Lecture 16 - Effector T cells
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
How do CD8 and CD4 T cell’s initially interact with target cells?
weak integrin adhesion (LFA-1 → ICAM, CD2 → CD58)
effector T cells have more LFA-1 and CD2 on their surfaces
the cell disengages if there isn’t a cognate TCR interaction
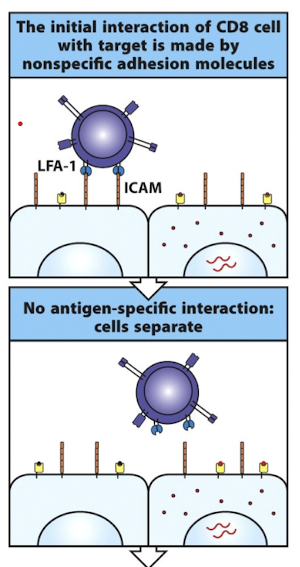
What happens when the TCRs of CD4/CD8 T cells are signaled by a target cell?
integrins adopt a high affinity conformation → tight adhesion
this allows for delivery of effector molecules so that ONLY the target cell undergoes apoptosis
CD8 = directed cytotoxicity
CD4 = cytokine release
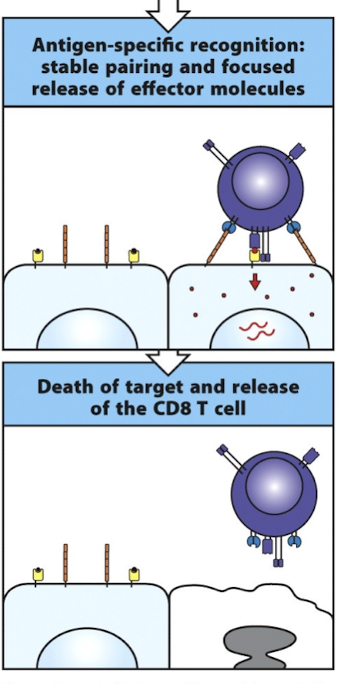
What is the immunological synapse?
the interface between T cells and APCs in which signaling molecules are spatially and temporally clustered
How is the immunological synapse organized?
pSMAC = outer ring of contact, LFA-1 and talin(connects LFA-1 to actin cytoskeleton) are present in T cell interface, ICAM-1 is present in APC interface
cSMAC = inner ring, T cell interface has TCR, CD4 or CD8, and PKCθ, APC interface have pMHC complex and B7 molecules
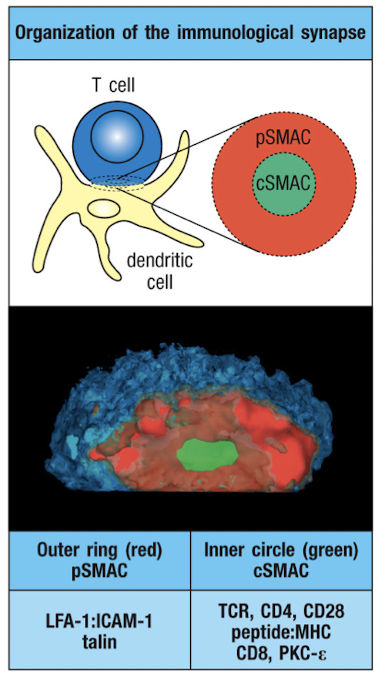
What occurs in the immunological synapse?
internalization of the TCR in cSMAC is thought to downregulate signaling
prolonged contacts are required for complete cytokine production of CD4+ T cells
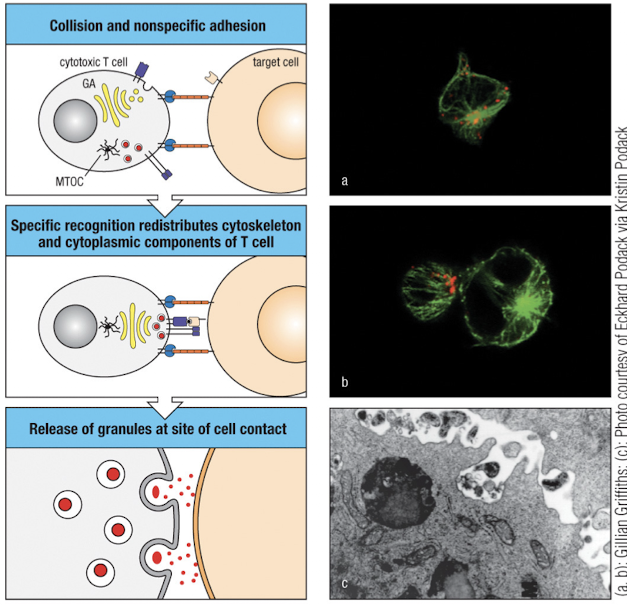
After TCR signaling, the cytoskeleton rearranges to bring the MTOC and golgi close to the contact area for local delivery of effectors
mTOC = microtubule organizing center
How do cytotoxic granules get released from CD8+ cells to target cells?
tight binding of T cell to target due to increase in integrin affinity
focusing of secretory apparatus at target cell. This is done through organization of the actin cytoskeleton (Vav → Wasp → CDC42 → actin), then MTOC and golgi move to synapse
effector molecules are released through the secretory zone.
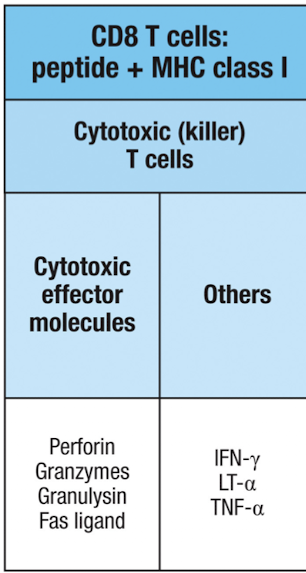
What are the effector molecules for CD8+ T cells?
cytotoxic effector molecules: perforin, granzyme, granulysin, Fas ligand
FasL induces apoptosis of target cells expressing FAS
cytokines: IFN-y , LT-α, TNF-α
IFN - y inhibits viral replication and increases MHCI, and activates macrophages
What are the most important effector molecules for CD4 TH1 cells and what do they do?
IFN-y - Mac activation, increases MHC-I and MHC-II on nearby cells
GM-CSF - increases myelopoiesis in bone marrow (more progenitors)
CXCL2 - recruits monocytes to enhance Type I responses
CD40L - activates dendritic cells, B cells, or macrophages
What are the most important effector molecules for CD4 TH2 cells and what do they do?
IL-4 - promotes IgE class switch, TH2 differentiation
IL-5 - eosinophil growth and activation
IL-13 - goblet cells increase mucus production
CD40L - activates DCs, B cells, or macrophages
What are the most important effector molecules for CD4 TH17 cells and what do they do?
IL-17 - indirect recruitment of neutrophils
IL-22 - stimulate epithelial cells to produce antimicrobial peptides
CD40L - activates DCs, B cells, or macrophages
What are the most important effector molecules for CD4 Treg cells and what do they do?
IL-10 - inhibits inflammatory cytokine release by macrophages, inhibits TH1
TGF-β - inhibits TH1 and TH2, promotes IgA class switch
What are the most important effector molecules for CD4 TFH cells and what do they do?
IL-21 - activates B cells and promotes germinal center formation
CD40L - critical for activating B cells
How does CTL kill targets serially?
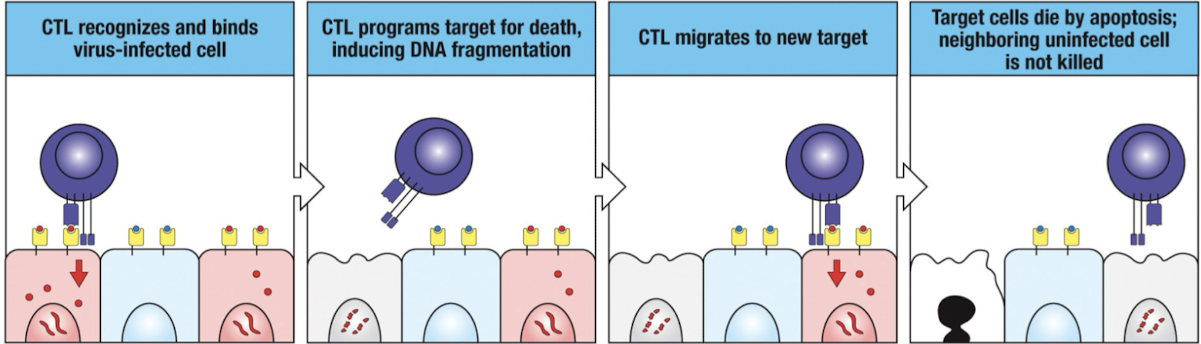
What are the 2 pathways through which CTL induce apoptosis?
Intrinsic: stress induced (UV damage, chemotherapy, or lack of growth factors)
Extrinsic: activation of death receptors by extracellular ligands (FasL, TNF-a, LT-a binding to Fas or TNFR-1 on target cells)
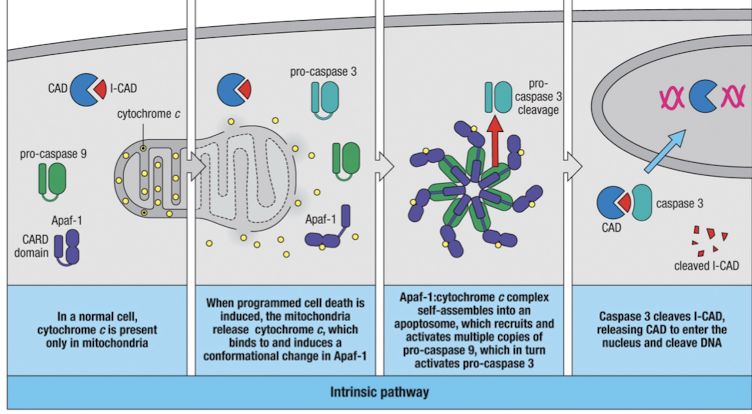
Intrinsic Pathway of Apoptosis
when apoptosis is induced, mitochondria release cytochrome C
cytochrome C binds to Apaf-1 causing conformational changes
Apaf-1:cytochrome C form the apoptosome whihc activated Caspase 9
Caspase 9 cleaves pro-caspase 3, which cleaves ICAD, releasing CAD to degrade DNA
other effector caspases are also activated and they cleave many proteins needed for cell integrity
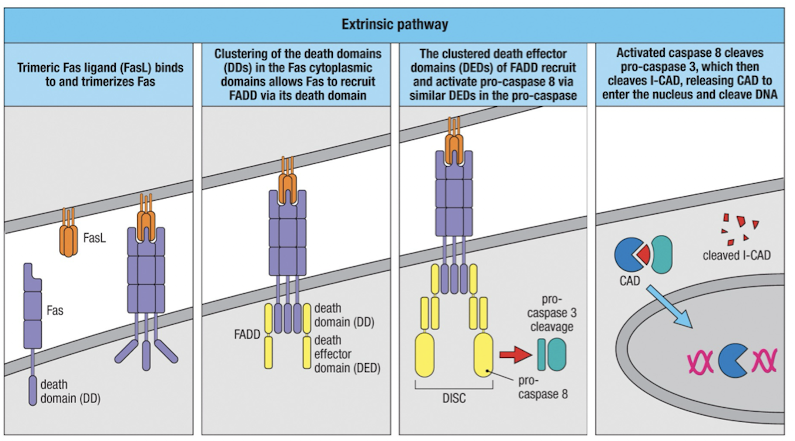
Extrinsic pathway of apoptosis
Induced when TNFR superfamily members containing death domains, like Fas, are crosslinked
clustered Fas recruits FADD via the death domains (DD)
FADD recruits pro-caspase 8 via the death effector domain (DED) and it is activated
Caspase 8 cleaves pro-caspase 3, which cleaves ICAD, releasing CAD to degrade DNA
Bcl2 family members regulate apoptosis
release of cytochrome C is regulated by Bcl-2 family members (BH domains
pro-apoptotic sentinels detect apoptotic stimuli and block protectors to promote activity of executioners
pro-apoptotic family members bind mitochondrial membranes to trigger cyt C release
anti-apoptotic family members are induced by stimuli that direct cell survival ( ex: AKT → Bcl2) to prevent cyt C release
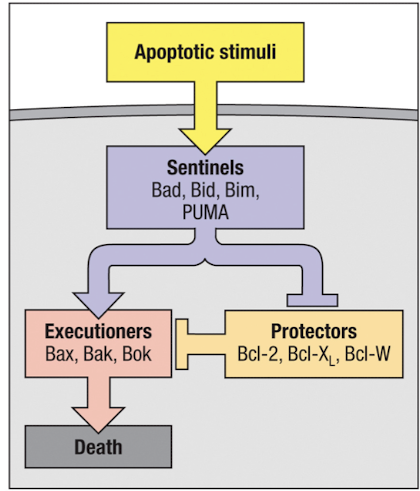
What molecules are sentinels?
Bad
Bid
Bim
PUMA
what molecules are protectors?
Bcl-2
Bcl-XL
Bcl-W
what molecules are executioners?
Bax
Bak
Bok
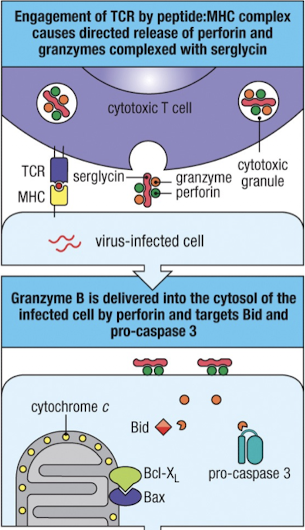
What is the significance of the cytotoxic granules? (CTL cytotoxicity I)
when TCR is engaged, granules reorient towards the target cell
perforin - aids in delivering contents of granules (like granzymes) into target cell, activating the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis
granzymes - serine proteases which activate apoptosis once in the cytoplasm
granzyme B cleaves Bid (sentinel) and pro-caspase 3
granulysin - has antimicrobial actions and can induce apoptosis
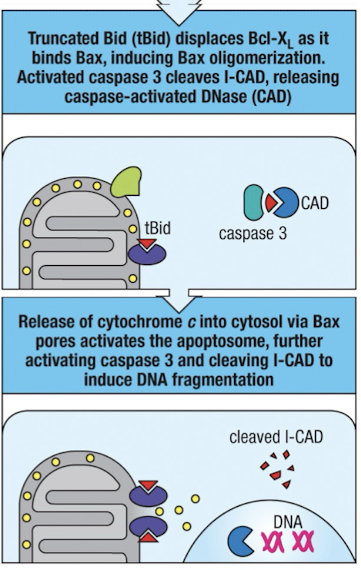
CTL cytotoxicity continued
cleaved BID displaces Bcl-XL (protector)
activates caspase 3 cleaves iCAD
cytochrome C release into cytosol → apopotosome activation
CAD cleaves DNA into 200 bp fragments between nucleosomes
CTLs induces target cell death with 5 mins
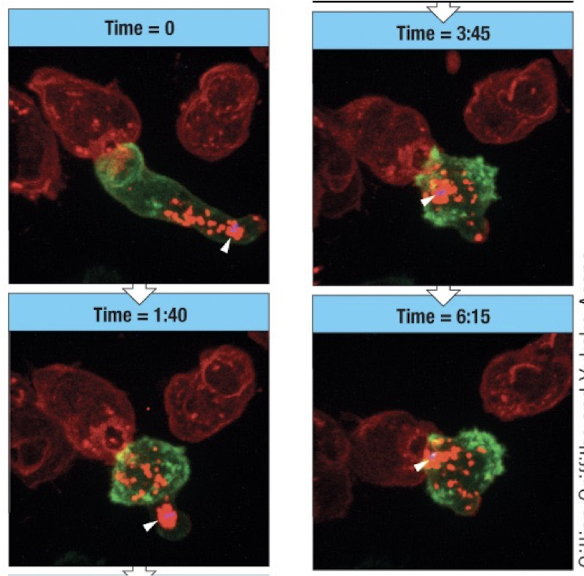
Timecourse of CTL cytotoxicity
T=0 cell contact
1:40 - granules and mTOC move towards immunological synapse
3:45 - MYOC approches interface
6:15 - large accumulation of granules with MTOC at interface
40 mins - granules have been released and cell is apoptotic
CTLs synthesize more cytotoxic proteins after encounter with antigen
apoptotic cells are reconized and ingested by macrophages