HOA 1: Egyptian Architecture
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
Nile
- the life of Egypt
- its gentle current was favorable for navigation
- trade and commerce prospered along its banks
- important religious structures were built in strategic places along this
Post and Lintel
principle of construction in Egypt
Mud brick
was the principle building material for domestic buildings
Stone
was favored for temples and tombs
Simple design, few windows, flat roof and massive walls
effect of climate on buildings
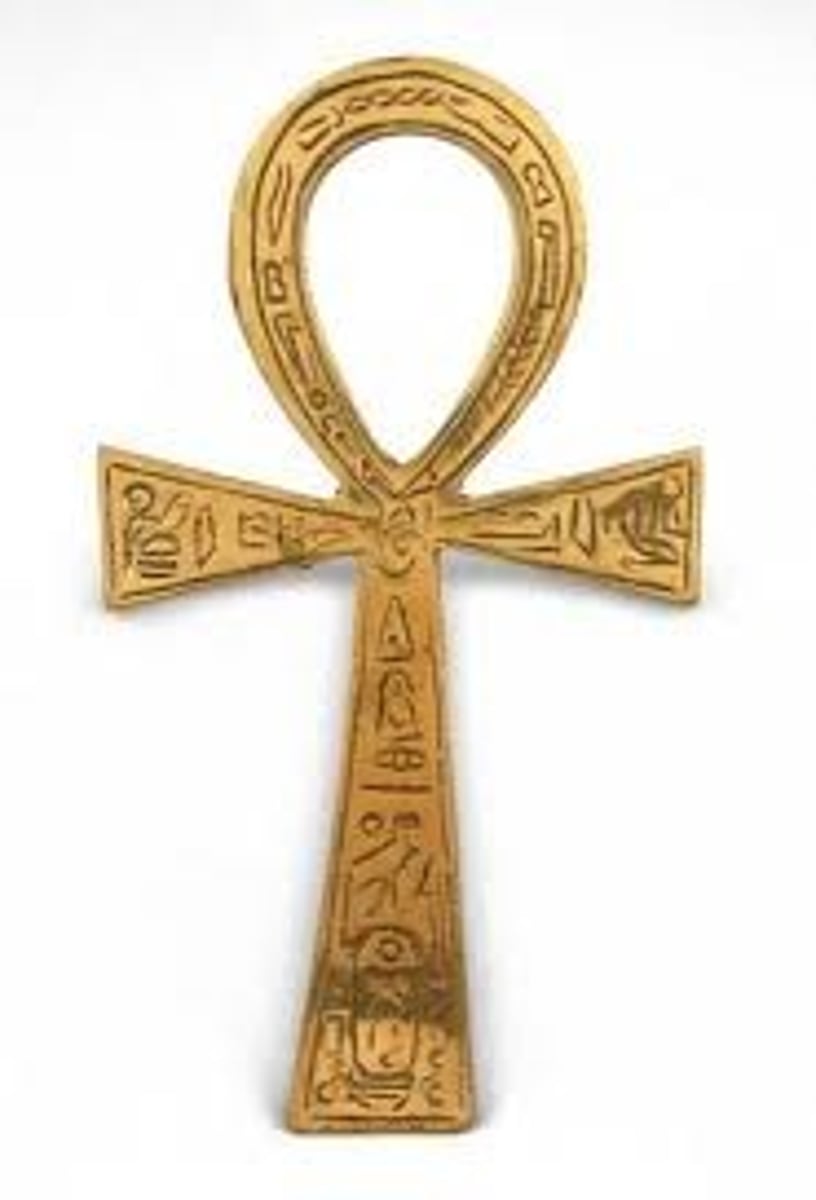
Ankh
symbolizes life, health & strength

Feather of Ma'at
represents justice, truth, mortality and balance

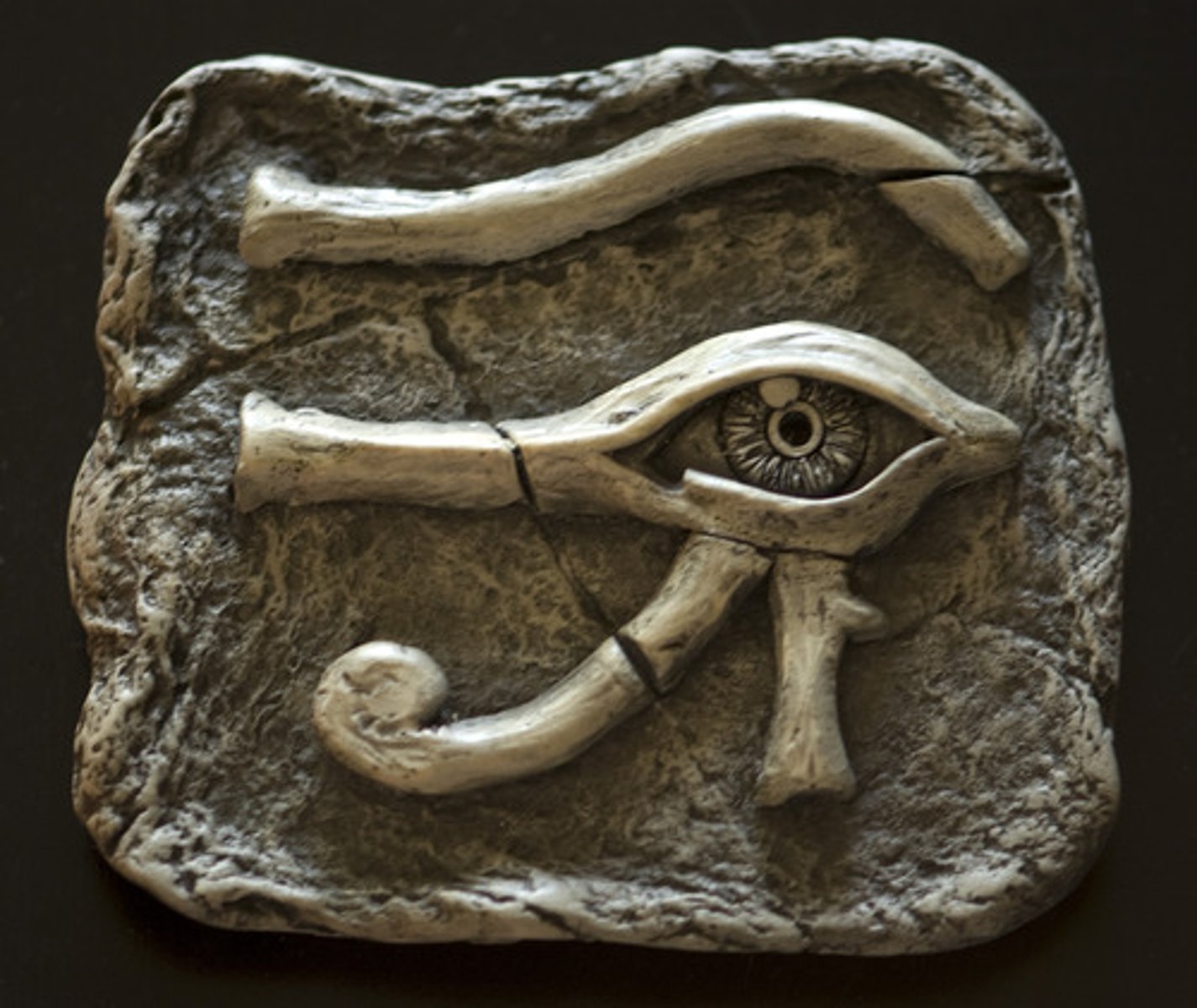
Eye of Horus
symbolizes protection & royal power

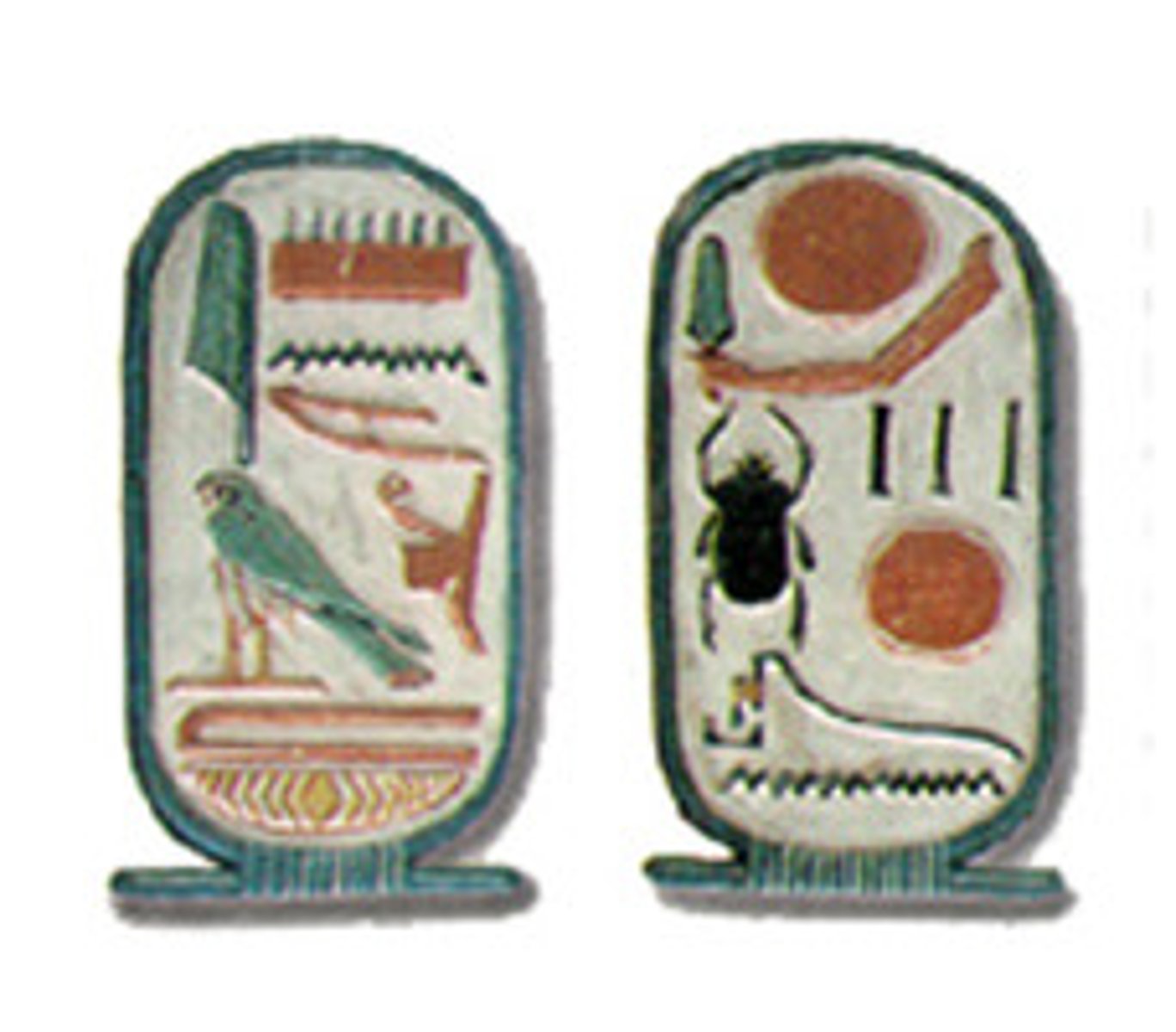
Cartouche
a rope enclosing a royal name thereby serving as the protector of that name

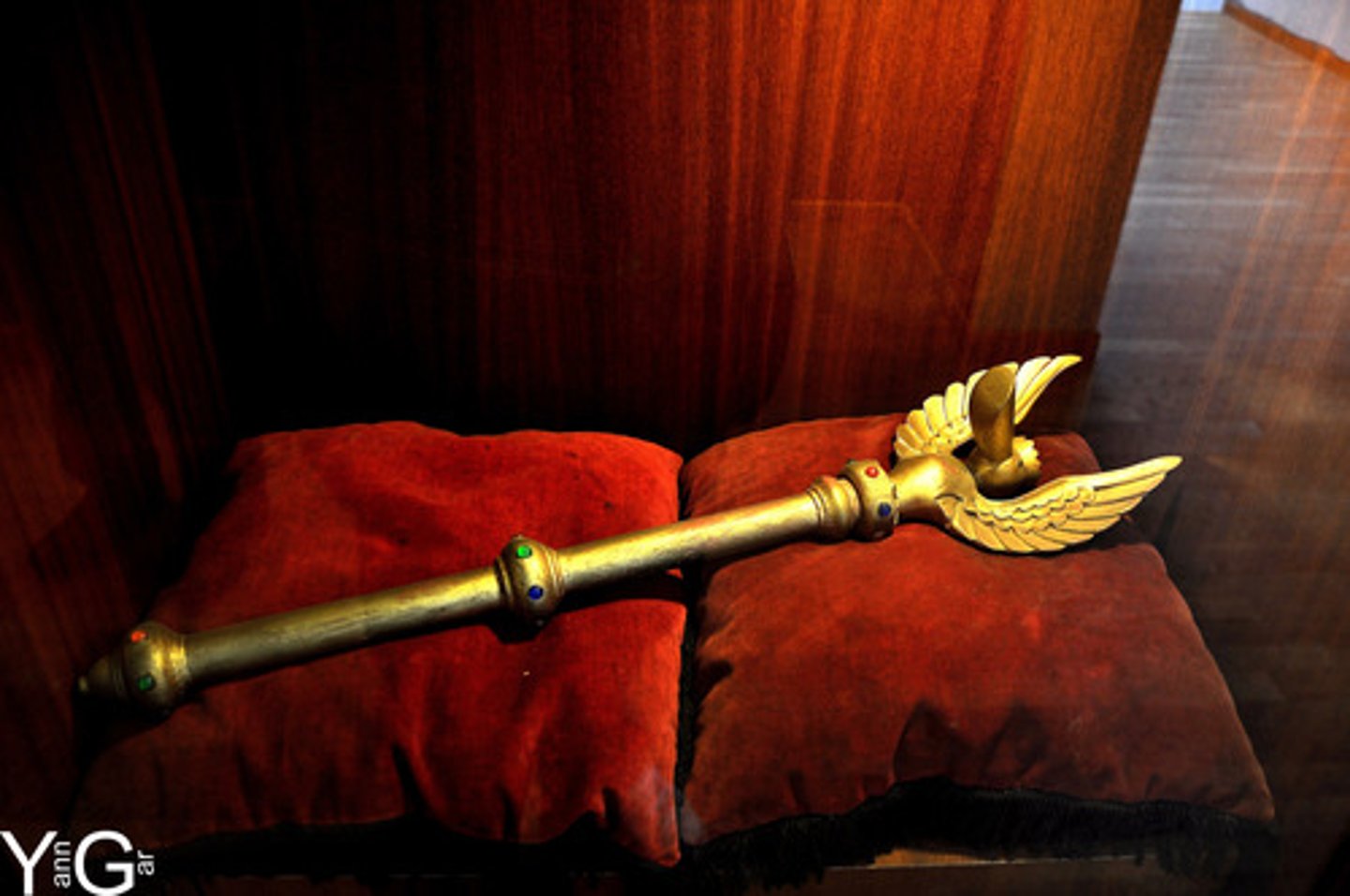
Scepter
symbolizes power, dominion & control

Sun Disk
represents light, warmth & growth

Scarab
symbolizes resurrection & rebirth

Boat of Ra
One must have a light heart to earn a place in this
Crook & Flail
are symbols of royalty, kingship, majesty and dominion.
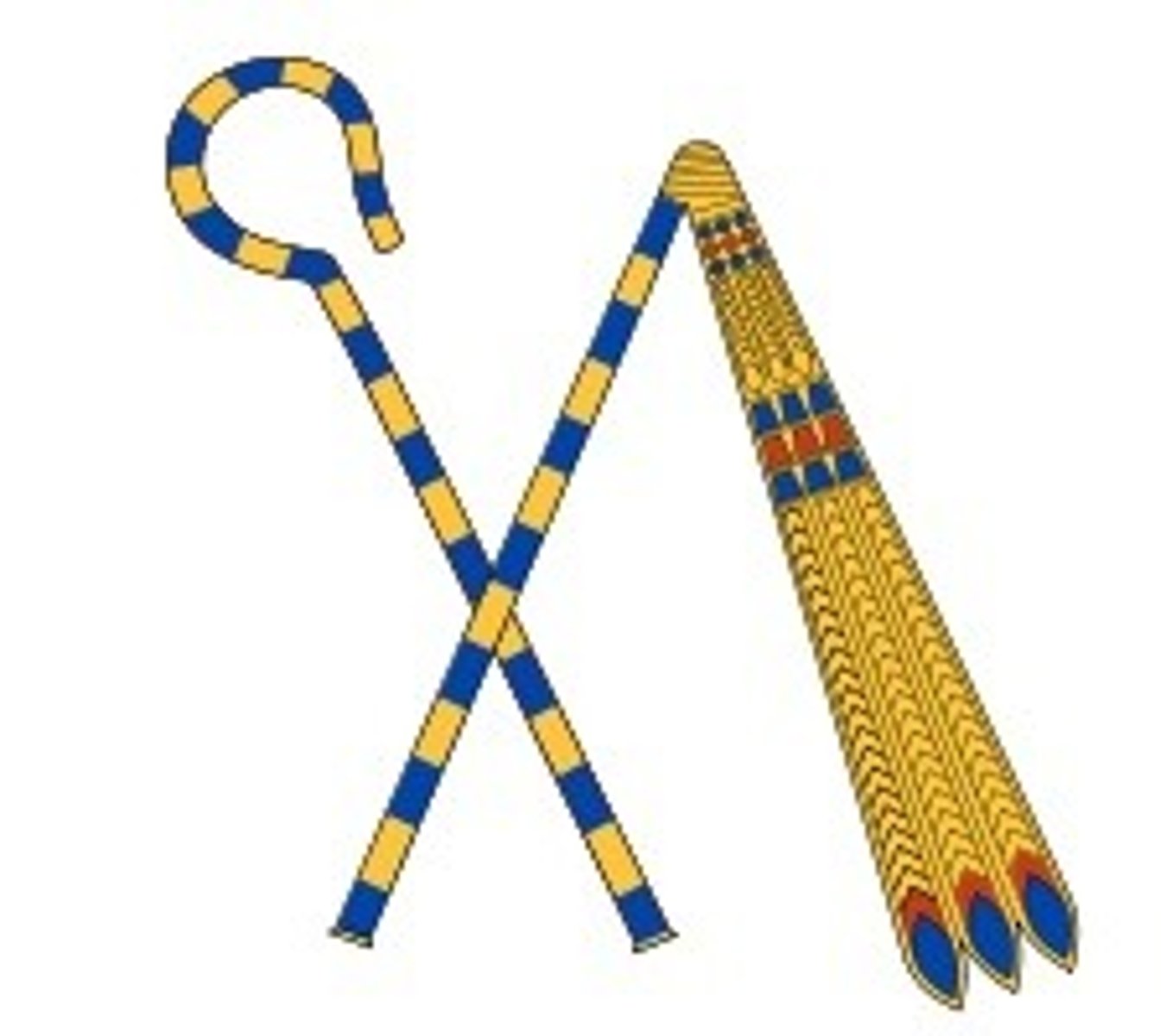

Crook
a scepter symbolizing government

Uraeus/ Cobra
symbolizes royal protection

Falcon
symbolizes divine kingship.
represent the unification of Upper Egypt and lower Egypt
Ibis
symbolizes reincarnation
Mummification
an outstanding feature of the religion.
"Without a physical body there is no shadow, no name, no spirit, no personality & no immortality
Temple of the gods and tomb pyramids of the kings
everlasting monuments for the preservation of the dead.
Papyrus
symbol for lower Egypt and fertility
Lotus
symbol for upper Egypt and fertility
Palm
symbol for Fertility
Columns
are indicative of plant stems gathered at the base with capitals derived from the lotus bud, papyrus flower and the palm.
geometric forms, animals, plants
three types of orientation
papyrus, lotus, palm
ornaments
Mastaba
a broad pit below ground covered with a rectangular flat mound with sides sloping at 75 degrees. It has a shaft descending to the tomb chamber that is dropped with stones for sealing
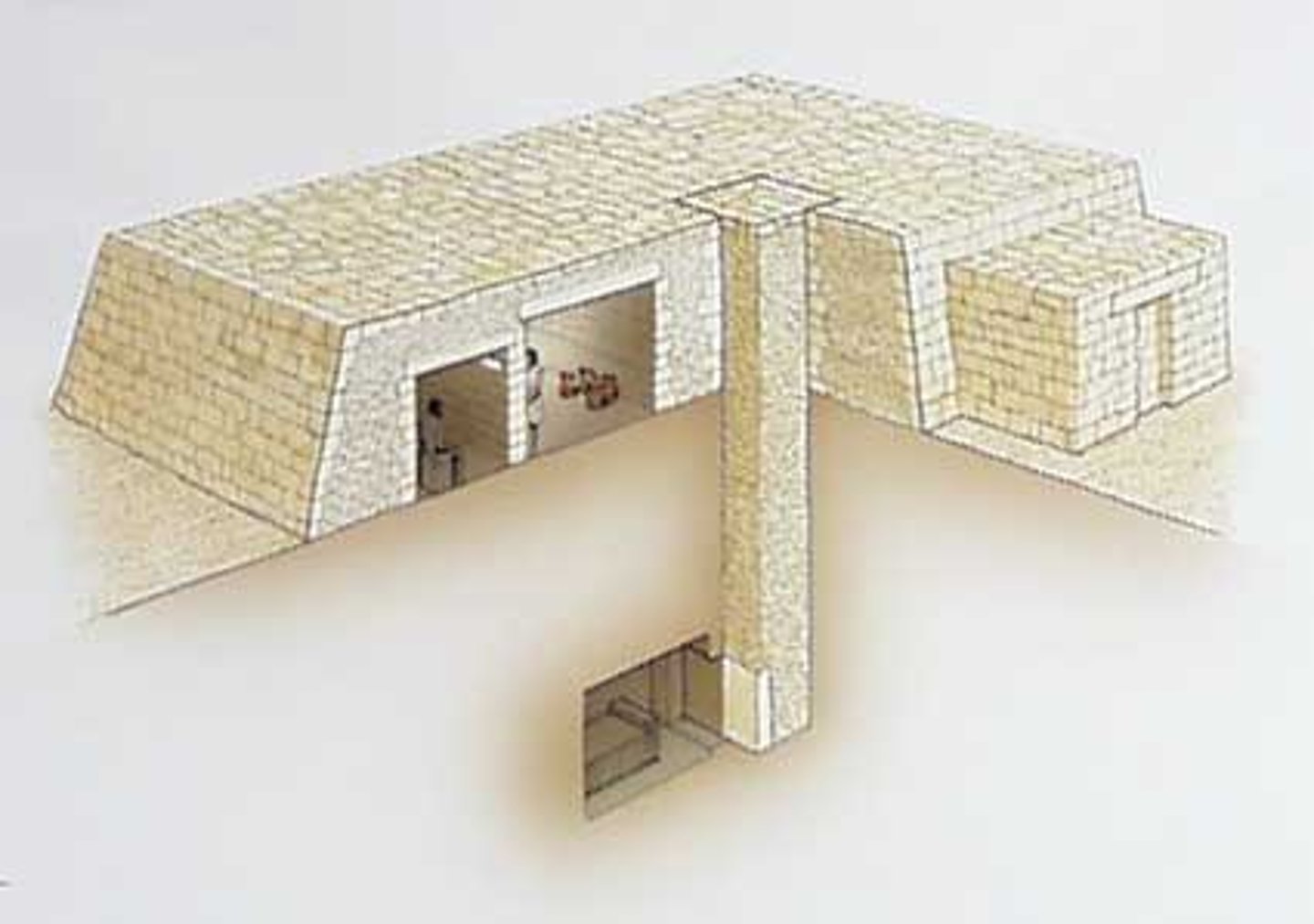

Portcullises
heavy stones that seal the chamber
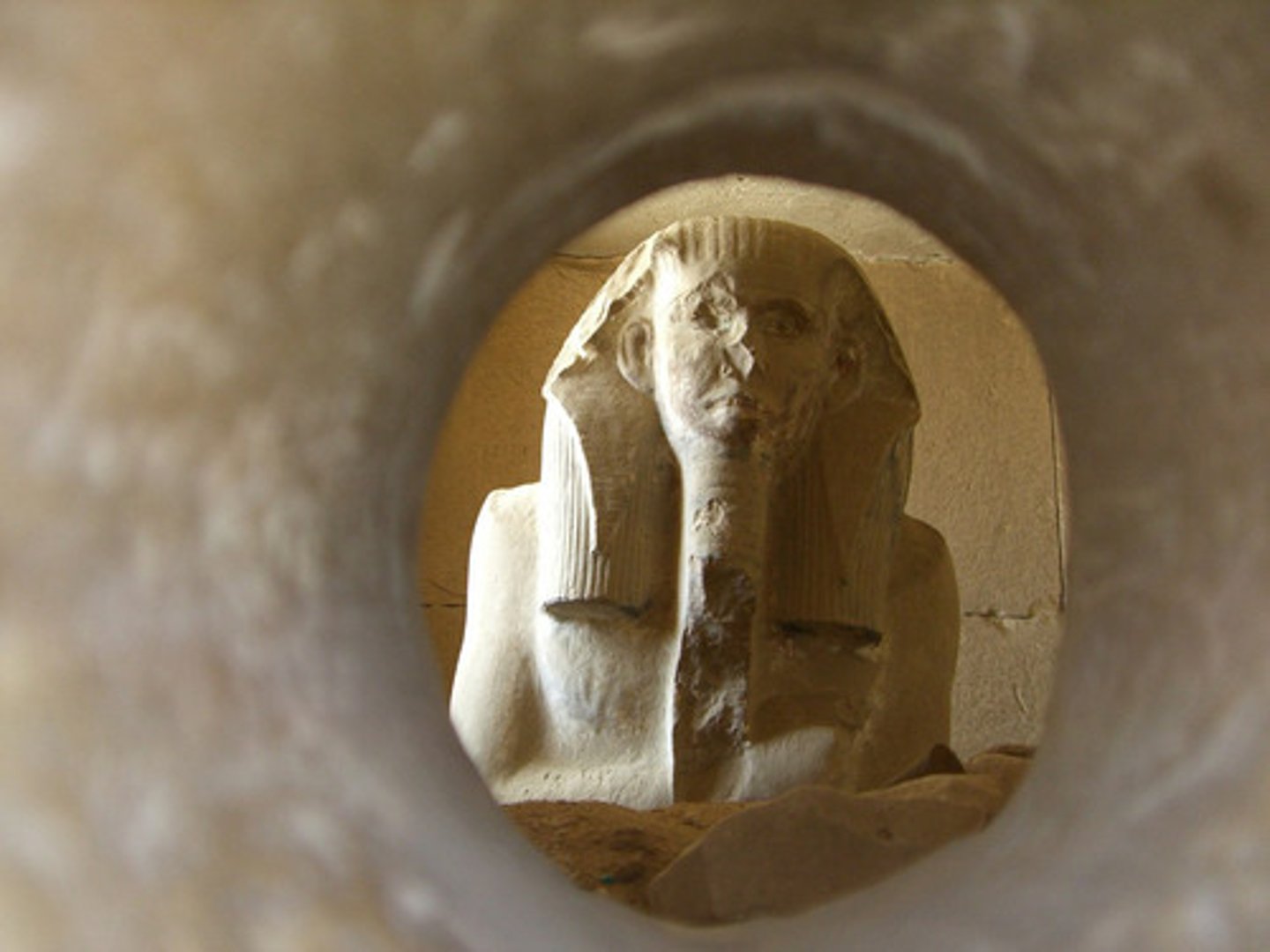
Serdab
is an enclosed room containing the statue of the deceased. It has a hole that allows the communication of the spirit of the dead to the living world

Stele
an offering chapel with the name of the deceased inscribed on it
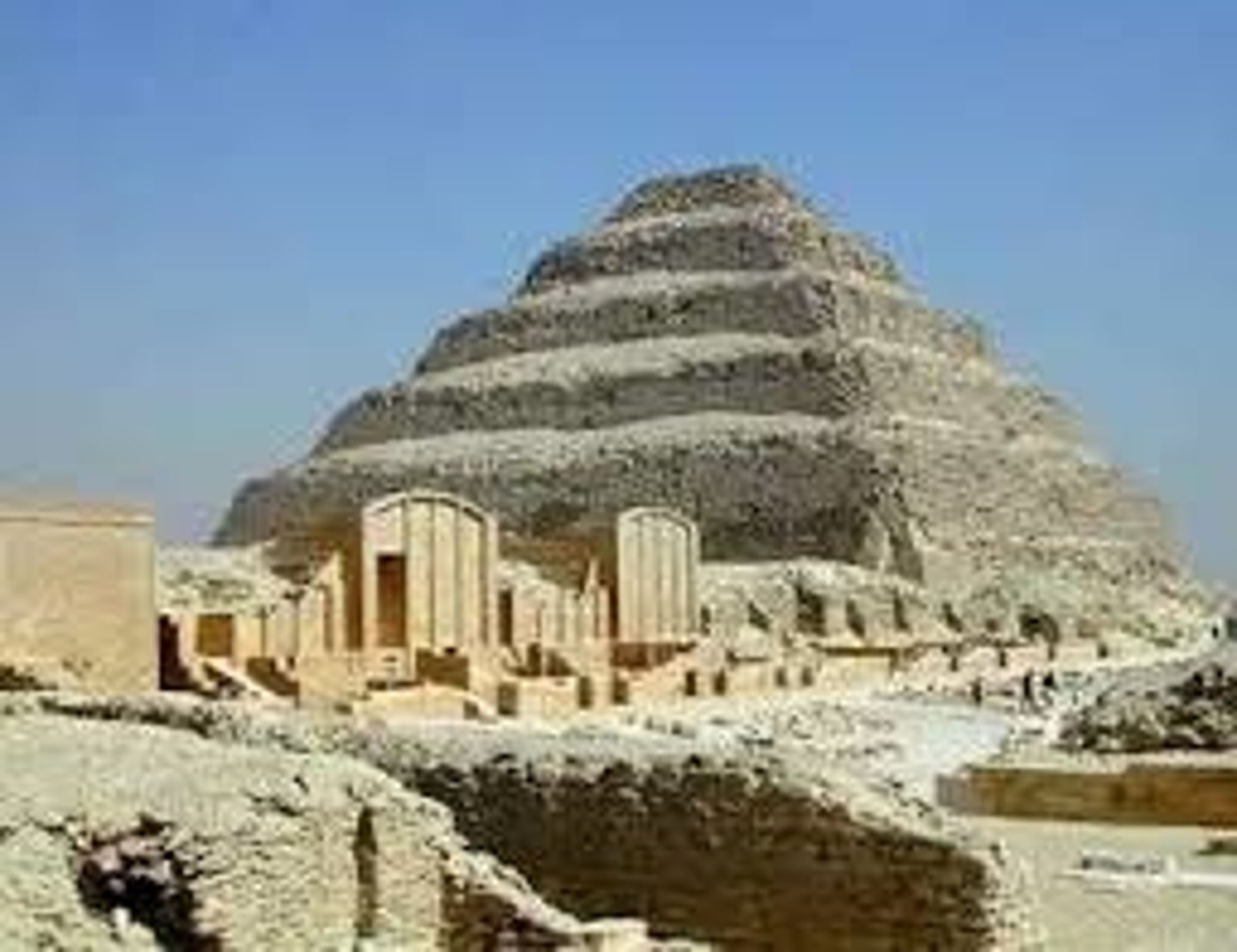
Step Pyramid of Djozer
- designed by Imhotep
- the world's first large scale monument in stone with no free-standing columns
- a series of 6 successively smaller mastabas one atop of another & originally clad in polished white limestone

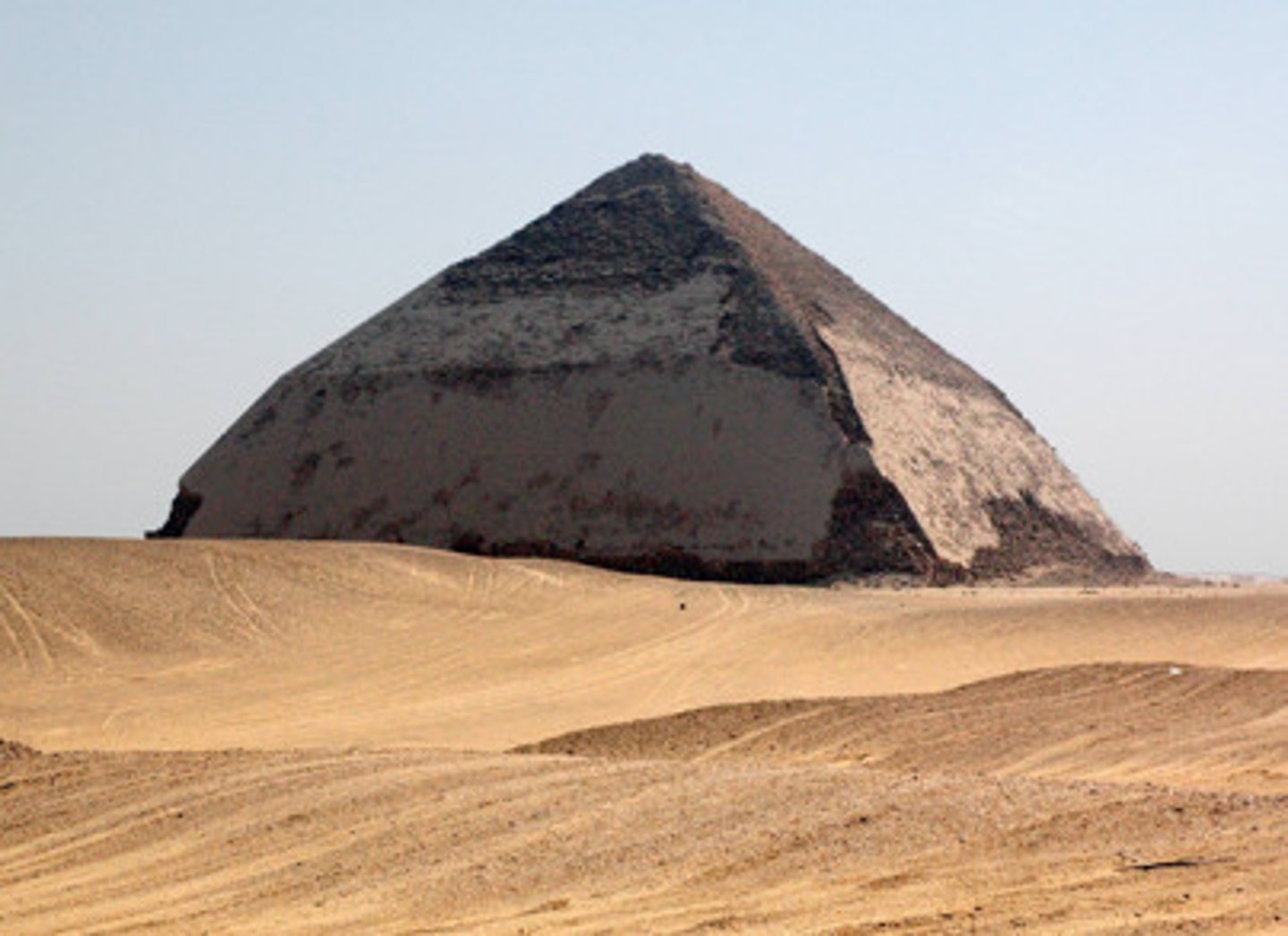
Bent Pyramid of Snefru
a unique example of early pyramid. The lower part rises at a 55 degree inclination & the top section at 43 degrees

Offering chapel, mortuary temple, causeway, valley building
parts of a pyramid
Causeway
a long walkway that joins the valley temple and mortuary temple
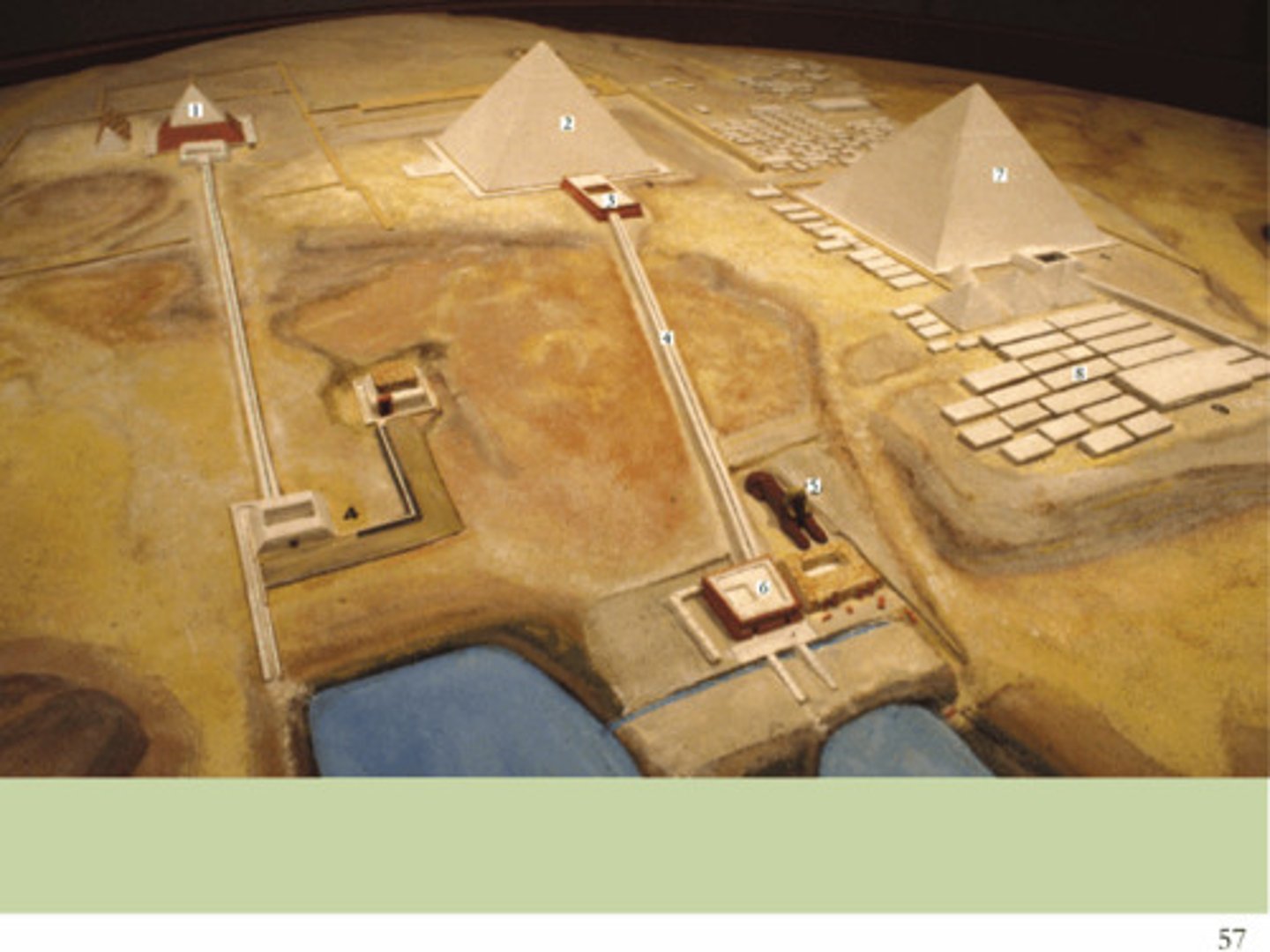

Mortuary Temple
for the worship of the dead

Valley building
for the interment and embalmment of the dead

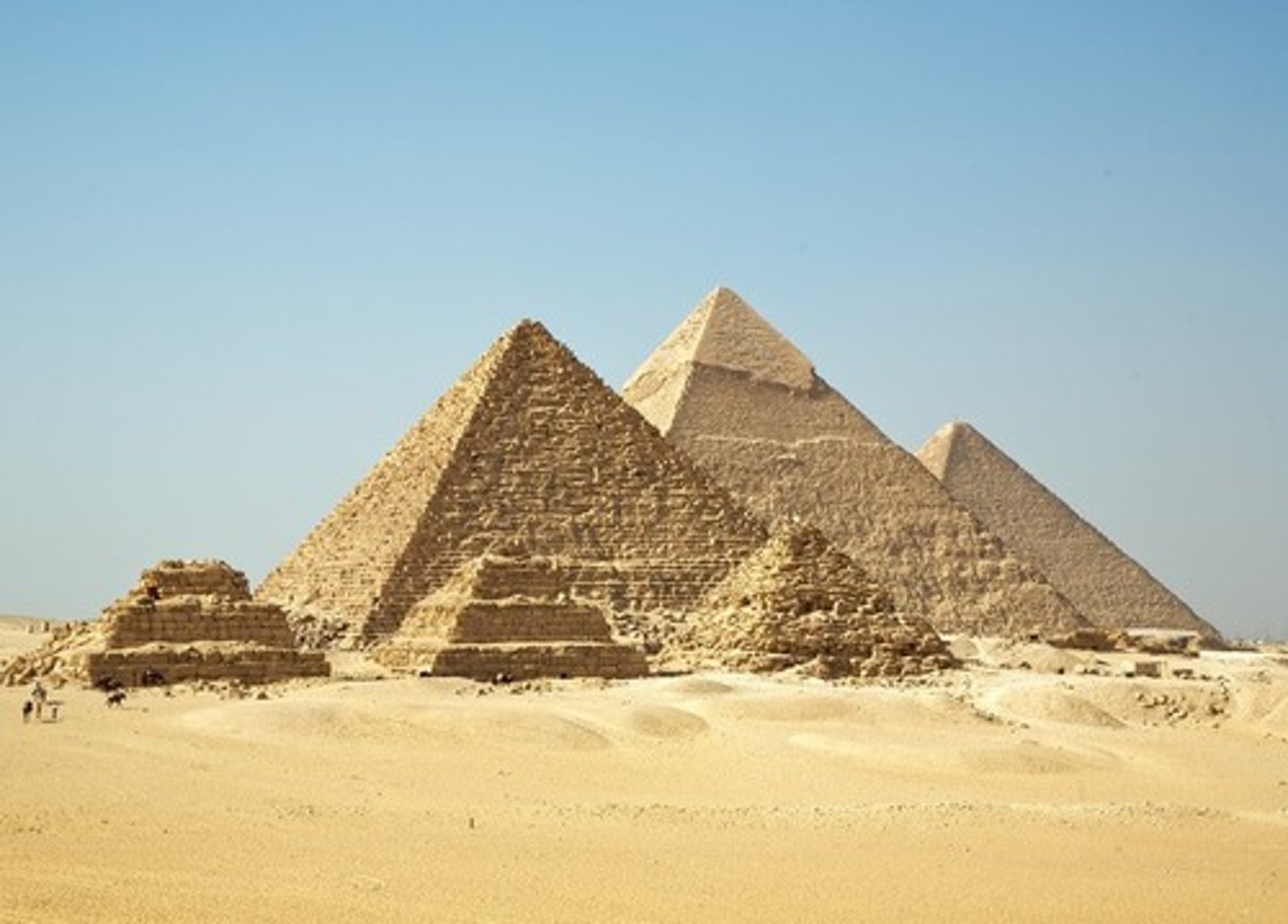
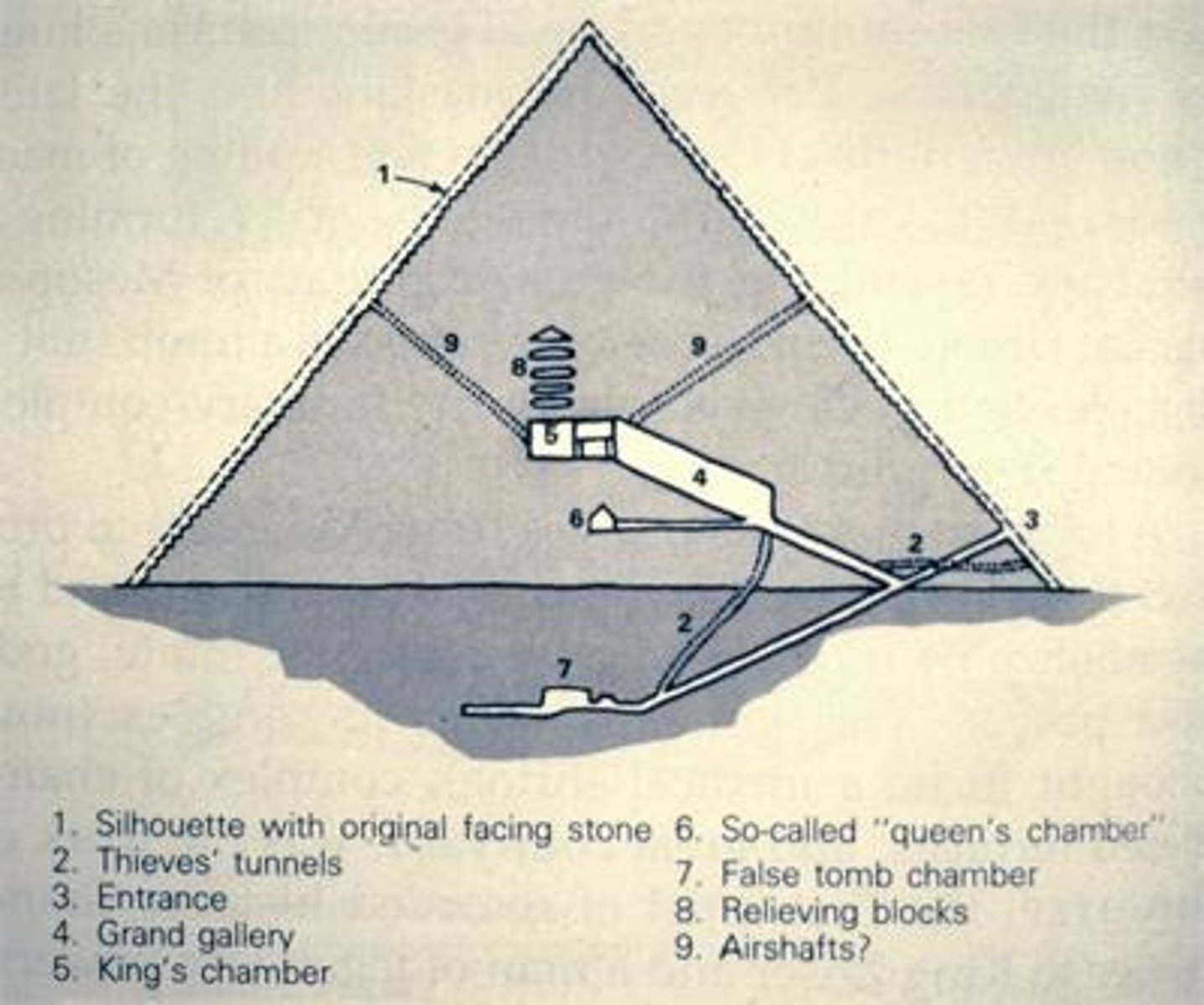
Pyramid of Cheops (Khufu)
the oldest and largest of the 3 pyramids in the Giza Necropolis. It is the oldest of the 7 wonders of the Ancient World and the only one to remain largely intact
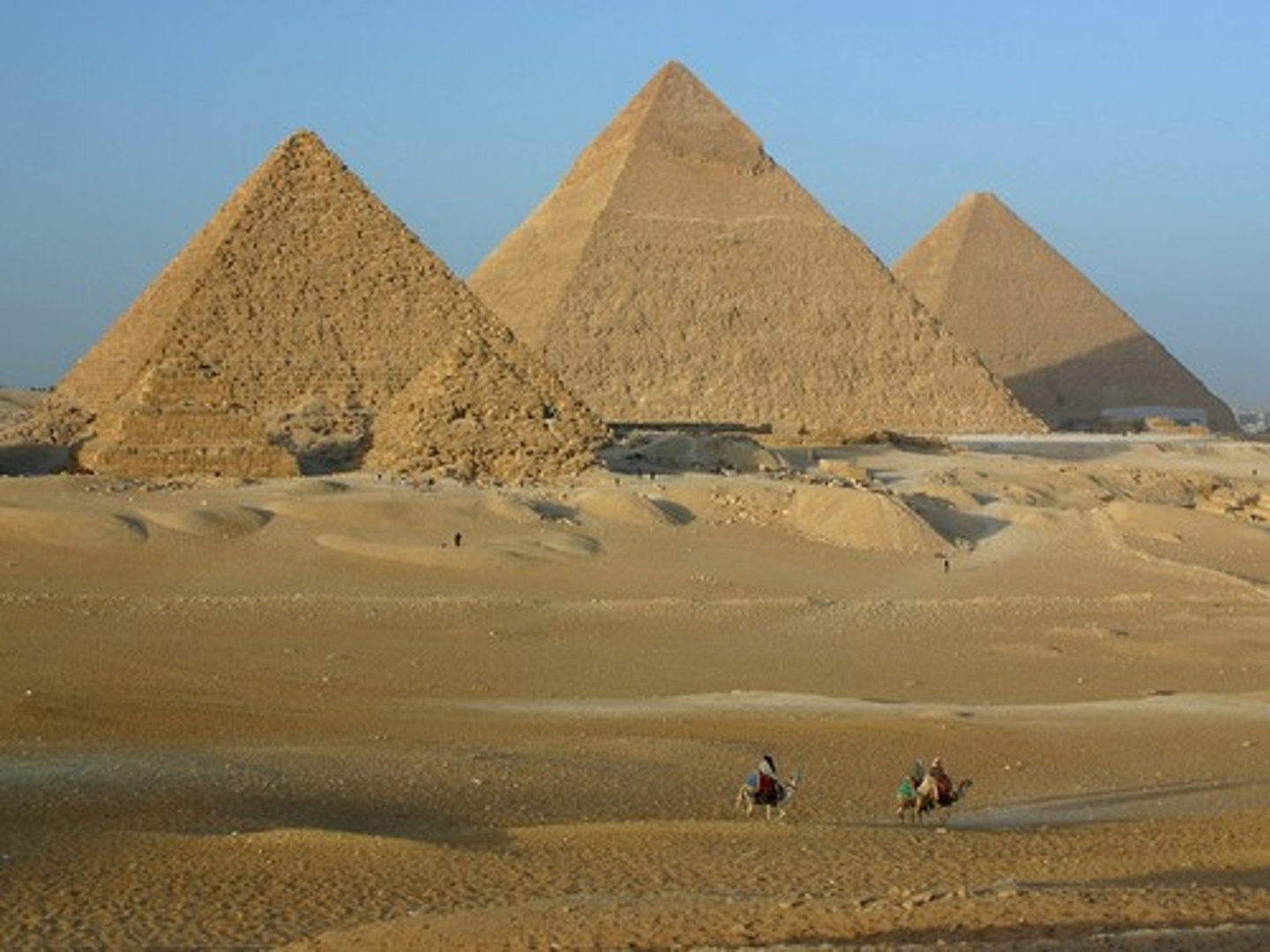

Pyramid of Chephren (Khafre)
is slightly smaller than the great pyramid of Cheops & guarded by the Sphinx believed to bear the face of the King Chephren
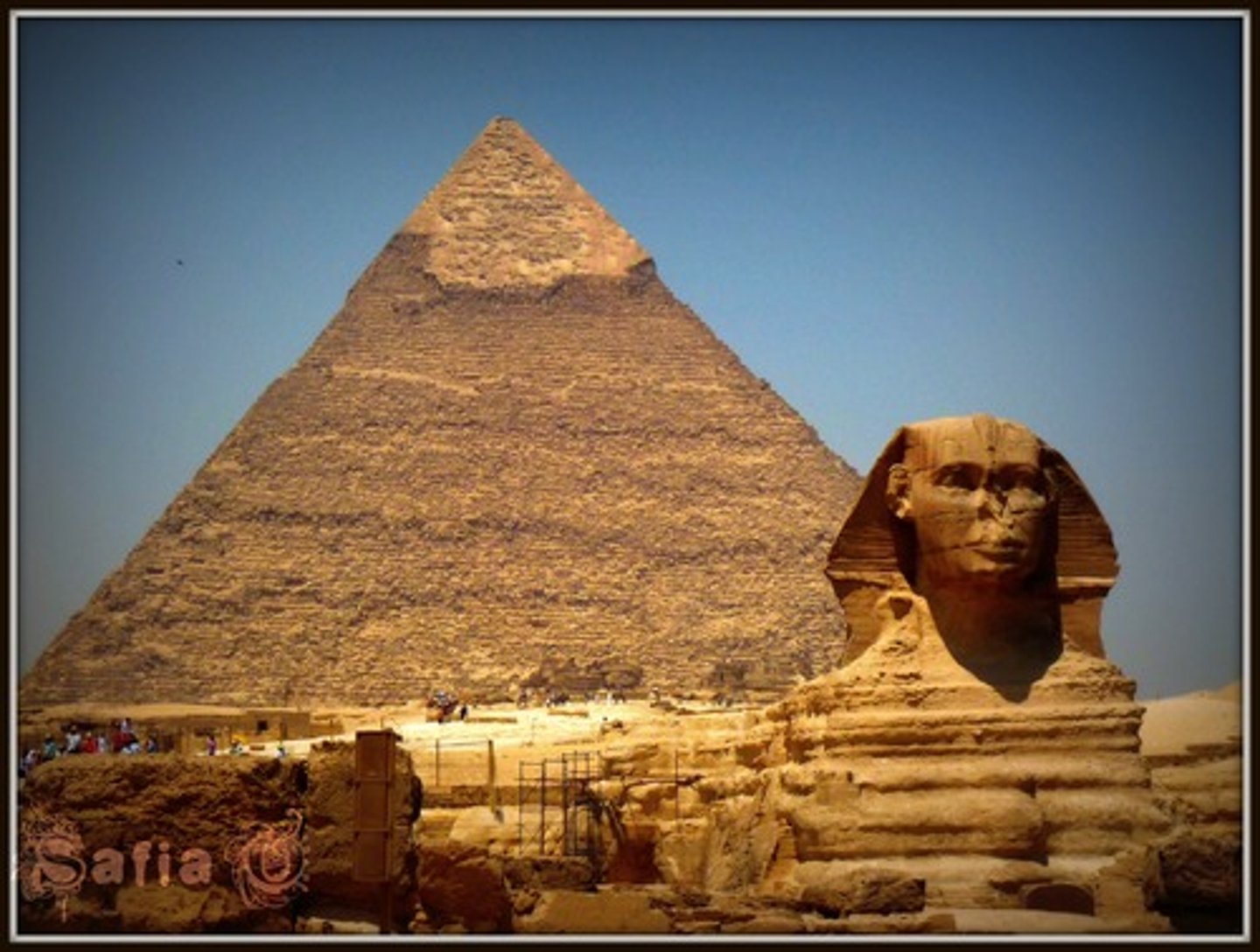

Pyramid of Mykerinos (Menkaura)
the smallest & the last among the 3 pyramids to be built in the Giza Plateau

Straight Ramps
pyramid construction

Zigzag & spiral ramps
pyramid construction
Pyramid construction
was hugely labor-intensive. Stones were dragged on a prepared slipway that was lubricated with oil. It was paid labor during slow agricultural seasons
King Tutankhamun
ruled Egypt from 1333-1324 BC, ascending the throne at age nine. His mummified body within three coffins or sarcophagi
Outer Coffin
Tutankhamun's sarcophagi that is made of gilded wood covered with gold
Middle Coffin
Tutankhamun's sarcophagi that is made of wood covered with gold semiprecious stones, glass and obsidian
Inner Coffin
Tutankhamun's sarcophagi that is made of solid gold and weighs 110k
Tutankhamun's shrine
Tutankhamun's sarcophagi that is made of granite. The 4th layer of sarcophagus
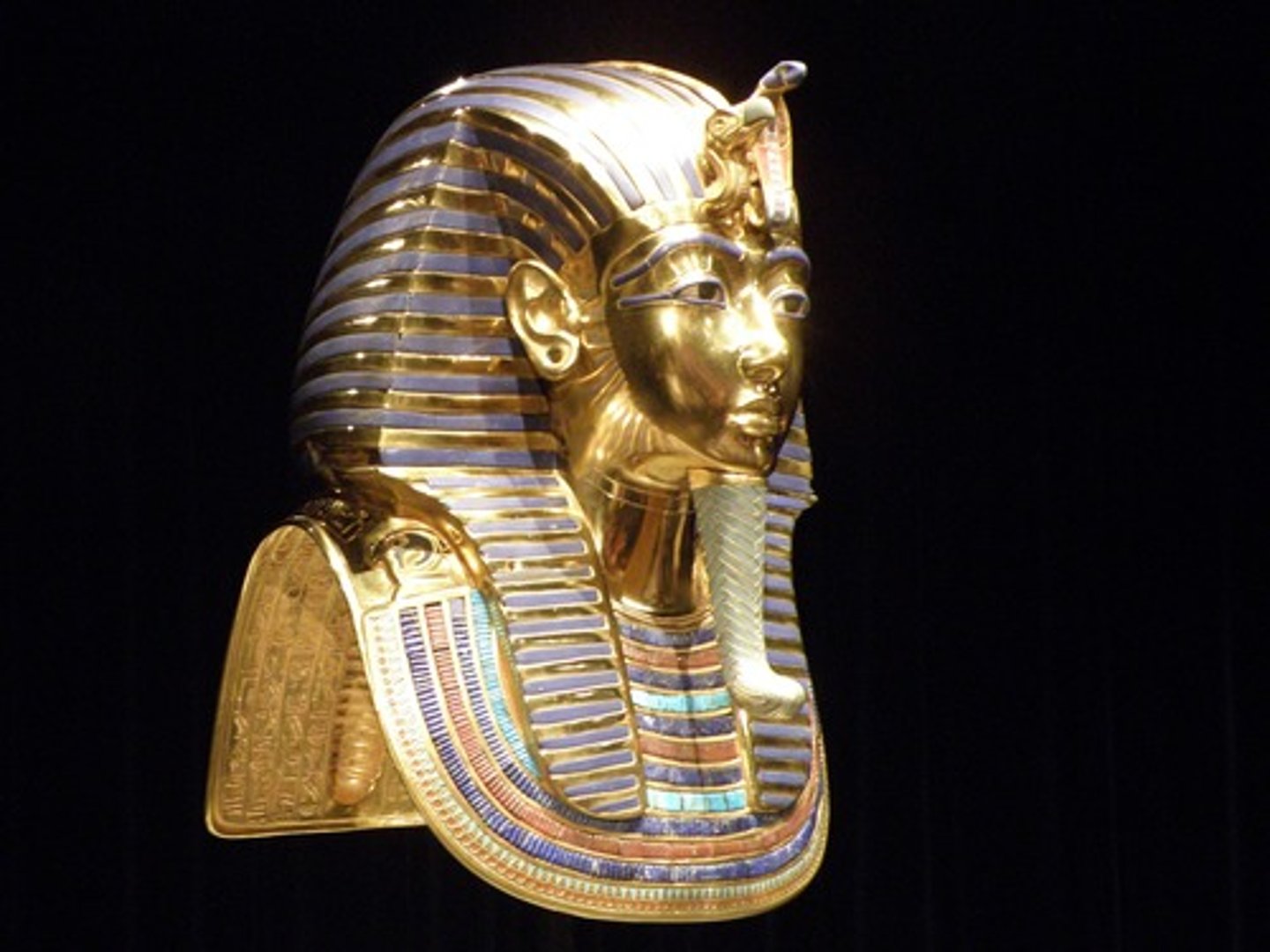
Tutankhamun's Death Mask
made of solid gold and inlaid with semi-precious stones, it weighs 11 kilograms
Hatshepsut
the first woman pharoah agter Thutmose II
Thutmose III
the Napoleon of ancient Egypt. known for his military genius and built structures.
Rameses II
one of the longest ruling pharoahs of ancient Egypt for 67 years.
Cleopatra
the queen of Nile. The last pharoah of ancient Egypt. The daughter of Ptolemy XII (Greek)
Beni Hasan
an example of a Hillside Tomb with 39 ancient elaborately decorated tombs carved into the limestone cliffs.
Valley of Kings
an example of a corridor tomb. It was the royal necropolis of Ancient Egypt where kings and nobles were buried
Valley of the Queens
a place near the Valley of the Kings where wives of Pharoahs were buried in ancient times
Mortuary Temple
a type of temple that is used for the ministrations to deified pharoahs
Cult Temple
is a type of temple used for the worship of the ancient & mysterious gods
Light and shadow
important features in temples.
Pylon
[Parts of an Egyptian Temple] serves as the monumental gateway
![<p>[Parts of an Egyptian Temple] serves as the monumental gateway</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/afdaf3ea-a767-416a-a3e8-c5e34a687353.jpg)
Great Court
[Parts of an Egyptian Temple] is surrounded by columns
Hypostyle Hall
[Parts of an Egyptian Temple] a forest of columns portraying the illusion of infinity and vastness of space
Sanctuary
[Parts of an Egyptian Temple] the holiest part; it is only accessible to the kings and high preists
Enclosure wall
[Parts of an Egyptian Temple]
the large wall which surrounded the entire Pyramid Complex
Obelisk
[Parts of an Egyptian Temple] a tall 4 sided narrow tapering column terminating in a pyramidion, its most sacred part
Avenue of Sphinxes
[Parts of an Egyptian Temple]
![<p>[Parts of an Egyptian Temple]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b5d22ede-60e9-4c85-be17-09e7d7eb3668.jpg)
Colossal Statues of the Pharoah
[Parts of an Egyptian Temple]
![<p>[Parts of an Egyptian Temple]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f7f3d260-035b-4fa0-ac20-f80f354f6252.jpg)
Temple od Isis, Philae
dedicated to goddess Isis, wife of osiris and mother of Horus
Batter walls
temple walls that were designed with inward inclinations
Temple of Isis
the last pagan temple to exist in the Mediterranean
Great Temple of Amun, Karnak
the grandest of all Egyptian temples & built by many kings.It has 6 pairs of pylons
Great Temple of Amun, Karnak
the most important sanctuary of the culit who worshipped Amun- Ra. A pair of obelisks flank the main entrance
Great Temple, Abu Simbel
a rock-hewn temple with 4 rock-cut colossal statues of Rameses II, over 20 meters high
Mortuary Temple of Mentuhetep
a cenotaph with a dummy burial chamber below it.
Mammisi Temple
the birth house of the gods
crude bricks of one to two storeys high with flat and parapeted roof
Domestic Architecture: Houses