homeostasis PART 2
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
homeostasis
maintaining a stable internal environment despite changes in the internal or external environment
importance of homeostasis (2)
-ensures cells function properly and avoid damage
-allows enzymes to work at their optimum temperature, ensuring efficient metabolic reactions.
factors that need to be kept constant (4)
-body temperature
-blood glucose concentration
-water potential of blood
-pH of blood
What conditions need to be maintained within cells? (5)
-pH
-temperature
-glucose concentration
-oxygen level
-carbon dioxide level
stimuli
change in environment
role of receptor
detects stimuli [and sends a signal to an effector]
examples of receptors (3)
-eyes
-skin
-ear
role of effector
makes a response to restore conditions to normal.
examples of effectors
-muscles
-glands
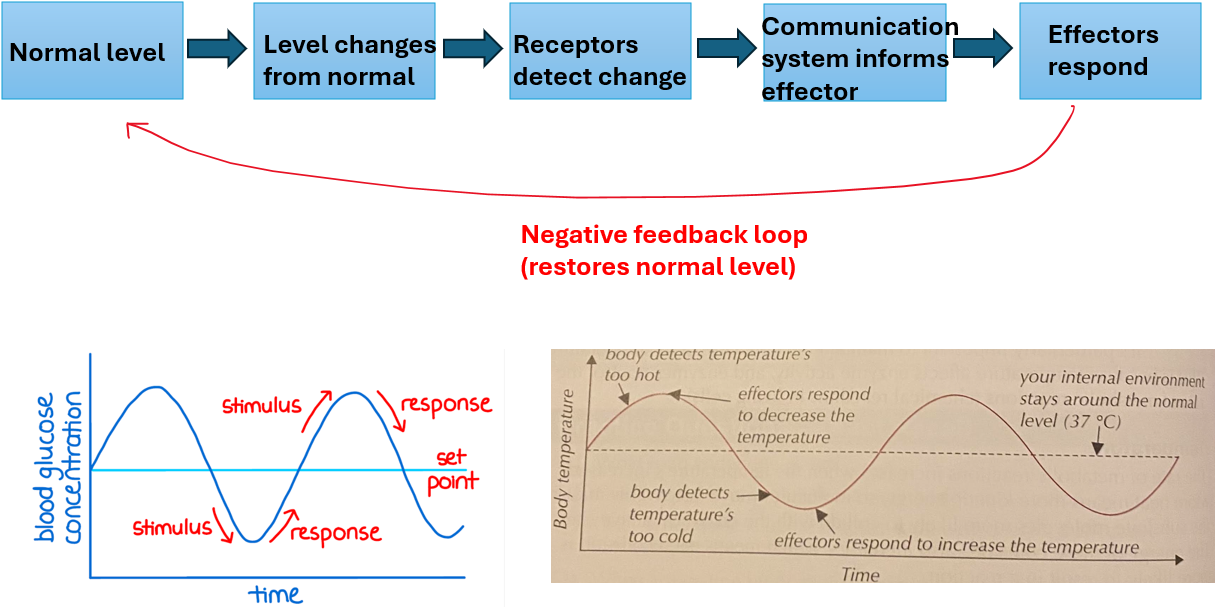
negative feedback
reverses the change in internal environment to restore the normal/optimum level
con of negative feedback
only works within certain limits→If a change is too large, the system may not be able to restore normal conditions.
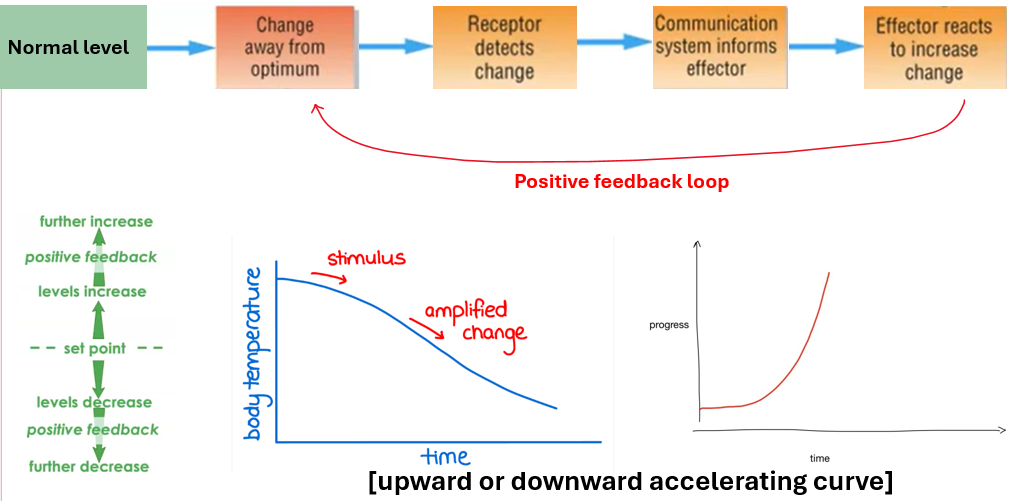
positive feedback
amplifies a change from the normal level.
positive feedback examples (2)
-blood clotting [platelets release a chemical which attract more platelets]
-childbirth [oxytocin stimulates uterine contractions]
why is positive feedback rare? (2)
-makes the internal environment unstable→ destabilises the system which is harmful for cells
-can cause harm if uncontrolled
pro of positive feedback
rapidly activates processes in the body
positive vs negative feedback
-change
-maintains homeostasis (yes or no)
positive feedback
-amplifies a change from normal level
-does not maintain homeostasis (as it doesn’t maintain a constant internal environment.)
negative feedback
-reverses change to restore normal level
-maintains homeostasis