Clinical Pathology Exam 1
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Reference intervals & data interpretation,
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
What are biological criteria used for defining a population?
species
age
sex
breed
what are environmental criteria used for defining a population?
climate
altitude
diet
season
Gaussian distribution is
symmetrical
non-gaussian distribution is
asymmetrical
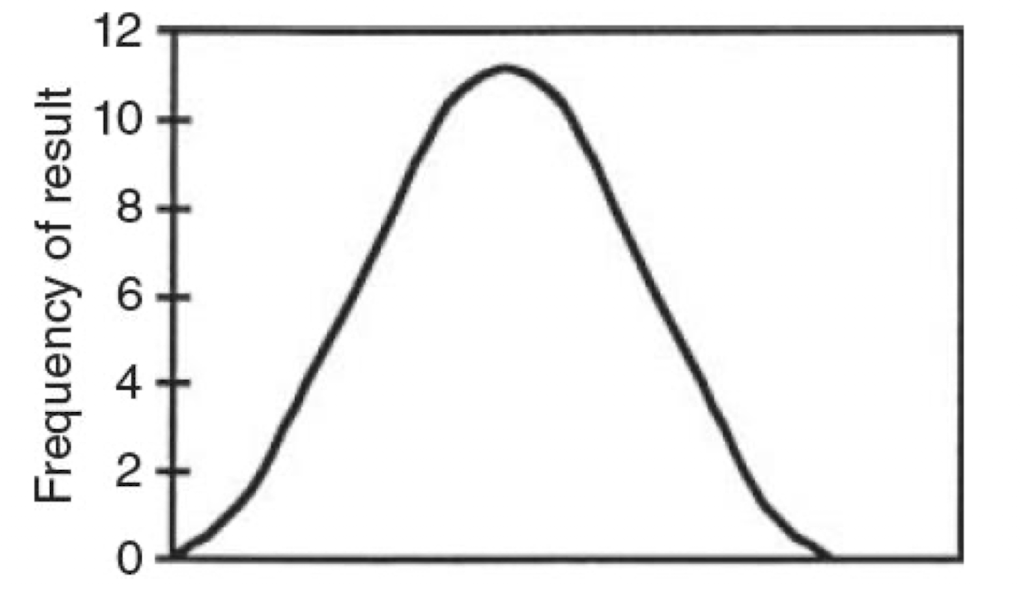
what distribution pattern is shown in this image?
Gaussian
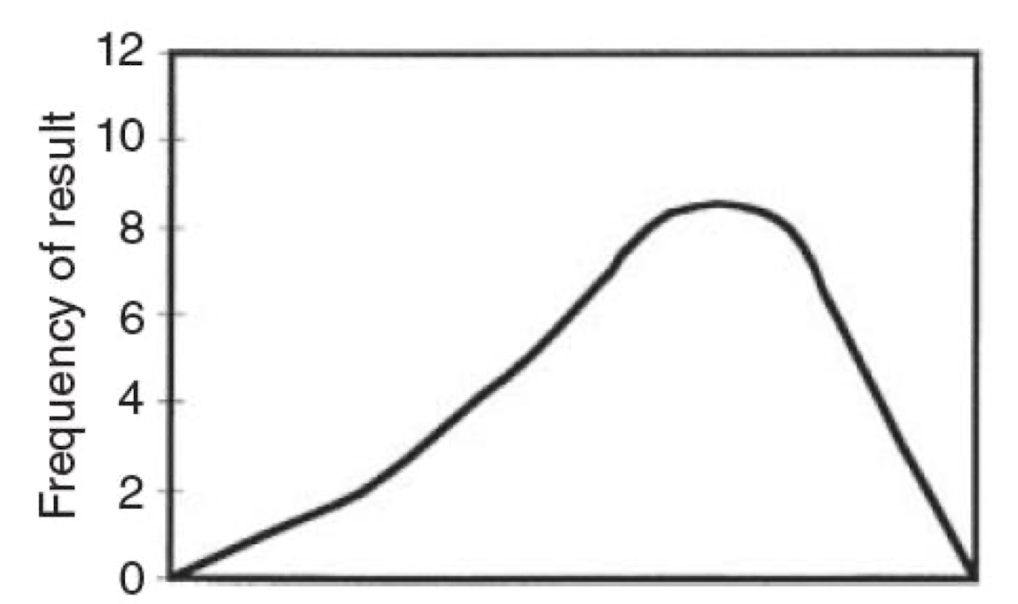
what distribution pattern is shown in this image?
non-gaussian
in Gaussian distribution, how is the reference interval calculated?
mean ± 2 SD
the reference interval only covers ___% of the population
95
what is the proportion of individuals that fall outside of the RI despite being “healthy”?
1:20
what number of individuals creates a population for the sake of RI?
120
T/F: every value outside of the RI is “abnormal” and should be treated as such
False
CBC includes the evaluation of
red blood cells
white blood cells
platelets
Direct RBC measurands include
RBC count
packed cell volume (PCV)
hemoglobin concentration
mean cell volume (MCV)
reticulocyte count
direct WBC measurands include
WBC/ total nucleated cell count
differential cell count
direct platelet measurands include
PLT count
mean platelet volume (MPV)
Red cell morphology, reticulocyte %, differential white/ nucleated cell % and platelet morphology are considered
microscopic procedures
what are RBC calculations included in CBC?
hematocrit
mean cellular hemoglobin concentration
red cell distribution width (RDW)
absolute reticulocyte count
what is the WBC calculation included in CBC?
absolute differential WBC count
describe impedance
electronic cell counting
cells are suspended in an electrolyte medium that conducts electricity
cells are relatively poor conductors of electricity
deflection in current are proportional to the size of the cell, allowing the counting and measuring of cells
what is the formula for red cell distribution width (RDW)?
RDW = SD/MCV
define anisocytosis
variation in the size of RBC
describe flow cytometry
light scatter measurement
cells pass through a flow cell that is intersected by a focused laser beam
physical properties of the cells scatter light to different degrees and different angles relative to the light source
number of scatter events are counted to derive the cell count
forward scatter is proportional to
size of the cell
side scatter is correlated to
cellular complexity
what contributes to a cells complexity?
the presence of granules
hemoglobin content
define PCV
% of erythrocytes volume over whole blood volume

what is 1?
normal PCV

what is 2?
severely hemolyzed

what is 3?
mildly hemolyzed

what is 4?
Dog or cat: icterus
Horse or ruminant: normal
refraction is proportionate to the _______ in a sample
solute concentration
what is the best layer on a blood smear to analyze morphology and count cells?
monolayer
what is the stain used to analyze and count reticulocytes?
new methylene blue (NMB)
define hematopoiesis
proliferation and progressive differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells into mature blood cells
define erythropoiesis
maturation and differentiation of RBC
define leukopoiesis
maturation and differentiation of WBC
define thrombopoiesis
maturation and differentiation of platelets
what is the main function of erythrocytes?
carry oxygen to tissues
what is the typical shape of erythrocytes in mammals?
no nuclei and no organelles
circular, flattened bi-concave
diameter: 4-8 um
what are the 2 important characteristics of erythrocytes?
discoid shape
plasticity
describe discoid shape
larger surface area to volume ratio
minimal diffusion distance
greater tolerance to osmotic swelling
describe plasticity
tolerance for shape change
cytoskeleton
Total RBC mass is regulated by
cellular oxygen levels
cellular hypoxia results in
increased secretion of EPO
what is the order of cells in erythropoiesis?
rubriblast
prorubricyte
basophilic rubricyte
polychromatophilic rubricyte
metarubricyte
reticulocyte
erythrocyte
what are the nutrients that are required for RBC production?
iron
vitamins B6, B9, B12
copper
cobalt
what organ is responsible for producing EPO?
kidney
where is the best area to examine RBC and WBC morphology on a blood smear?
monolayer
describe marcocytosis
larger RBCs
typically less mature cells
polychromatophils
describe microcytosis
smaller cells
iron deficiency
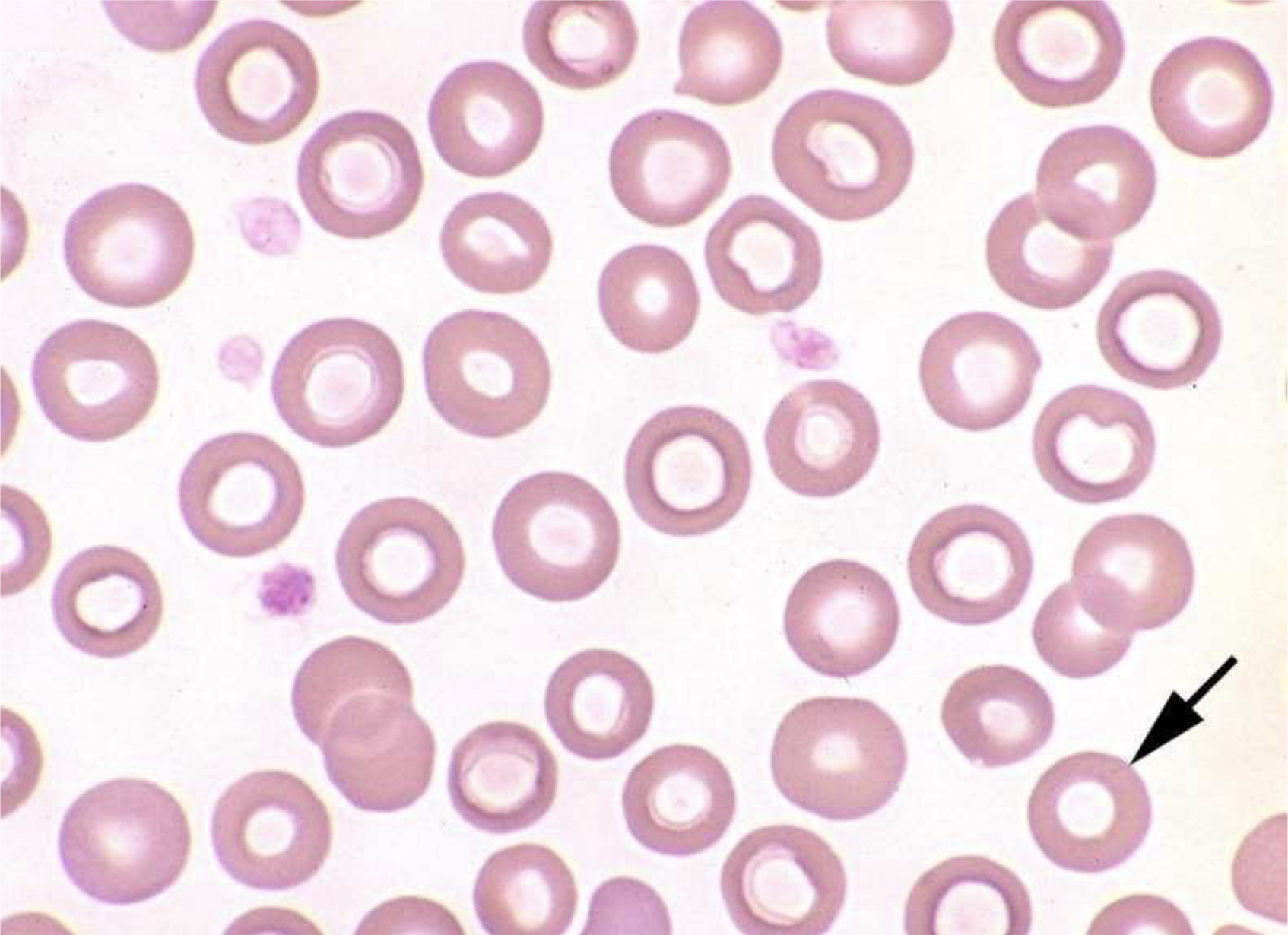
what is the arrow pointing to in this image?
shows an abrupt change from color to pale
normal artifact where the hemoglobin is concentrated on the edge
what is the stain used to count reticulocytes?
new methylene blue
when reticulocytes are stained with Wrights stain, they appear as
polychromatic RBC
describe echinocytes
numerous short spicules
crenation
in vivo formation electrolyte imbalances
rattlesnake envenomation
non-specific diseases (ex. kidney disease)
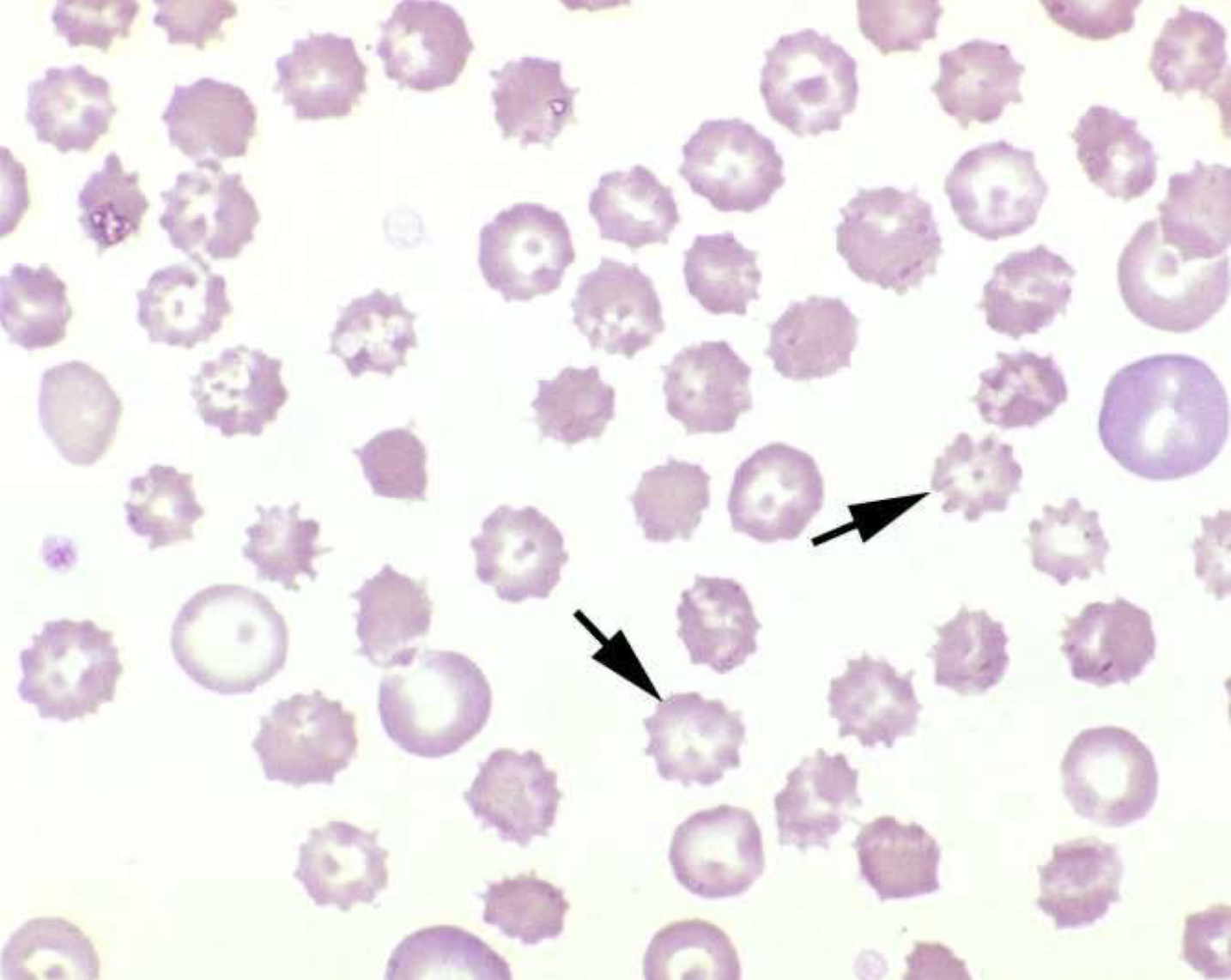
what type of cell is shown in this image?
echinocytes
describe acanthocytes
few unevenly distributed projection due to changes in lipid concentrations in RBC membrane
humans with liver disease
cats with hepatic lipidosis
dogs with hemangiosarcoma
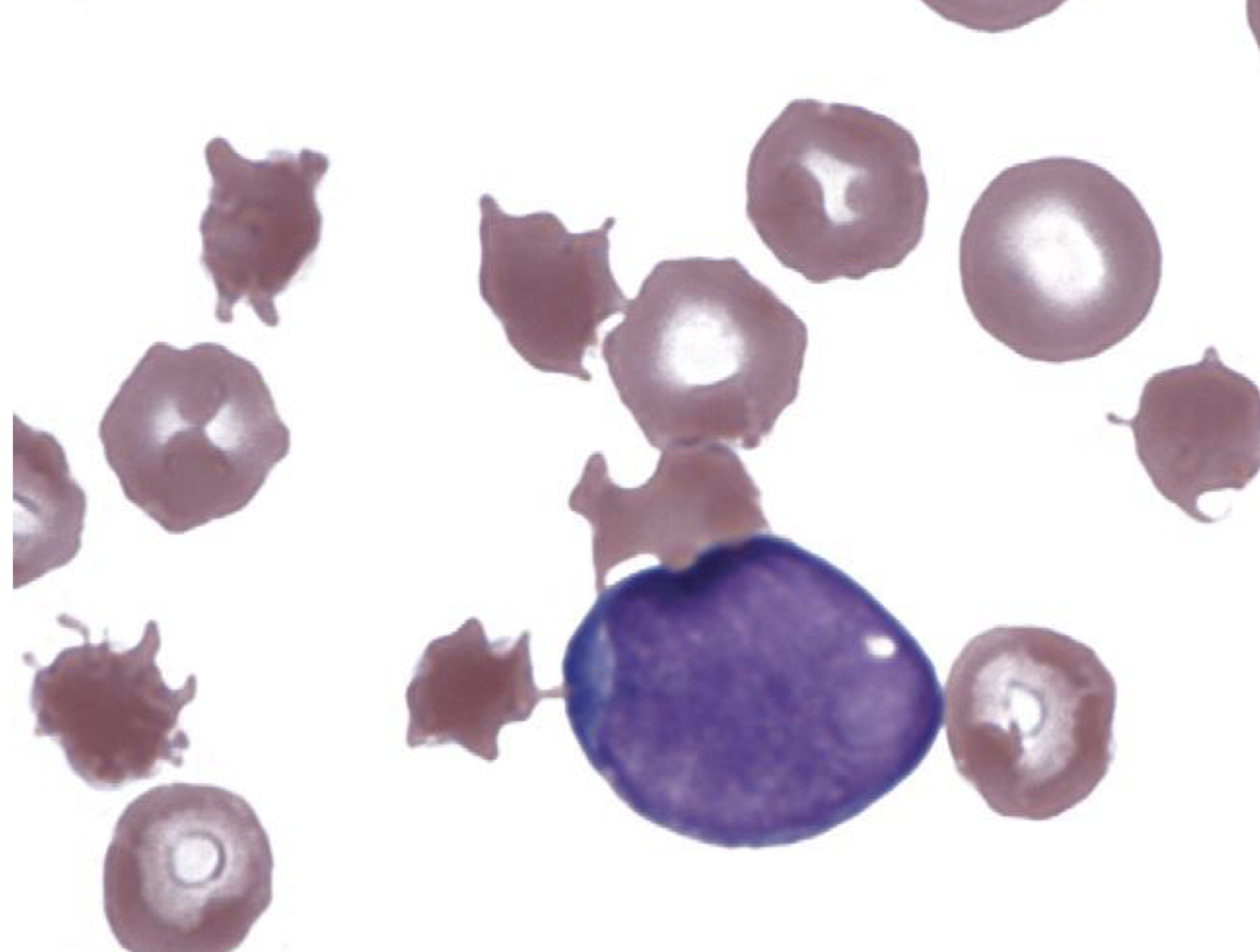
what type of cell is shown in this image?
acanthocytes
describe schistocytes
erythrocyte fragments
intravascular trauma
DIC, vascular tumors
iron deficiency
anemia
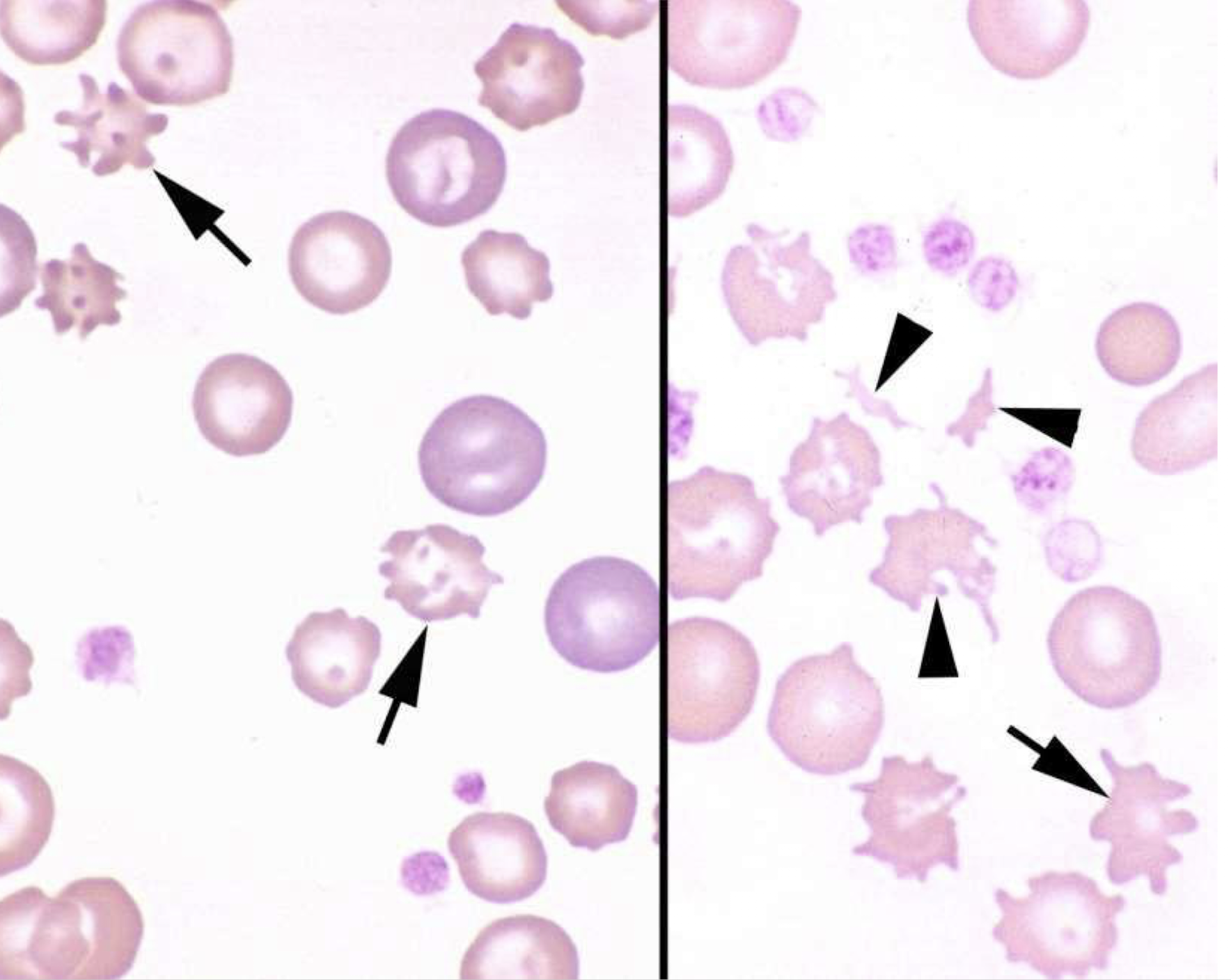
what is the arrow pointing to in this image? arrow-head?
arrow: acanthocyte
arrow head: schistocyte
describe keratocyte
one or two spicules, often formed by breaking open of “blisters”
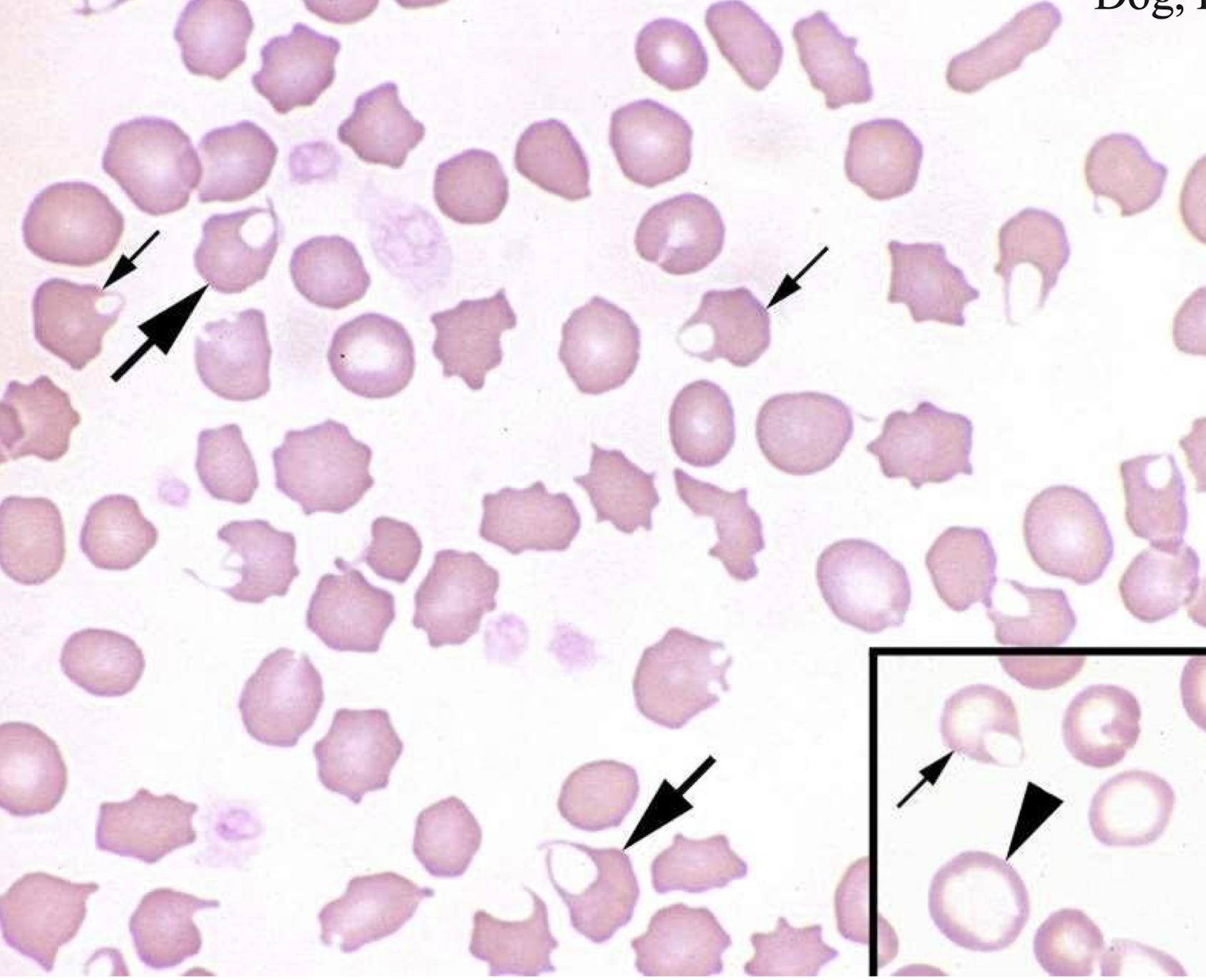
what is the arrow pointing to in this image?
keratocytes
describe spherocytes
erythrocytes that appear small and lack central pallor
volume is normal
presence suggests IMHA
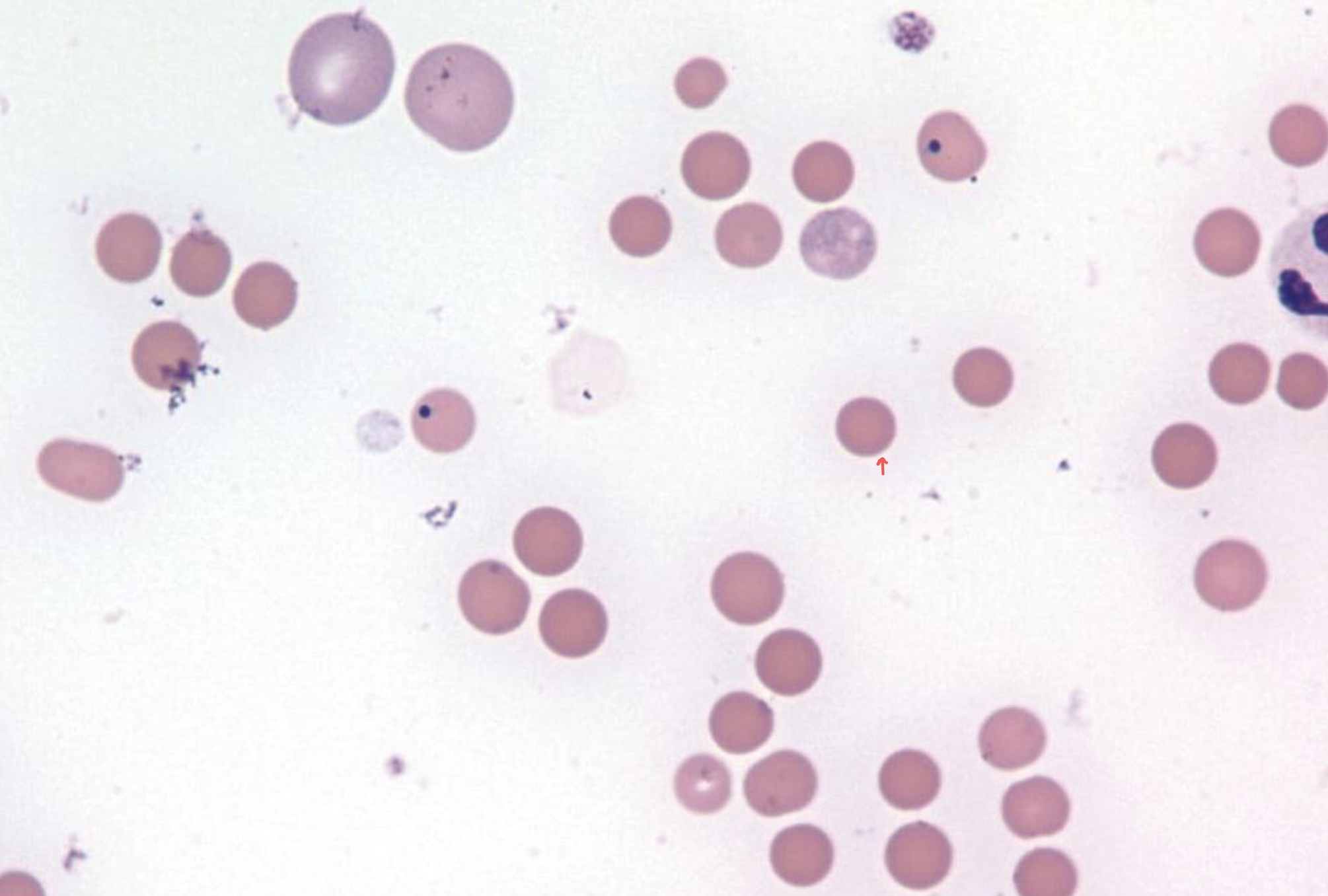
what is the red arrow pointing to in this image?
spherocyte
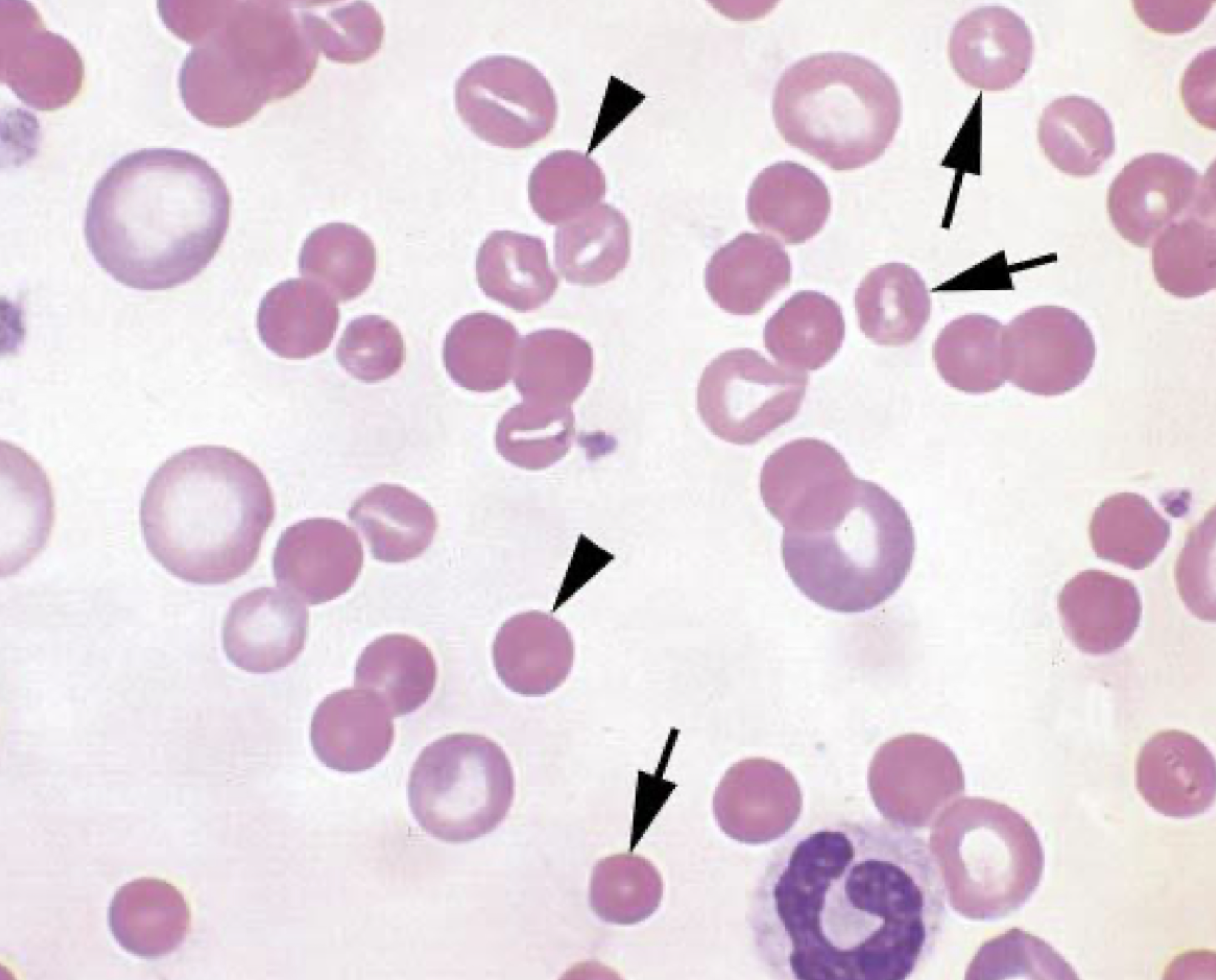
what is the arrow pointing to in this image? arrow head?
arrow: imperfect spheres
arrow head: spherocytes
briefly describe how spherocytes are formed?
macrophages attack part of the RBC that is marked with the antibody
describe heinz bodies
oxidatively denatured hemoglobin
what causes heinz body formation?
acetaminophen
propylene glycol
illnesses: lymphoma, hyperthyroidism, diabetes
onions
cephalosporins
zinc toxicosis
what causes heinz body formation in horses?
phenothiazine
wilted red maple leaves
what causes heinz body formation in cattle?
kale
onions
what causes heinz body formation in sheep?
copper toxicosis
describe eccentrocytes
shifting of hemoglobin to one side of cell, resulting in clear zone outlined by membrane
caused by oxidative damage such as may be seen with ingestion of onions in dogs
often seen in conjunction with heinz body formation
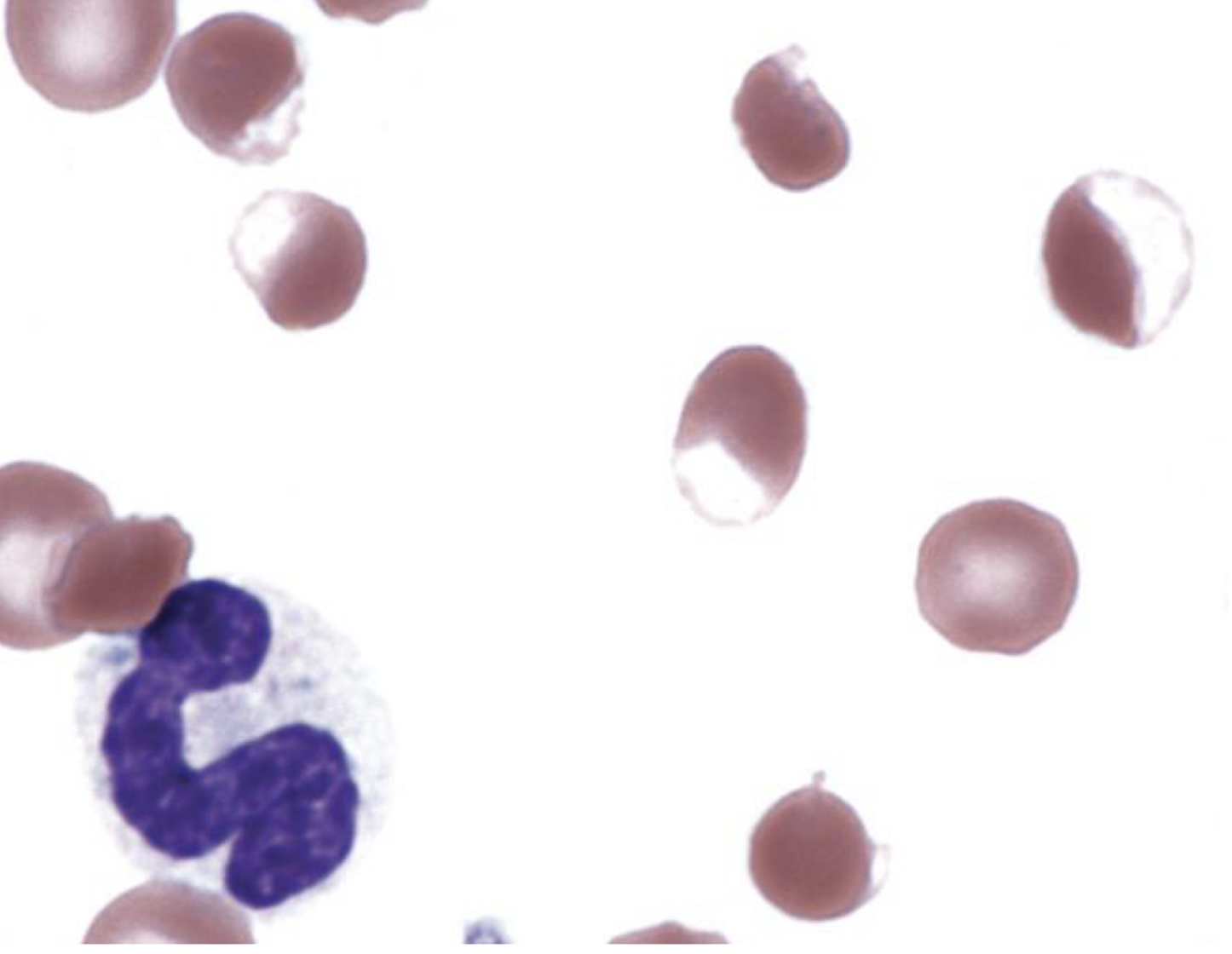
what is shown in this image?
eccentrocytes
describe leptocytes and codocytes
“target cells”
“bowl” shaped cells
folded cells
of little diagnostic significance
describe stomatocytes
mouth-like clear area in the center of the RBC
a few are usually present and are insignificant
hereditary stomatocytosis reported in
alaskan malamutes
miniature schnauzers
drentse partrijshond