N236: Introductory Concepts in Microbiology
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
Biology
The study of living things
Microbiology
The study of microscopic organisms
Living microbes
Bacteria, algae, protozoa, fungi (CELLULAR)
Non-living microbes
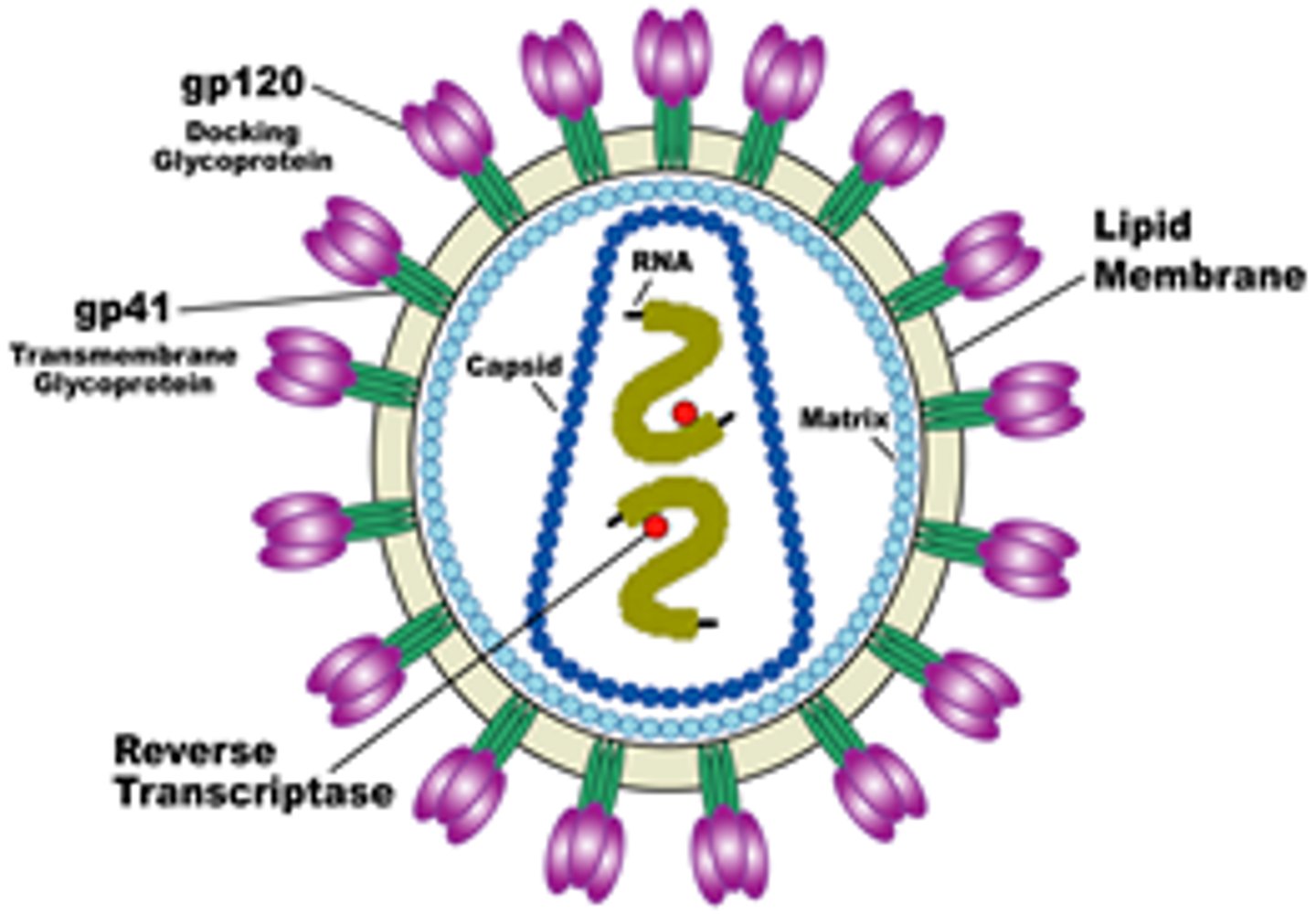
Viruses, viroids, prions (ACELLULAR)
Prokaryotes
Cells that do not contain nuclei (bacteria)
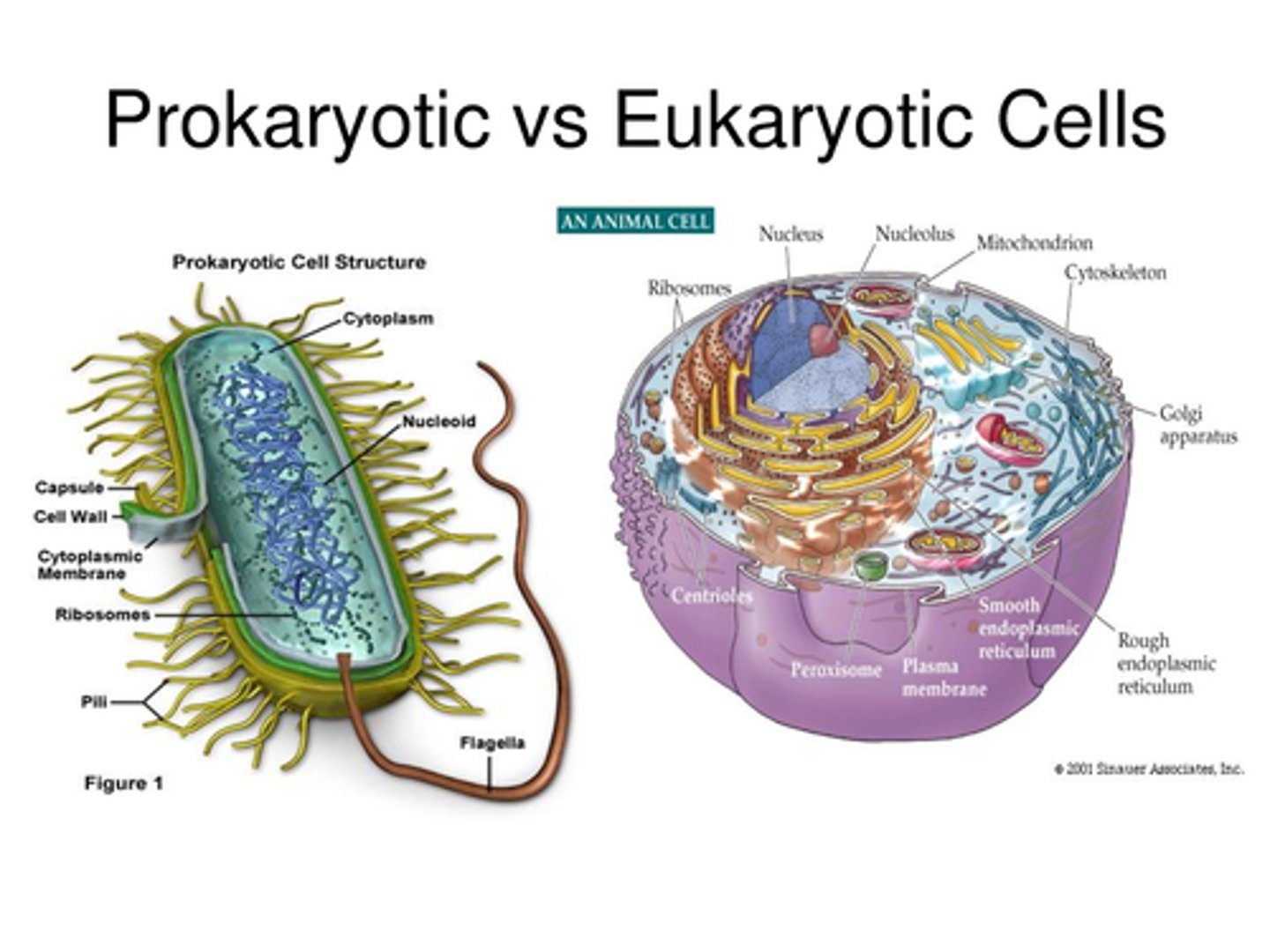
Eukaryotes
Cells that contain nuclei
Pathogens
Microbes that cause disease
Non-pathogenic organisms
Microbes that do not cause disease or infection (97% of microbes)
Microbiologist
Someone who studies microscopic organisms

Medical microbiology
Involves the study of the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of infectious diseases

Microbiome
All of the microorganisms in a particular environment

Physical microbiome environments
Soil, ocean, atmosphere

Biological microbiome environments
Plants, animals, humans

Human microbiota
All of the microbes living in and on the human body
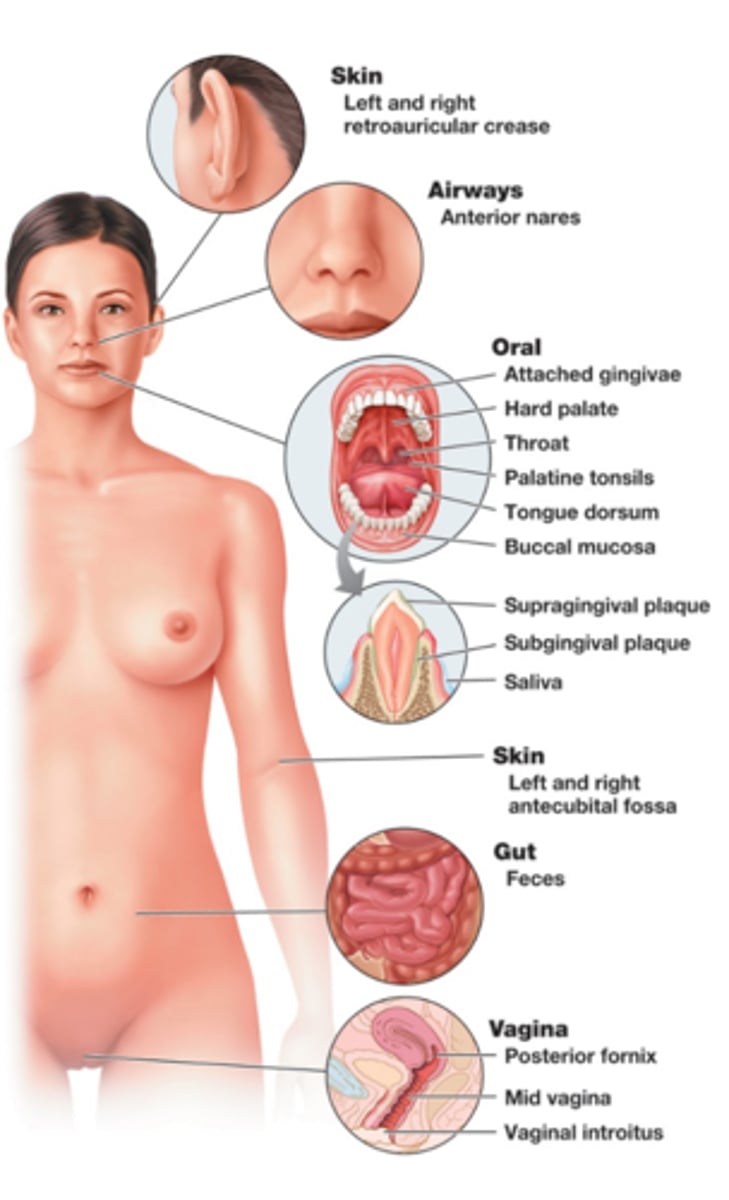
What does the human microbiota do?
Helps protect us against pathogens, and aids in the breakdown/synthesis of nutrients
Microbiota colonization
Babies are first colonized during birth --> the human microbiota expands throughout life

Opportunistic pathogens
Normal human microbiota that can cause infections when they travel somewhere they do not belong
Example: UTI

How does antibiotic therapy affect microbiota?
Antibiotics can kill harmless bacteria along with the intended target bacteria
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea
Loose, watery diarrhea that occurs over 3 times per day as a result of taking antibiotics

Saphrophytes
Microorganisms that feed off dead animals, insects, and leaves

Probiotics
Live microbes that are digested --> can restore and supplement the intestinal microbiota

Taxonomy
The science of classifying organisms
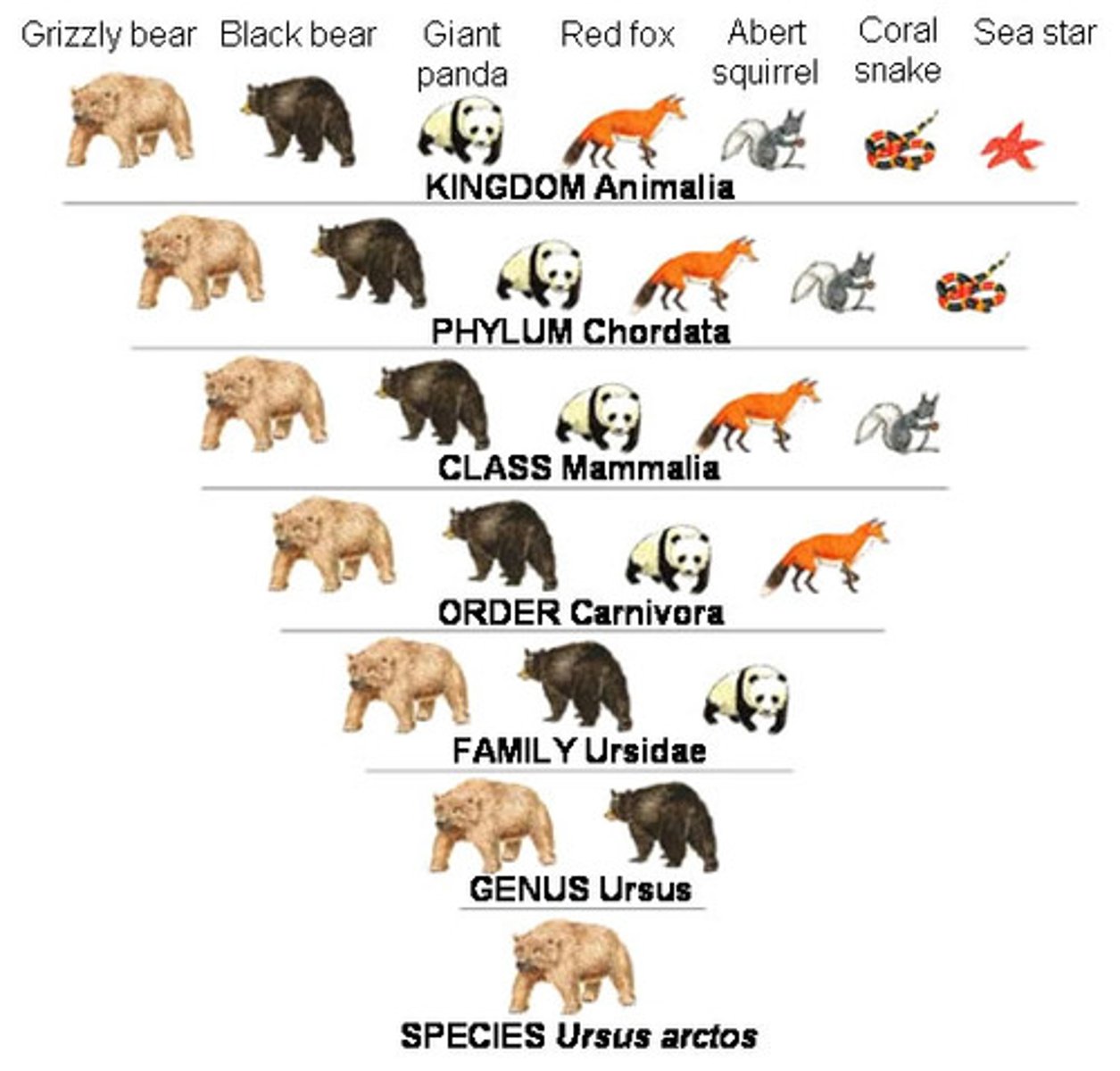
Taxa
Groups of organization into which organisms are classified
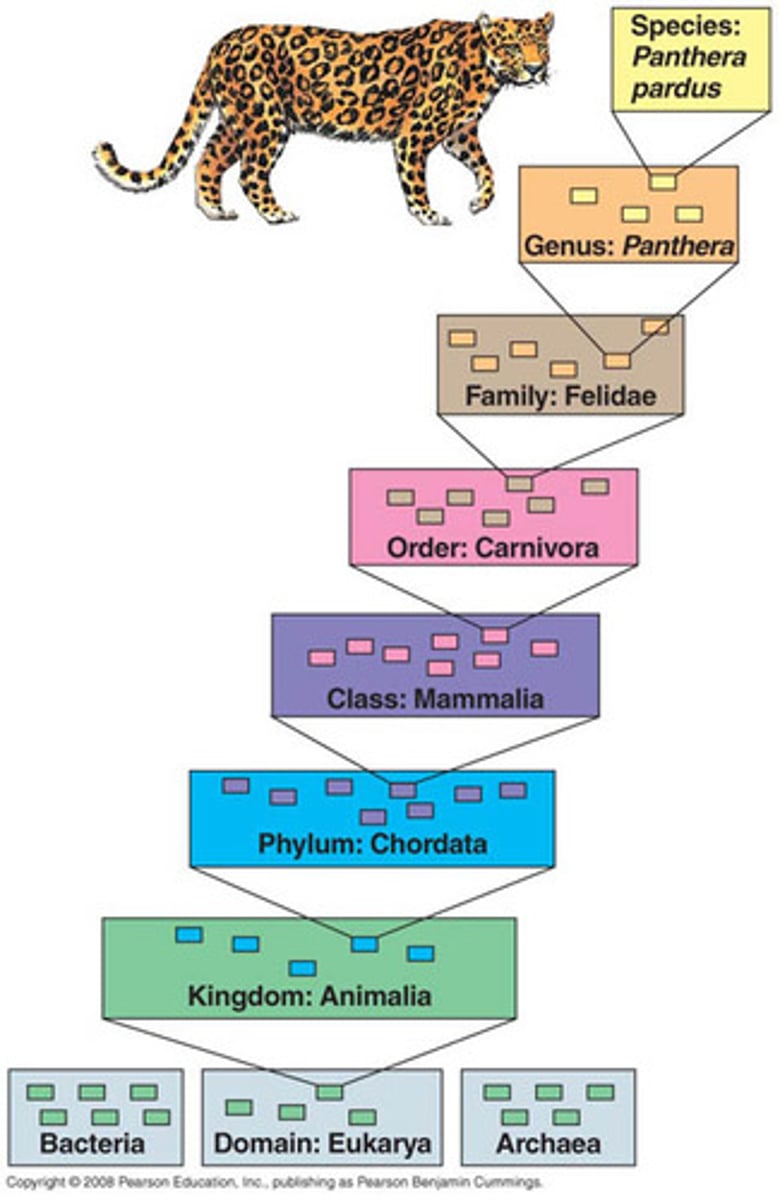
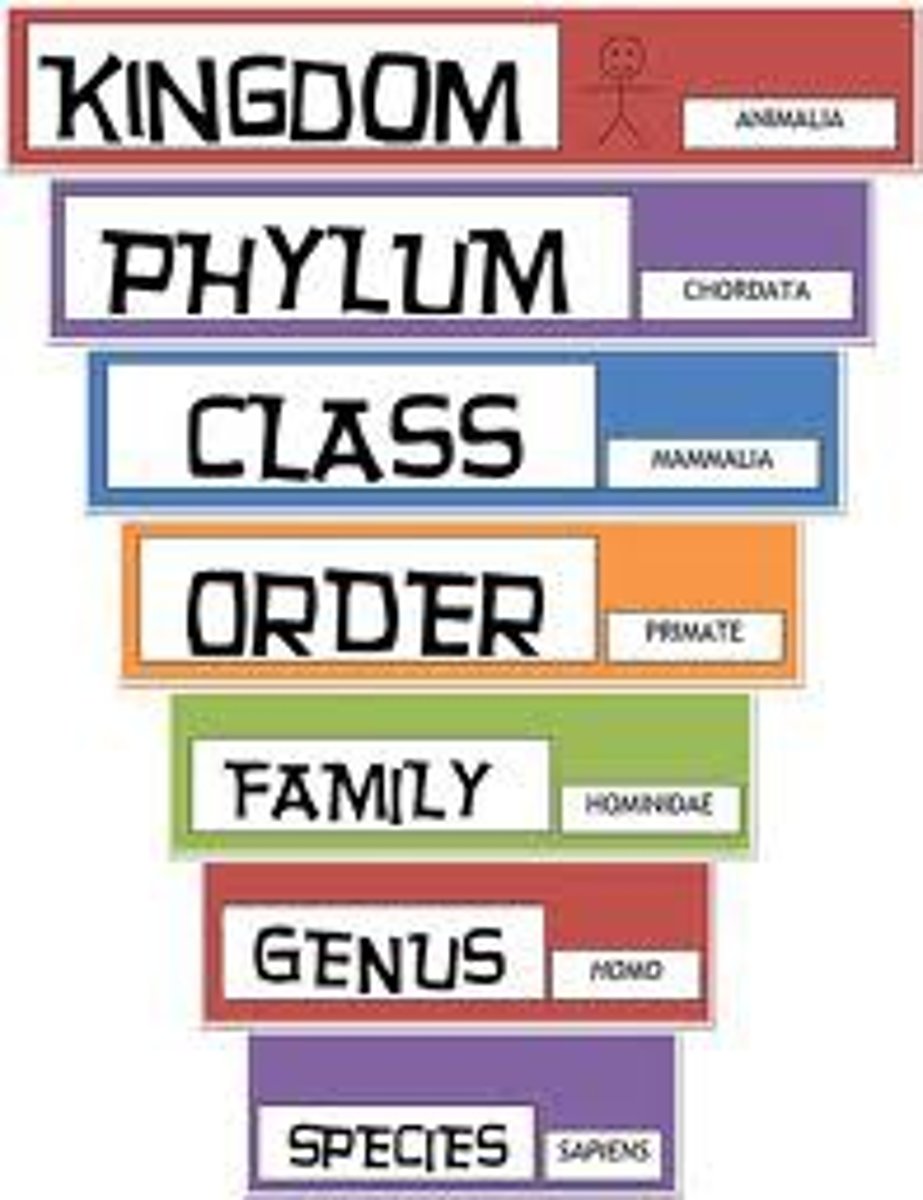
Taxonomic ranks (7)
Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
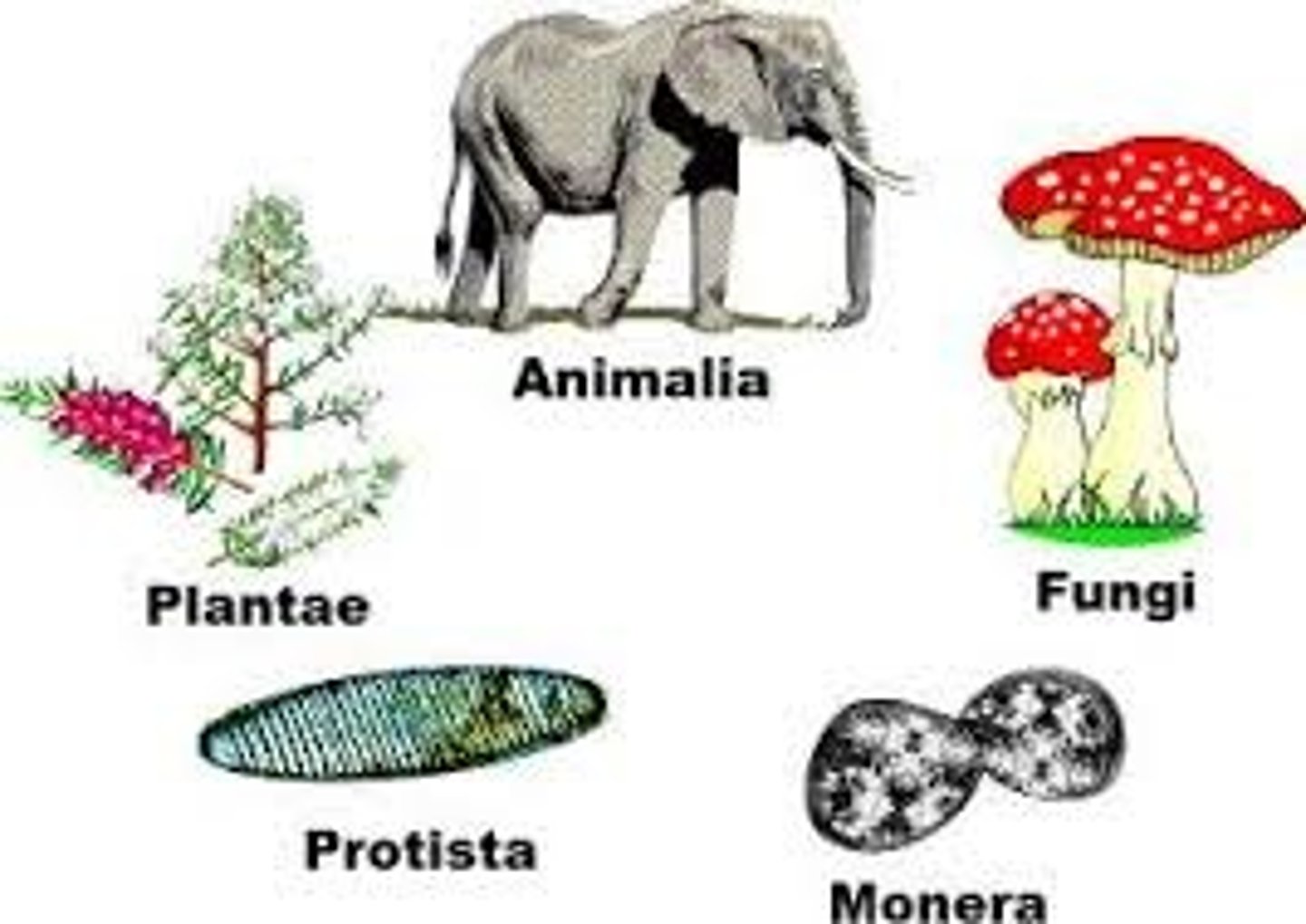
Five Kingdoms of Life
1. Monera
2. Protista
3. Fungi
4. Plantae
5. Animalia
Generic Name
Indicates the organism's genus and is written in upper case letters
Example: Homo
Specific Name
Indicates the organism's species and is written in lower case letters
Example: sapiens
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
Father of microbiology, invented the microscope and was the first to observe bacteria and protozoa
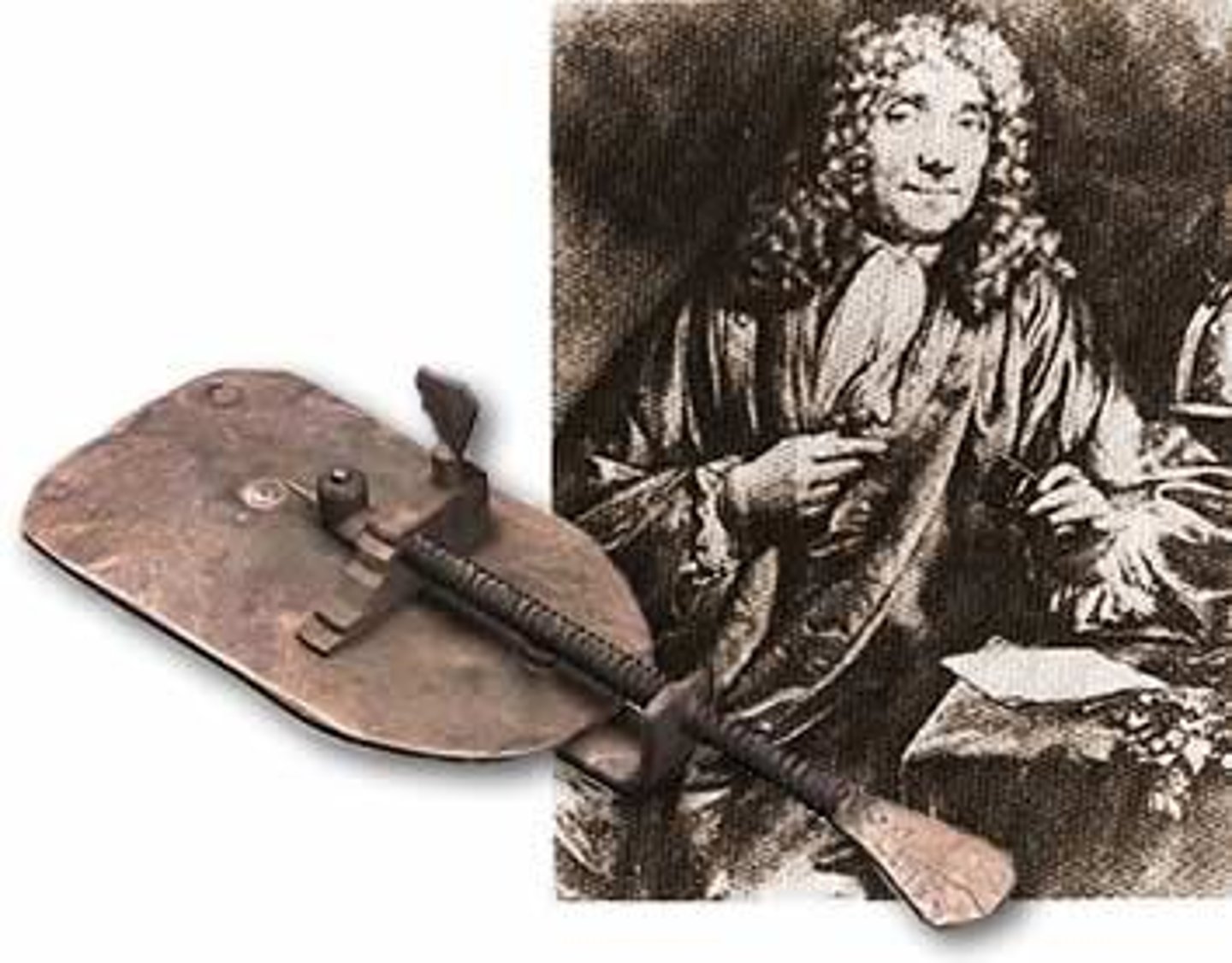

Animalcules
A microscopic "animal"; first observed by Anton van Leeuwenhoek

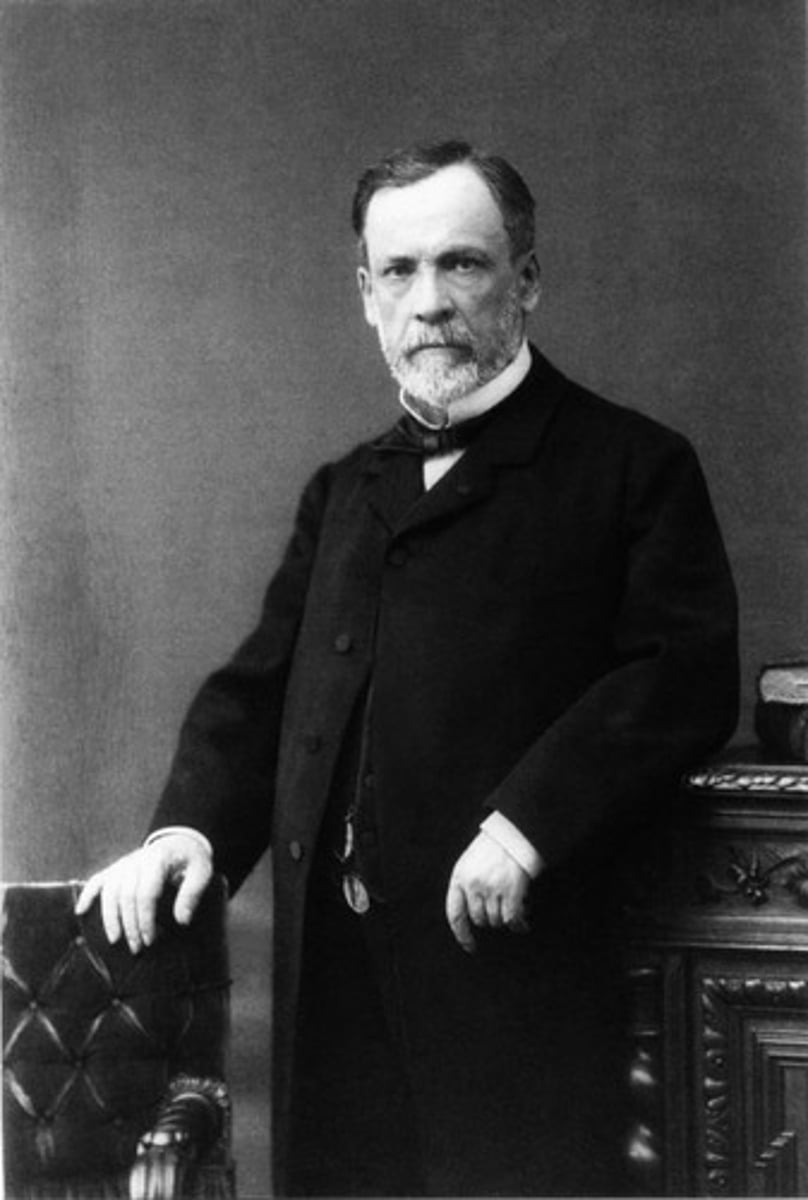
Louis Pasteur
A French chemist who discovered that life could exist in the absence of oxygen

Aerobes
Bacteria that require oxygen to grow

Anaerobes
Bacteria that grow in the absence of oxygen and are destroyed by oxygen

Pasteurization
A process of heating food/drinks to a temperature that is high enough to kill harmful bacteria
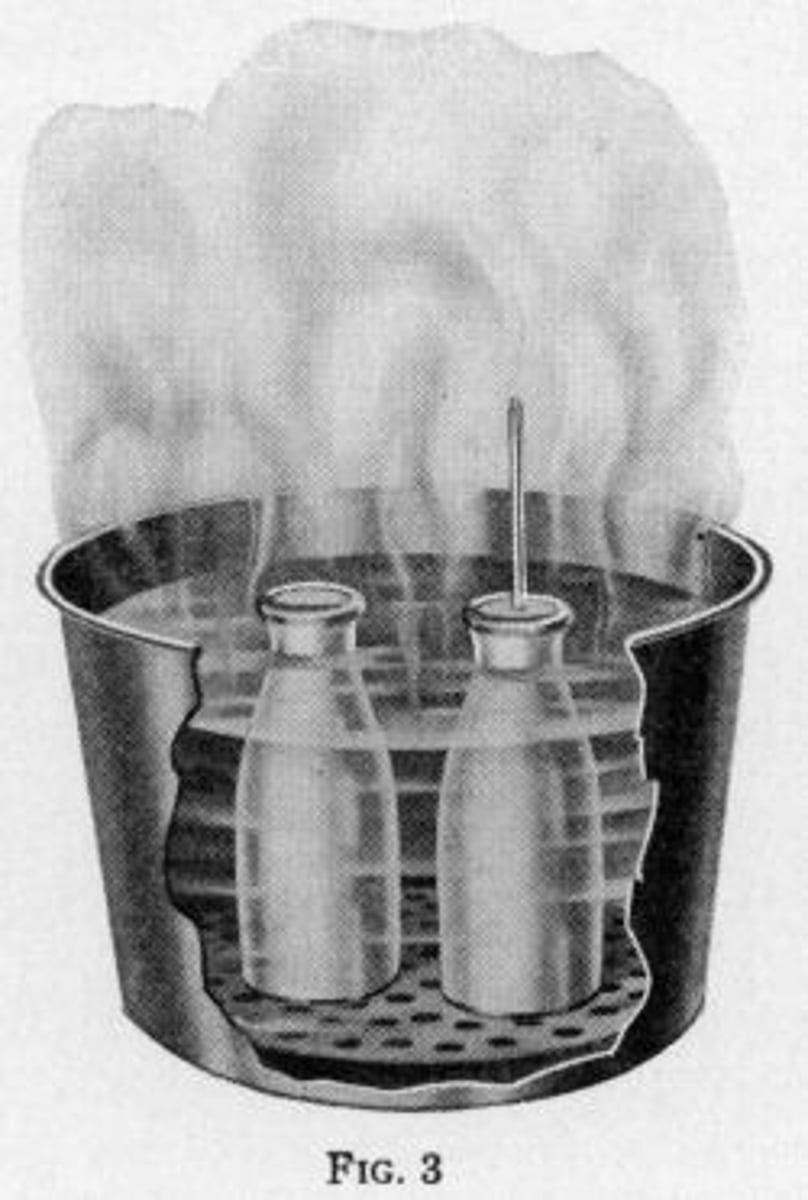
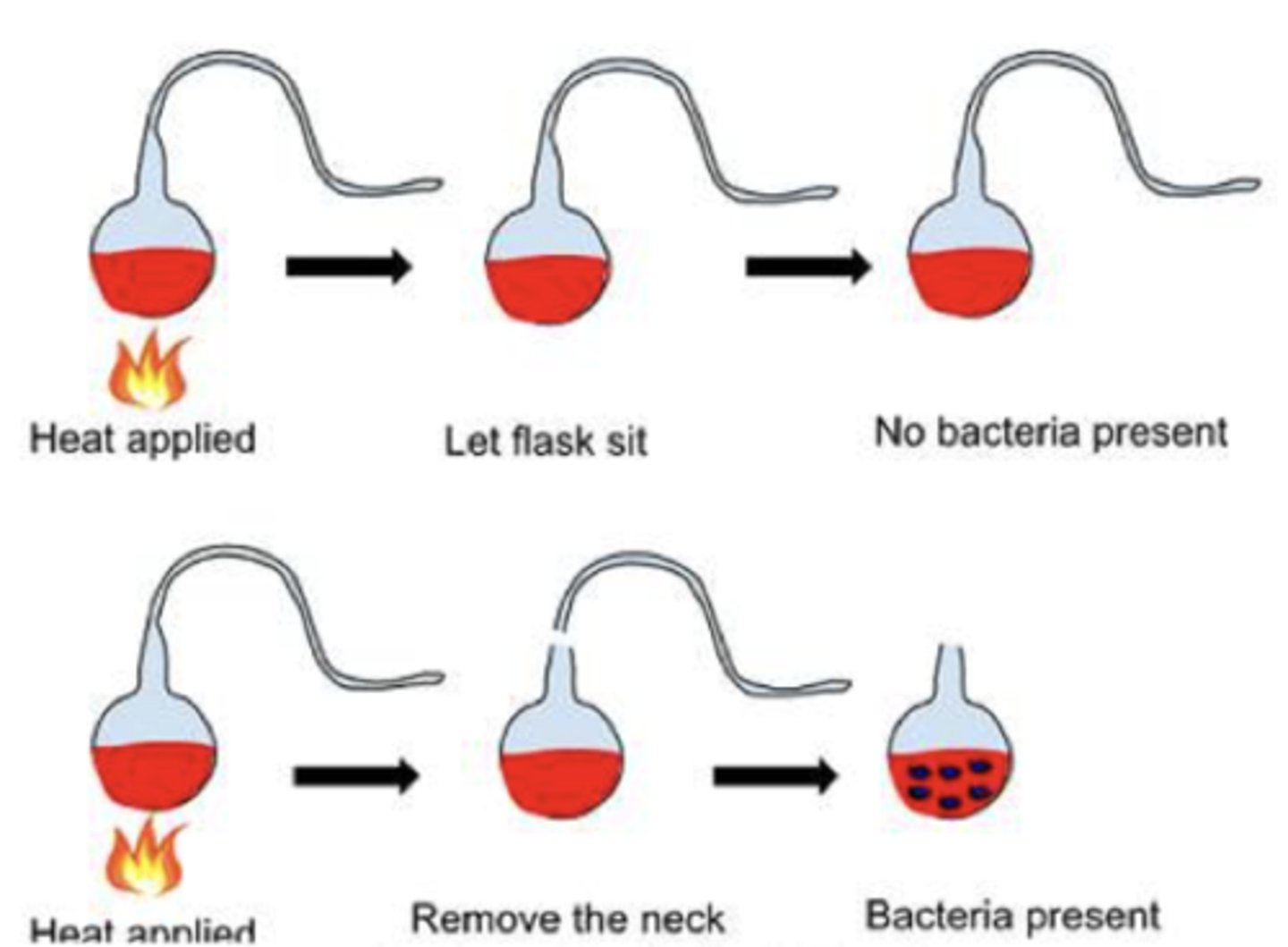
Swan-neck flask experiment
Pasteur proved that microbes cannot be spontaneously generated from nonliving things
Robert Koch
A German physician and microbiologist who developed methods for fixing and staining bacteria on a glass microscope slide
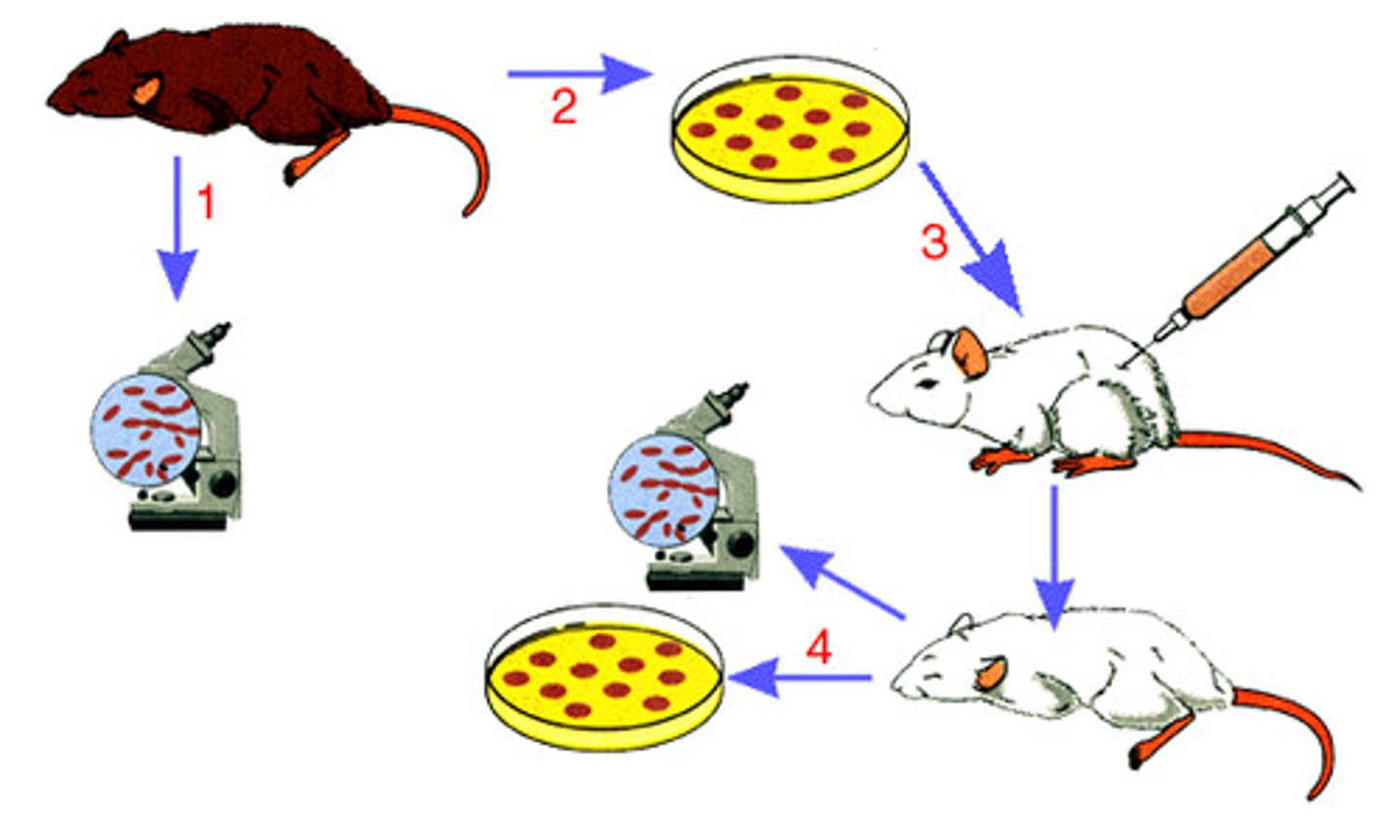
Koch's Postulates
A set of rules that proves that specific microorganisms cause specific diseases
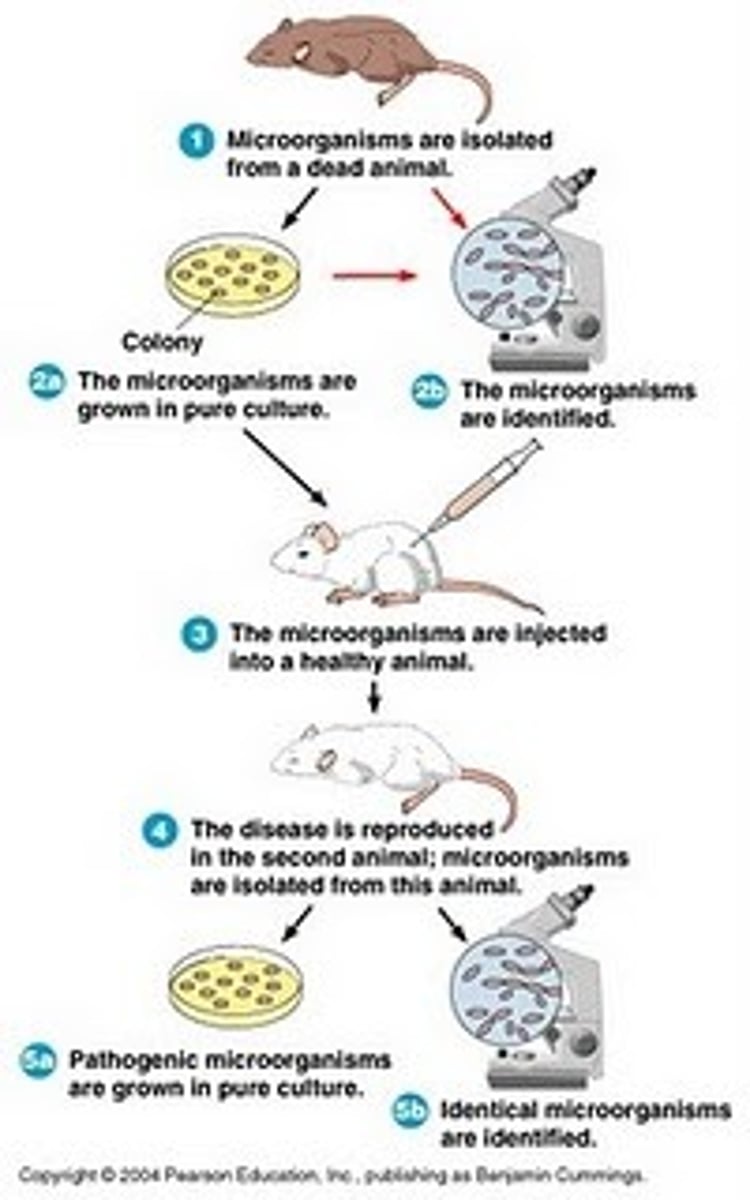
Postulate 1
Microorganism must always be found in similarly diseased animals but no healthy ones
Postulate 2
The microorganism must be isolated from a diseased animal and grown in a pure culture
Postulate 3
The isolated microorganism must cause the original disease when inoculated into a healthy animal
Postulate 4
The microorganism can be re-isolated from the experimentally infected animal
Obligate Intracellular Pathogens
Pathogens, such as viruses, that can only grow when inside cells --> violates postulate 2
Species-specific pathogens
Pathogens that are unable to infect certain species --> violates postulate 3
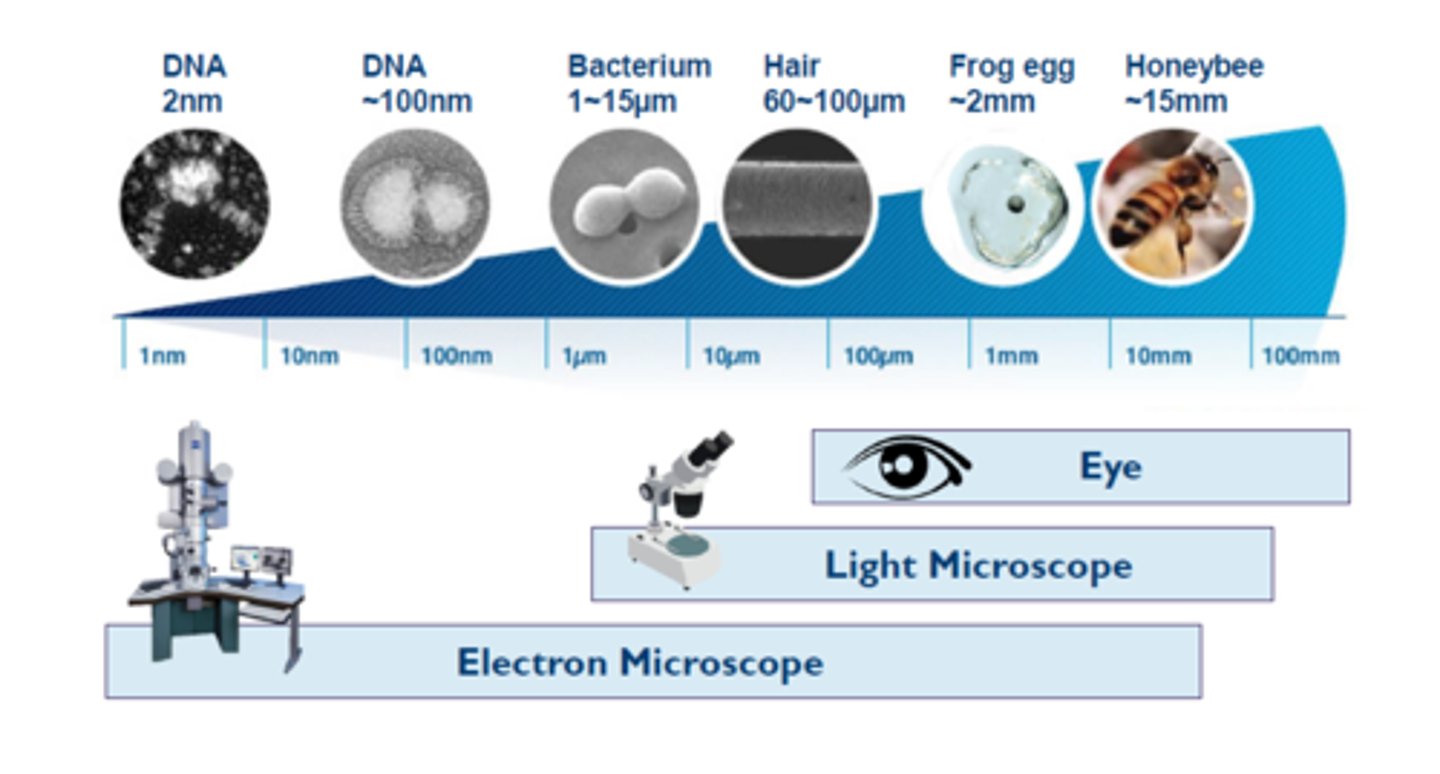
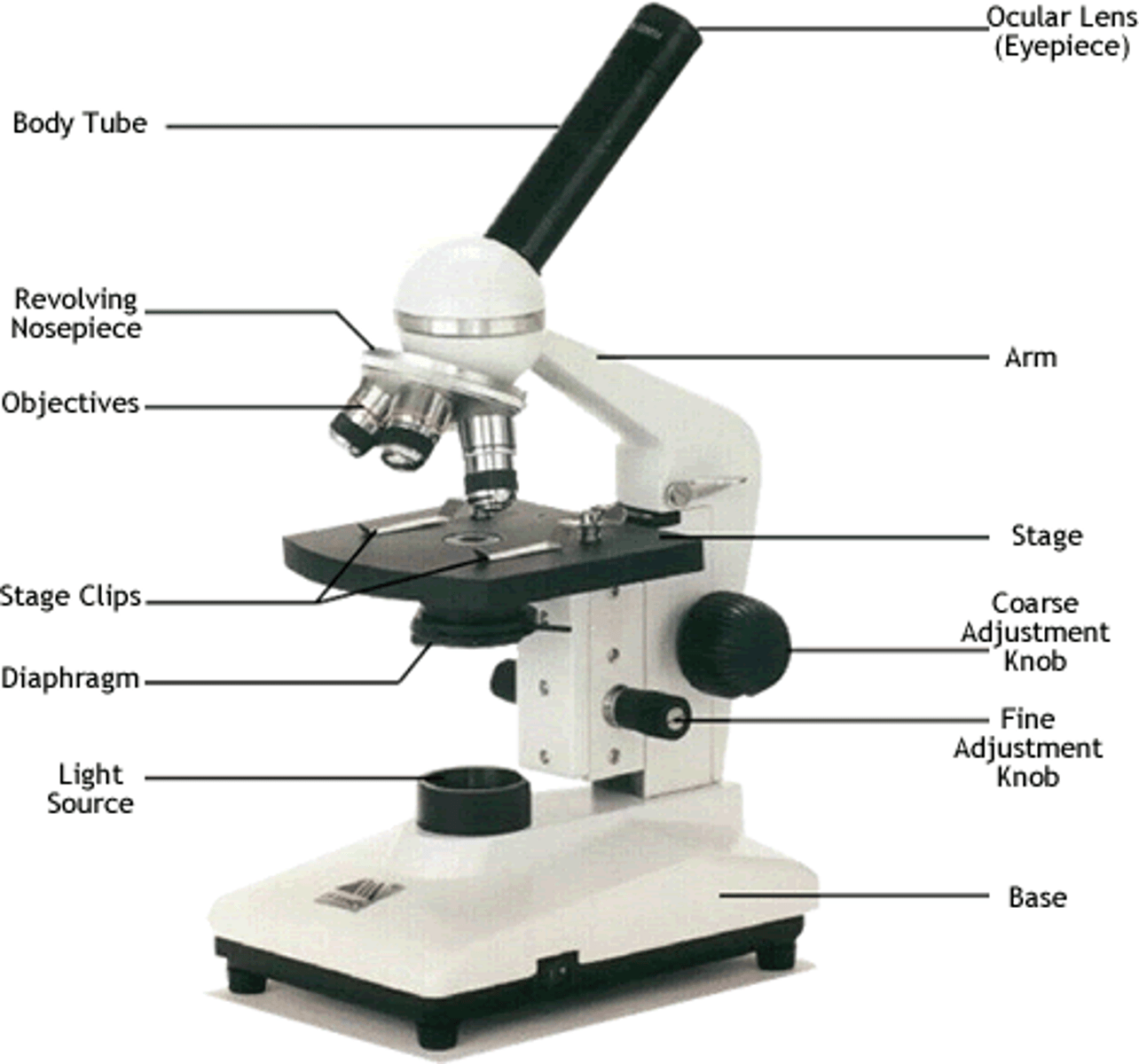
Microscope
A device that magnifies images of structures that are too small to see with the naked eye

Resolving power
The ability of an microscope to show two objects as separate
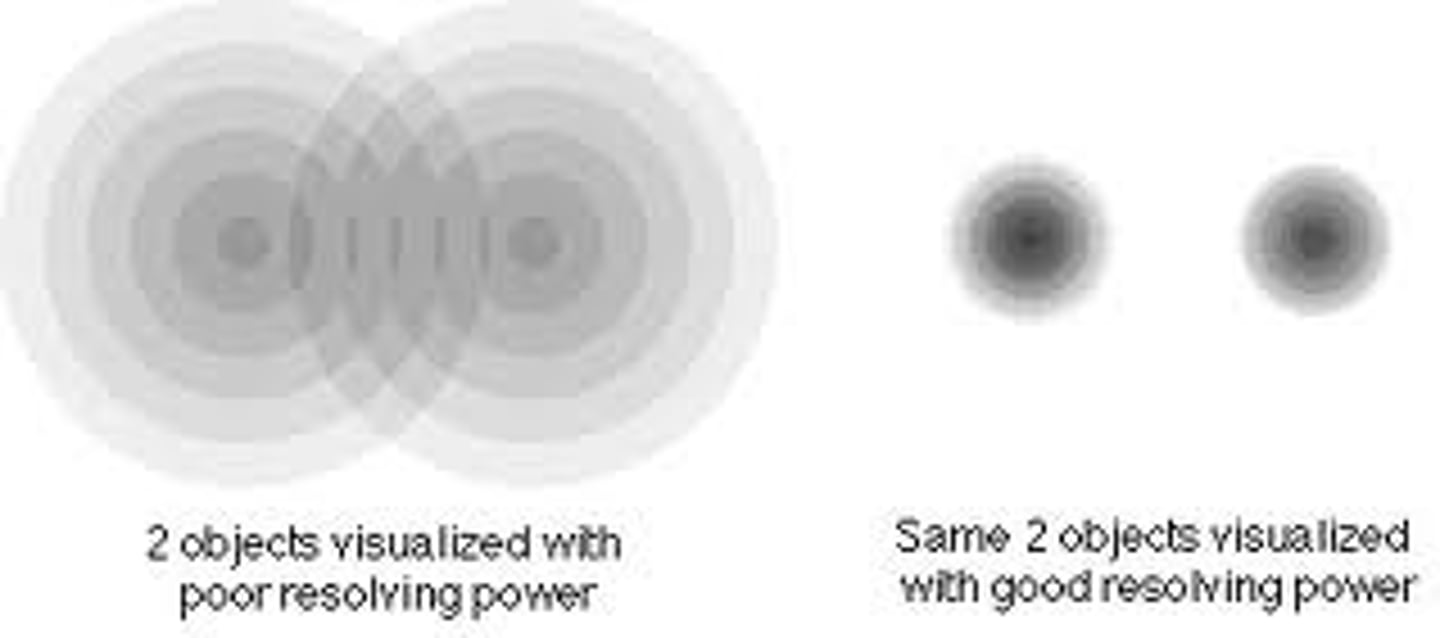
What is the resolving power/resolution of the human eye?
0.2 millimeters (mm)
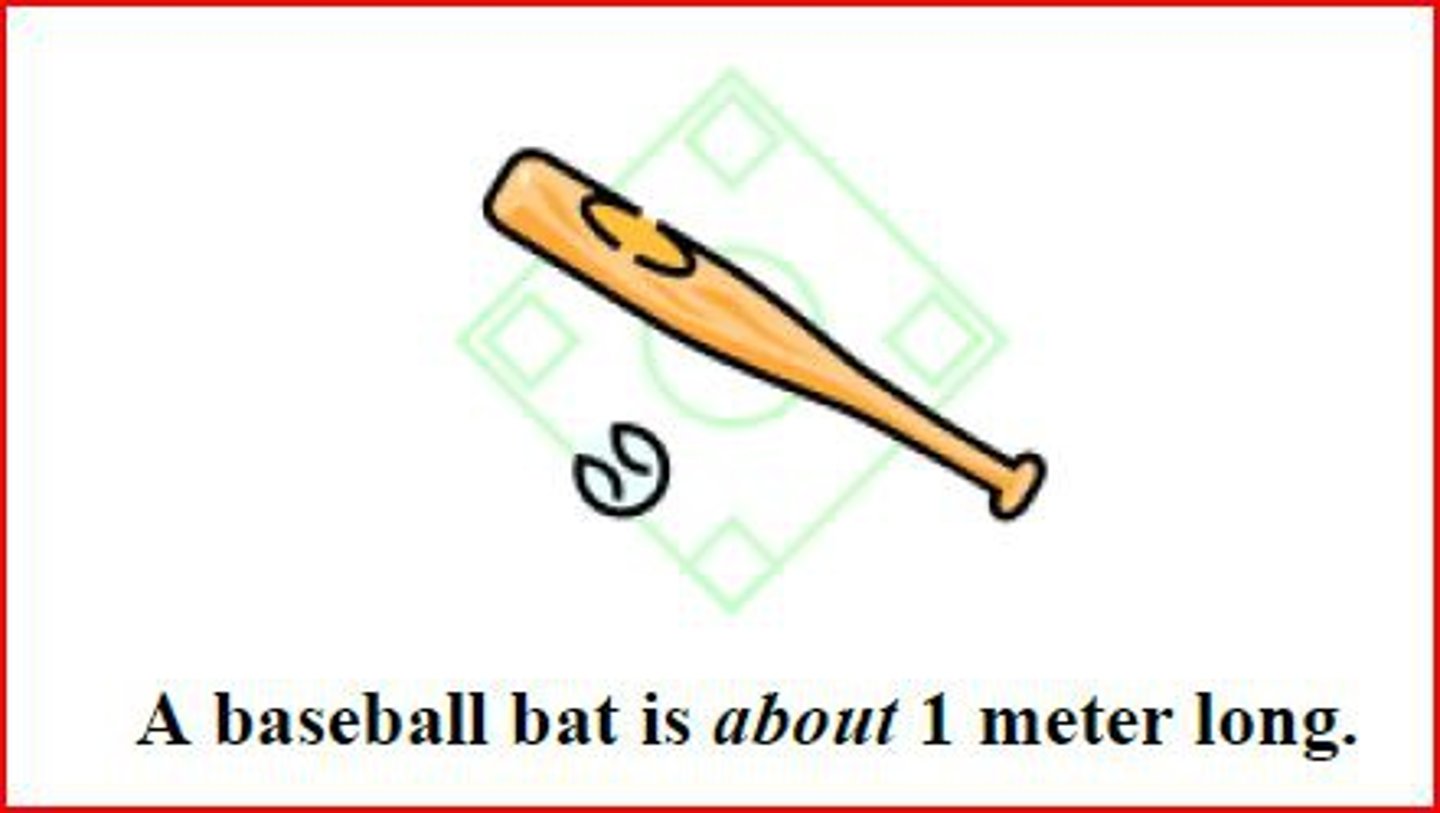
How many inches in a meter?
39.37 inches
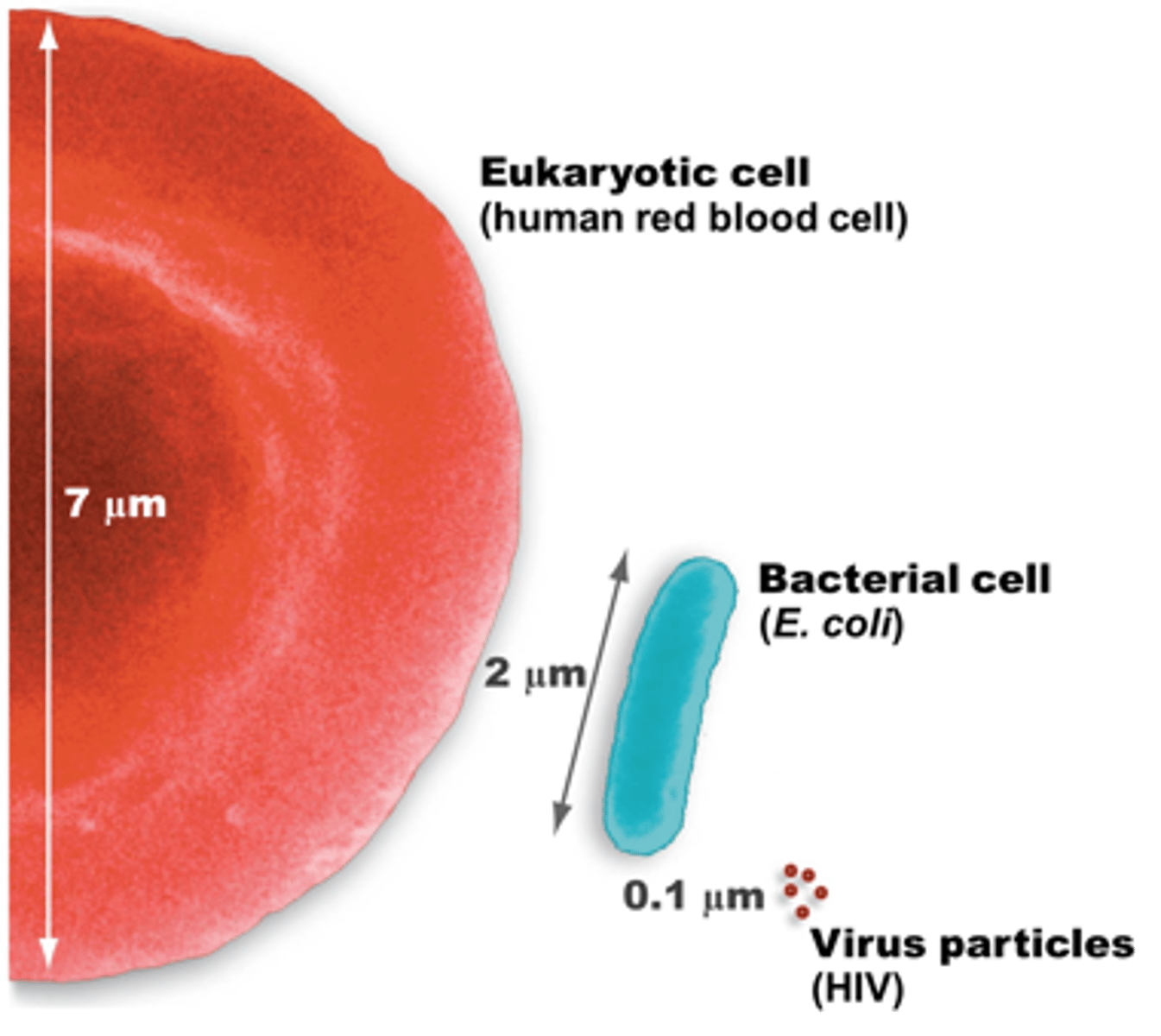
How big are bacteria?
1-10 micrometers long
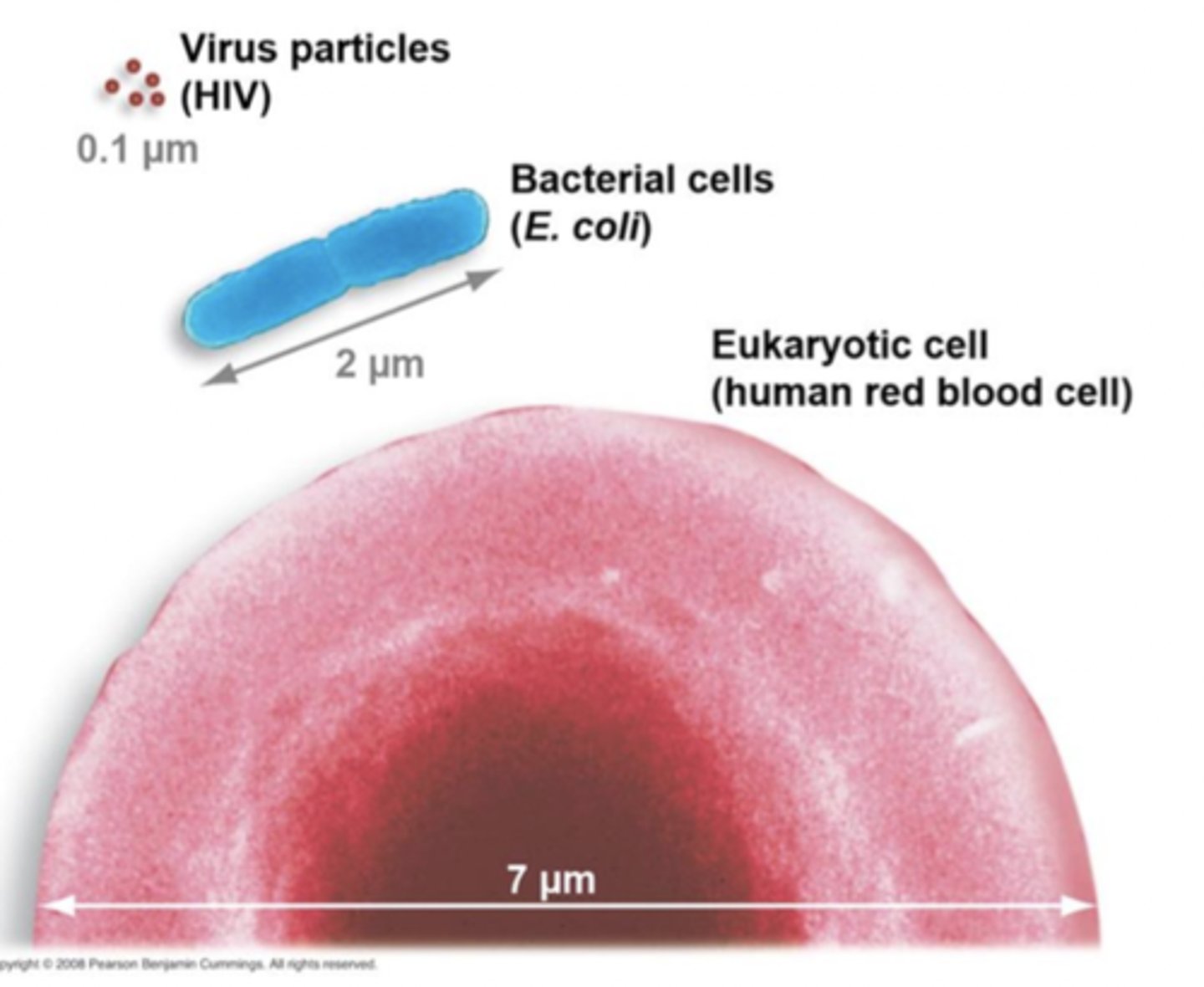
How big are viruses?
10-30 nanometers (SO SMALL)
Simple microscope
A microscope that contains only one lens (3-20x naked eye)

Compound microscope
A light microscope that has more than one lens (1,000x naked eye)
Photomicrograph
Photograph of an image seen using a compound microscope
Electron Microscopes
A powerful microscope that uses beams of electrons (not light) to produce images

Transmission electron microscope
A microscope that uses an electron beam to study the internal structure of cells
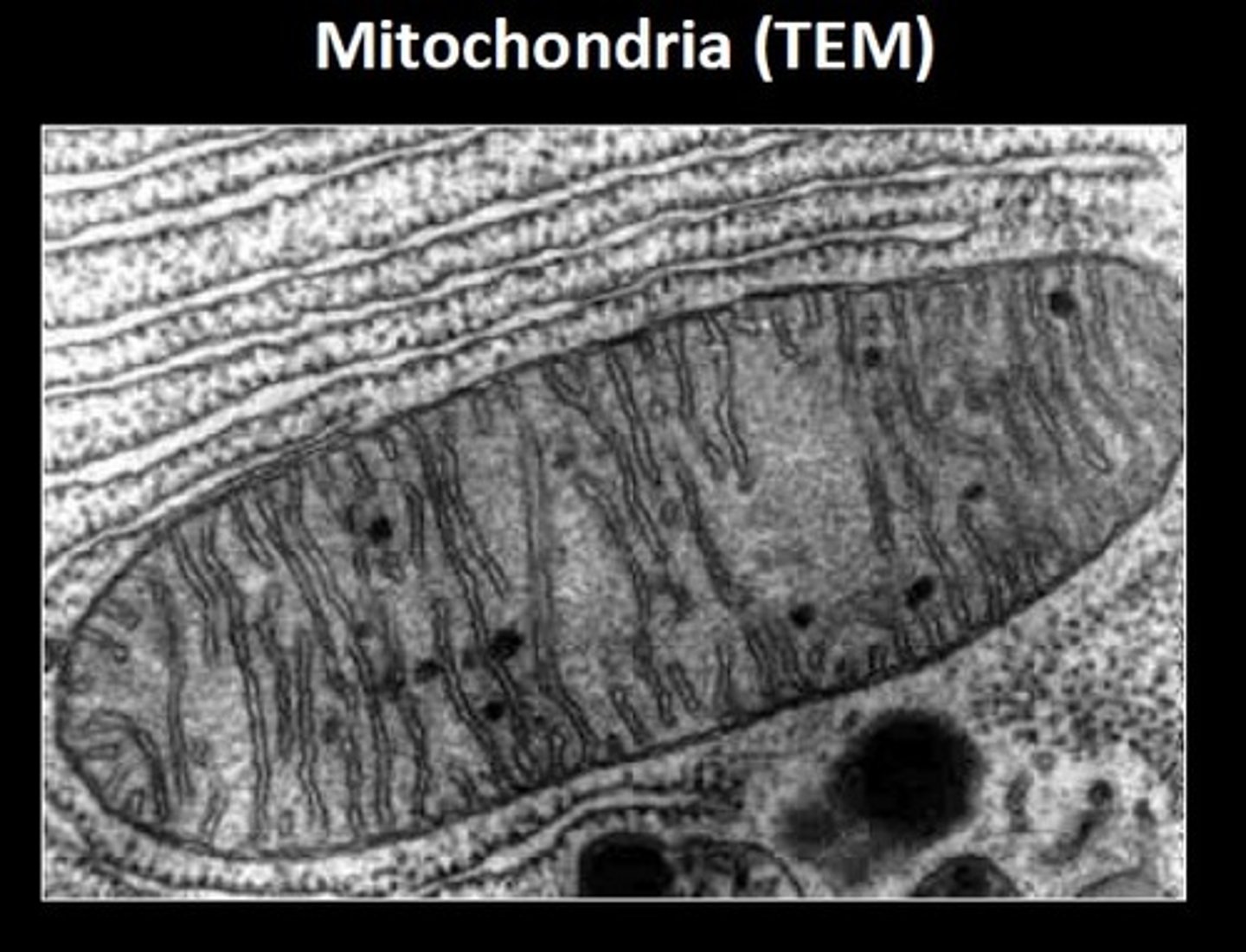
Scanning electron microscope
A microscope that uses an electron beam to study the external structure of cells

Electronmicrograph
Photograph of an image seen using an electron microscope
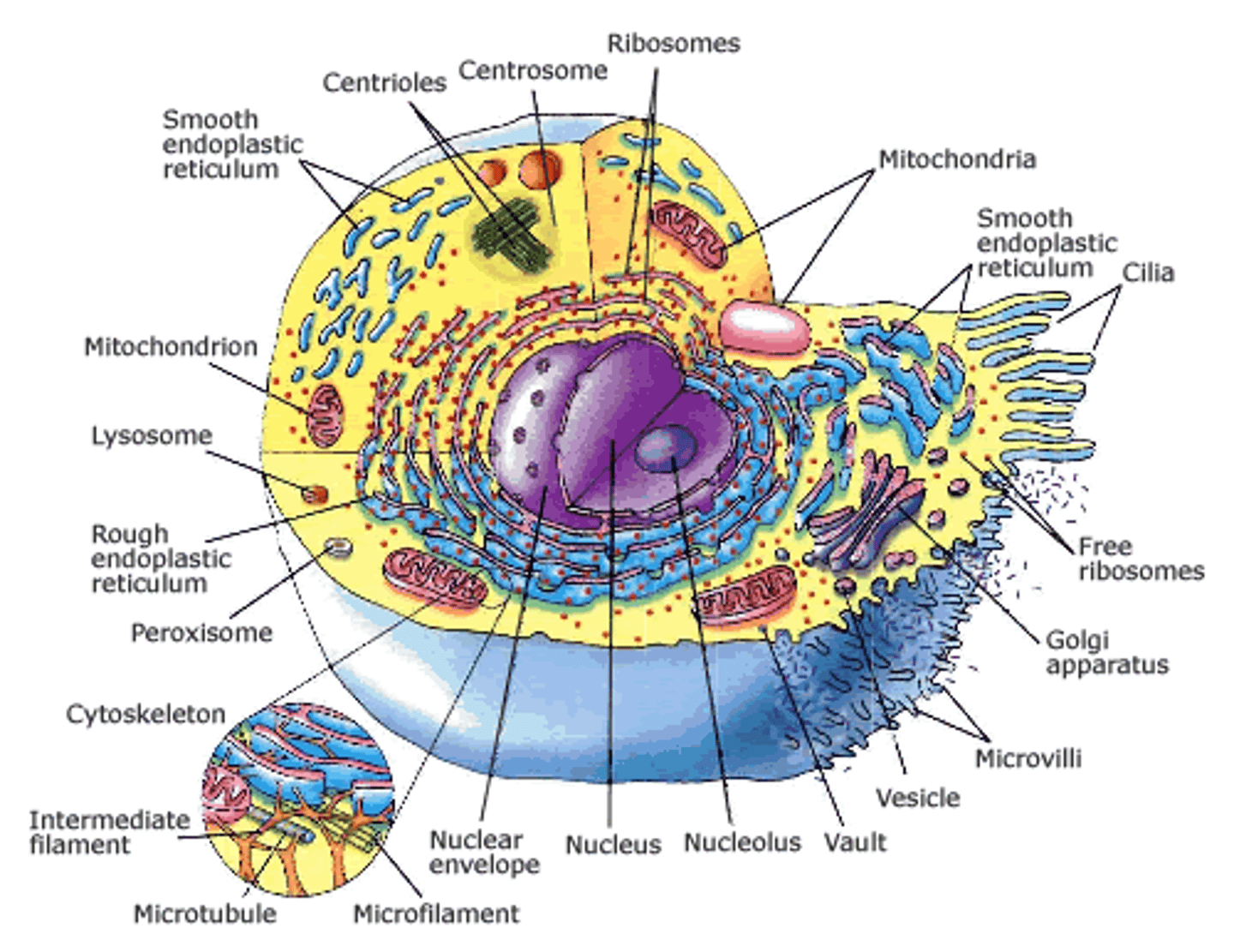
Cytology
The study of the structure and function of cells
Cell membrane
A semipermeable membrane that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell
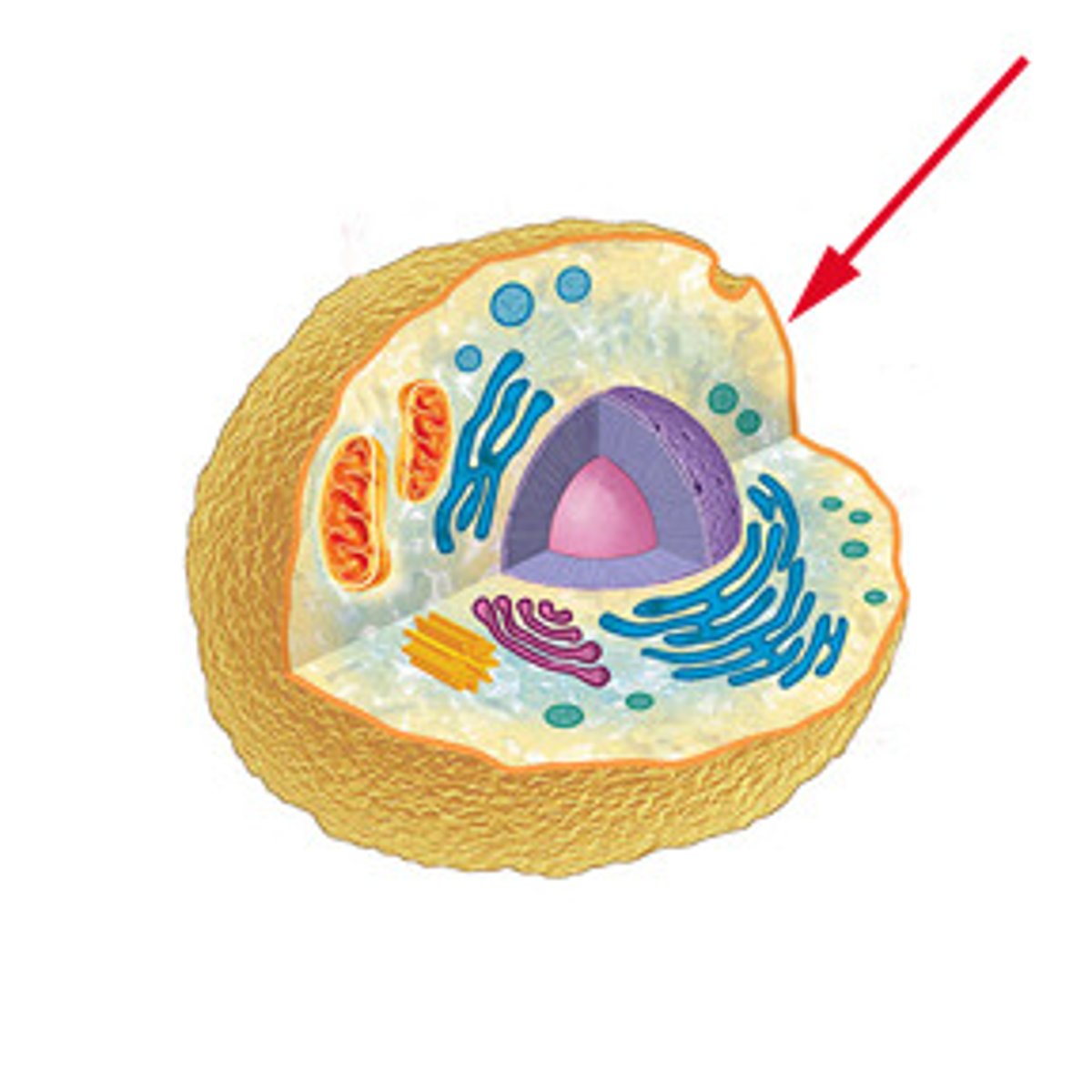
Cytoplasm
The portion of the cell outside the nucleus
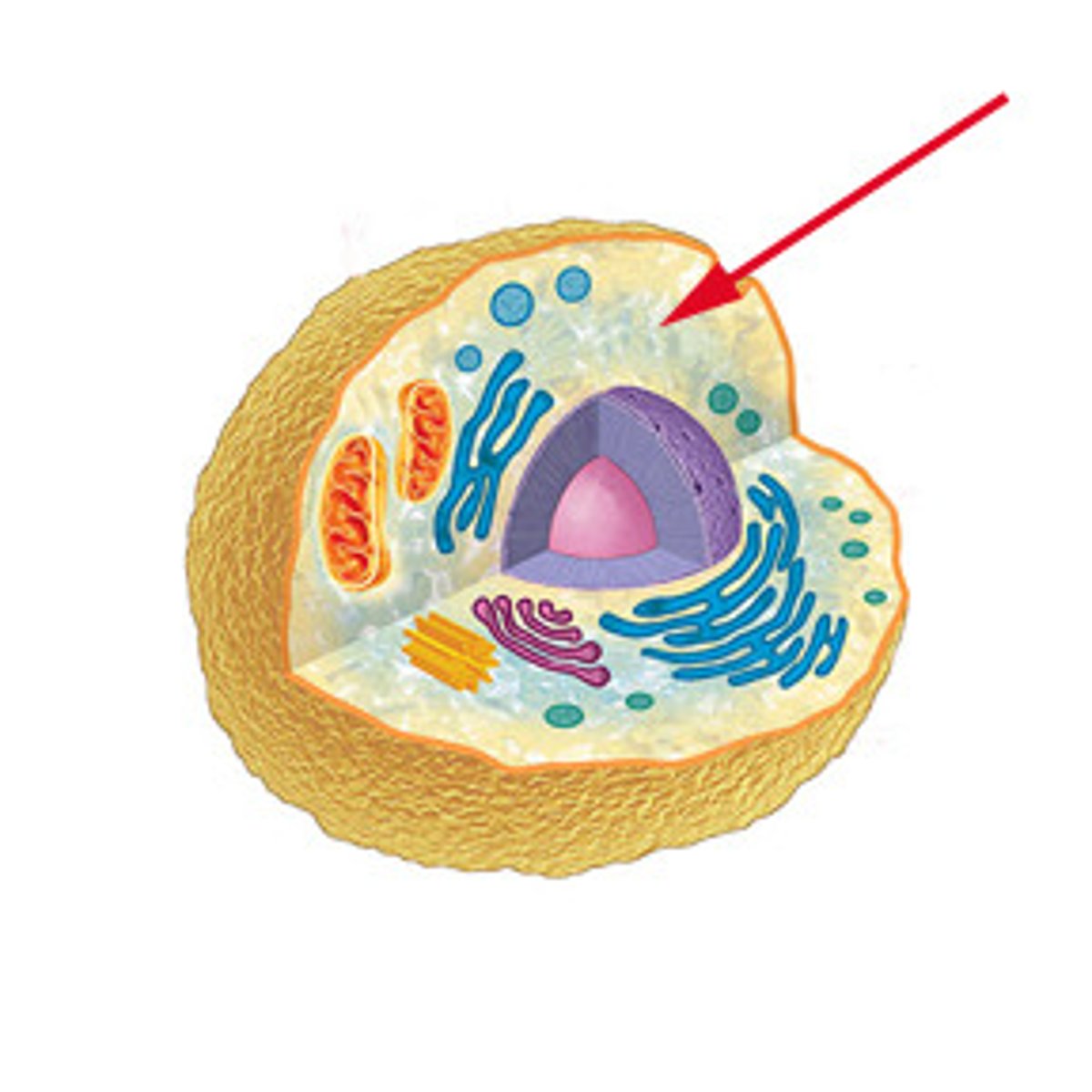
Cytosol
Fluid portion of cytoplasm
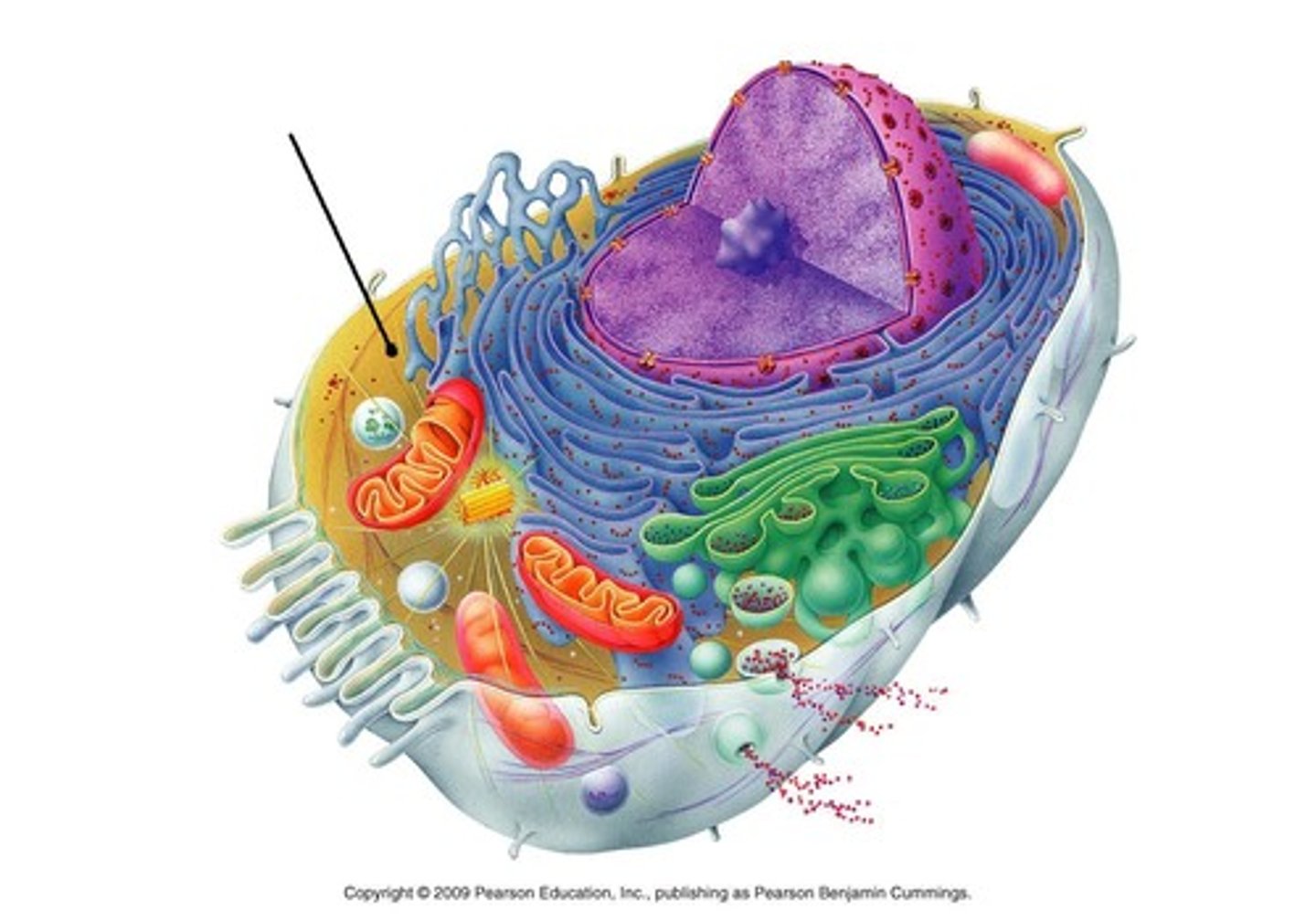
Nucleus
Control center of the cell where the DNA is stored
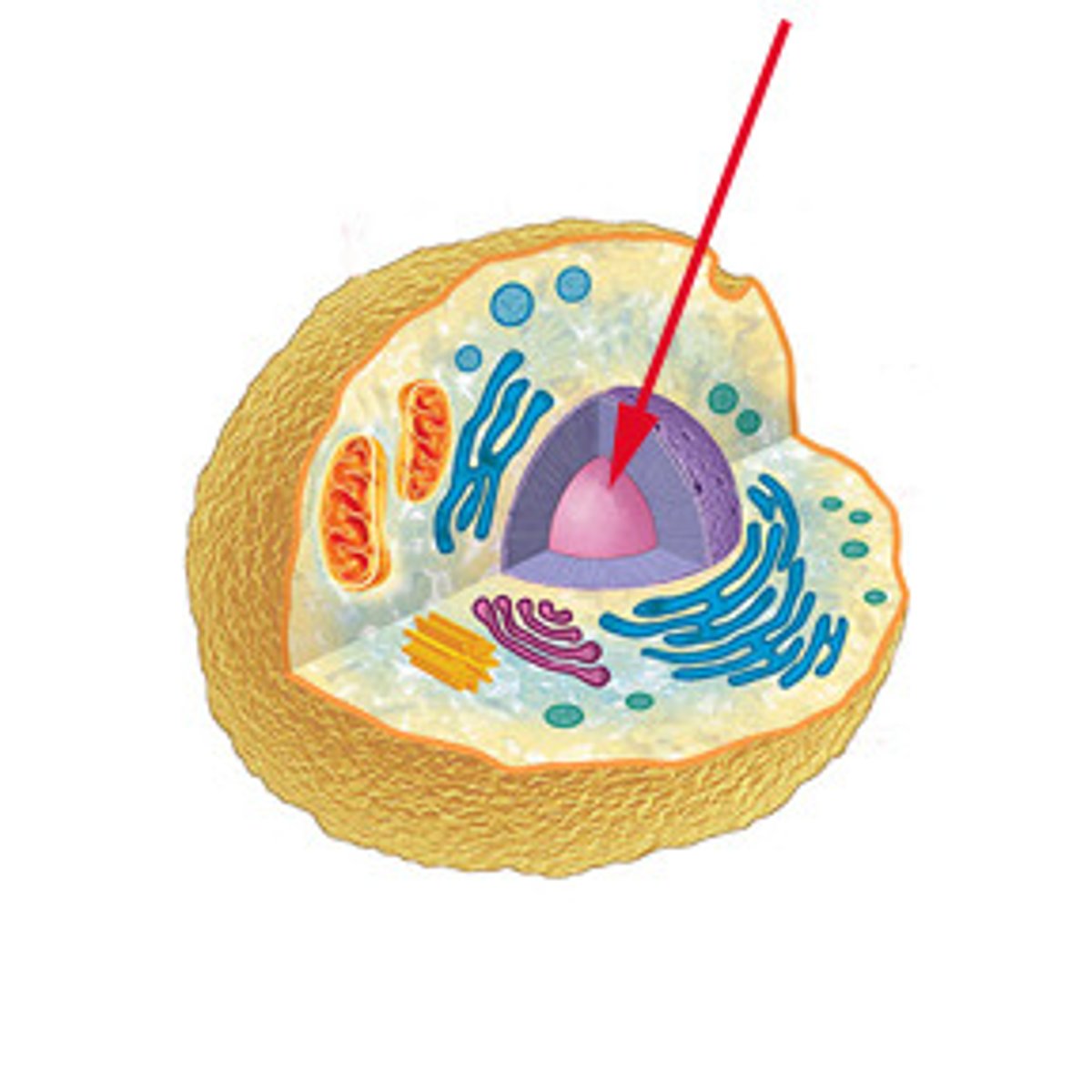
Nucleoplasm
Gelatinous fluid inside the nucleus
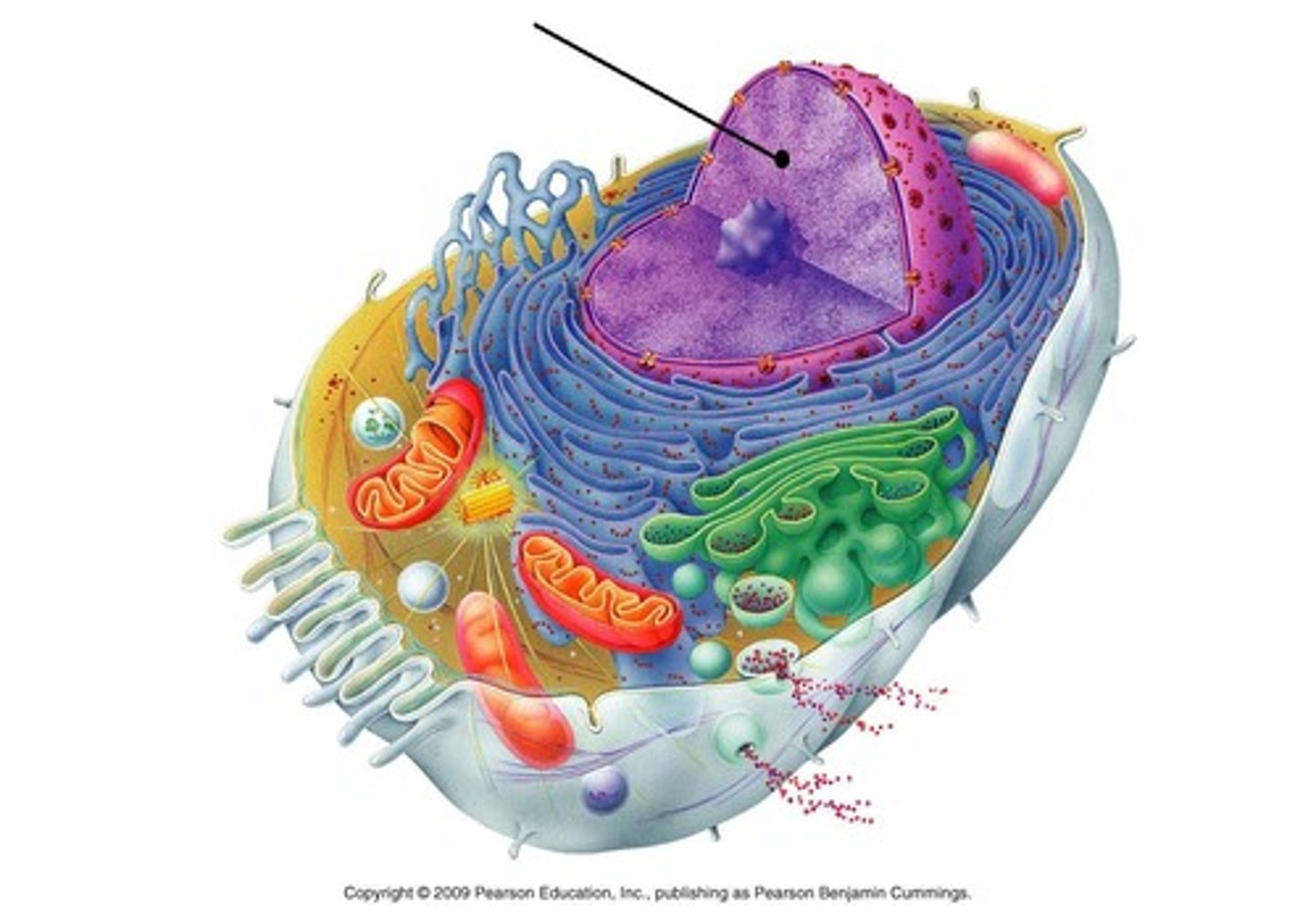
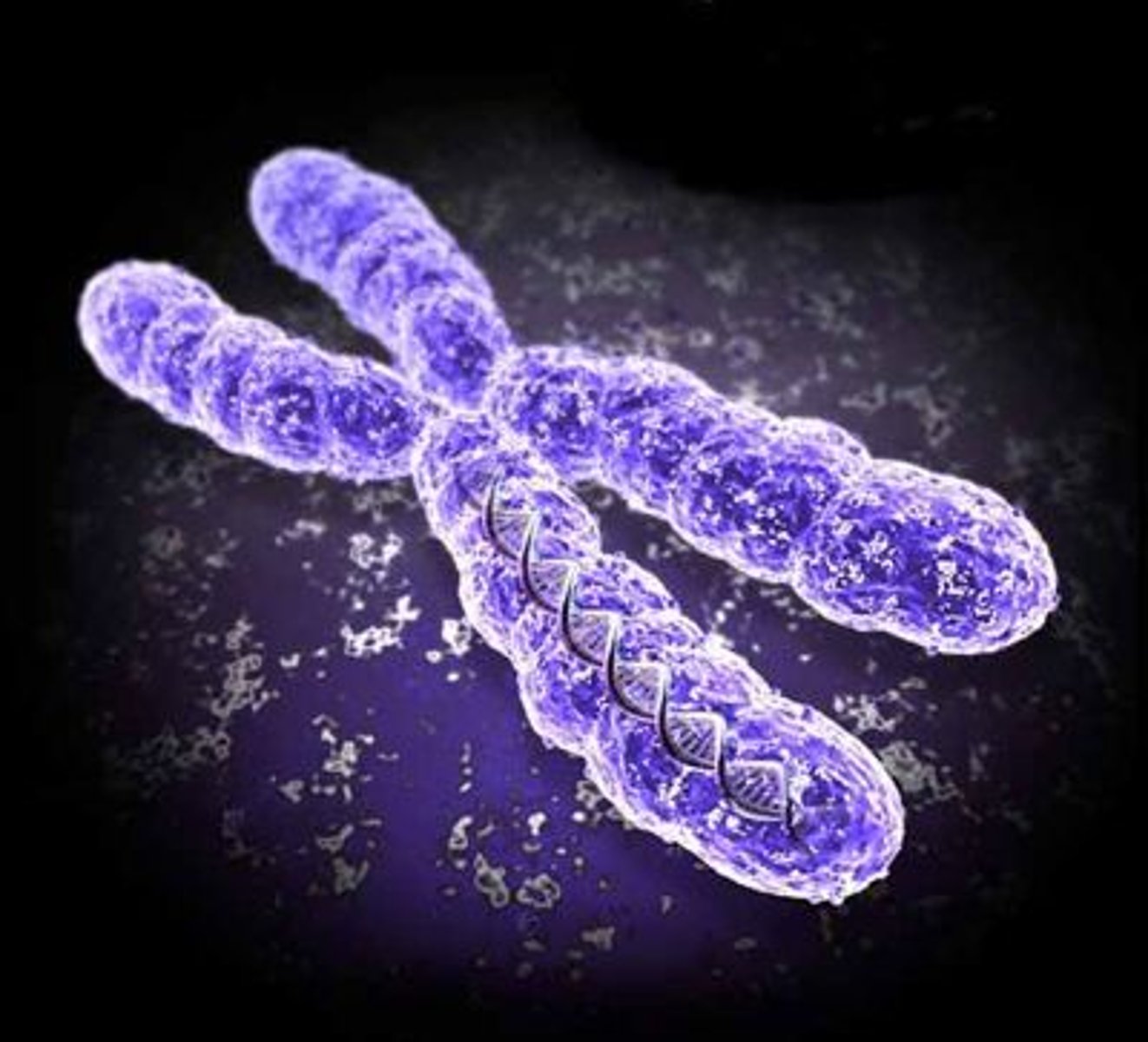
Chromosomes
DNA molecules and proteins inside the nucleoplasm
Nuclear membrane
A membrane that controls what goes in and out of the nucleus
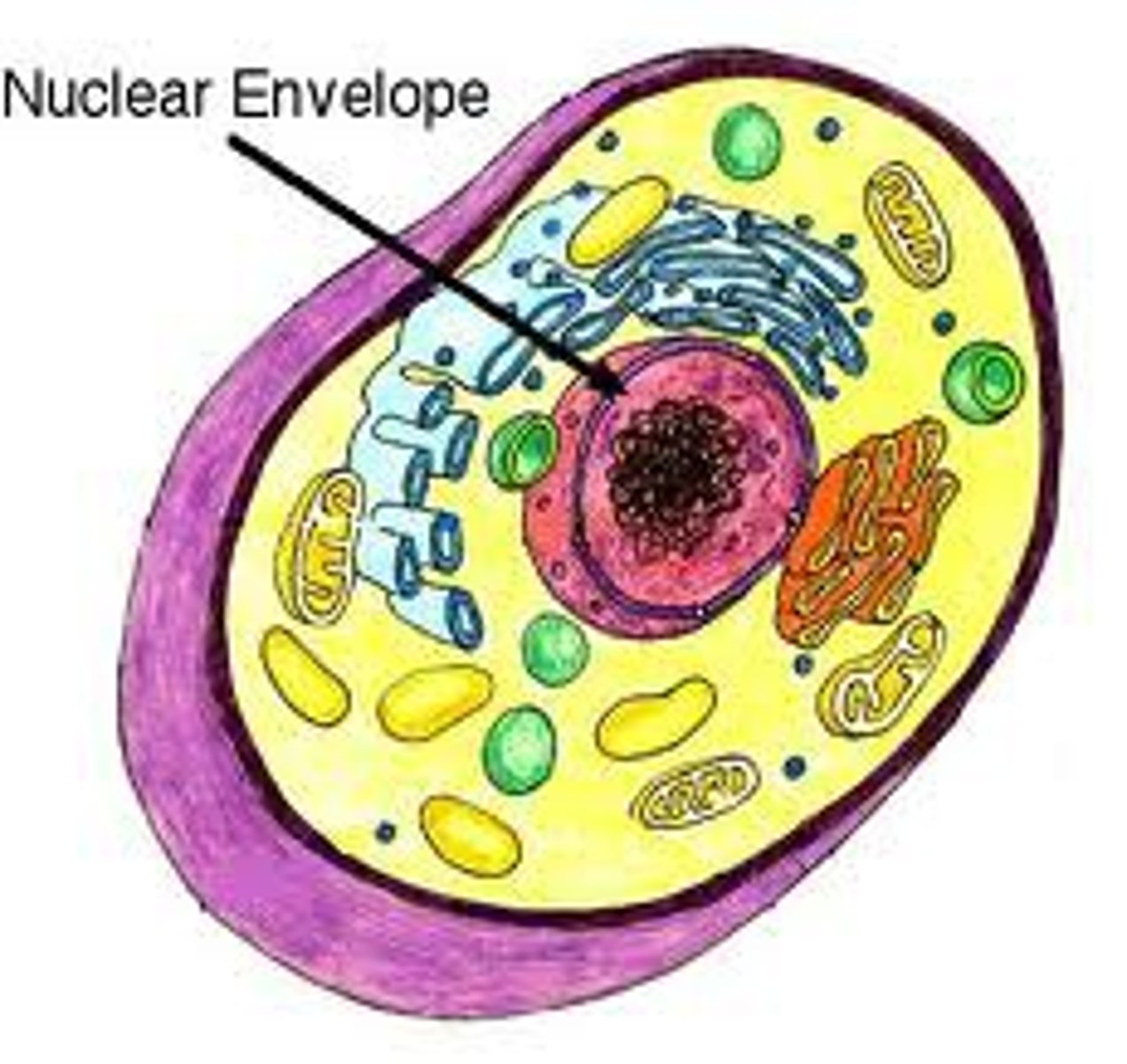
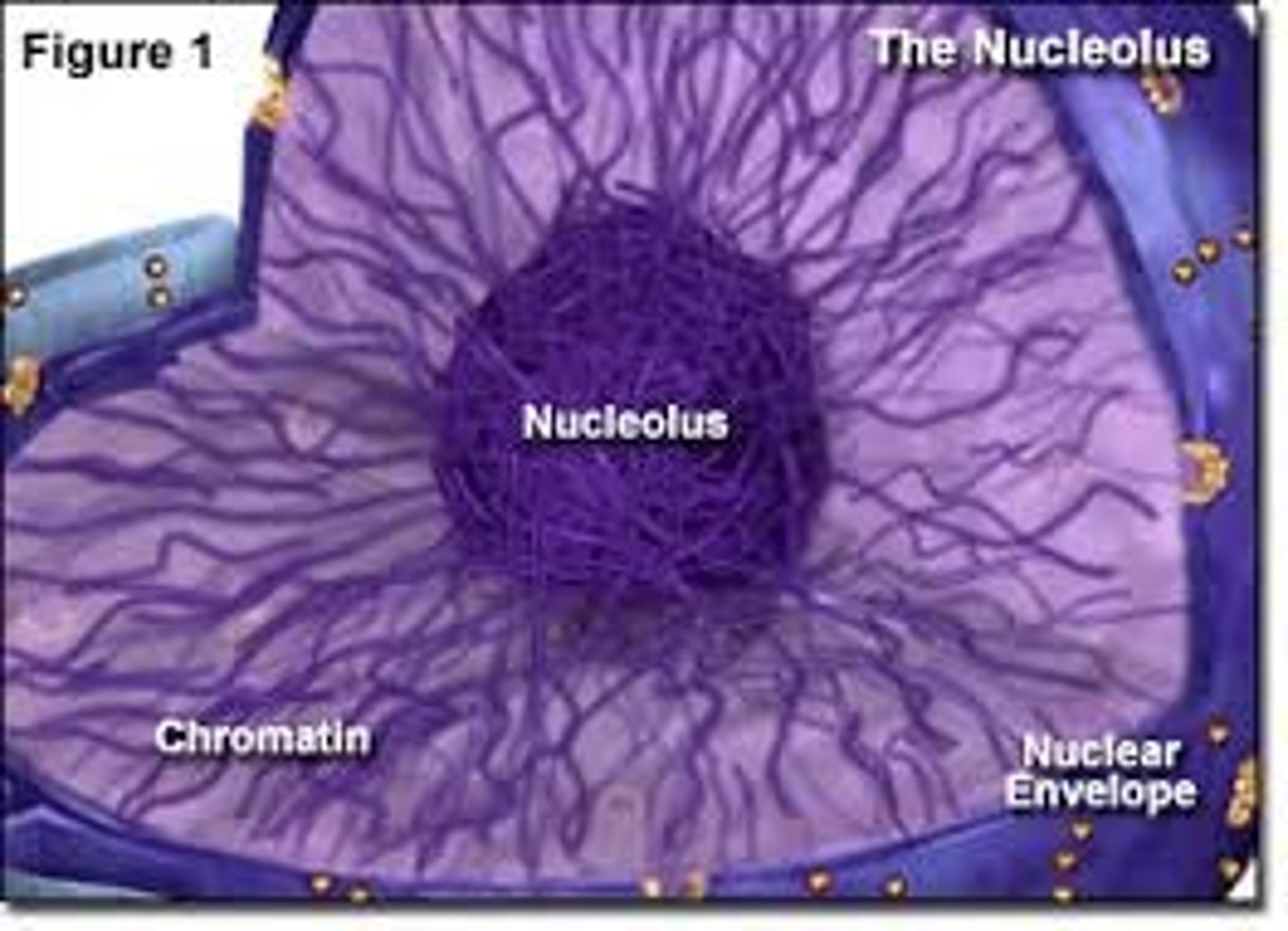
Nucleolus
A sphere in the middle of the nucleus that produces ribosomes
Endoplasmic reticulum
An organelle composed of several convoluted folded membranes that form passageways for proteins/materials to travel within the cell
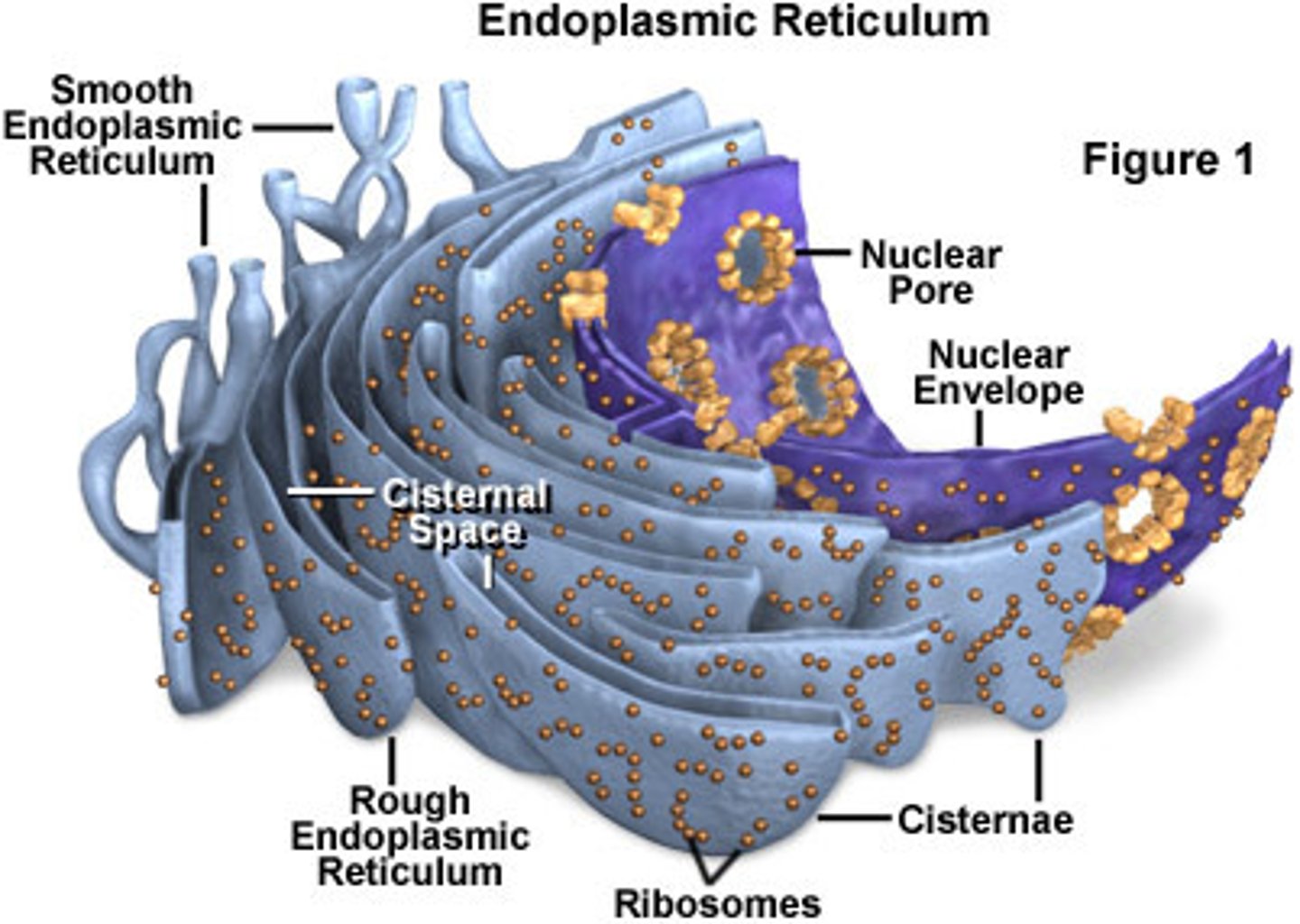
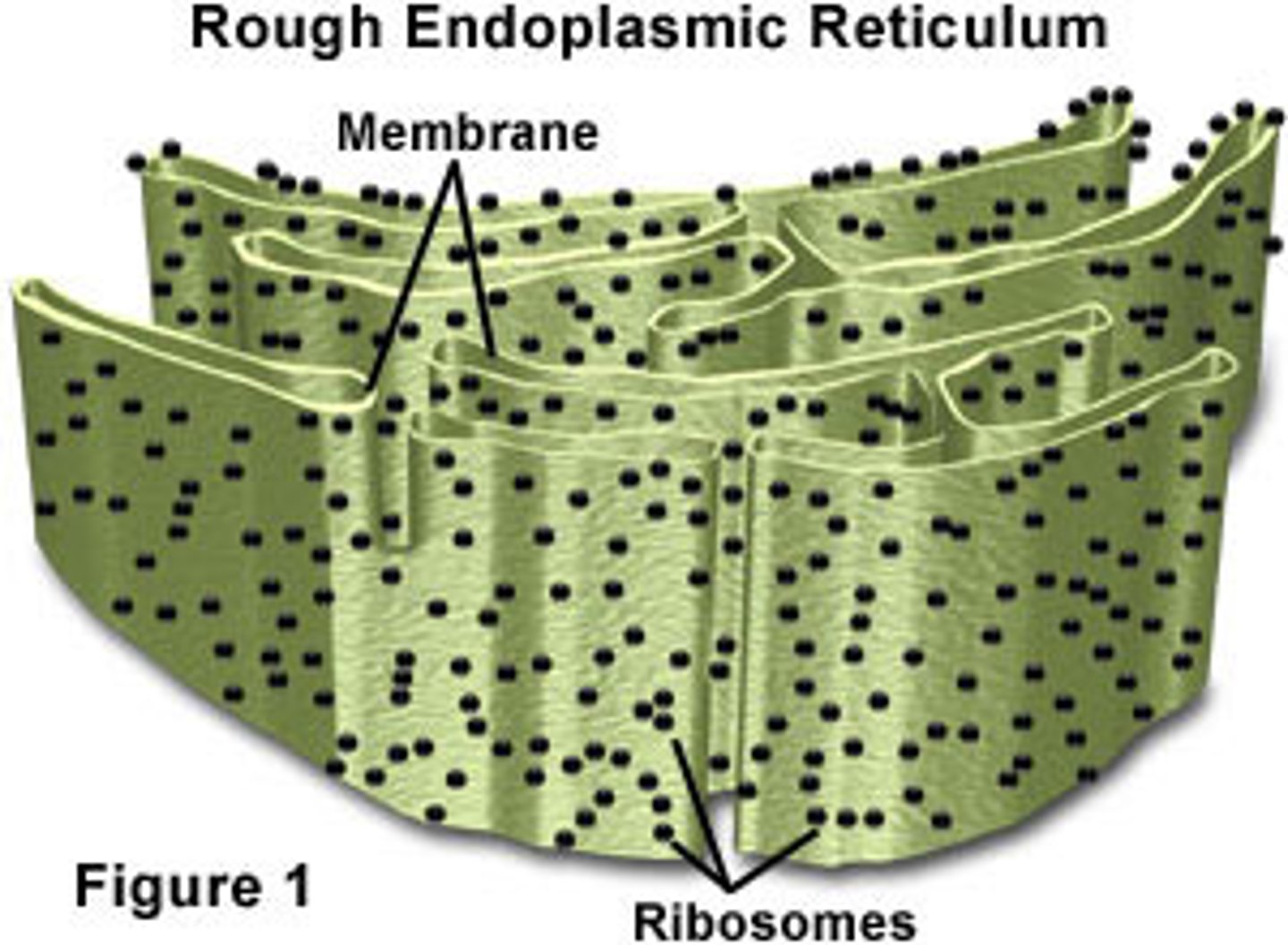
Rough ER
Section of the ER that contains ribosomes
Smooth ER
Section of the ER that does NOT contain ribosomes
Ribosomes
Organelles that synthesize proteins
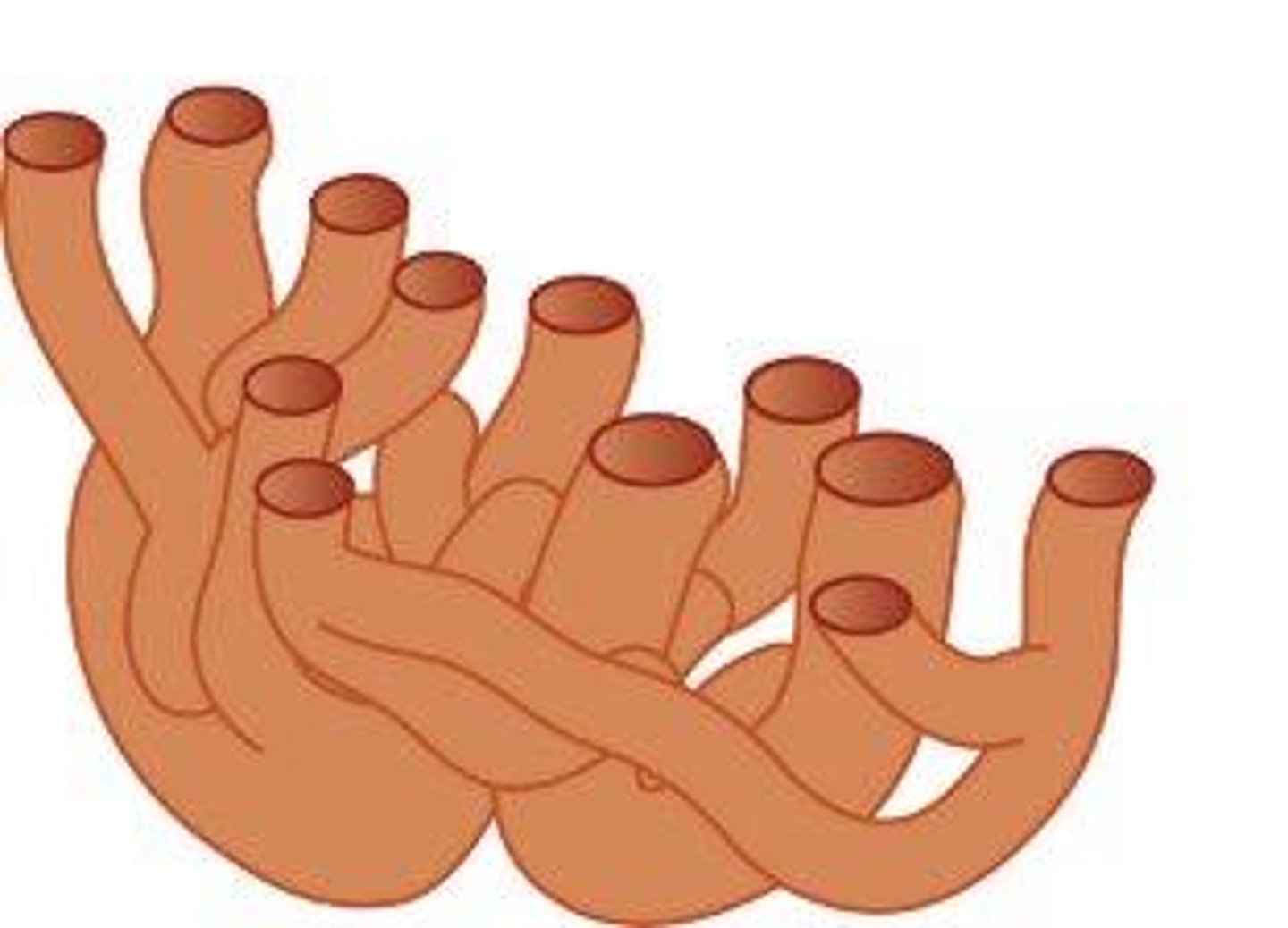
Golgi complex
Organelle that packages and distributes proteins

Lysosomes
An organelle that contains digestive enzymes
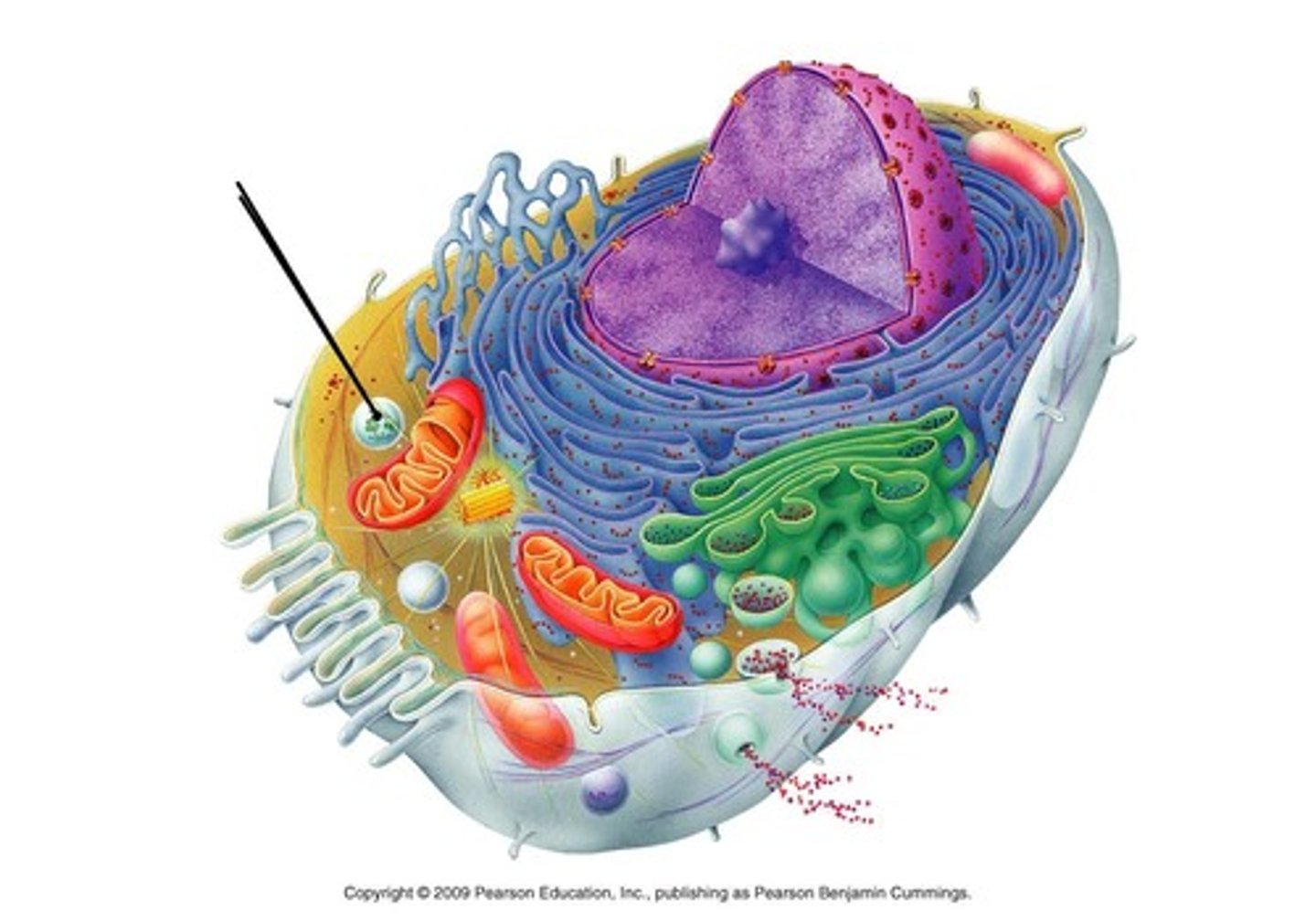
Peroxisomes
Organelles that contain catalase which speeds up breakdown of H2O2
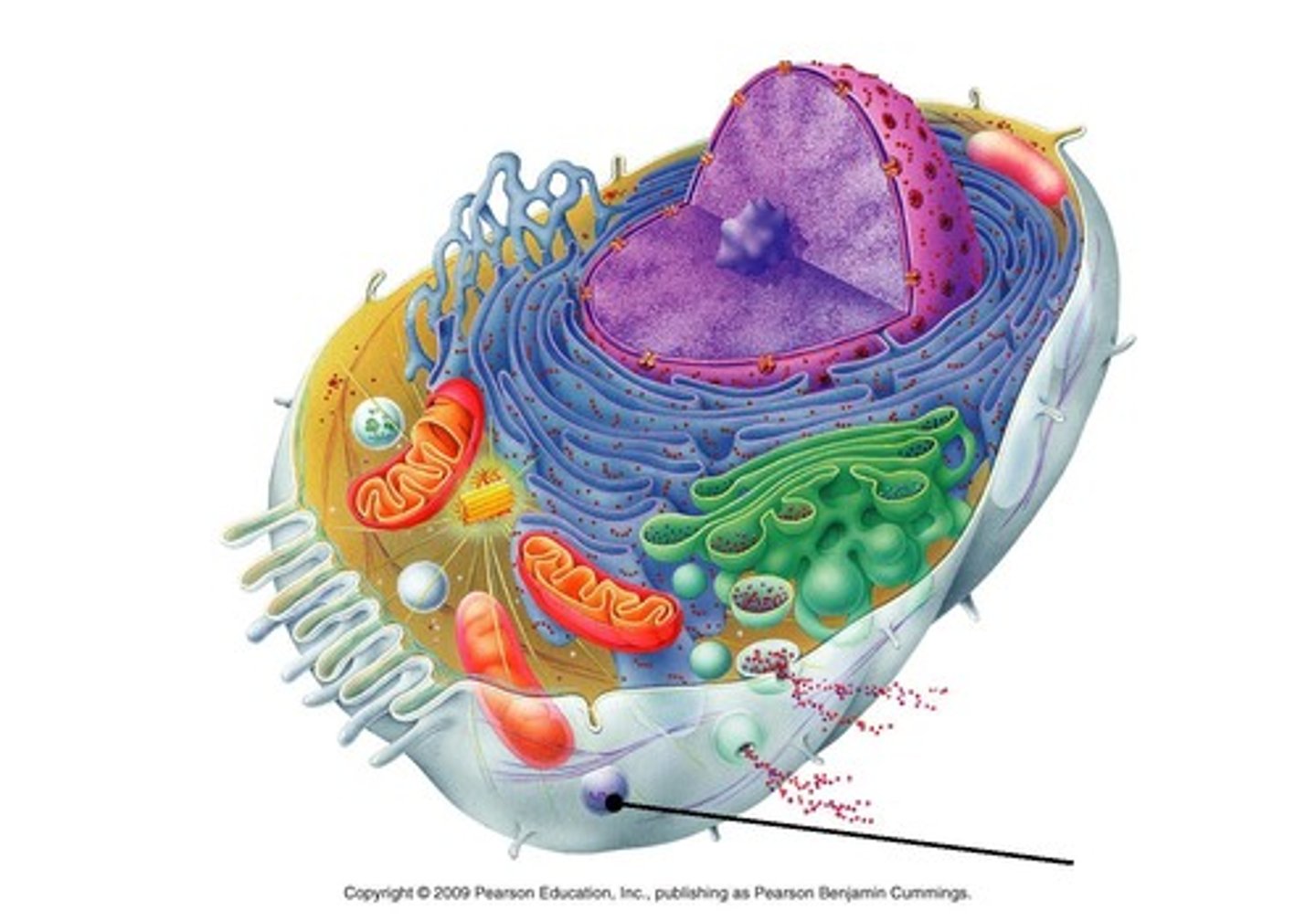
Mitochondria
POWERHOUSE OF THE CELL, organelle that is the site of ATP production
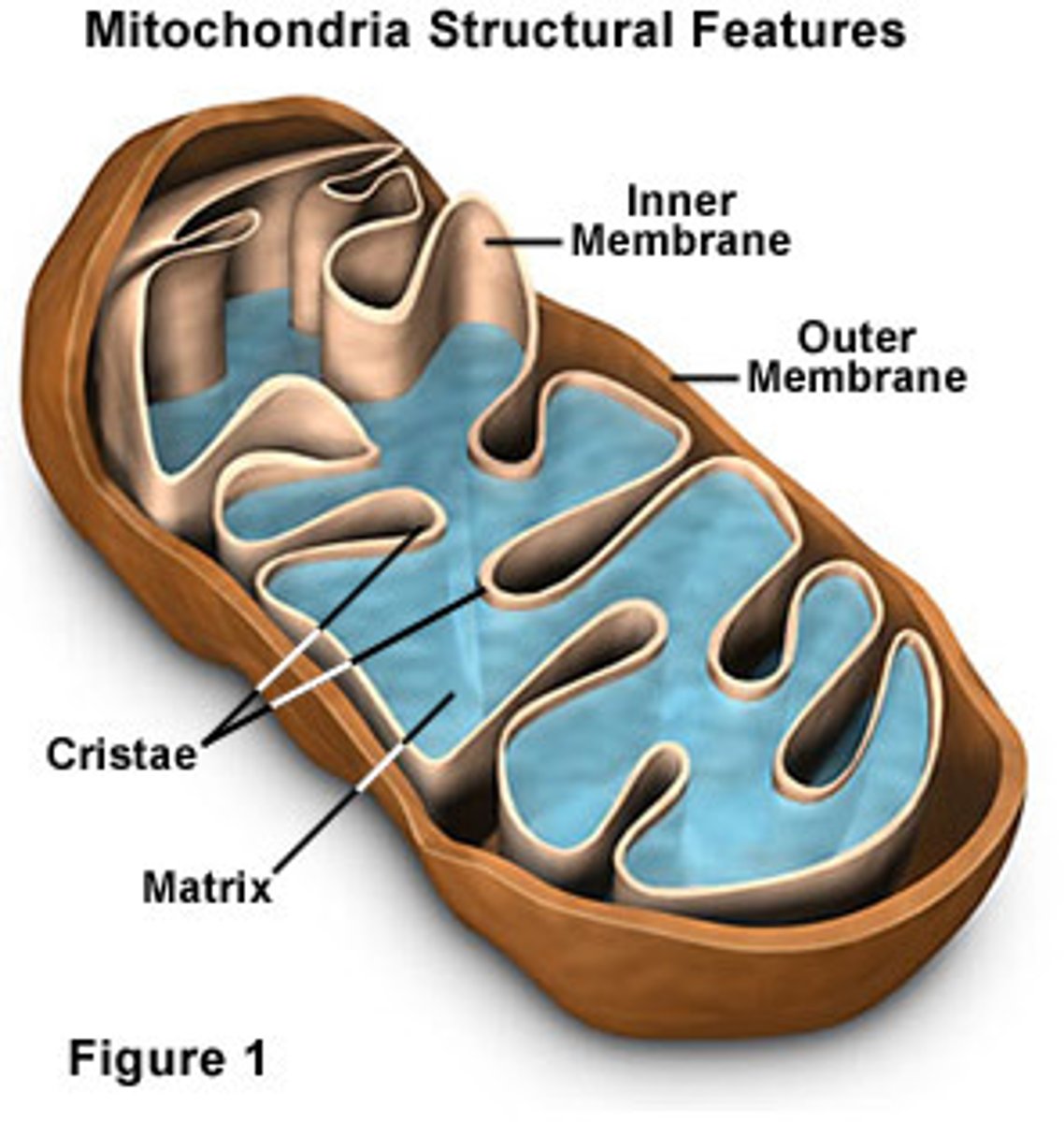
Plastids
Organelles that carry out photosynthesis in plants
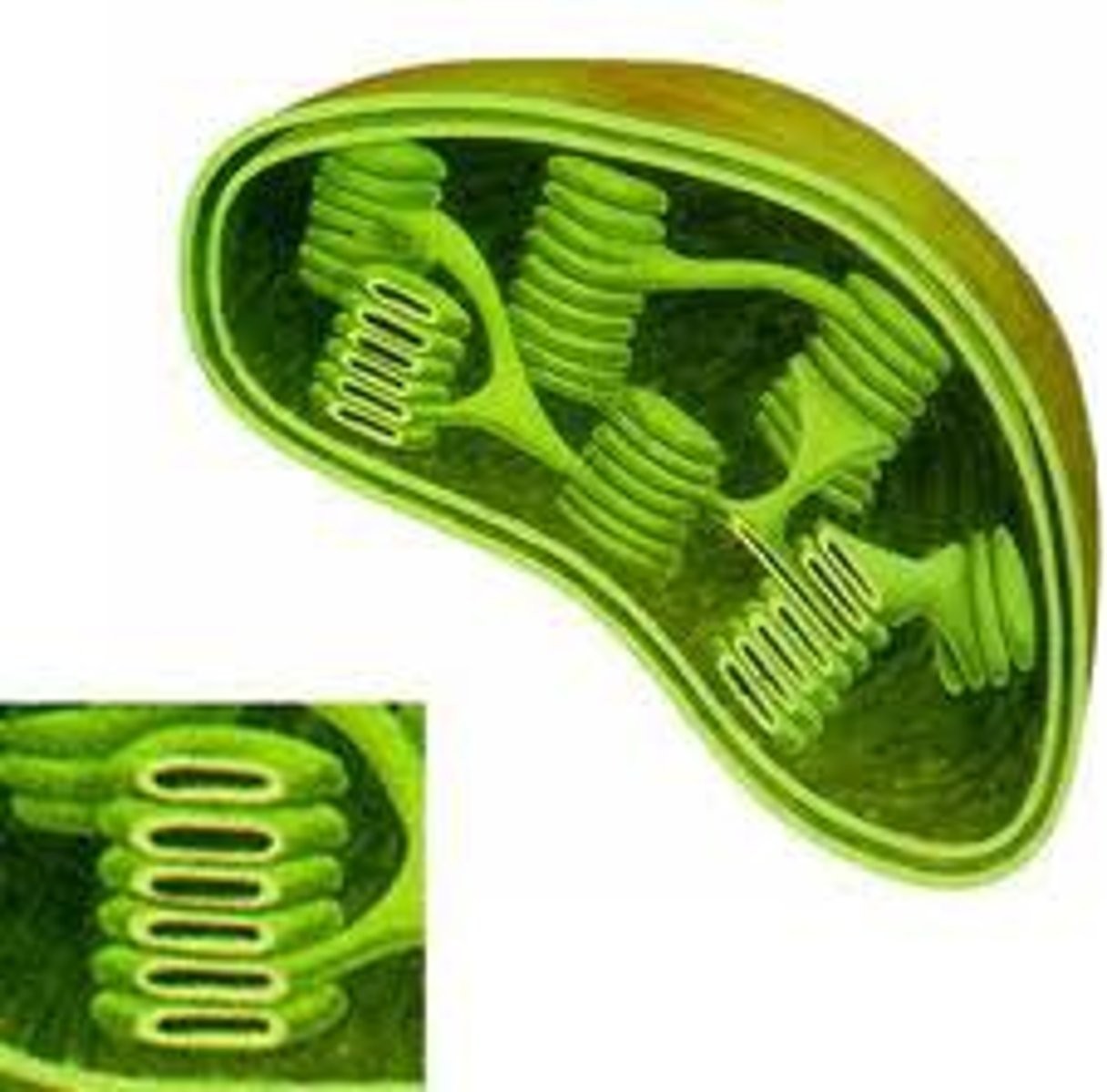

Cytoskeleton
A network of long protein strands in the cytosol that helps support the cell structure
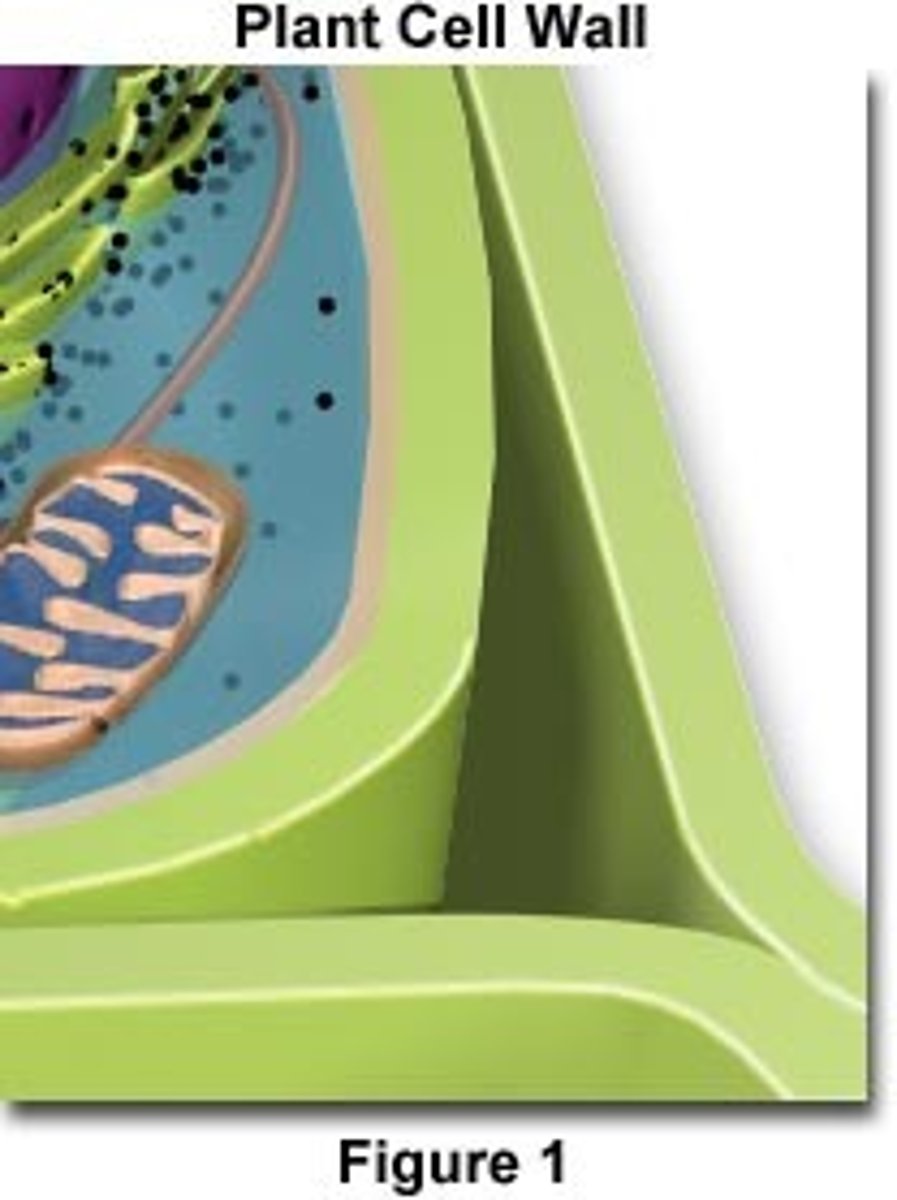
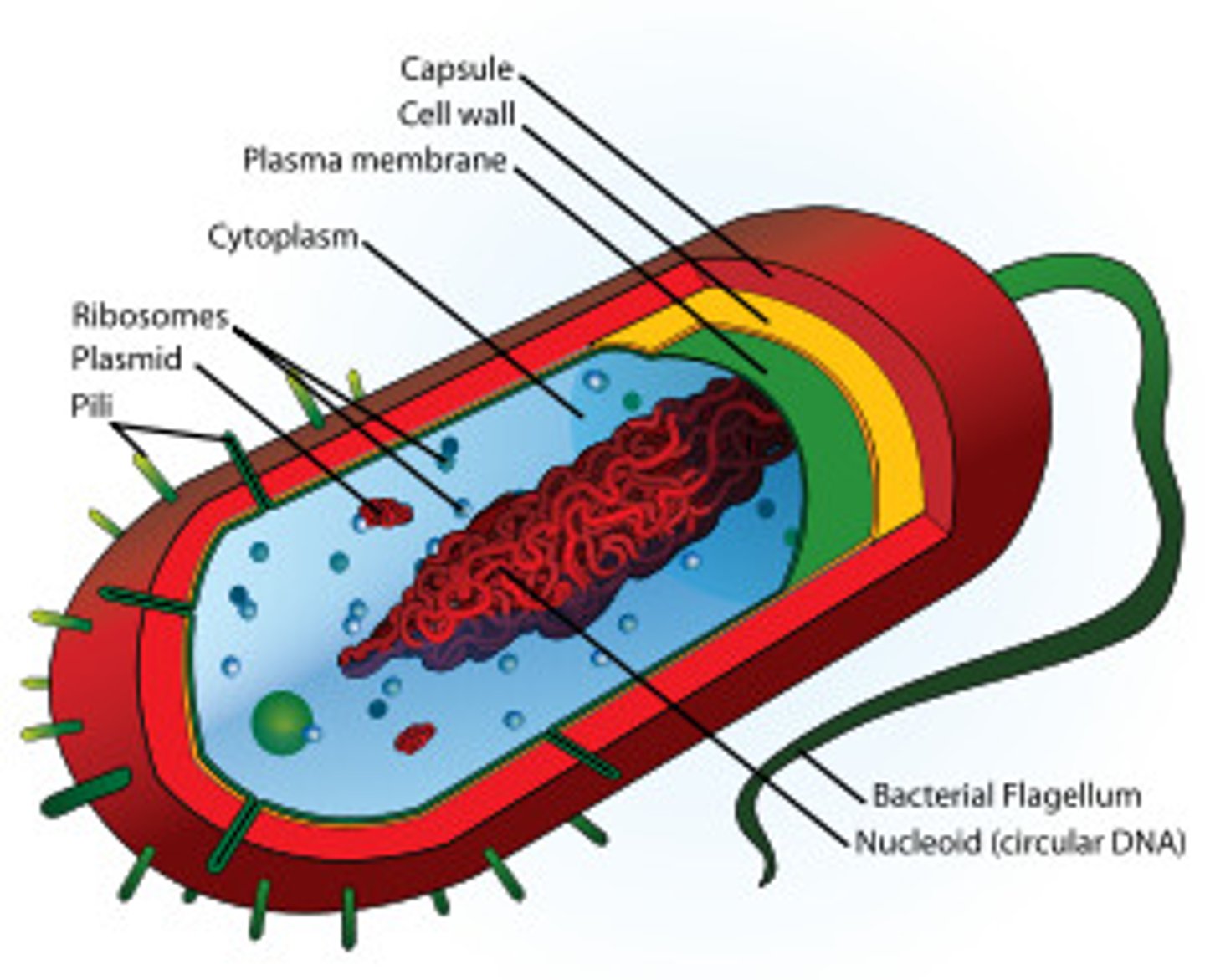
Cell wall
A rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane protects the cell
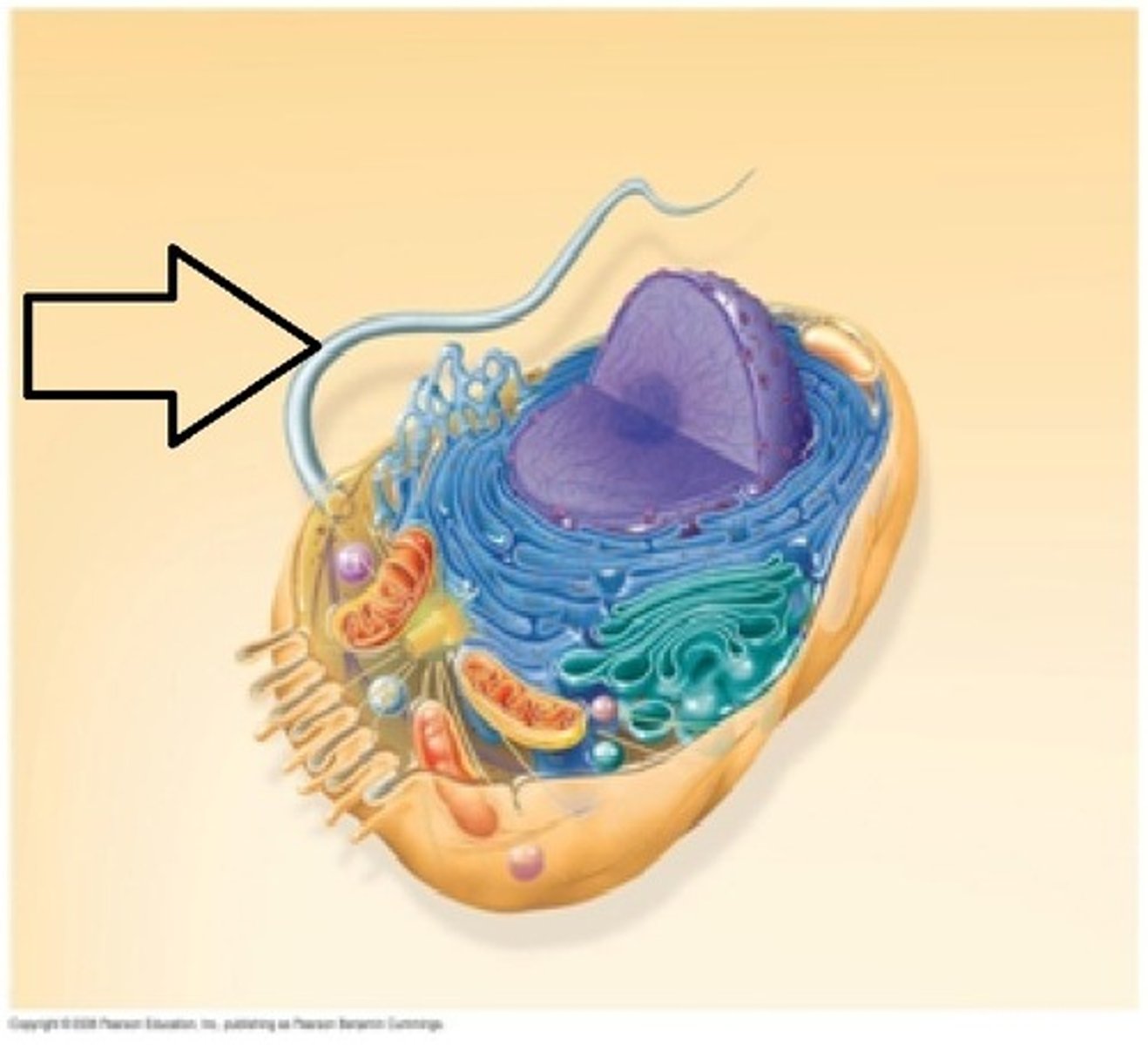
Flagella
A whiplike tail that one-celled organisms use to swim
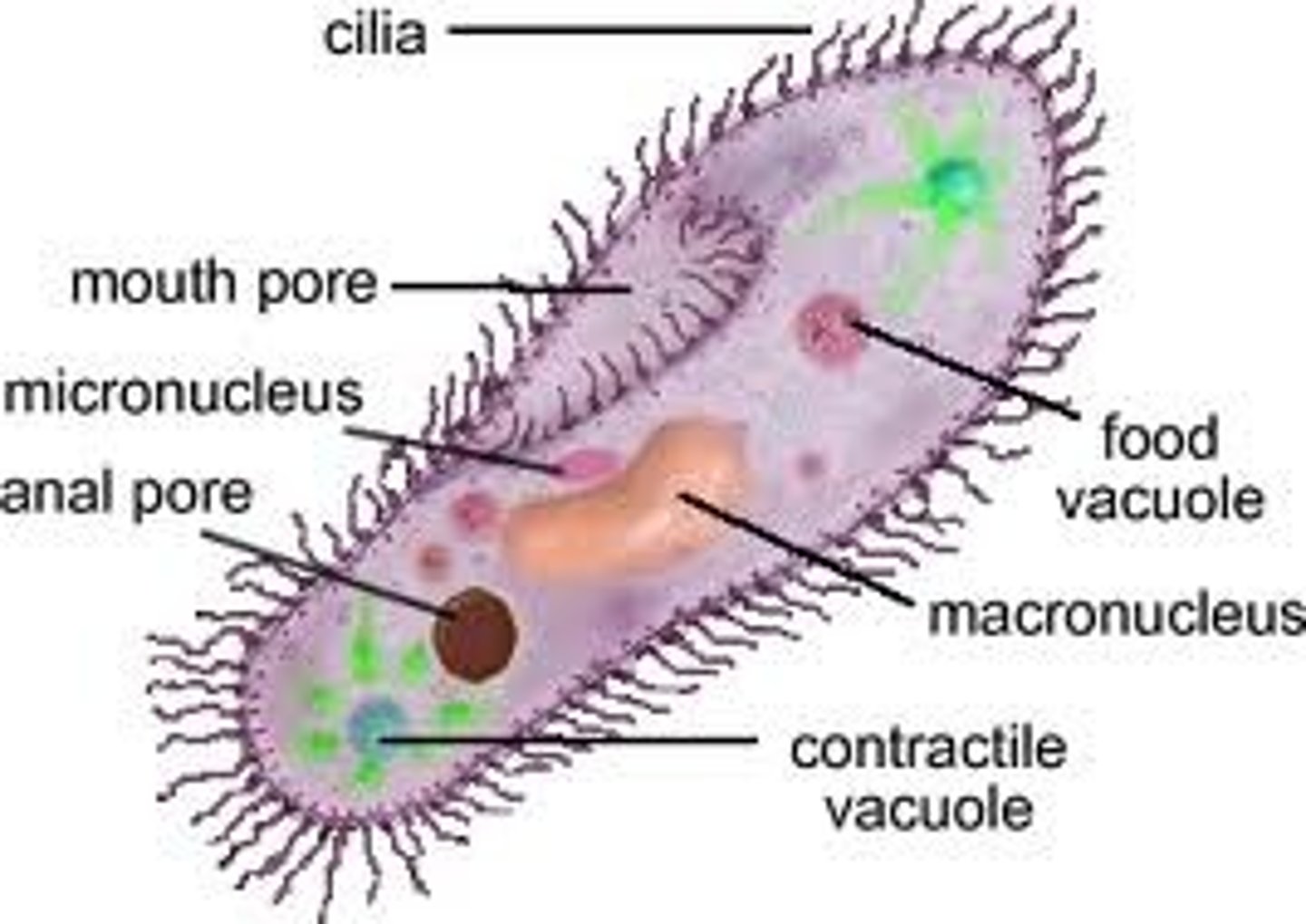
Cilia
The hair-like projections on the outside of cells that allow the cell to move
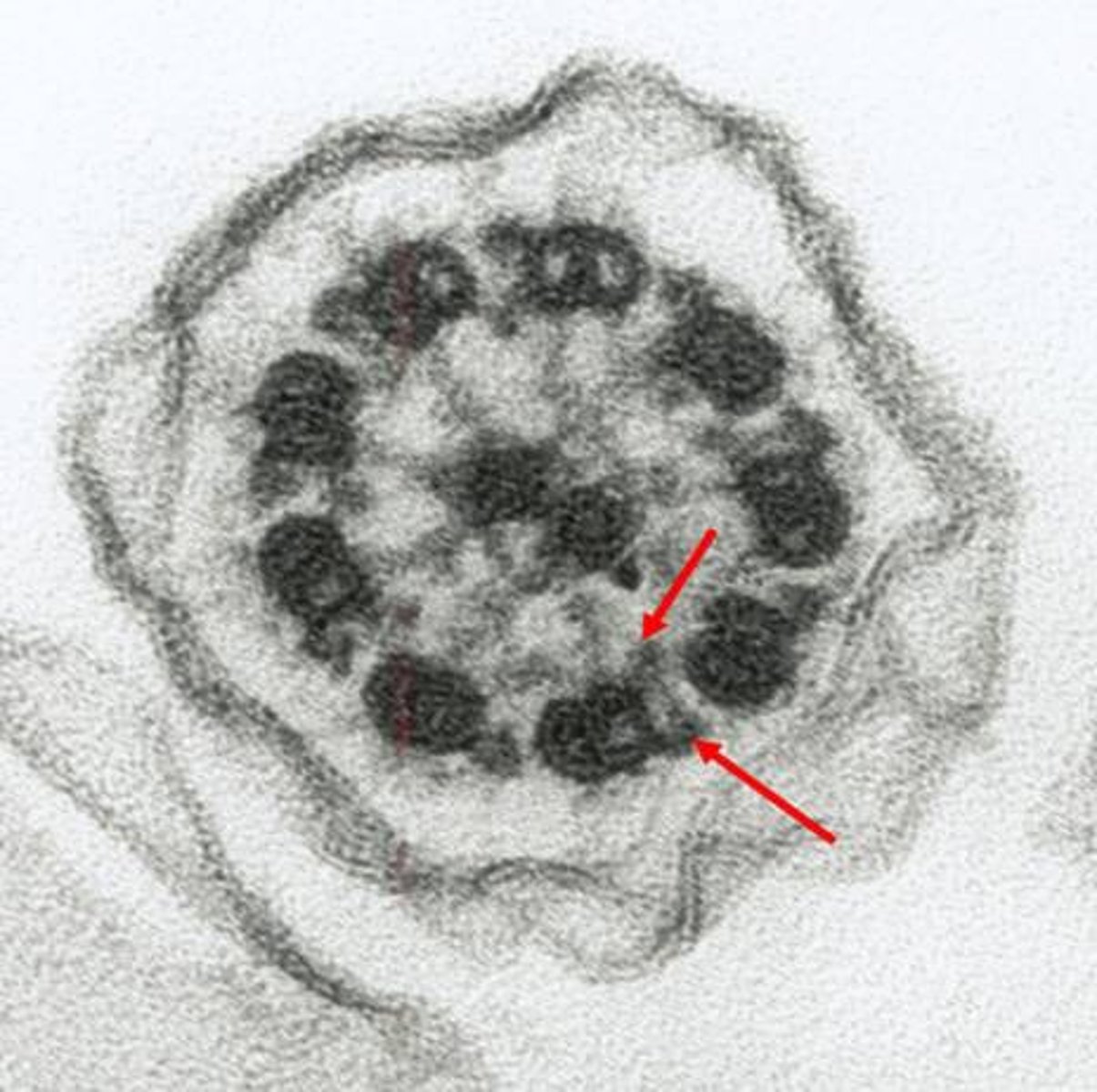
9+2 arrangement
Eukaryotic flagella + cilia have 9 pairs of microtubules that form a circle around two lone microtubules
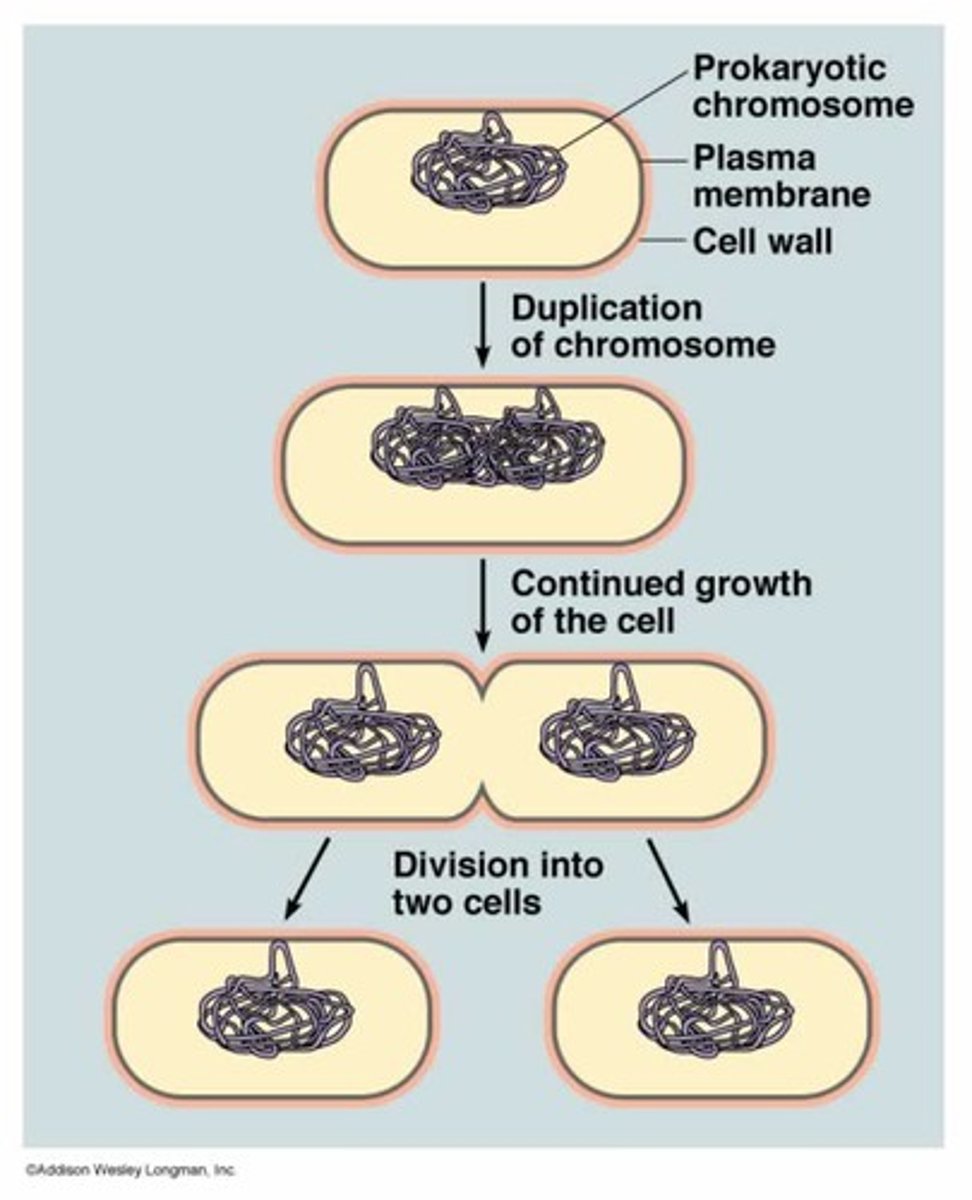
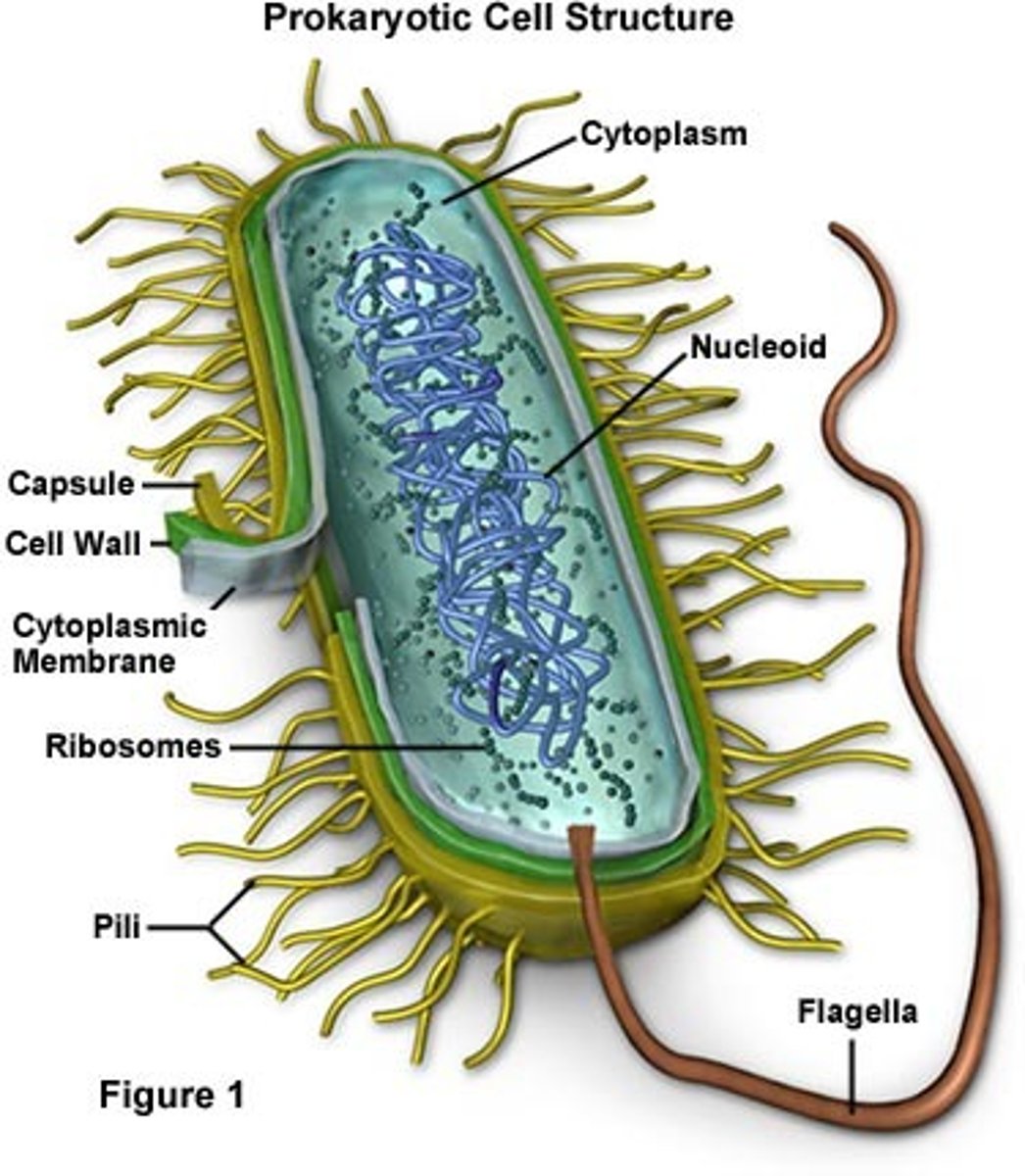
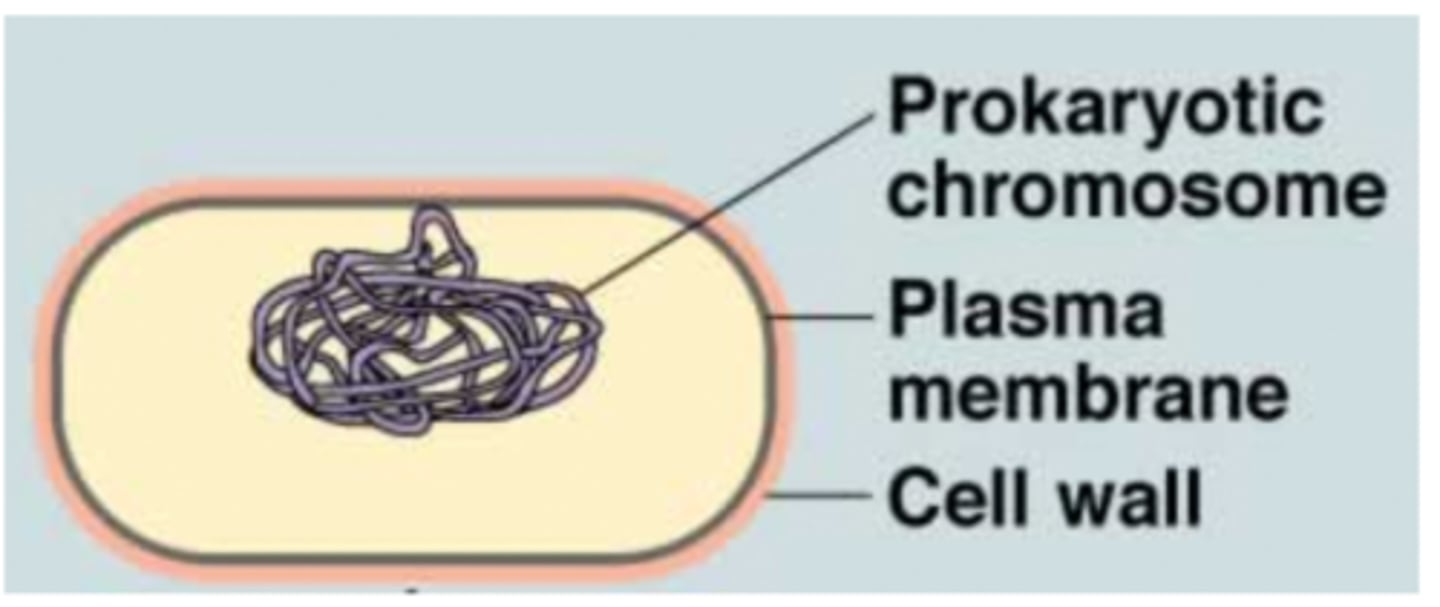
Prokaryotic chromosome
A single, circular DNA molecule that is found in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes
Plasmid
A small ring of DNA that carries accessory genes separate from those of the bacterial chromosome
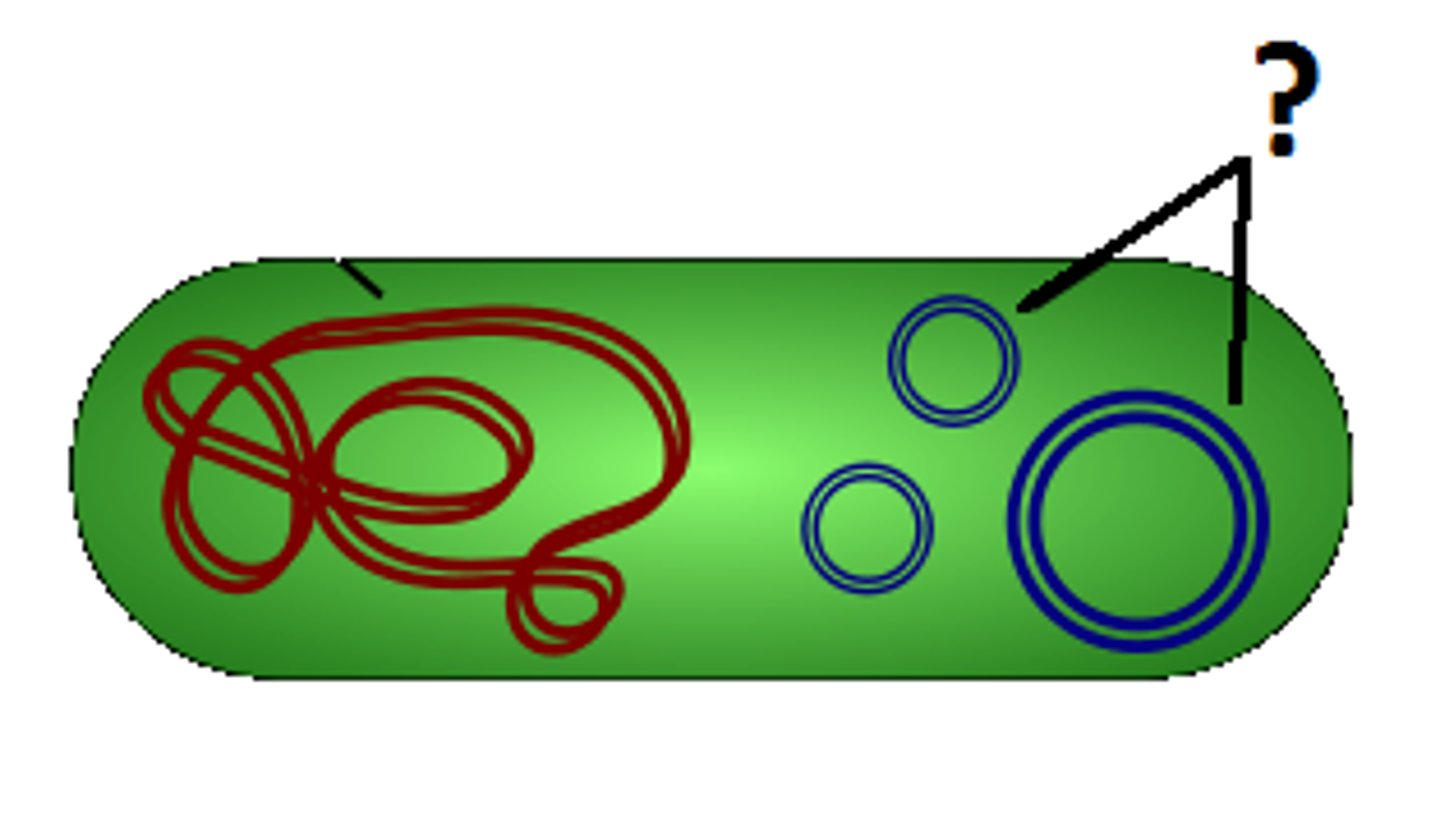
Cytoplasmic particles
Small ribosomes in prokaryotes, which synthesize proteins
Prokaryotic cell wall
A rigid, chemically complex wall that protects the prokaryotic cell and helps maintain its shape
Peptidoglycan
A protein-carbohydrate compound that makes the cell walls of bacteria rigid
Cell-wall deficient bacteria
Some bacteria lose their ability to produce cell walls
Pleomorphism
Cell-wall deficient bacteria can change their size and shape
Gram +
Bacteria with a thick peptidoglycan layer --> stains purple
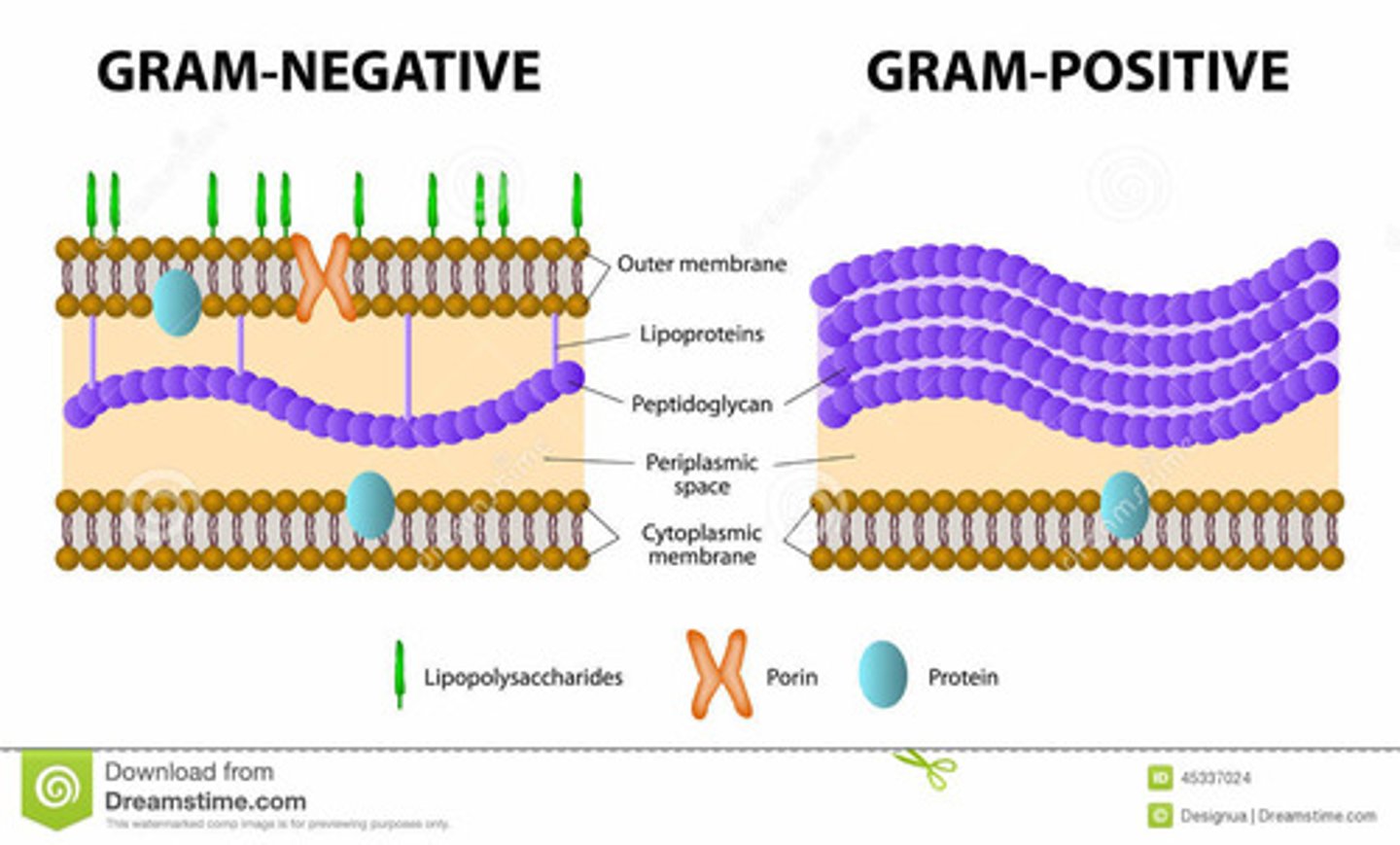
Gram -
Bacteria with a thin peptidoglycan layer --> does not stain
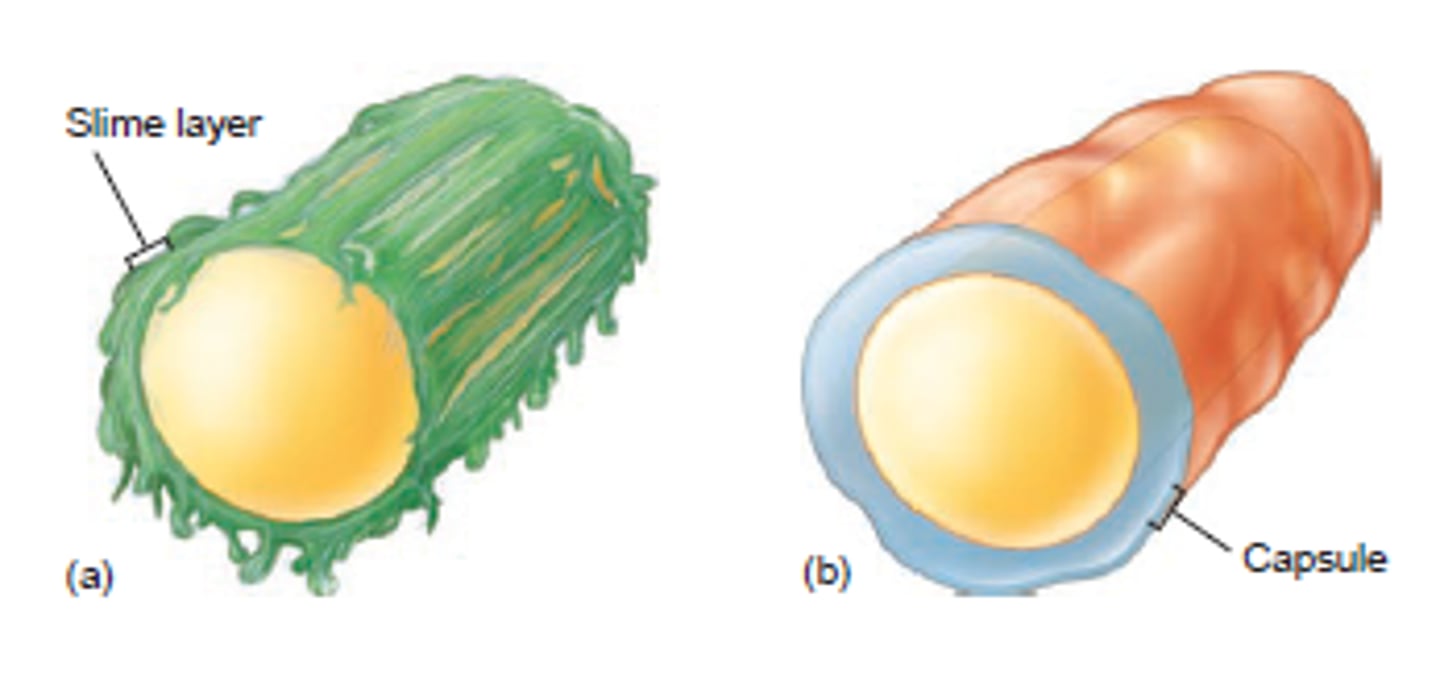
Glycocalyx
A bacterial capsule that is made of a fuzzy coat of sticky sugars
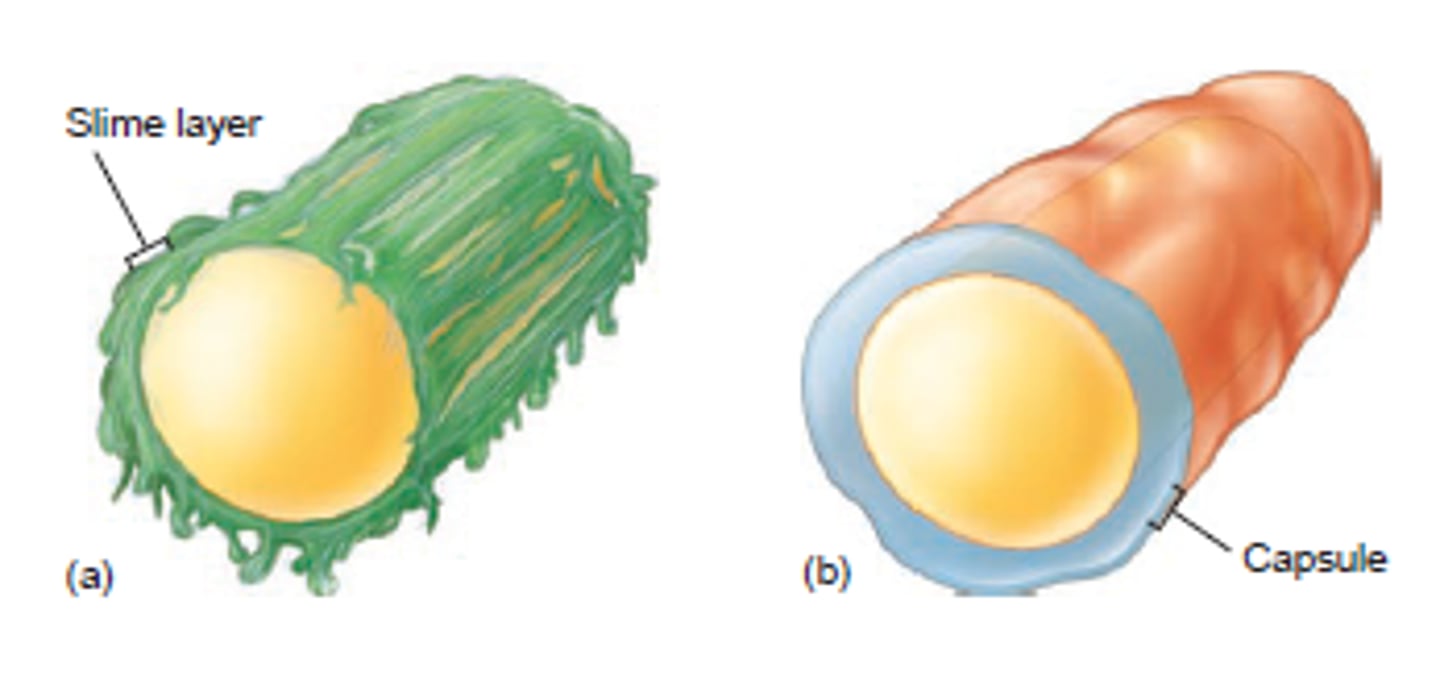
Slime layer
A glycocalyx that is loosely attached to the cell wall --> helps bacteria slide/glide
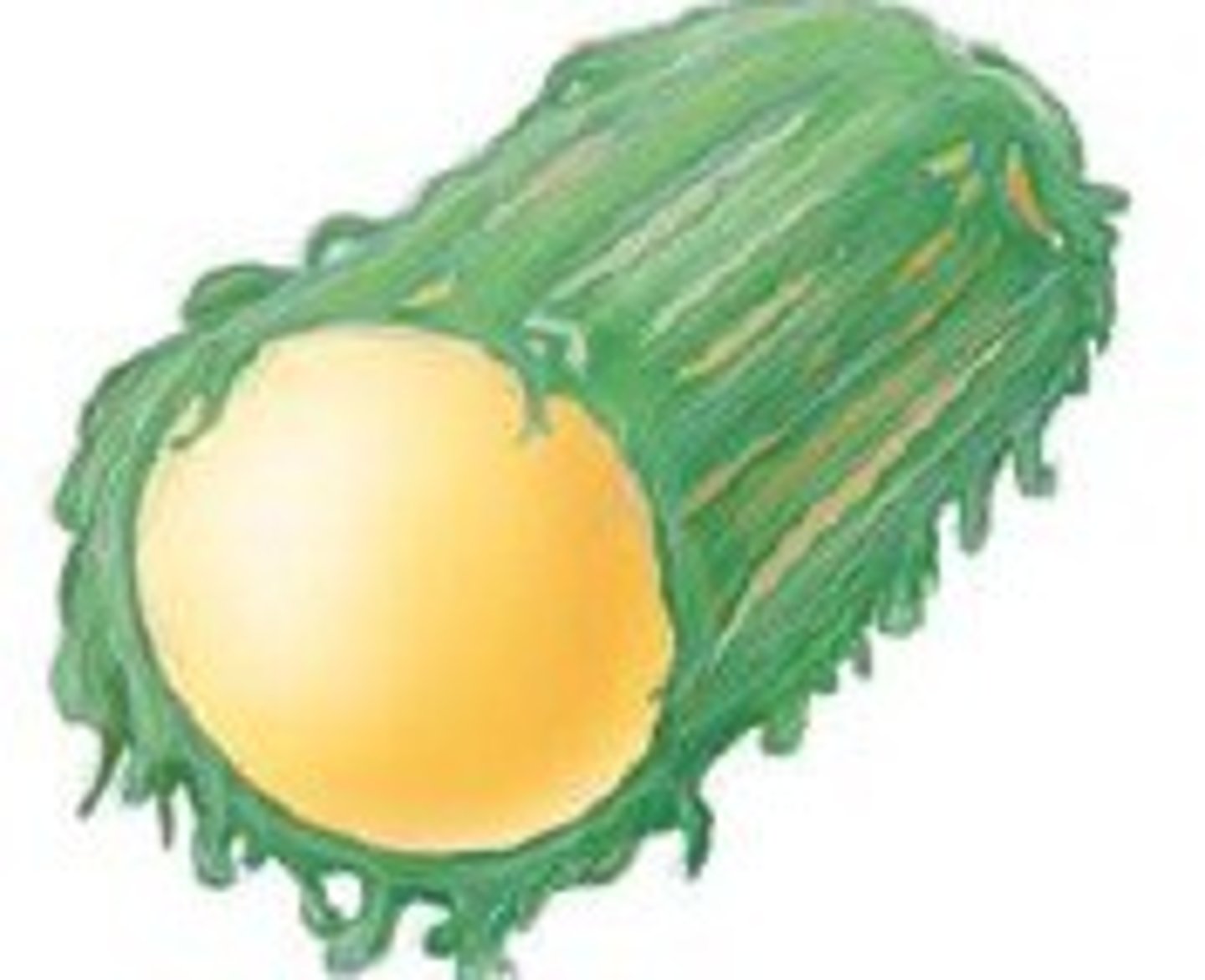

Capsule
A glycocalyx that is firmly connected to the cell wall --> protects bacteria from phagocytosis
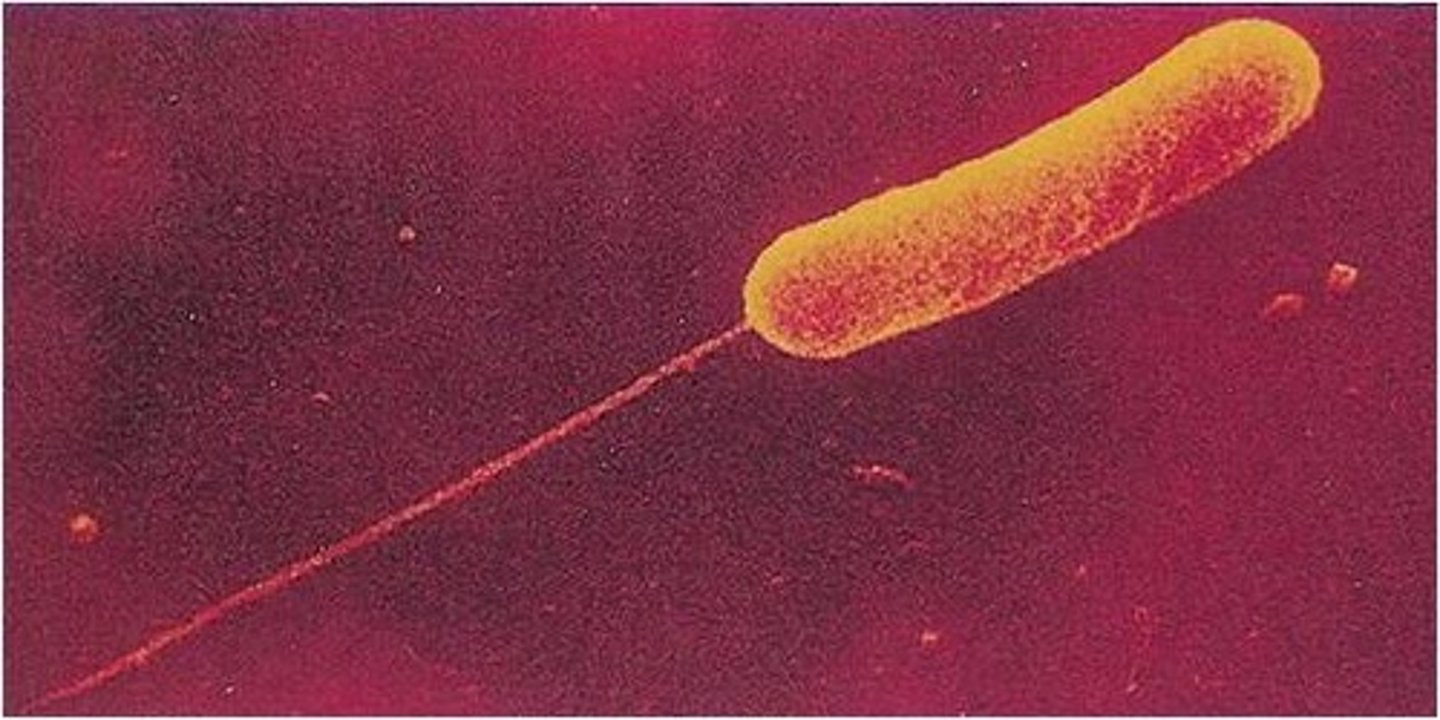
Prokaryotic Flagella
A tail that propels the cell through its liquid environment (NOT arranged in 9+2 for prokaryotes)
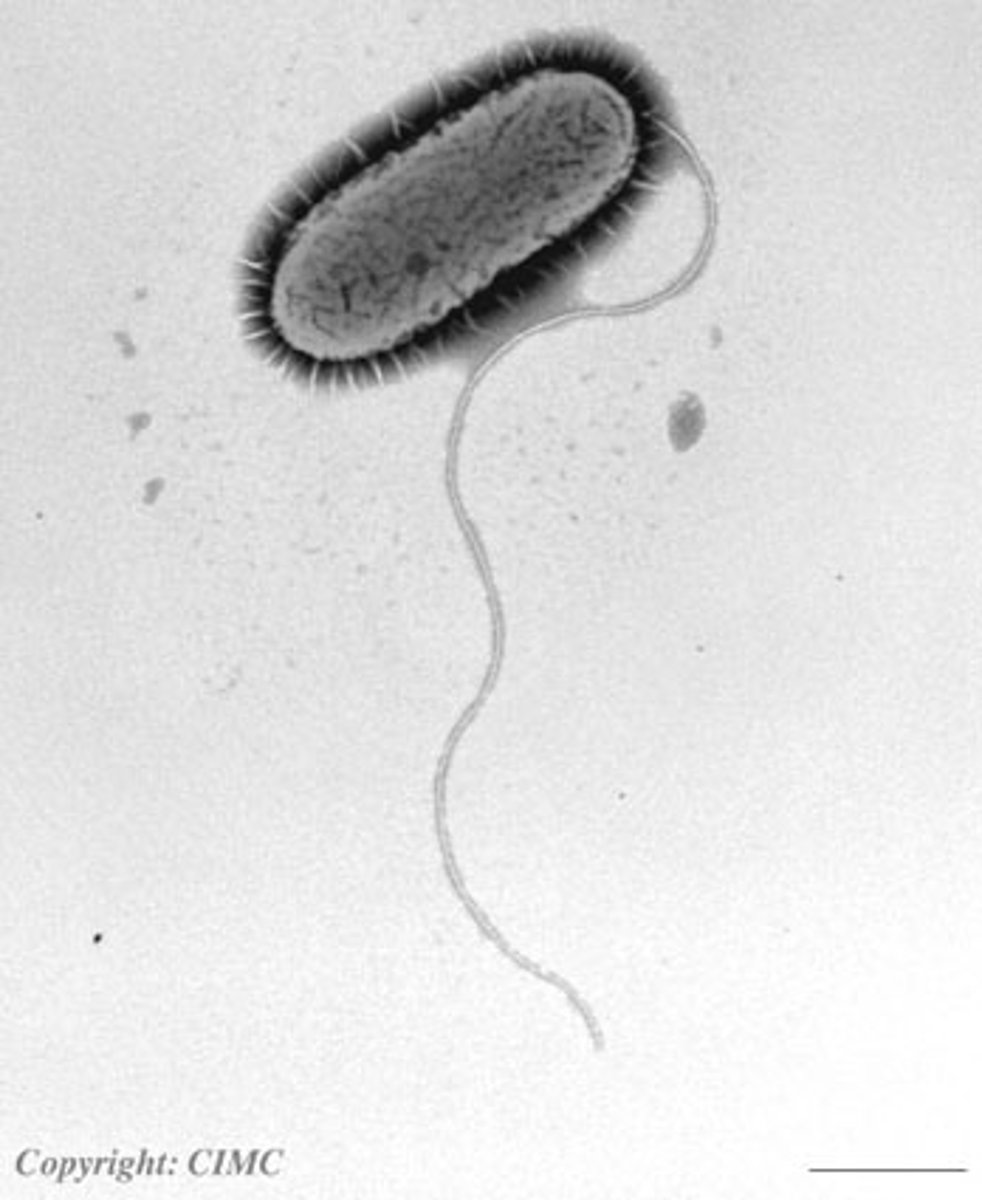
Monotrichous bacteria
Bacteria with single flagellum
Lophotrichous bacteria
Bacteria with multiple flagella at one end
Amphitrichous bacteria
Bacteria with a flagellum at each end

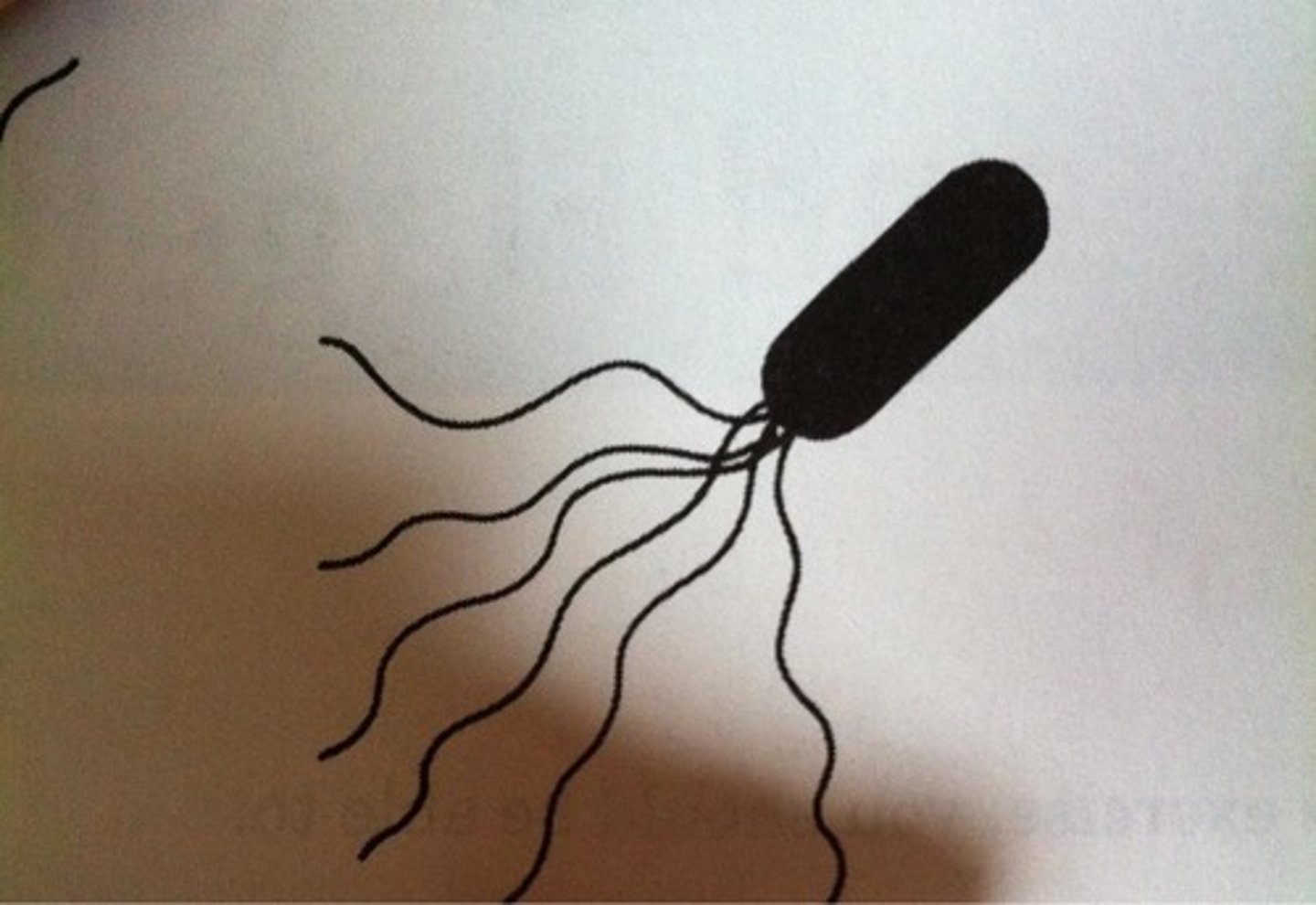
Peritrichous bacteria
Bacteria with flagella all over their surface
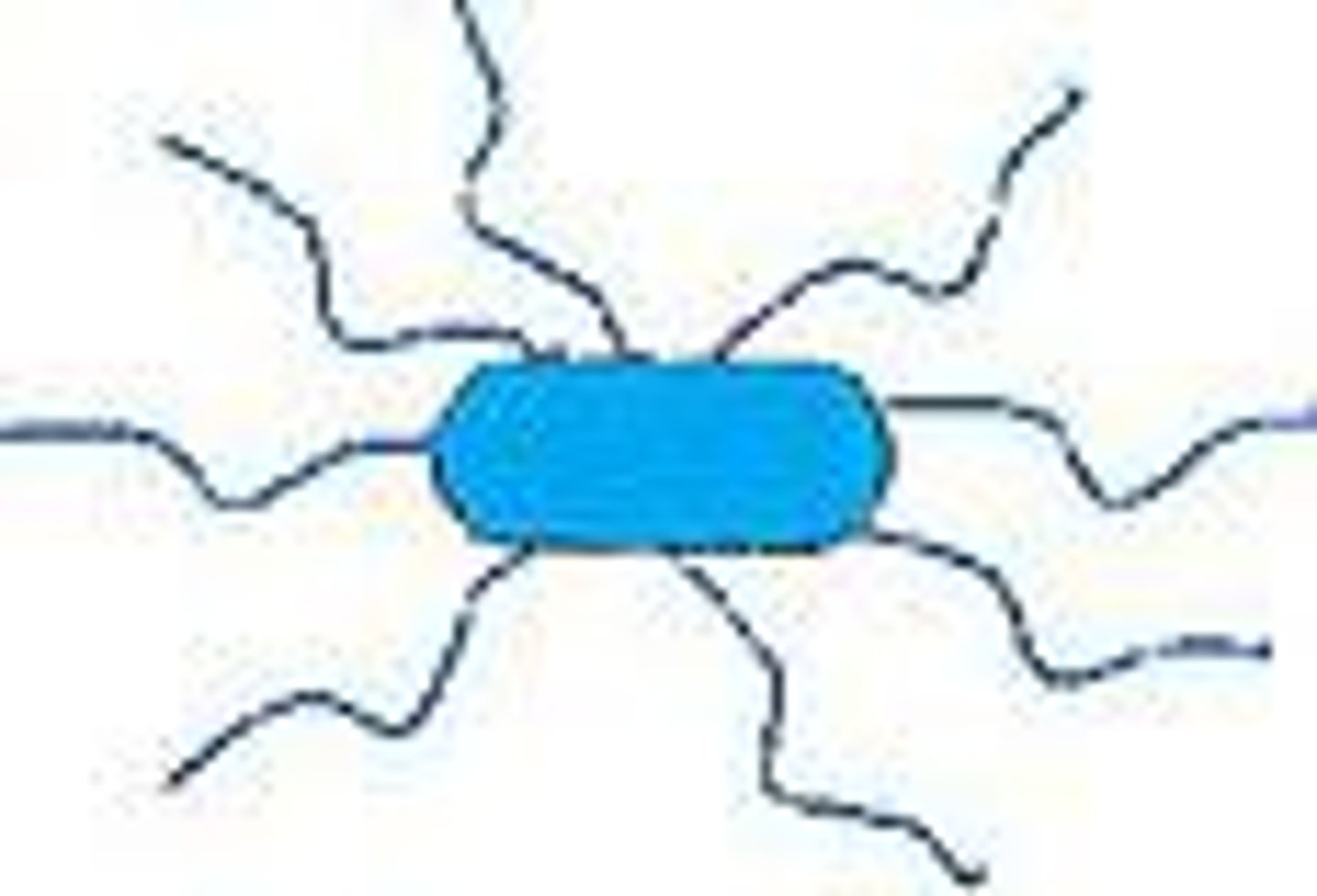
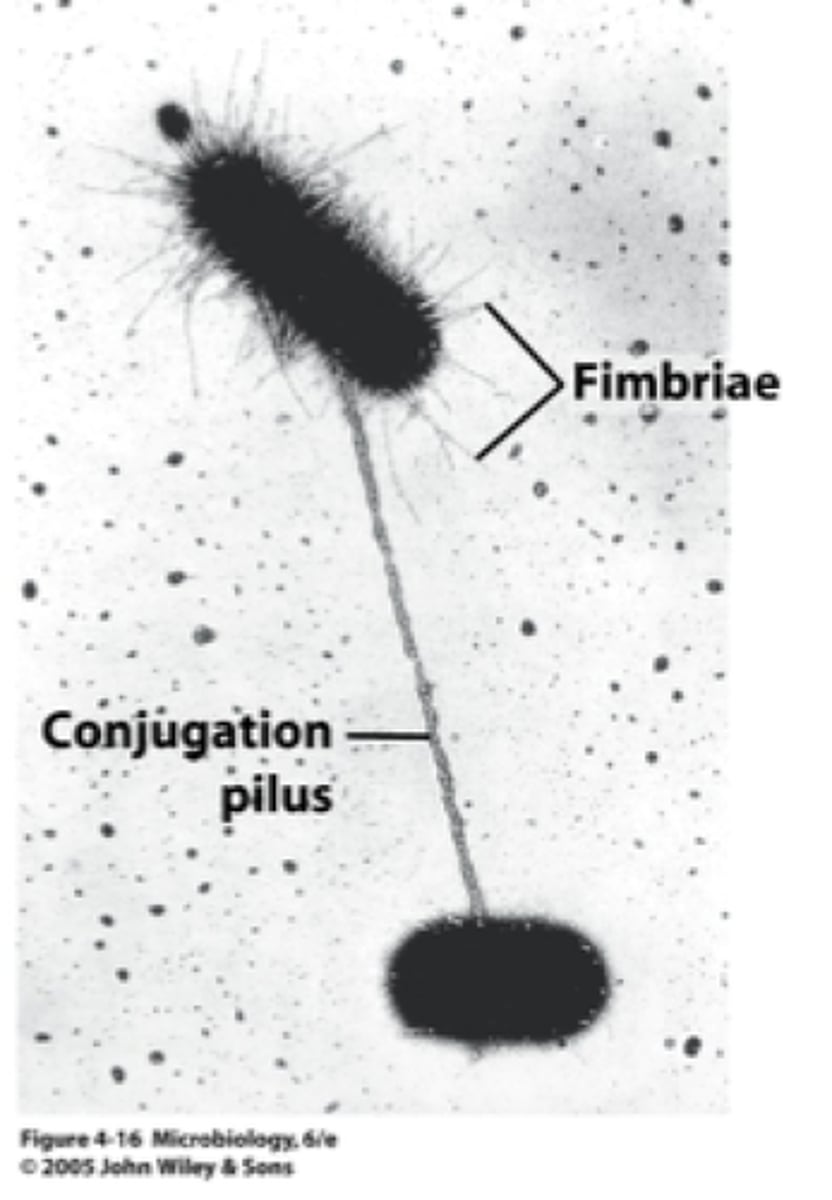
Pili
Appendages that allow bacteria to attach to each other and to transfer DNA
Spores
Dormant, non-reproductive structures that are highly resistant to cold and heat damage; capable of generating new organisms

Terminal spores
Endospores that are found at the end of a bacterial cell
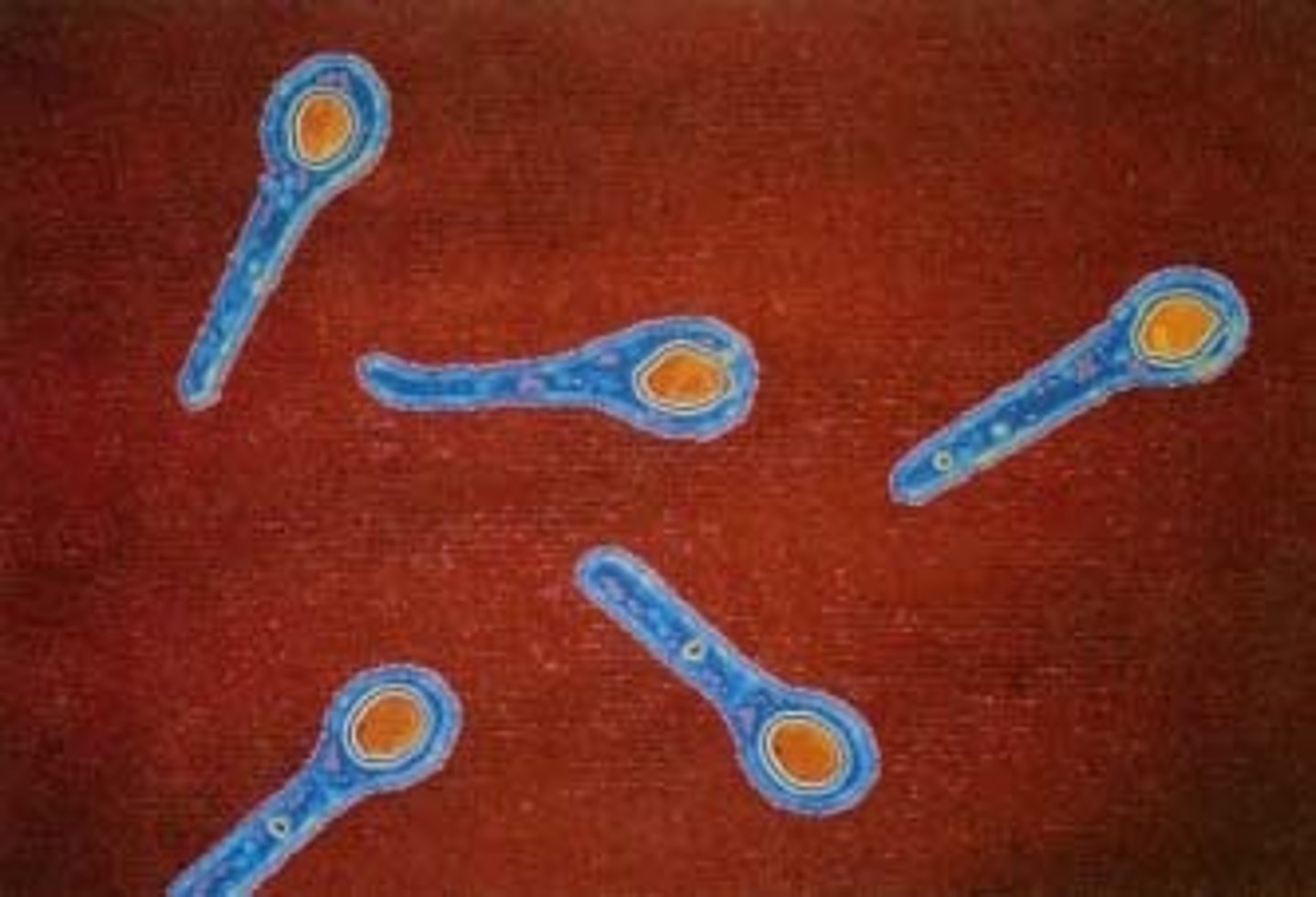
Subterminal spores
Spores that form between the center and the end of a bacterial cell
Binary fission
A form of asexual reproduction in which one prokaryotic cell divides to form two identical cells