voluntarily and for free by individuals
Citizen Science
Scientific research by amateur scientists
Participatory GIS (PGIS)
Community based mapping, representing local knowledge and information, people in the community work voluntarily to address local problems
Poststructuralist geography
Geographic approach should examines how the powerful in a society dominate, or seek to control, less powerful groups, how the dominated groups occupy space, and confrontations that result from the domination
Diffusion
The process by which a feature spreads from one place to another over time
Hearth
A place from which an innovation originates
Relocation Diffusion
The spread of a feature or trend through bodily movement of people from one place to another
Someone with one culture moving to a new area and bringing their culture and language with them (EX: languages coming to America)
Hierarchical Diffusion
The spread of a feature or trend from one key person or node of authority or power to other persons or places
(Spread of ideas from big cities to less populated areas like music)
Contagious diffusion
The rapid, widespread diffusion of a feature or trend throughout a population
(Things going viral online due to thousands of people on a platform)
Stimulus Diffusion
The spread of an underlying principle
(a idea or trait is spread, but it is modified by a different culture to fit it better EX: McDonalds in India changing their menu to fit their diet and beliefs)
Distance decay
The diminished importance and eventual disappearance of a phenomenon with increasing distance from its origin
(as the distance between two places increase, the interaction between those two places decreases)
Space-time compression
The reduction in the time it takes to diffuse something to a distant place as a result of improved communications and transportation systems
(The shrinking of space and time due to advancements and transportation, which makes distant places feel closer and easier to interact with)
environmental determinism
Made by Alexander von Humboldt and Carl Ritter
The belief that the physical environment shapes societies and their development, influencing cultural, economic and political aspects
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC)
Informally called Greenwich Mean Time
The time at the prime meridian (0 degrees longitude) is the master reference time for all points on earth, the time at longitude 0 degrees, the prime meridian
Formal region (uniform region)
An area in which most people share in one or more distinctive characteristics, like the same language, climate, or political system
Functional region (or nodal region)
An area organized around a node or focal point connected by functions (transportation, communication, or economic activity) where interactions and influence radiate outwards from that node
Vernacular Region (perceptual region)
An area that is defined by people’s cultural perceptions rather than formal boundaries and often have informal names to identify them
“the South” in America isn’t an exact area, more like a general understanding of the area
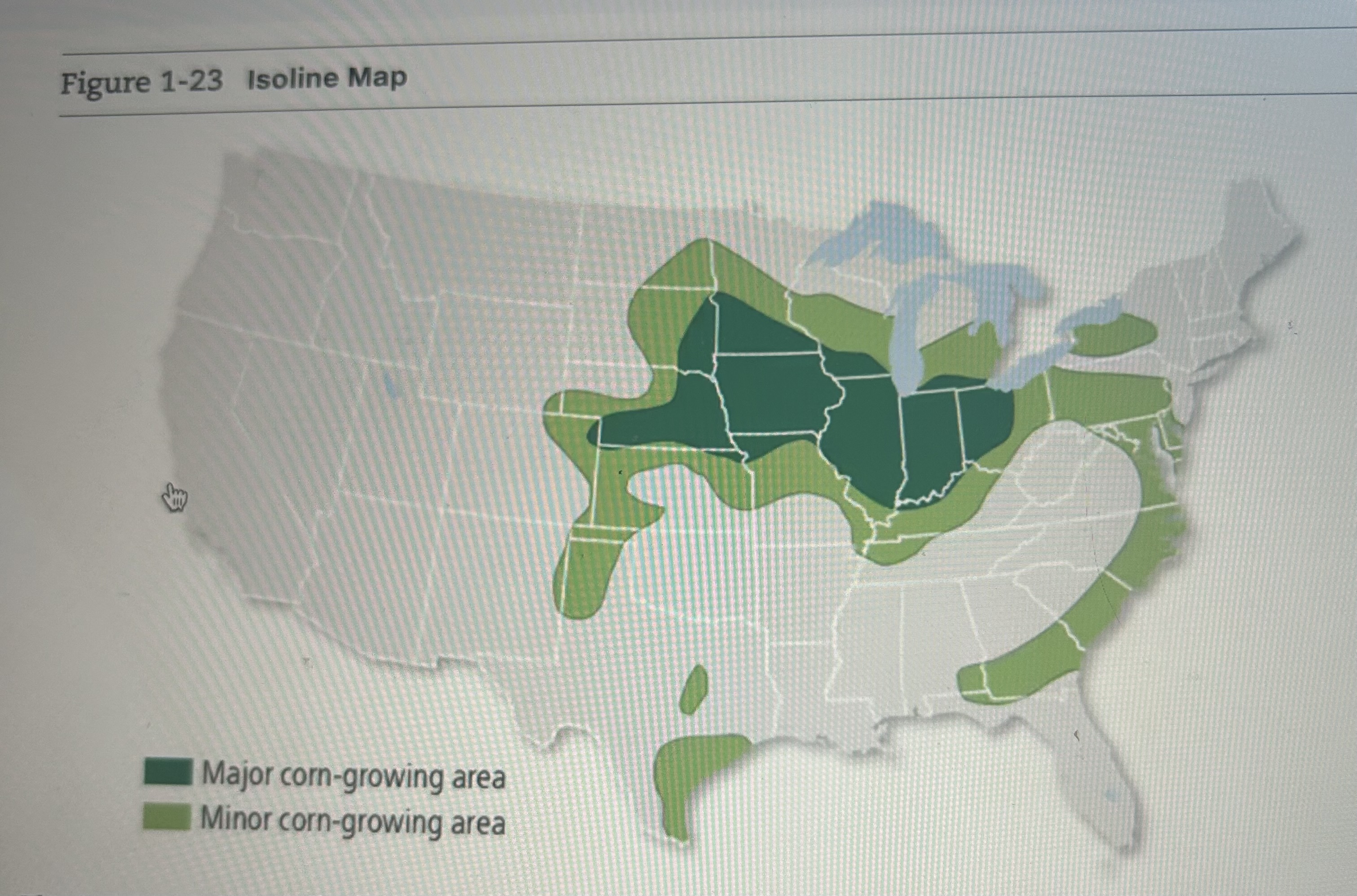
Isoline Map
A map that connects places of a particular value by lines
Lithosphere
Earths crust and a portion of upper mantle directly below the crust
Hydrosphere
All the water on and near Earths surface
Photogrammetry
The science of taking measurements of Earths surface from photographs
Possibilism
The theory that the physical environment may set limits on human actions, but people have the ability to adjust to the physical environment and choose a course of action from many alternatives
Toponym
The name given to a portion of Earths surface (country names, any name on a map)
Polder
Land that the Dutch have created by draining water from an area
Cultural Ecology
A geographic approach that emphasizes human-environment relationships
Geographic information science (GIScience)
Analysis of data about Earth acquired through satellite and other electronic information technologies
Geographic information system (GIS)
A computer system that captures, stores, queries, and displays geographic data
Humanistic Geography
An approach to human geography that emphasizes the different ways that individuals form ideas about places and give those placed symbolic meanings
(EX: a person of one race can feel comfortable in an area where their race is most common, while someone of another race might feel uncomfortable)
Scale
The relationship between the portion of Earth being studied and Earth as a whole
Transnational corporation
A company that conducts research, operates factories, and sells products in many countries, not just where its headquarters or shareholders are located
Uneven development
The increasing gap in the economic conditions between core and peripheral regions as a result of the globalization of the economy
reference map
-Aims to prove a broad understanding of the locations geography
-shows the location of geographic features and political boundaries about the organization of space
thematic map
a type of map that displays a particular theme or attribute, such as population density, income levels, or disease rates
remote sensing
the acquisition of information about the Earths surface from a distance, typically using sensors on satellites or aircraft
scale of analysis
the level of geographic inquiry - global, regional, national, or local - at which a phenomenon is studied
time-space compression
the process through which improvements in transportation and communication technologies have effectively reduced the distance and and time separating places