muscular system TEST
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
acetylcholine
the neurotransmitter responsible for muscle contraction, will be released into the synapse
contract
movement of the body occurs because muscles ___ or shorten, pulling on tendons which pull on bones
cardiac
skeletal
smooth
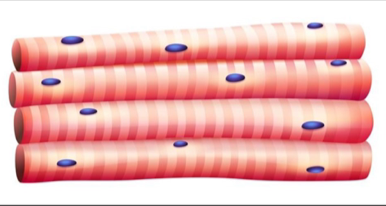
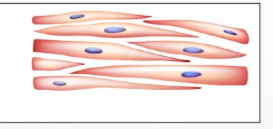
3 types of muscle tissue
cardiac
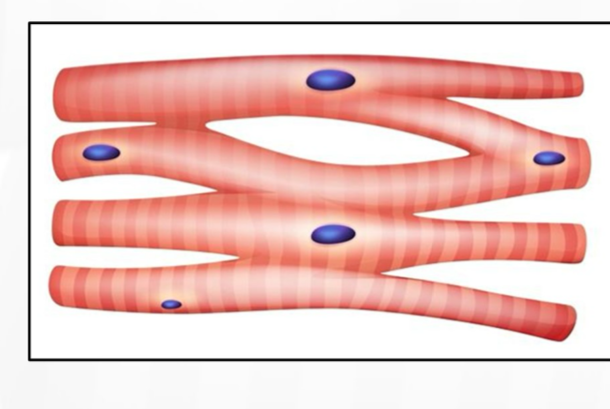
skeletal
smooth
myosin head
attaches to the binding site on actin
myocardium
muscular heart tissue
muscle fiber
a muscle cell is a __
skeletal
type of muscle that is voluntary, striated, attached to bone
epimysium
connective tissue sorrounding muscle
perimysium
connective tissue surrounding fascicle
endomysium
connective tissue surrounding muscle fiber
origin
muscle attachment to immovable bone
insertion
skeletal muscle attachment to movable bone
pairs
because muscles can only pull when they contract, they often work in ___
agonist
biceps is the prime mover or ___
antagonist
triceps is the __
cell membrane
what is sarcolemma
sarcoplasmic reticulum
where are the ions stored in muscle cells
largest to smallest
muscle fiber
myofilaments
myofibrils
move substance
generate heat
produce movement
maintain posture
4 major functions of muscles:
MGPM
Facial Expressions
Manipulation
Locomotion
examples of movement produced by muscular system FML
stabilize joints
hold body upright against gravity
maintain balance
maintaining posture involves:
SHM
heat
by product of muscle activity that helps maintain body temp
Transport blood in body and Food in digestion
examples of muscular system’s ability to move substances from one part of the body to antoher
ACh
neurotransmitter responsible for muscle contractions
ACh released
occurs when a nerve impulse reaches the axon terminal
sodium and potassium
ions responsible maintaining the resting state of a muscle
resting potential
high concentration of Na+ outside of the cell and a high concentration of K+ inside the the cell with an overall net positive charge outside the cell relative to inside
sarcolemma
once generated, the action potential continues over the entire surface of the ____ and results in contraction of the muscle cell
contraction
once generated, the action potential continues over the entire surface of the sarcolemma and results in ____ of the muscle cell
ATP
provides the energy to release and reset each myosin head so it’s ready to aRach to the next site
1
steps
Nerve impulse reaches the axon terminal
2
step
ACh is released into the synapse
3
step
calcium ions are released
4
step
myosin heads bind to actin
5
step
the sarcomere shortens
fused tetanus
successive contractions are added together to produce a smooth, sustained contraction
sodium-potassium pump
restores the resting state of the muscle membrane
all or none law
if a muscle is stimulated, it will never contract fully; it will never partially contract
forcefully contracts a muscle
the number of muscle cells that are stimulated
oxygen debt
primary cause of muscle fatigue
isotonic contractions
occur when the muscle shortens and movement occurs
isometric contraction
occurs when the muscles do not shorten; no movement occurs
muscle tone
State of continuous partial contractions that leads to firm, healthy muscles that are constantly ready for action
aerobic exercise
increase strength, endurance, flexibility
regular exercise
increases muscle size, strength, and endurance
atrophy
muscles that are not used regularly will waste away or __
resistance training
the muscle enlarges when new contractile filaments are made
gross reflex movement
which type of muscle movement develops first in infant
decreases with age
changes that occur in the muscular system of elderly people in the amount of muscle mass and muscle issue ___
cramps
result from overuse, dehydration, or muscle strain
muscle fibers are torn
describe the damage that occurs in a muscle strain, pull or tear
nerve damage
paralysis or the inability to move a muscle, results from ___
muscular dystrophy
group of inherited disorders which leads to progressively weaker muscles
calcium ions
released from sarcoplasmic reticulum
are reabsorbed into sarcoplasmic reticulum
triggers binding site of myosin x actin
irritability
ability to receive and respond to a stimulus
skeletal muscle
primary function is to produce movement: locomotion and manipulation
actin
contains myosin binding sites that are covered by regulatory proteins until calcium ions are present
cardiac
also responsible for transporting blood
motor unit
one motor neuron and all the skeletal muscles it stimulates
smooth muscle
responsible for transporting substances like blood or food from one part of the body to another
action potential
electrical current generated by “upset” or charge in charge across the muscle cell membrane
contractility
ability to shorten
myosin
thick purple filament
actin
thin light green filament
synapse
space between two structures of the neuromuscular junction
negative
when a membrane charge is reversed or “upset”
what is the net charge OUTSIDE of the cell
positive
when a membrane is a rest
what is the net charge on the OUTSIDE of the cell
Acetylcholine
If enough ___ is released, the sarcolemma becomes temporarily permeable to Na+ and K+
Neuromuscular Junction
The _____ is where the axon terminal of a neuron and sarcolemma of a muscle cell meet
Negative
when a membrane is a rest,
what is the net charge on the INSIDE of the cell
Positive
when a membrane is a rest, what is the net charge on the outside of the cell
neurotransmitter
which of the following diffuses across the synapse
crossbridge
attachment of a myosin head on actin’s binding site
Sliding Filament Theory
states that the sarcomere shortens when thin and thicc filaments slide past each other
calcium
which of the following is required to move a regulatory protein out of actins binding site
positive
when a membrane is reversed or “upset”
what is the net charge on the INSIDE of the cell
synaptic cleft
Acetylcholine diffuses across the ___ to bind with receptors on the sarcolemma
acetylcholinesterase
enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine to prevent further contraction of muscle cell
sarcolemma
Ach crosses synapse & binds to receptors on ____
sarcoplasmic reticulum
Calcium is stored in the ___ before the action potential stimulates its release
ATP
____ is required each time a crossbridge attaches and detaches
fascicle
bundle of muscle fiber
sarcomere
Functional unit of muscle fibers; made of actin & myosin
Sarcomere
as myosin attach and detach, the actin filaments are pulled toward the center of ____
tendon
Composed of fibrous connective tissue
Attach muscle to bone
Temporalis
Buccinator
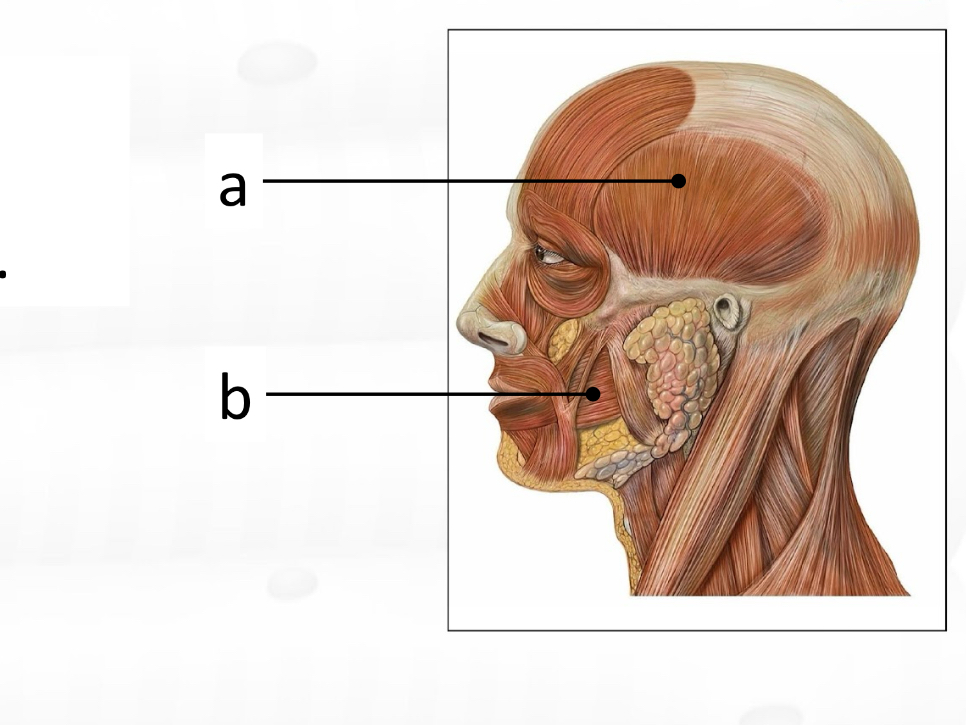
Frontalis
Zygomaticus
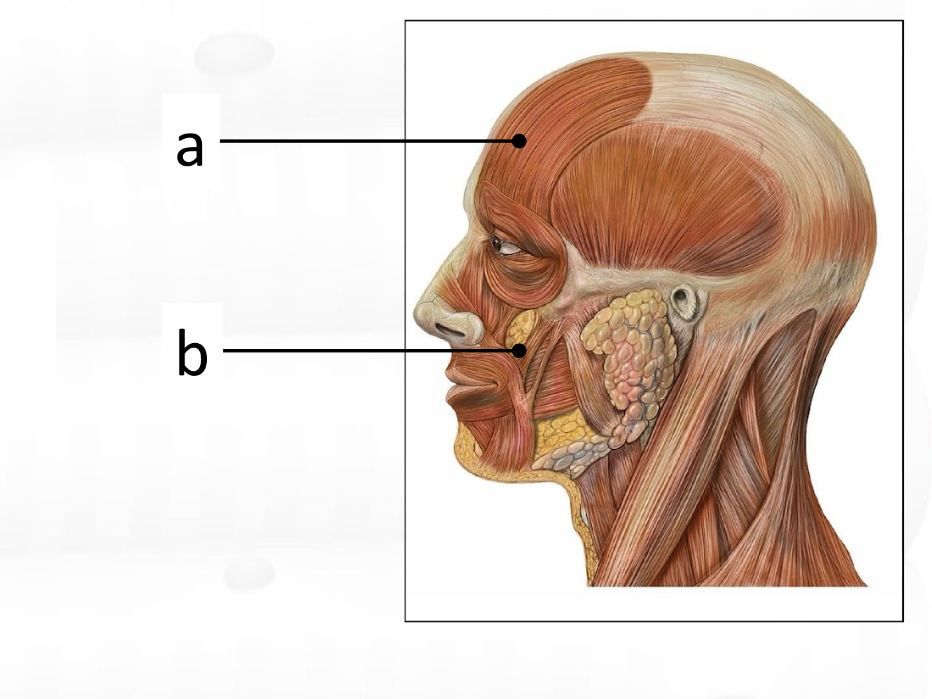
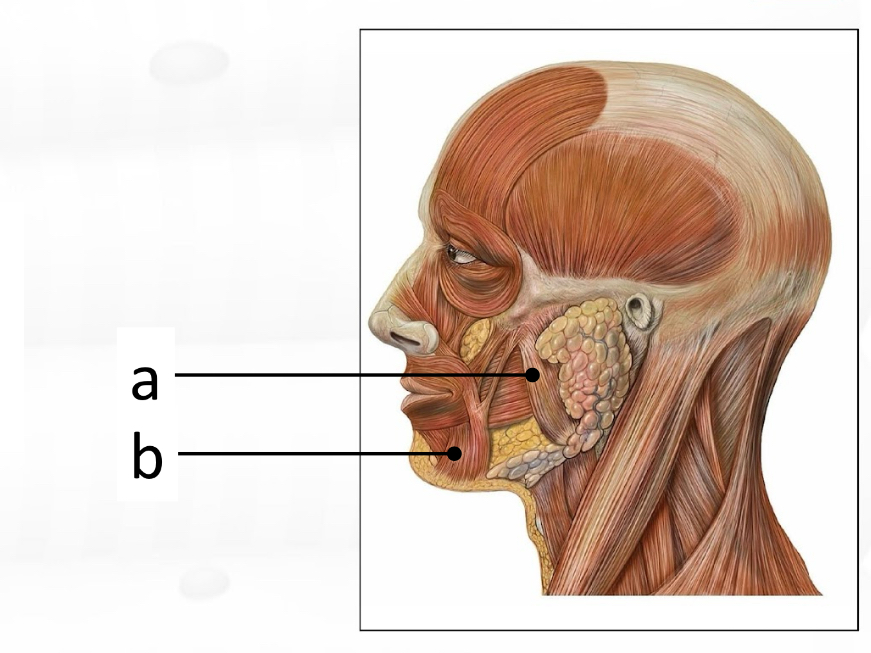
masseter
depressor anguli oris
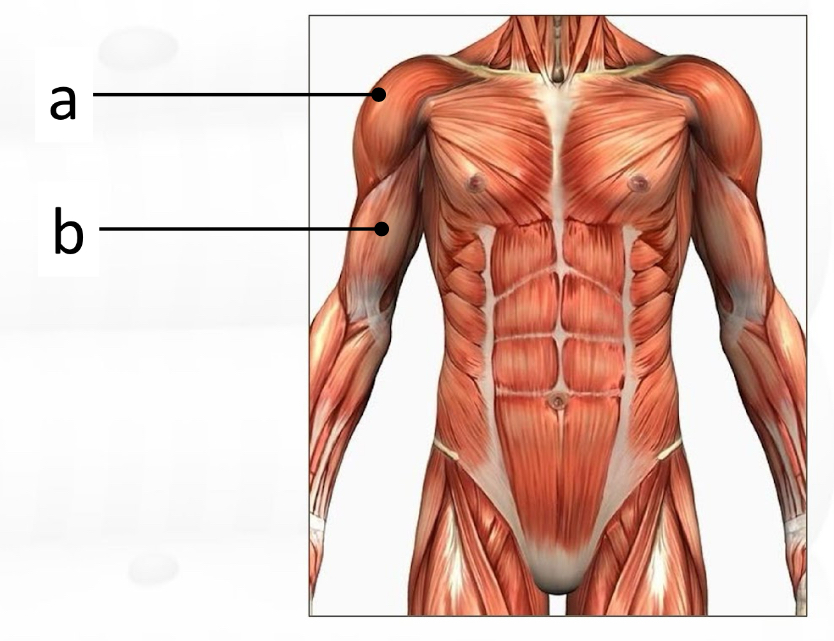
deltoideus
biceps brachii
serratus anterior
rectus abdominis
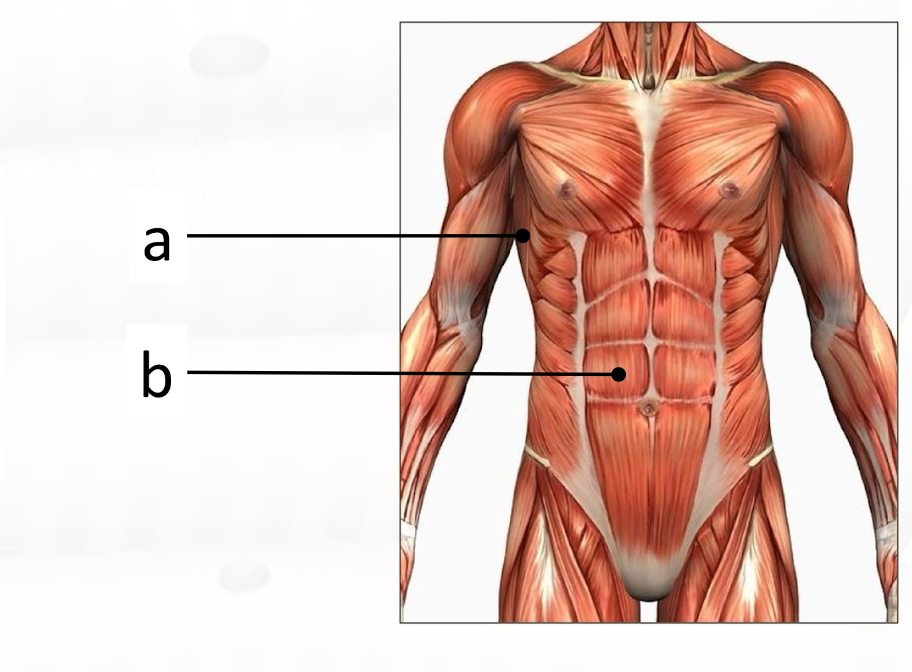
pectoralis major
external obliques
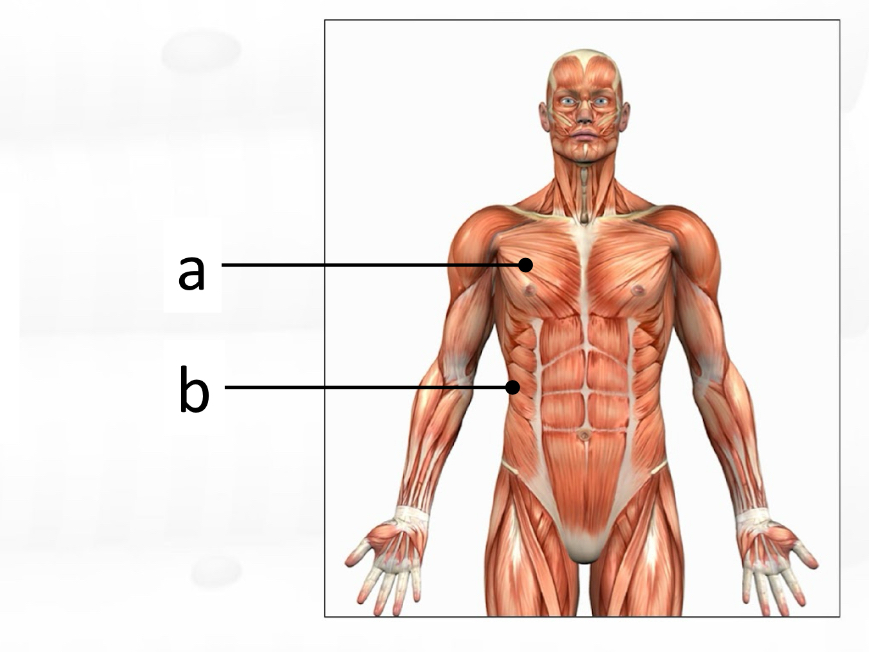
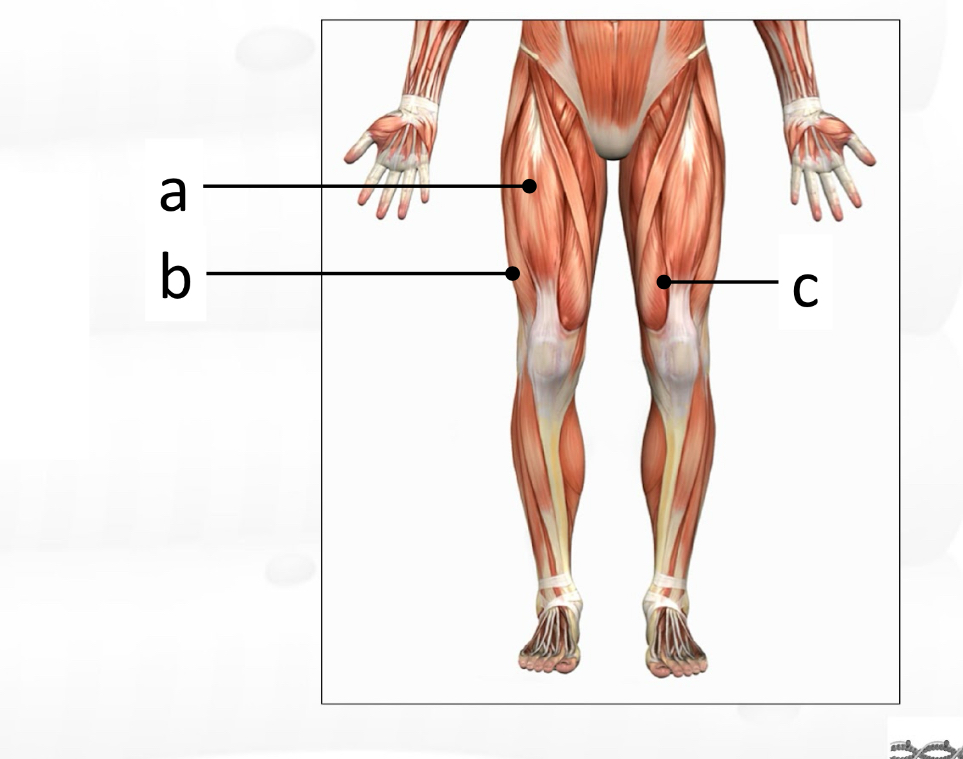
rectus femoris
vastus lateralis
vastus medialis
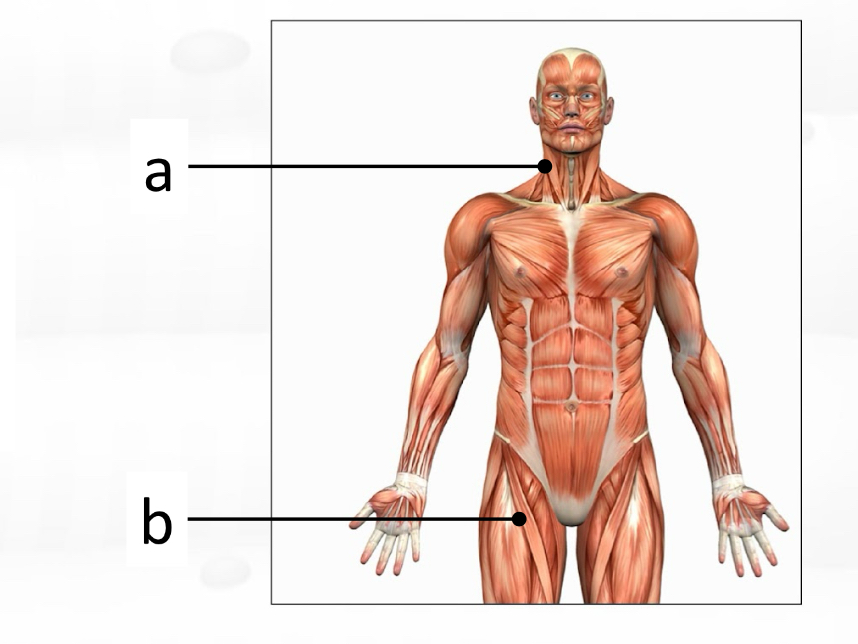
sternocleidomastoid
sartorius
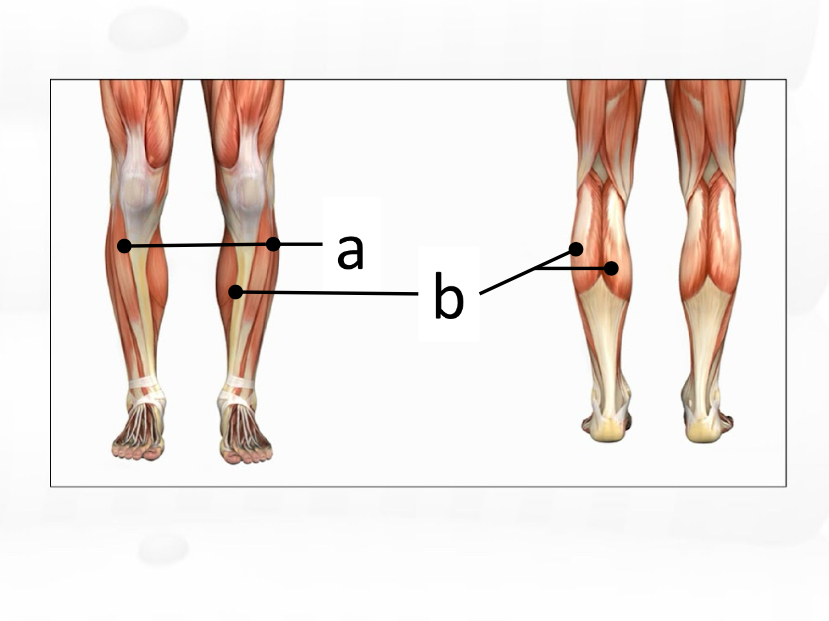
tibialis anterior
gastrocnemius
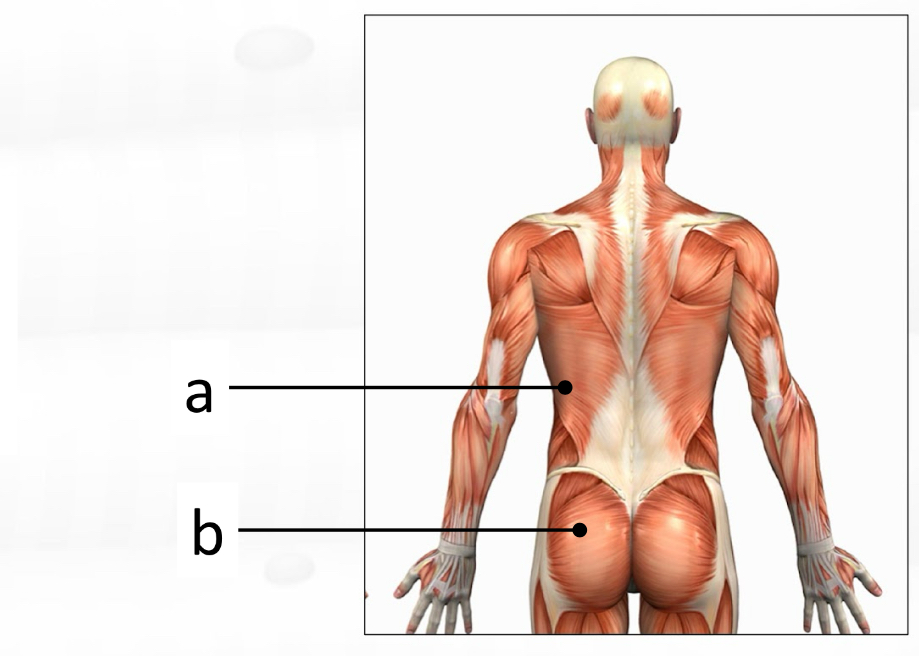
trapezius
triceps brachii
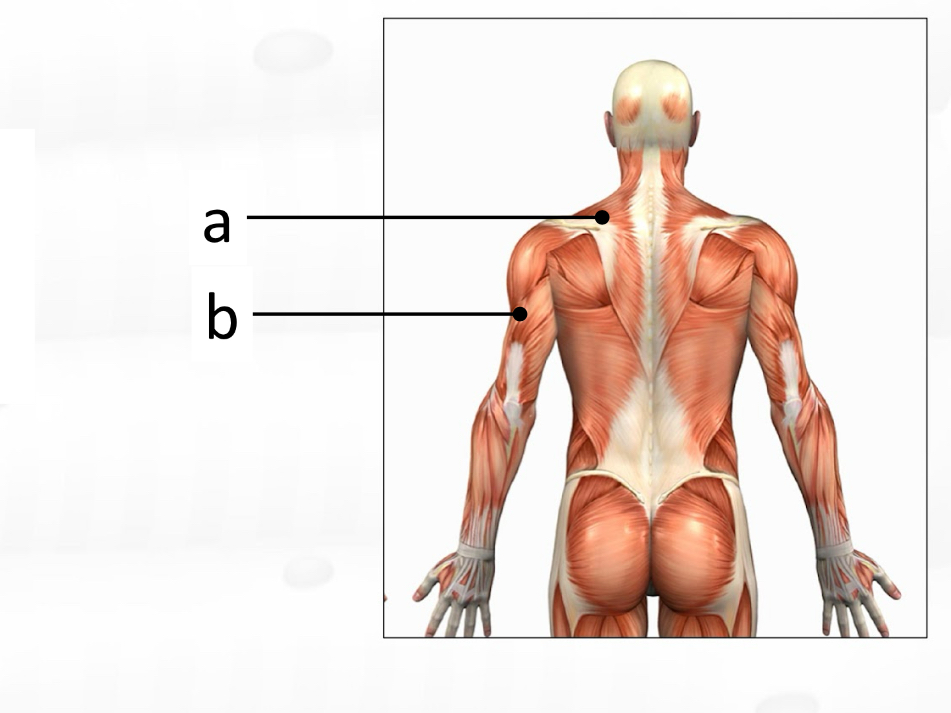
latissimus dorsi
gluteus maximus