LECTURE 9: PAIN SYNDROMES
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 6:45 PM on 4/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
1
New cards
syndrome
collection of signs and symptoms where we don’t know the cause
2
New cards
disease
something with a known cause, recognizable and discreet symptoms
3
New cards
pain in different parts of the body are comorbid with each other
diagnosis, with same signs and symptoms, can be different depending on which specialist you go see
4
New cards
gastroenterology speciality
irritable bowel syndrome, non-ulcer dyspepsia = syndromes commonly seen by this specialist
5
New cards
gynaecology
premenstrual syndrome, chronic pelvic pain = syndromes commonly seen by this specialist
6
New cards
rheumatology
fibromyalgia = syndromes commonly seen by this specialist
7
New cards
cardiology
atypical or non-cardiac chest pain = syndromes commonly seen by this specialist
8
New cards
respiratory medicine
hyperventilation syndrome = syndromes commonly seen by this specialist
9
New cards
infectious disease
chronic (postviral) fatigue syndrome = syndromes commonly seen by this specialist
10
New cards
neurology
tension headache
11
New cards
dentistry
temporomandibular joint dysfunction, atypical facial pain
12
New cards
ear, nose and throat
globus syndrome
13
New cards
allergy
multiple chemistry sensitivity
14
New cards
3 types of clinical pain
1. acute pain
2. cancer pain
1. oncologist
2. palliative care
3. chronic non-cancer pain
1. inflammatory
2. neuropathic
3. idiopathic/functional - no specific cause
4. headache
15
New cards
causes of acute pain
* burns
* fracture
* dental pain
* back pain
* acute back pain: 6-7 weeks
* sub acute back pain: 7-12 weeks
* chronic back pain: more than 12 weeks
* fracture
* dental pain
* back pain
* acute back pain: 6-7 weeks
* sub acute back pain: 7-12 weeks
* chronic back pain: more than 12 weeks
16
New cards
input of nociceptors happens on 2 occasions
1. nociceptors are activated when skin and muscle are cut
2. nociceptors input information from the inflammation after waking up from anaesthetic/ post-surgery inflammation
17
New cards
difference between analgesic and anesthetic
* Analgesic = relief of pain
* Anesthetic = loss of physical sensation
* Anesthetic = loss of physical sensation
18
New cards
postsurgical pain prevention by scott reuben
* he claimed that analgesic before surgery would entail no pain after waking up
* above claim = false
* nociceptors can’t fire because you’re anesthetized
* above claim = false
* nociceptors can’t fire because you’re anesthetized
19
New cards
if postsurgical pain doesn’t go away after 3 months
this is now considered chronic postsurgical pain
20
New cards
Different surgeries and possibility of getting CPSP
* cosmetic surgery leads to 21-50% chance of CPSP
* breast augmentation → 13% of developing CPSP
* vasectomy → 15% of developing CPSP
* breast augmentation → 13% of developing CPSP
* vasectomy → 15% of developing CPSP
21
New cards
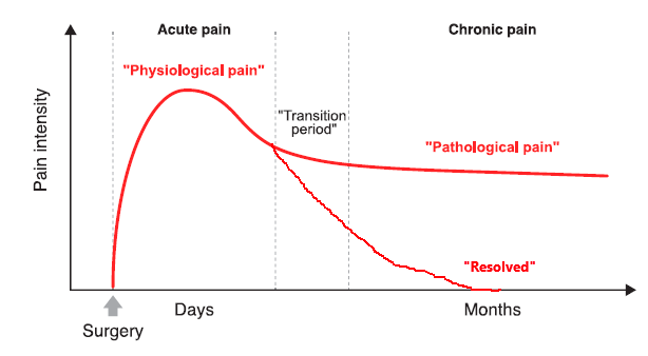
acute-to-chronic pain transitioning
2 leading theories
1. pain persists and transitions into chronic pain
1. pain persists and transitions into chronic pain
22
New cards
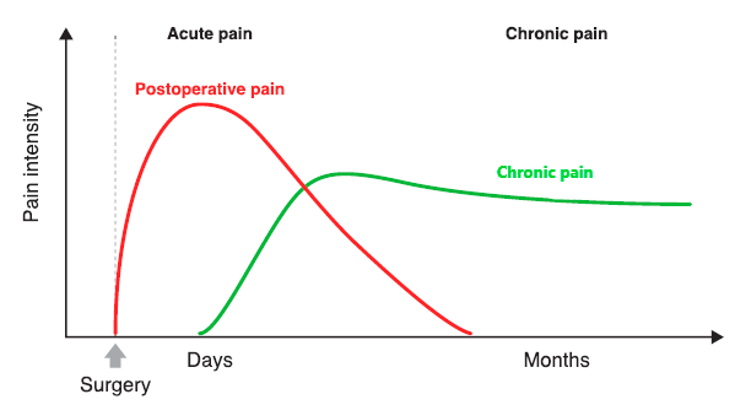
chronic pain might be independent of the acute pain and starts independently of the acute pain
23
New cards
what is responsible for the chronification of back pain
* cortical shrinking/thinning of the brain
* gray matter volume decreases
* gray matter volume decreases
24
New cards
study done by Baliki et al
2 groups of people
1. those with subacute back pain (lasting 7-12 weeks)
2. no back pain
Found 2 subgroups
1. subacute back pain resolving → cortex didn’t shrink
2. subacute back pain progressing/persisting → gray matter of cortex shrinking
1. those with subacute back pain (lasting 7-12 weeks)
2. no back pain
Found 2 subgroups
1. subacute back pain resolving → cortex didn’t shrink
2. subacute back pain progressing/persisting → gray matter of cortex shrinking
25
New cards
prevalence of cancer pain depends on what?
the type of cancer
* primary cancers are more painful
* i.e. oral cancer = very painful; leukemia unlikely to be painful
* primary cancers are more painful
* i.e. oral cancer = very painful; leukemia unlikely to be painful
26
New cards
true or false: cancer pain metastasizes into bone
* true
* pain is always an issue with cancer patients
* the timeframe for when pain becomes an issue varies
* pain is always an issue with cancer patients
* the timeframe for when pain becomes an issue varies
27
New cards
breakthrough pain
sudden and brief flare-up of pain from chronic condition
28
New cards
how is cancer pain managed
* by 1 drug that managed to work well enough against average cancer pain
* 2nd drug administered to manage breakthrough pain
* 2nd drug administered to manage breakthrough pain
29
New cards
side effects of chemotherapeutics
* painful neuropathy (damage to the peripheral nerves)
* it is called chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy→ CIPN
* Pain becomes too much => chemotherapeutics have to be reduced
\*reminder\* higher dosage of chemotherapeutics = higher success in treating ppl’s cancers
* it is called chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy→ CIPN
* Pain becomes too much => chemotherapeutics have to be reduced
\*reminder\* higher dosage of chemotherapeutics = higher success in treating ppl’s cancers
30
New cards
what causes cancer pain?
multiple causes such as:
* inflammation from the immune system attacking the tumour
* tumour is pressing on nerves
* tumour is disrupting nearby tissue
* tumours release algogens
* inflammation from the immune system attacking the tumour
* tumour is pressing on nerves
* tumour is disrupting nearby tissue
* tumours release algogens
31
New cards
what is arthritis
chronic inflammatory pain that occurs in joints
32
New cards
describe a normal joint
* cartilage: cushion/shock absorber so that the bones don’t hit each other
* synovial fluid which is kept inside by the synovial membrane that keep the cartilage together
* synovial fluid which is kept inside by the synovial membrane that keep the cartilage together
33
New cards
2 types of arthritis
1. osteoarthritis (disease of old age)
2. rheumatoid arthritis (can occur in younger people)
34
New cards
osteoarthritis causes
* more common than rheumatoid arthritis
* disease of old age
* cartilage degrades and gets thinner causing bones to rub
OR
* synovial fluid leaks out of membrane causing bones to hit
* disease of old age
* cartilage degrades and gets thinner causing bones to rub
OR
* synovial fluid leaks out of membrane causing bones to hit
35
New cards
rheumatoid arthritis cause
* can occur in younger people
* autoimmune disease: immune system is attacking your own tissue
* leads to inflammation
* autoimmune disease: immune system is attacking your own tissue
* leads to inflammation
36
New cards
What leads to inflammation in RA?
1. ^^proteins such as macrophages and monocytes release TNF-a and interleukin-1 → cause tissue damage^^
1. these are cytokines that trigger the immune system response
2. TNF-alpha → inflammation
3. IL-1 is → cartilage and bone destruction + impeding cartilage repair
37
New cards
arthritis leads to
* pain
* disability
* severity of arthritis is not indicative of the amount of pain
* disability
* severity of arthritis is not indicative of the amount of pain
38
New cards
rheumatoid arthritis treatment
* monoclonal antibodies
39
New cards
how do monoclonal antibodies help RA?
* they are TNF-alpha blockers
* w/o TNF-alpha
* less tissue damage
* less inflammation
* w/o TNF-alpha
* less tissue damage
* less inflammation
40
New cards
examples of TNF-alpha blockers
* AKA monoclonal antibodies
* infliximab
* etanercept
* adalimumab
* certolizumab
* golimumab
* infliximab
* etanercept
* adalimumab
* certolizumab
* golimumab
41
New cards
why are monoclonal antibodies injected and not made into pills
* the molecules are too big to be made into pills
* allows physicians to see side effects while patient is being administered drugss
* allows physicians to see side effects while patient is being administered drugss
42
New cards
treatment for osteoarthritis
* NSAID
* opioids
* opioids
43
New cards
causes of chronic neuropathic pain
* nerve trauma
* iatrogenic nerve injury
* caused by the medical treatment itself (i.e. surgeon nicks a nerve while performing mastectomy)
* nerve compression
* parasitic, bacterial or viral infection
* inflammation (sterile)
* metabolic/ nutritional/ ischemic
* toxic
* ionizing radiation
* hereditary neuropathies
* autoimmune, idiopathic
* iatrogenic nerve injury
* caused by the medical treatment itself (i.e. surgeon nicks a nerve while performing mastectomy)
* nerve compression
* parasitic, bacterial or viral infection
* inflammation (sterile)
* metabolic/ nutritional/ ischemic
* toxic
* ionizing radiation
* hereditary neuropathies
* autoimmune, idiopathic
44
New cards
example of nerve trauma
* stump pain
* phantom limb
* CRPS2 (complex regional pain syndrome II) = causalgia: intense burning
* bone fractures
* penetrating injuries
\
* phantom limb
* CRPS2 (complex regional pain syndrome II) = causalgia: intense burning
* bone fractures
* penetrating injuries
\
45
New cards
examples of iatrogenic nerve injury (surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy)
* scar pain
* post-thoracotomy pain
* a surgical procedure in which a cut is made between the ribs to see and reach the lungs or other organs in the chest or thorax.
* ==post==-mastectomy pain
* accident intraneural injection
* vincristine (a chemotherapy drug) neuropathy
* post-thoracotomy pain
* a surgical procedure in which a cut is made between the ribs to see and reach the lungs or other organs in the chest or thorax.
* ==post==-mastectomy pain
* accident intraneural injection
* vincristine (a chemotherapy drug) neuropathy
46
New cards
examples of nerve compression due to entrapment
* carpal tunnel (occurs when nerves are compressed in wrist)
* ulnar nerve entrapment
* occurs when the ulnar nerve in the arm becomes compressed or irritated
* foraminal (lateral) stenosis
* Each of the 33 bones of the spine has a large central opening for the spinal cord. Additional openings called foramen, which can get clogged, allow the nerves branching from the spinal cord to travel to the arms, legs and other parts of the body.
* ulnar nerve entrapment
* occurs when the ulnar nerve in the arm becomes compressed or irritated
* foraminal (lateral) stenosis
* Each of the 33 bones of the spine has a large central opening for the spinal cord. Additional openings called foramen, which can get clogged, allow the nerves branching from the spinal cord to travel to the arms, legs and other parts of the body.
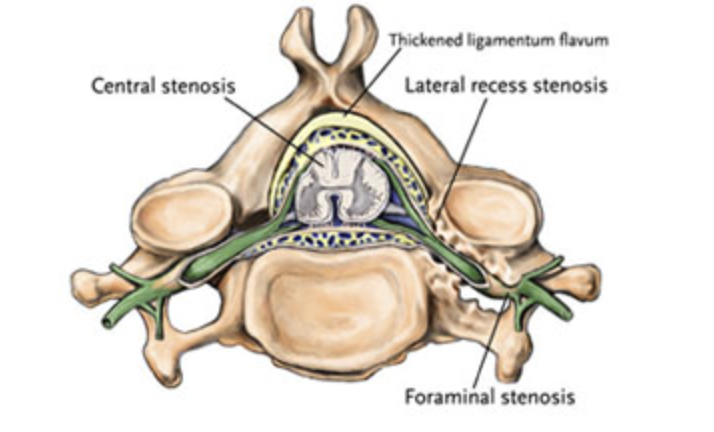
47
New cards
examples of compression due to tumor, artery, edema (swelling caused by too much fluid), herniated intravertebral disc
* cancer pain
* sciatica (pain, weakness, numbness, or tingling in the leg) caused by compression on sciatic nerve
* trigeminal neuralgia (type of chronic pain disorder that involves sudden, severe facial pain) caused by compression of the trigeminal nerve
* sciatica (pain, weakness, numbness, or tingling in the leg) caused by compression on sciatic nerve
* trigeminal neuralgia (type of chronic pain disorder that involves sudden, severe facial pain) caused by compression of the trigeminal nerve
48
New cards
examples of parasitic, bacterial or viral infection
* nerve abscess (hole)
* Hanson’s disease (leprosy) infection caused by slow-growing bacteria called Mycobacterium leprae
* tabes dorsalis caused by untreated syphilis infection
* postherpetic neuralgia
* HIV/Aids neuropathy
* Hanson’s disease (leprosy) infection caused by slow-growing bacteria called Mycobacterium leprae
* tabes dorsalis caused by untreated syphilis infection
* postherpetic neuralgia
* HIV/Aids neuropathy
49
New cards
examples of inflammation
* acute and chronic demyelinating neuropathy
* dorsal root ganglionitis
* tumor infiltration of nerves or innervated tissues
* dorsal root ganglionitis
* tumor infiltration of nerves or innervated tissues
50
New cards
examples of metabolic/nutrional/ischemic
* diabetic neuropathy
* sickle cell anemia
* occlusive/ischemic angiopathy
* alcoholic neuropathy
* vitamin deficiency
* sickle cell anemia
* occlusive/ischemic angiopathy
* alcoholic neuropathy
* vitamin deficiency
51
New cards
toxins
* lead
* mercury
* ethanol
* vincristine neuropathy
* other chemotherapeutics
* mercury
* ethanol
* vincristine neuropathy
* other chemotherapeutics
52
New cards
example of ionizing radiation
* radiation burns
* radiation therapy for cancer
* radiation therapy for cancer
53
New cards
examples of hereditary neuropathies
* some Marie-Carcot-Tooth neuropathies (group of disorders that cause damage to periphiral nerves)
* Fabry’s disease (a serious genetic disorder that can lead to life-threatening heart and kidney problems)
* Fabry’s disease (a serious genetic disorder that can lead to life-threatening heart and kidney problems)
54
New cards
examples of autoimmune, idiopathic
* Guillain-Barré
* small fiber
* small fiber
55
New cards
56
New cards
57
New cards
sensory deficits associated with neuropathic and nociceptive pain
* neuropathic pain: numbness, tingling, pricking
* nociceptive pain: uncommon to have sensory deficits
* nociceptive pain: uncommon to have sensory deficits
58
New cards
hypersensitivity in neuropathic vs nociceptive pain
* neuropathic pain: leads to allodynia (pain evoked by non-painful stimuli) or hyperalgesia (increased sensitivity to pain)
* nociceptive pain (pain to tissue): uncommon except for hypersensitivty surrounding area of acute injury
* nociceptive pain (pain to tissue): uncommon except for hypersensitivty surrounding area of acute injury
59
New cards
how does pain move in neuropathic vs nociceptive pain
* neuropathic pain: distal radiation (moving pain from center to the extremities)
* nociceptive pain: distal radiation less common
* nociceptive pain: distal radiation less common
60
New cards
paroxysms (a sudden attack) for neuropathic vs nociceptive pain
* neuropathic pain: worsening is common and unpredictable
* nociceptive pain: worsening is less common and associating with activity
* nociceptive pain: worsening is less common and associating with activity
61
New cards
autonomic signs (part of the nervous system that controls __muscles of internal organs__ such as the heart, blood vessels, lungs, stomach, and intestines; and __glands__ such as salivary glands and sweat glands) for nociceptive vs neuropathic pain
* neuropathic pain: color changes, temperature changes, swelling, sweating occur in 1/3 to 1/2 of patients
* nociceptive pain: uncommon
* nociceptive pain: uncommon
62
New cards
Painful diabetic neuropathy (PDN)/diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN)
nerve damage caused by untreated diabetes
63
New cards
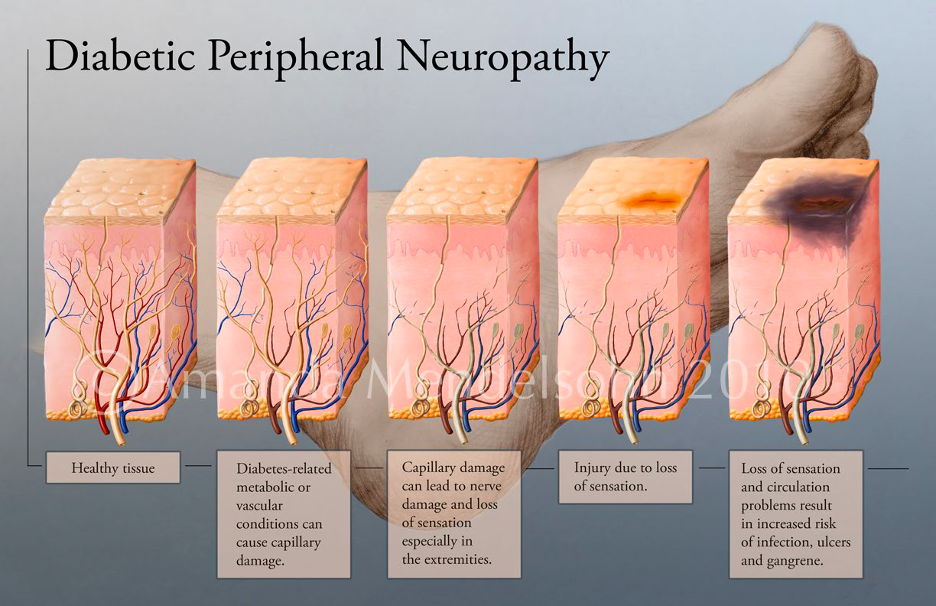
how does diabetic peripheral neuropathy damage tissue
* healthy tissue is damage due to capillary damage (no blood supply)
* leads to nerve damage
* leads to numbness + pain
* injury becomes more common (due to numbness and pain)
* injury can get infected which can lead to amputation
* leads to nerve damage
* leads to numbness + pain
* injury becomes more common (due to numbness and pain)
* injury can get infected which can lead to amputation
64
New cards
why is painful diabetic neuropathy worse in feet
* feet (most extremities) already get very low blood circulation
* the above is worsened with age
* this causes PDN to be more common in feet
* glove and stock distribution
* the above is worsened with age
* this causes PDN to be more common in feet
* glove and stock distribution
65
New cards
shingles
* caused by a complication after chicken pox infection (varicella virus)
* virus goes dormant in one of the dorsal root ganglia
* becomes active
* causes rash
* \
* virus goes dormant in one of the dorsal root ganglia
* becomes active
* causes rash
* \
66
New cards
post-herpetic neuralgia
* complication of shingles
* pain lasts long after the rash goes away
* pain lasts long after the rash goes away
67
New cards
phantom limb pain
* results after an amputation
* neuropathic pain syndrome
\
* neuropathic pain syndrome
\
68
New cards
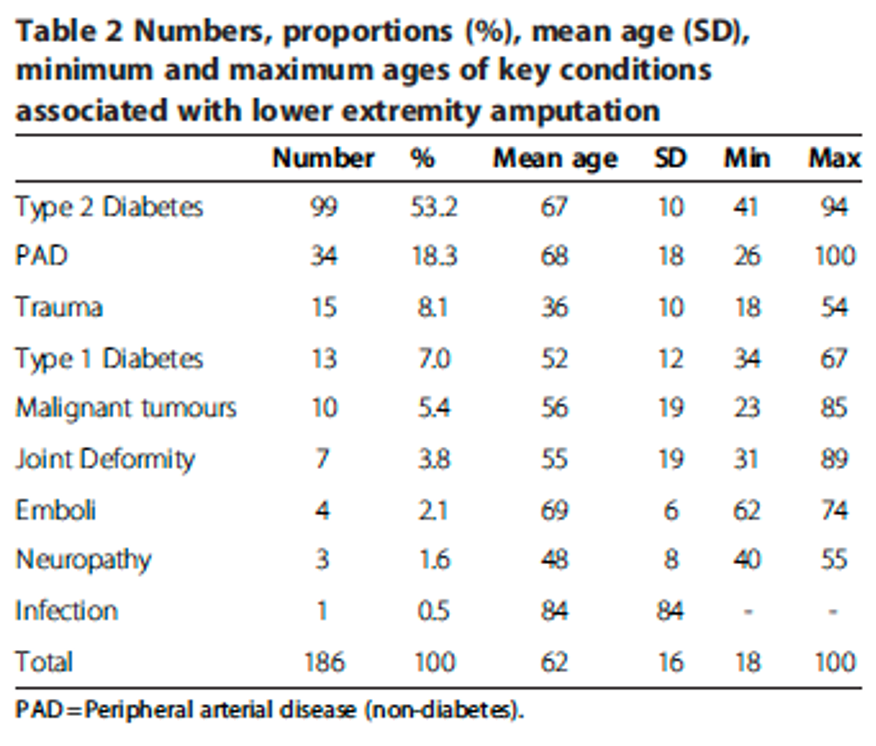
phantom limb pain (PLP)
* over 50% of amputations are caused by diabetes complications
* second cause of amputations = peripheral artery disease (PAD)
* amputation is not NECESSARY for PLP
* certain individuals born w/o limbs can also experience PLP
* second cause of amputations = peripheral artery disease (PAD)
* amputation is not NECESSARY for PLP
* certain individuals born w/o limbs can also experience PLP
69
New cards
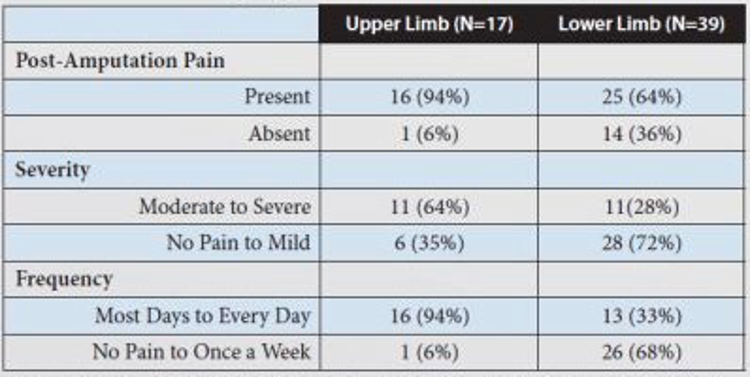
study by Davidson et al
* upper limb pain presents more serious pain, severity and frequency compared to lower limb pain
70
New cards
phantom limb symptoms
* shooting, stabbing, burning, cramping
* can also feel heat/cold
* can feel movement of phantom limb
* change of size
* can feel itch
* phenomenon of telescoping (feeling of limb retracting into body)
* phantom hand can’t be opened, stays clenched as a fist
* can also feel heat/cold
* can feel movement of phantom limb
* change of size
* can feel itch
* phenomenon of telescoping (feeling of limb retracting into body)
* phantom hand can’t be opened, stays clenched as a fist
71
New cards
referred pain
**pain** that's originating from a different location in your body is felt elsewhere.
72
New cards
causes of phantom limb pain
2 schools of thought, changes in the brain happening
1. central changes (brain + spinal cord)
2. peripheral changes (nerves that branch off from spinal cords to different parts of the body)
1. central changes (brain + spinal cord)
2. peripheral changes (nerves that branch off from spinal cords to different parts of the body)
73
New cards
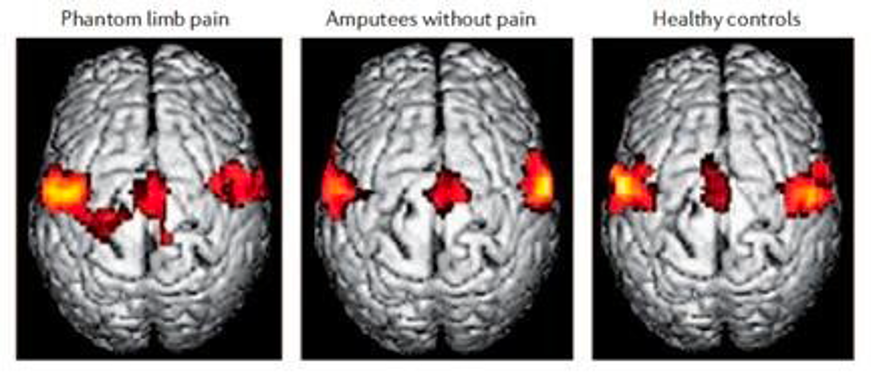
Cortical reorganization (changes happening centrally)
* people with PLP, area of the cortex that is responsible for amputated limb can take over the function of other body parts
* how was the above discovered?
* people with PLP pursed their lips and motor cortex area responsible for phantom limb lit up
* how was the above discovered?
* people with PLP pursed their lips and motor cortex area responsible for phantom limb lit up
74
New cards
PLP interventions (hypothesis for peripheral nervous system)
* lidocaine eliminated PLP in amputees suggesting that its primary driver is hyperexcitable afferent neurons rather than maladaptive cortical plasticity.
* mirror box theory
* mirror box theory
75
New cards
mirror box theory
* phantom limb pain reduced
* involves putting in functioning arm in a box that has a mirror
* mirror therefore, reflects the functioning arms movements
* supposedly provides relief to individuals with PLP
* tricks the brain because it gives the illusion that the amputated limb is not missing
* cannot be replicated => mirror therapy = ineffective
* involves putting in functioning arm in a box that has a mirror
* mirror therefore, reflects the functioning arms movements
* supposedly provides relief to individuals with PLP
* tricks the brain because it gives the illusion that the amputated limb is not missing
* cannot be replicated => mirror therapy = ineffective
76
New cards
how does lidocaine work
* prevents pain by blocking the signals at the nerve endings in the skin
77
New cards
Complex regional pain syndrome
2 types
1. CRPS I (RSD = reflex sympathetic dystrophy)
2. CRPS II (Causalgia)
1. CRPS I (RSD = reflex sympathetic dystrophy)
2. CRPS II (Causalgia)
78
New cards
CRPS I (RSD) characteristics
* pain is circumferential
* responds well to sympathetic blocks
* used to treat pain involving nerves from the sympathetic nervous system
* no response to nerve blocks
* thermal and mechanical allodynia
* ==allodynia==: pain due to a stimulus that normally doesn’t provoke pain
* leads to swelling, redness and change in skin temperature
* responds well to sympathetic blocks
* used to treat pain involving nerves from the sympathetic nervous system
* no response to nerve blocks
* thermal and mechanical allodynia
* ==allodynia==: pain due to a stimulus that normally doesn’t provoke pain
* leads to swelling, redness and change in skin temperature
79
New cards
CRPS II (causalgia)
* discrete nerve distribution
* since only 1 nerve is damaged
* variable response to sympathetic block
* responds well to nerve block
* mechanical allodynia
* since only 1 nerve is damaged
* variable response to sympathetic block
* responds well to nerve block
* mechanical allodynia
80
New cards
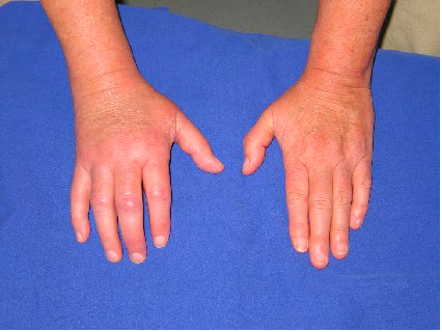
Which type of CRPS is this?
CRPS II - Causalgia
81
New cards
What are some possible causes of CRPS I?
* inflammation
* central sensitization
* cortical plasticity
* sympathetic processes
* psychological factors
* genetic predisposition
* peripheral sensitization
* central sensitization
* cortical plasticity
* sympathetic processes
* psychological factors
* genetic predisposition
* peripheral sensitization
82
New cards
fibromyalgia
* nociplastic disorder
* pain that arises from altered nociception
* no inflammation, no nerve damage, no tissue damage
\
* pain that arises from altered nociception
* no inflammation, no nerve damage, no tissue damage
\
83
New cards
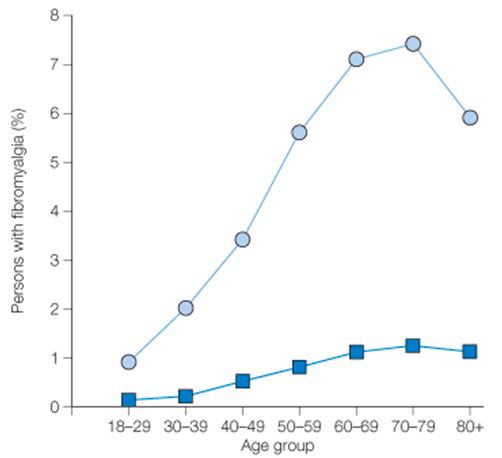
prevalence of fibromyalgia
* circles → women
* squares → men
* characterized by chronic widespread pain + fatigue
* affects 7% of women
* squares → men
* characterized by chronic widespread pain + fatigue
* affects 7% of women
84
New cards
fibromyalgia tender points
* rheumatologists would press on tender points
* if tender points hurt + fatigue => fibromyalgia
* how it was diagnosed previously
* if tender points hurt + fatigue => fibromyalgia
* how it was diagnosed previously
85
New cards
windup pain in patients with fibromyalgia
windup pain = phenomenon in which pain signal increases and fires more frequently
\
\
86
New cards
2 competing theories of windup pain in FS
1. increase in ascending transmission
1. The pathway that goes upward carrying sensory information from the body via the spinal cord towards the brain
2. too much info being carried to the brain
2. decrease in descending emission
1. the descending pathway inhibits pain
87
New cards
decreased conditioned pain modulation in fibromyalgia
* women with FMS have impaired conditioned pain modulation
* CPM = psychophysical assessment used to estimate the efficiency of an individual's central nervous system which reduces or augments pain
* CPM used as a predictive assessment for the development of chronic pain and responses to pain interventions
* CPM = psychophysical assessment used to estimate the efficiency of an individual's central nervous system which reduces or augments pain
* CPM used as a predictive assessment for the development of chronic pain and responses to pain interventions
88
New cards
through which test was it discovered that women with FMS have impaired conditioned pain modulation?
* through cold pressor test
* CPT → used for examining pain threshold and tolerance by subjects placing their forearm in an ice bath
* CPT → used for examining pain threshold and tolerance by subjects placing their forearm in an ice bath
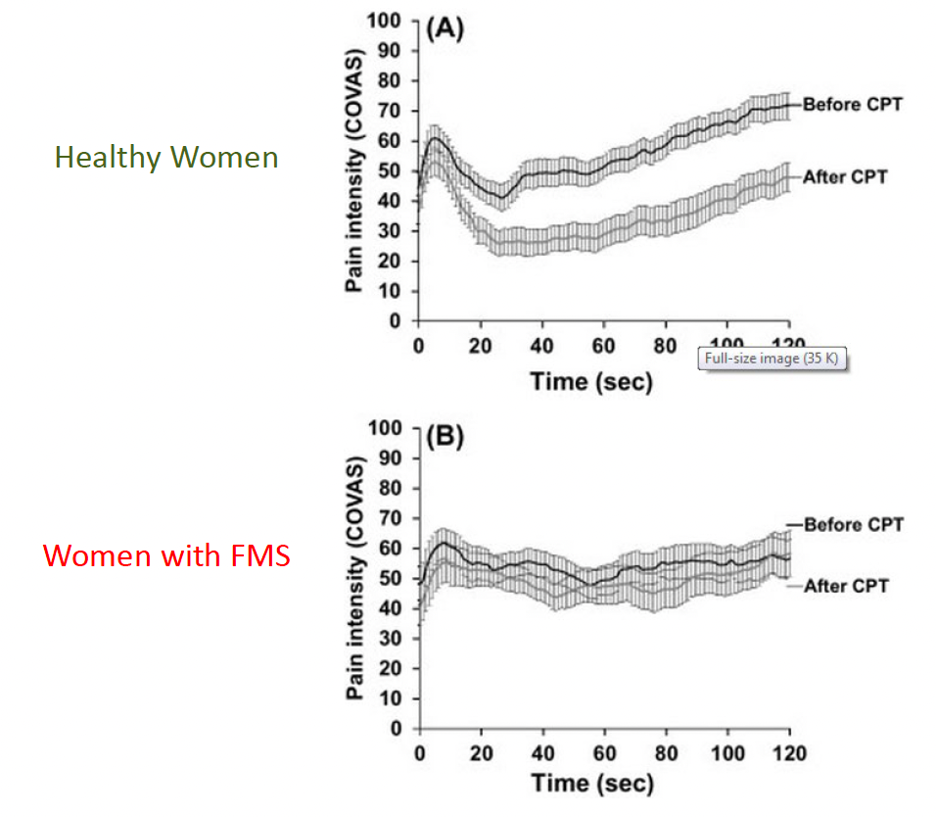
89
New cards
is fibromyalgia really small-fiber neuropathy?
* density of nociceptors nerve endings of those with FMS is less dense
* as if they have a neuropathy selectively affecting small fibers such as the nerve endings of the nociceptors
* as if they have a neuropathy selectively affecting small fibers such as the nerve endings of the nociceptors
90
New cards
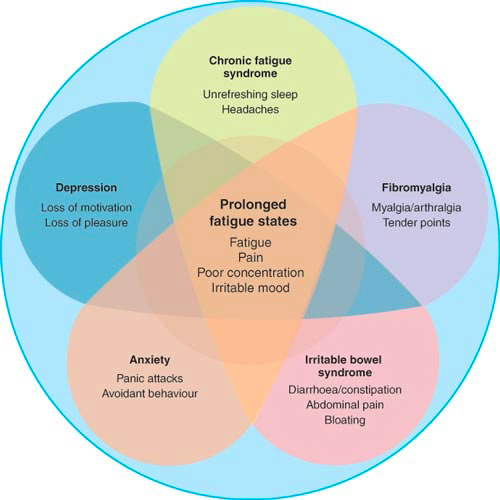
overlap between idiopathic pain conditions
\*reminder\* idiopathic = we don’t know
* idiopathic pain conditions share symptoms
* different presentation of the same thing
* idiopathic pain conditions share symptoms
* different presentation of the same thing
91
New cards
conditions comorbid with fibromyalgia
PEOPLE with FMS are more likely to get
* IBS
* TMJ
* anxiety
* osteoarthritis
* carpel tunnel
* etc.
* IBS
* TMJ
* anxiety
* osteoarthritis
* carpel tunnel
* etc.
92
New cards
pain location in idiopathic pain syndromes
2 studies
1. IBS
1. lower threshold to shoulder pressure
2. lower threshold to pressure to fingernails
3. lower heat pain threshold
why do they have lower sensitivity if they have IBS?
→ cause they also have FMS
1. vestibulodynia = allodynia of the vulvar vestibule
1. lower threshold to other place
conclusion: people with these conditions actually have widespread pain
1. IBS
1. lower threshold to shoulder pressure
2. lower threshold to pressure to fingernails
3. lower heat pain threshold
why do they have lower sensitivity if they have IBS?
→ cause they also have FMS
1. vestibulodynia = allodynia of the vulvar vestibule
1. lower threshold to other place
conclusion: people with these conditions actually have widespread pain
93
New cards
4 types of headaches
1. cluster → pain socket
2. sinus → pain in sinus cavity
3. tension → across forehead
4. migraine
94
New cards
characteristics of migraines
* pulsating
* more severe
* activity make it worse
* nausea
* vomit
* photophobia and phonobia = sensitivity to light and sound
* can be disabling because pain forces you to withdraw
* 4-72 hours
* more severe
* activity make it worse
* nausea
* vomit
* photophobia and phonobia = sensitivity to light and sound
* can be disabling because pain forces you to withdraw
* 4-72 hours
95
New cards
tension headaches
* pressing/tightening
* no aggravation due to physical activity
* no nausea or vomit
* no aggravation due to physical activity
* no nausea or vomit
96
New cards
4 stages of migraine
1. prodrome
1. happen before the actual migraine
2. photophobia or phonobia
3. few days before
2. aura
1. right before the migraine
2. an hour before
3. headache
4. post-drome
1. pain is gone
2. reminder that migraine occurred such as tender scalp, mood change
97
New cards
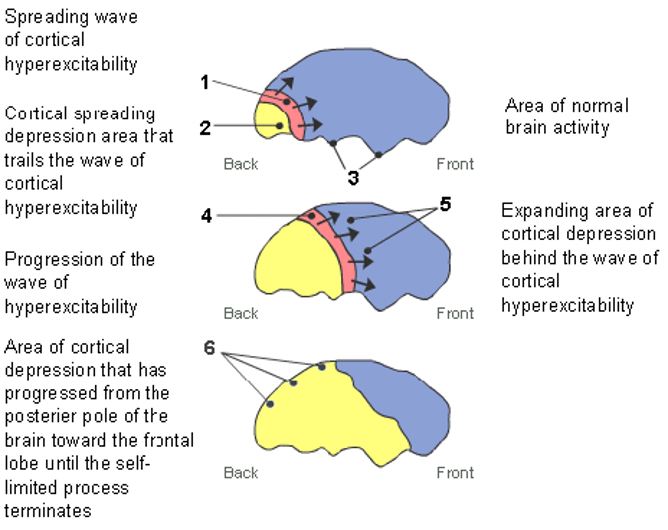
aura/cortical spreading depression
* wave of electrical excitability
* starts at the back of the brain where the occipital cortex is and waves forward
* neurons fire but then they get depressed and can’t fire
* starts at the back of the brain where the occipital cortex is and waves forward
* neurons fire but then they get depressed and can’t fire
98
New cards
cause of aura
cortical spreading depression
* experiement done where speed of aura matches the speed that CSD moves
* CSD might not actually cause the pain of migraine
* experiement done where speed of aura matches the speed that CSD moves
* CSD might not actually cause the pain of migraine
99
New cards
how mant migrainers are affected by aura?
20%
100
New cards
cause of migraine
1. vasodilation
2. neuronal