Dental Specialties Proc & Exp Funct- Ch 54- complete
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Endodontics
The specialty of dentistry that manages the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of the dental pulp and the perio radicular tissues surrounding the root of the tooth
Causes of Pulpal Nerve Damage
Physical irritation
Extensive decay moving into the pulp
Trauma
Blow to a tooth or jaw
Signs and Symptoms of Pulpal Nerve Damage
Pain when occluding
Pain during mastication
Sensitivity to hot or cold beverages
Facial swelling
Fever
Tenderness of surrounding gums
Cracked or discolored teeth
Endodontic Diagnosis: Subjective Examination – Patient Describes
Chief complaint
Painful stimuli
Character and duration of pain
Sensitivity to biting and pressure
Endodontic Diagnosis: Objective Examination – Dentist Findings
Extent of decay
Periodontal conditions
Extensive restoration
Tooth mobility
Swelling or discoloration
Pulp exposure
Percussion Test
Determines whether the inflammatory process has extended into the periapical tissues
The dentist taps on the incisal or occlusal surface with the end of the mouth-mirror handle held parallel to the long axis of the tooth
Palpation Test
Determines whether the inflammatory process has extended into the periapical tissues
The dentist applies firm pressure to the mucosa above the apex of the root
Thermal Sensitivity
Necrotic pulp will not respond to cold or heat
Cold test
Ice, dry ice, or carbon dioxide is used to determine the response of a tooth to cold
Heat test
A piece of gutta-percha or an instrument handle is heated and applied to the facial surface of the tooth
Electric Pulp Testing
A small electrical stimulus is delivered to the pulp-determine if tooth is vital or nonvital.
Factors that may influence readings include:
The patient has extensive restorations
The patient has teeth with more than one canal
Failing pulp produces a variety of responses
Control teeth don’t respond as anticipated
There is moisture on the tooth during testing
The batteries in the tester weaken over time
Five (5) Radiographic Imaging Taken for Endodontic Treatment
Initial radiograph: Diagnosis
Working length image: To determine the length of the canal
Final instrumentation image: Final size files in all canals
Root canal completion image: Taken after the tooth has been temporized
Recall image: Taken at posttreatment evaluations
Requirements of Radiographic Images
Must show apex of the tooth and the surrounding bone or pathologic condition
Must present an accurate image
Must exhibit good contrast so that all pertinent structures are readily identifiable
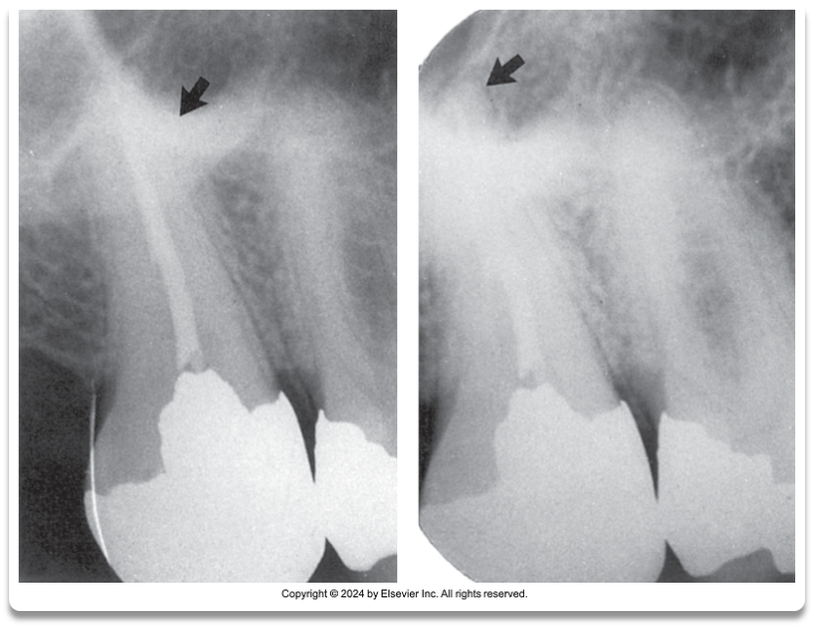
A. Good contrast around apex
B. Poor Contrast around apex
Diagnostic Conclusions
Normal pulp
No subjective symptoms or objective signs are noted
The tooth responds normally to sensory stimuli, and a healthy layer of dentin surrounds the pulp
Pulpitis
The pulp tissues have become inflamed
Reversible pulpitis
The pulp is irritated, and the patient is experiencing pain in response to thermal stimuli
Irreversible pulpitis
The tooth displays symptoms of lingering pain (pulp incapable of healing)
Diagnostic Conclusions: Periradicularor Periapical Abscess
This inflammatory reaction surrounding the tip of the root has pulpal infection which can be chronic or acute onset with pain, tenderness of the tooth due to pressure, pus(exudate), and swelling of the tissues.
Tooth has experienced bone loss and bacteria having access along the root.
Chronic-presence of a draining sinus tract
Acute-pain, tenderness, swelling because of the necrosis (dying)
Diagnostic Conclusions: Periodontal Abscess
Inflammatory reaction caused by bacteria trapped in the periodontal sulcus
A patient will experience rapid onset of pain, tenderness of the tooth in response to pressure, pus formation, and swelling
Chronic
Acute
Diagnostic Conclusions: Periradicular or Perioapical Cyst
This type of cyst develops at or near the root of a necrotic tooth
The cyst develops as an inflammatory response to pulpal infection and necrosis of the pulp
Diagnostic Conclusions: Pulp Fibrosis
A decrease in living cells within the pulp causes fibrous tissue to take over the pulpal canal
(Mostly seen in older patients.
Patients with recent trauma to a tooth may be susceptible)
Diagnostic Conclusions: Necrosis
The tooth may also be referred to as nonvital
The term is used to describe a tooth that does not respond to sensory stimulus
Endodontic Procedures: Pulp Capping
Pulp capping is an attempt to save the tooth.
Calcium hydroxide is placed over an exposed or nearly exposed pulp to encourage the formation of dentin at the site of injury
2 types of capping:
Indirect pulp capping (IPC) is indicated when a thin portion of dentin is still intact
Direct pulp capping (DPC) is indicated when the pulp has been slightly exposed
Endodontic Procedures: Pulpotomy
This procedure involves removal of the coronal portion of an exposed vital pulp
It is used to preserve the vitality of the remaining portion of the pulp within the root of the tooth
The procedure is commonly indicated for vital primary teeth, teeth with deep carious lesions, and emergency situations
Endodontic Procedures: Pulpectomy
This procedure involves the complete removal of the dental pulp
Also referred to as root canal therapy
Instruments and Accessories for Endodontic Procedures
Hand instruments
Explorer
Endodontic spoon excavator
Spreaders and pluggers
Glick Number 1-used to remove excess gutta
percha
ORDER OF INSTRUMENTS USED IN ENDO
TREATMENT
1. Endo Explorer
2. Files
3.Paper Points
4.Gutta Percha
5. Glick Number 1
Hand-operated files
K-type file- cleaning of canal initially
Hedstrom file- spiral edges, cutting occurs only in the pulling stroke
Reamer file- remove dentin, to smooth and increase size of canal
Broaches- remove necrotic pulp tissue from canal
Rotary-operated files and burs
Gates-Glidden burs-first instrument used to enlarge
the cervical portion of the root canal.
Pesso files-to prepare canal for endodontic post
Auxiliary instruments
Rubber stops
Paper points-used to dry canal
Microscopic Endodontics
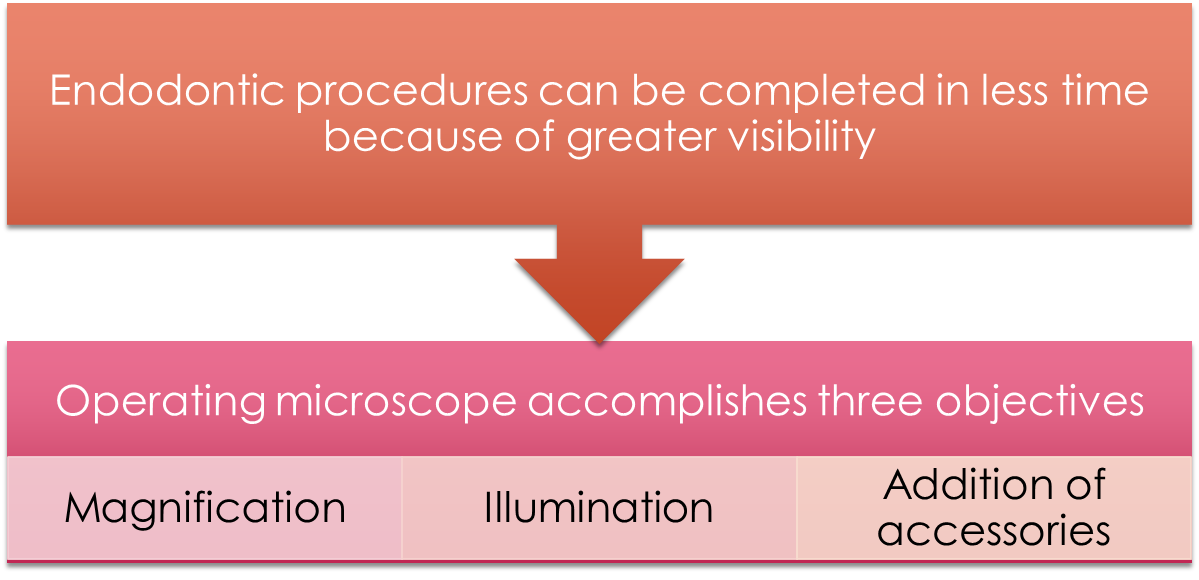
Medicaments and Dental Materials in Endodontics
Irrigation solutions
Sodium hypochlorite (Bleach)
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA)
Chlorhexidine (Peridex)
Intracanal medicaments
Calcium hydroxide
Chlorhexidine gel
Root canal sealers
Root canal filling materials
Gutta-percha points
Overview of Root Canal Therapy
Anesthesia and pain control
Isolation and disinfection of the operating field(rubber dam)
Access preparation
Estimated working length (files)
Electronic apex locator
Debridement and shaping of the canal
Obturation (filling and sealing a tooth with root canal material)
Surgical Endodontics
Indications for surgical intervention
Endodontic failure
Persistent infection, severely curved roots, perforation of the canal, fractured roots, extensive root resorption, pulp stones, or accessory canals that cannot be treated
Exploratory surgery
To determine why healing did not occur
Biopsy
Apicoectomy and Apical Curettage
To surgically remove the apical portion of the root with the use of a high-speed handpiece and bur
To evaluate the following:
Inadequate sealing of the canal
Accessory (extra)canals
Fractures of the root
Pathologic tissue around the root apex
Retrograde (root-end filling) Restoration
This procedure is undertaken when an apical seal is not adequate
A small class I preparation is made at the apex and sealed with filling materials such as gutta-percha, amalgam, or composite
Root Amputation and Hemisection
Root amputation
This surgery is performed to remove one or more roots of a multirooted tooth without removing the crown
Hemisection
The root and the crown are cut lengthwise and removed
abscess
a localized infected area with accumulating pus
acute
sudden or onset illness or pain with a short duration
apical curettage
a surgical procedure that involves the removal of tissue surrounding the apex of a tooth
apicoectomy
a surgical procedure to remove the apex of a tooth's root, usually to treat infection.
chronic
a long-lasting condition or illness that persists over time.
control tooth
A tooth that is used as a reference for comparison in dental studies or treatments.
debridement
The process of removing decayed or infected tissue from a tooth or surrounding area and cleaning out the pulpal canal
direct pulp cap
application of a dental material with an exposed or nearly exposed dental pulp
endodontist
A dental specialist who diagnoses and treats dental pulp and root canal issues, focusing on saving teeth with advanced procedures.
gutta-percha
A biocompatible material used to fill and seal the pulpal canal during root canal treatment.
indirect pulp cap
placement of a sedative material when pulp tissue is close to the surface but not completely exposed
irreversible pulpitis
A painful condition occurring when the dental pulp becomes inflamed and irreversibly damaged, often requiring root canal therapy.
nonvital
dead
obturation
The process of filling a root canal space after endodontic therapy to seal it and prevent reinfection.
palpatation
The act of applying pressure to a specific area of the body to assess for pain, swelling, or other abnormalities.
percussion
The act of tapping on a surface to elicit sounds or vibrations in order to assess underlying structures or conditions.
periodontal abscess
localized infection within the periodontal sulcus
periradicular
refers to the area of nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue surrounding the apex of a tooth root.
periradicular abscess
inflammatory reaction to pulpal infection
pulpectomy
a dental procedure that involves the removal of the pulp tissue from the tooth to treat infection or decay.
pulpitis
inflammation of the dental pulp
pulpotomy
a dental procedure involving the removal of only the crown portion of the pulp tissue to preserve the tooth.
retrograde restoration
a procedure in which a filling is placed into the root canal after the tooth has been treated, often used to seal the canal and prevent further infection.
reversable pulpitis
a condition where the inflammation of the dental pulp is temporary, typically allowing for recovery if treated promptly.
root canal therapy
a dental procedure used to treat infection or damage to the dental pulp by removing it and sealing the root canals, thereby preserving the tooth.