Functional Groups and Biomolecules
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What do functional groups determine?
how a molecule behaves as it gives functionality to specific molecules?
What functional groups are we concerned with?
Hydroxyl, Carbonyl, Carboxyl, Amino, Phosphate, and Methyl
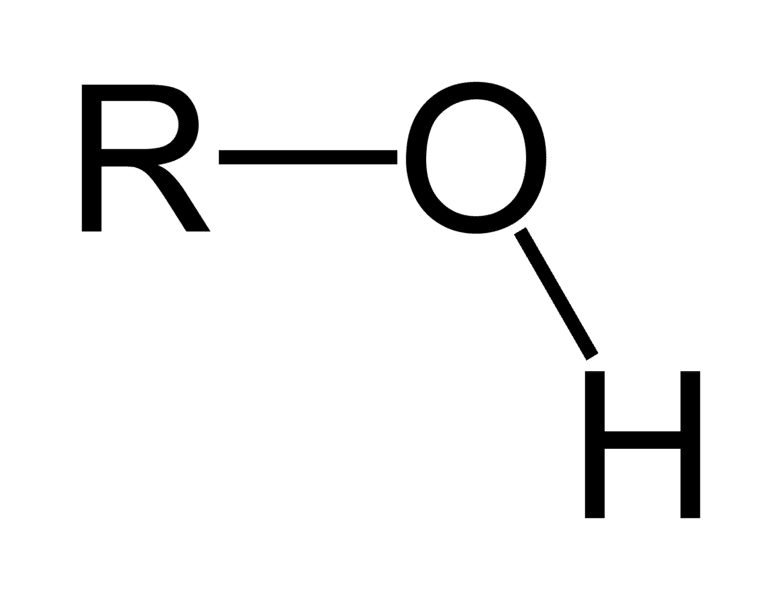
What group?
hydrophilic or hydrophobic? this makes it?
where are they typically found? do they dissolve?
hydroxyl
hydrophilic due to polar covalent bond as O is more electronegative
sugars and alcohols like glycerol, methanyl, so they dissolve in water
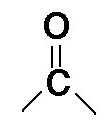
What group?
how is it characterized?
what are its two types? what is the difference?
polar or non?
where can it be found
Carbonyl
characterized by C double bond with O
forms aldehydes at the end of the molecule and ketones if it occurs in the middle
polar
found in sugars
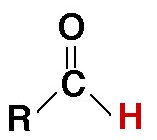
What group is this from?
what type?
carbonyl
aldehyde
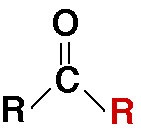
What group is this from?
what type?
carbonyl
ketone
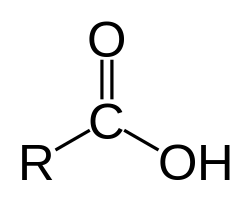
What group?
polar or non?
where is it found?
what is it considered? why?
carboxyl
polar
fatty and amino acids and any acids involved with metabolism
an acidic group because H often disassociates from O in solution becoming a hydrogen ion
By definition any molecule with carboxyl group is a?
acid
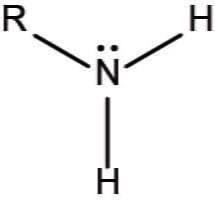
what group is it?
how does it act? why?
what does it form?
Amino group
acts as a base because it can pick up free H+
forms one end of an amino acid
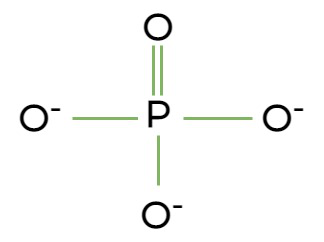
What group is it?
hydrophilic or hydrophobic? makes it polar or non? why?
important constituents of? where are they found?
Phosphate group
hydrophilic and polar because they can donate H+
important constituents of nucleotides that make up DNA, RNA, and ATP
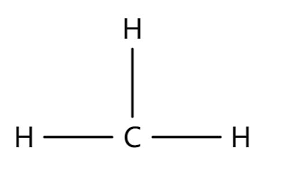
What group is it?
compound at end? middle?
polar or non?
where is it found?
methyl
R-CH3 (end), R-CH2-R (middle)
non polar, making them hydrophobic
found in lipids and hydrocarbons
By definition biological molecules contain? What are they needed for?
what do all of them contain? What may some of them contain additionally?
carbon, essential for life
all contain CHO, some may additionally contain N or P
Fundamental Units: Biomolecules are considered to be?
large molecules are?
small molecules are?
large molecules made up of smaller subunits
polymers
monomers
How are polymers made?
adding monomers through dehydration synthesis (removing H and OH)
How are polymers broken down?
through hydrolysis, by adding H and OH to the ends that were separated
Order of presence of biomolecules
1) proteins
2) lipids
3) nucleic acids
4) carbohydrates
Carbohydrates
What are its monosaccharides
What are its disaccharides (how are they made)
What are the polysaccharides, these are?
what is its main function
ribose, glucose, fructose, and galactose, fundamental unit
sucrose (glucose+fructose), maltose (glucose+glucose), and lactose (glucose+galactose)
starch, glycogen, cellulose, are complex carbohydrates
long term energy storage, structural
Polysaccharides: structure, bond, and organism
starch
glycogen
cellulose
coiled molecule due to polar bonds, energy storage in plants
coiled molecule with many side chains due to polar bonds, energy storage in animals
long and straight chains due to hydrogen bonds, structural in plants cell walls
Simple sugars like fructose have a high glycemic index, why?
Why are complex carbohydrates better?
glucose is absorbed faster causing a quick peak and drop in blood sugar levels
complex carbs have a lower glycemic index because they take longer to digest and absorb glucose, so blood sugar rises slowly, does not peak as high, and maintains a steady rate for longer
Can we break down cellulose
no, but our beneficial gut bacteria in large intestine can
Carbohydrates: summary
general formula
fundamental unit
polar or non?
functions
caloric equivalences
CnH2nOn (C and O in equal amounts)
FU: monosaccharides
polar
energy source and storage (glucose, glycogen, and starch)
structure: cellulose and polysaccharides in EC matrix
Signaling: glycoproteins and lipids
4 cal/g
Lipids are the most?
made out of …? mainly?
nonpolar or polar?
structurally diverse
made out of CHO but mainly CH
non polar and hydrophobic
Lipids
what are its subclasses?
which one is the fundamental unit
fatty acids
triglycerides
phospholipids
steroids
is a steroid a monomer or polymer?
neither
Lipids) Fatty Acids
what groups do they consist of?
what makes them high energy?
what are its two types? how? how are they at room temp
methyl group and carboxyl
CH bonds and CC Bonds
saturated, have no double bonds, solid
unsaturated, when they have double bonds (mono or poly, liquid
Fatty acids:
cis isomer
trans isomer, solid or liquid? good or bad?
cis: H is on the same side causing the kink in molecule
trans: H is on opposite sides causing it to be straight (solid), bad becausel it raises LDL
Triglycerides
how much do they account for lipids?
structure
caloric equivalence
90%
glycerol back bone and three fatty acid tails
energy storage 9 cal/g
Phospholipids
what property does it have?
main component of?
what is its structure?
amphipathic
cell membrane, makes up semipermeable phospholipid bilayer
phosphate head (philic), glycerol back bone (philic), and two fatty acids (phobic),
Cholesterol
is the most common?
what are its main functions?
where is it made? broken down?
steroid
fluidity of the membrane, prevents changes due to temperature
base of many steroid hormones
made in the liver from saturated fatty acids and broken down in liver as well
Cholesterol is hydrophobic, how is it transported through blood?
what is the difference? which one is good? which is bad, and why?
through carrier proteins HDL and LDL (high/low density lipoproteins)
HDL is more soluble and is able to go straight to the liver
LDL has less proteins and more cholesterol causing it to be sticky and potentially stick to arteries in plaques causing atherosclerosis, narrowing our BV and increasing BP, which can potentially cause parts of heart/ brain to not receive oxygen and lead to myocardial infraction or stroke
Is cholesterol diverse structurally?
what is this an example of?
no but are functionally
shows how small changes in molecule can have big outcomes
Lipids summary
general formula
fundamental unit
polar or non?
functions
caloric equivalences
CHO
fatty acids
nonpolar
energy storage: triglycerides
cell membranes: phospholipids and cholesterol
signaling: steroid hormones
9 Cal/g
Proteins
are the most?
are always made out of?
polar or non?
fundamental unit
CHON
most functionally diverse
polar backbone (also depends of R group)
amino acid
what are the groups of amino acids?
central carbon
amino (NH2)
carboxyl (COOH)
Hydrogen
Side Chain (variable)
How do amino acids form proteins?
linked by peptide bonds to form polypeptide/protein
What are the N terminus an C terminus
N-terminus (amino-terminus) and C-terminus (carboxyl-terminus) are the two distinct ends of a protein or polypeptide chain
Does order of amino acids matter?
yes it can form a completely different protein and in times where R groups are completely different (ex: charged to non polar) it can cause severe mutations
Primary structure
order of amino acids
Secondary structure
Alpha Helix (small R) and beta pleated sheets (big R)
Tertiary structure
overall 3D folding (chaperone protein) held by R groups interaction
Quaternary Structure
complete protein with four polypeptide sub units
Conjugated proteins
proteins combined with carbohydrates and/or lipids
function of proteins
1) Facilitate chemical reactions (enzymes)
2) Transport
3) Movement of muscles
4) Structure
5) Cell signaling
6) Nutrition
7) Defense
8) Components of cell membrane
9) Immune response
10) Hormones (insulin)
Protein summary
chemical formula
fundamental unit
polar or non
functions
caloric equivalence
CHON, sometimes S
amino acids
mainly polar sometimes non
most cellular/organismal activity relies on proteins
4 Cal/g
Nucleic Acids
are made out of? always?
are the most?
nucleotides
CHONP
structurally complex
Nucleotides consist of?
1) five carbon sugar: deoxyribose or ribose
2) phosphate 1+
3) nitrogenous base: ACTG or AUCG
How are nucleic acids held together?
what order?
In the double helix nitrogenous bases are bonded through?
through sugar phosphate bonds
to carbon 5 and 3
hydrogen bonds
Function of nucleic acids
store genetic information and CARRY energy
ATP
where is the energy stored
why is it released little at a time?
is this reused?
the last phosphate group, little bursts of energy released a little at a time
yes from cellular respiration chemical energy is harvested from fuel molecules creating ATP to be used for cellular work
Nucleic Acids Summary
chemical formula
fundamental unit
polar or non
function
caloric equivalence
CHONP
nucleotides
polar
information storage (DNA, RNA)
energy carriers (ATP, NADH, FADH2)
0 cal/g