Varicella Zoster Virus Infections (Smarty PANCE)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus presents with multiple crops of lesions in various stages from vesicles to crusts?
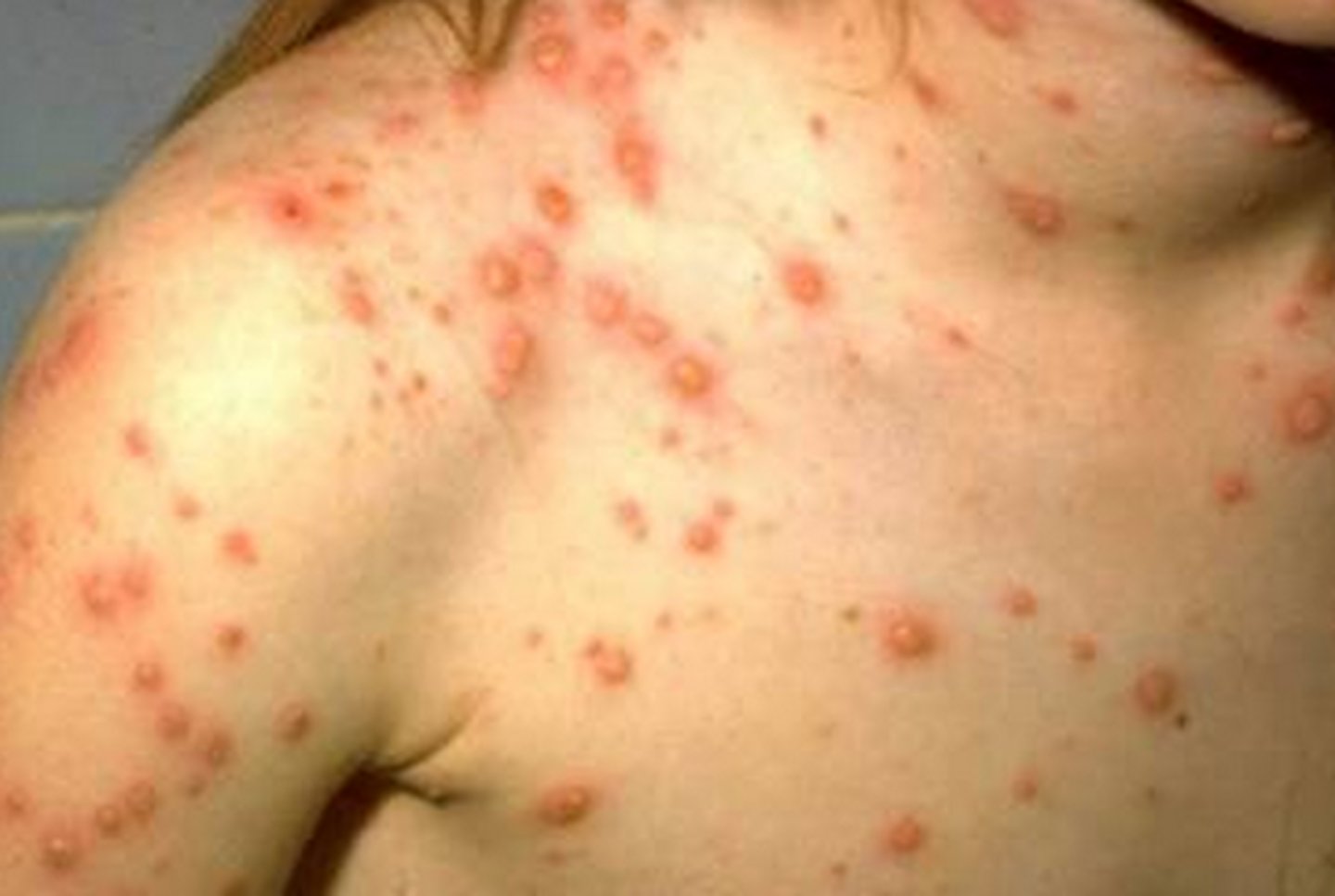
Varicella is a disease caused by the varicella zoster virus that presents with multiple crops of lesions in various stages from vesicles to crusts.
What is a disease caused by reactivation of the varicella zoster virus that usually presents with a rash in a very specific dermatomal distribution?
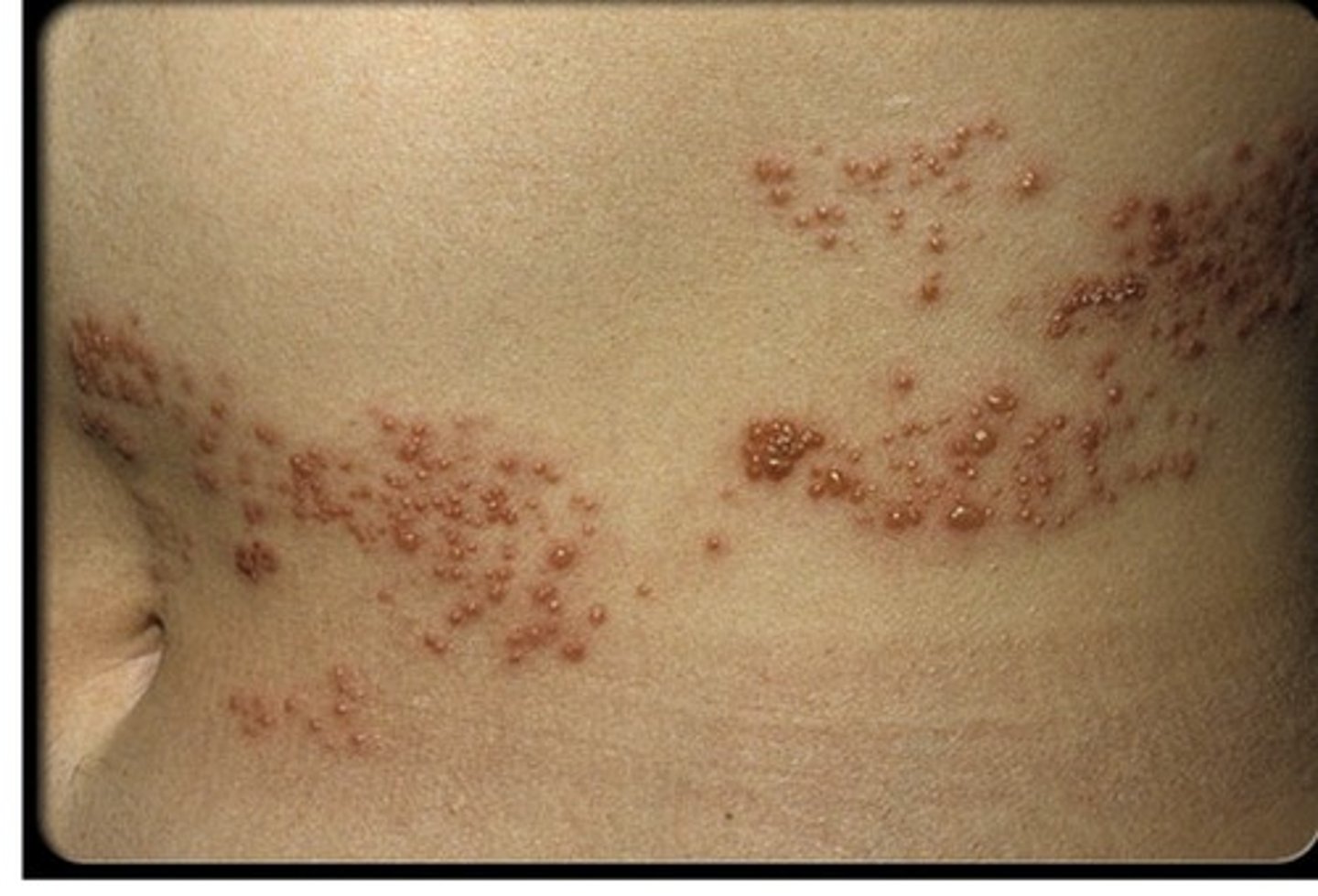
Herpes zoster is a disease caused by reactivation of the varicella zoster virus that usually presents with a rash in a very specific dermatomal distribution. Also known as shingles
What is a childhood hepatic encephalopathy associated with viral infection, especially varicella zoster virus and influenza B, that has been treated with aspirin.
Reye syndrome is a childhood hepatic encephalopathy associated with viral infection, especially varicella zoster virus and influenza B, that has been treated with aspirin.
Recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV, Shingrix) is recommended to prevent shingles in adults at what age?
Recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV, Shingrix) is recommended to prevent shingles in adults 50 years and older. It is administered in two doses 2-6 months apart.
What is the most common complication of shingles (from varicella zoster virus)?
Most common complication of shingles (from varicella zoster virus) is postherpetic neuralgia.
Pain in affected dermatome how many days = postherpetic neuralgia
Pain in affected dermatome > 90 days (3 months) = postherpetic neuralgia
Is the varicella vaccine live or killed?
The varicella vaccine used for routine immunization against varicella zoster virus is a live attenuated vaccine. Pregnant women should not get chickenpox vaccine. They should wait to get chickenpox vaccine until after they have given birth. Women should not get pregnant for 1 month after getting chickenpox vaccine.
When is the varicella vaccine given?
At 12-15 months and 4-6 years of age. (Same as MMR schedule). People 13 years of age and older who have never had chickenpox or never received chickenpox vaccine should get two doses, at least 28 days apart
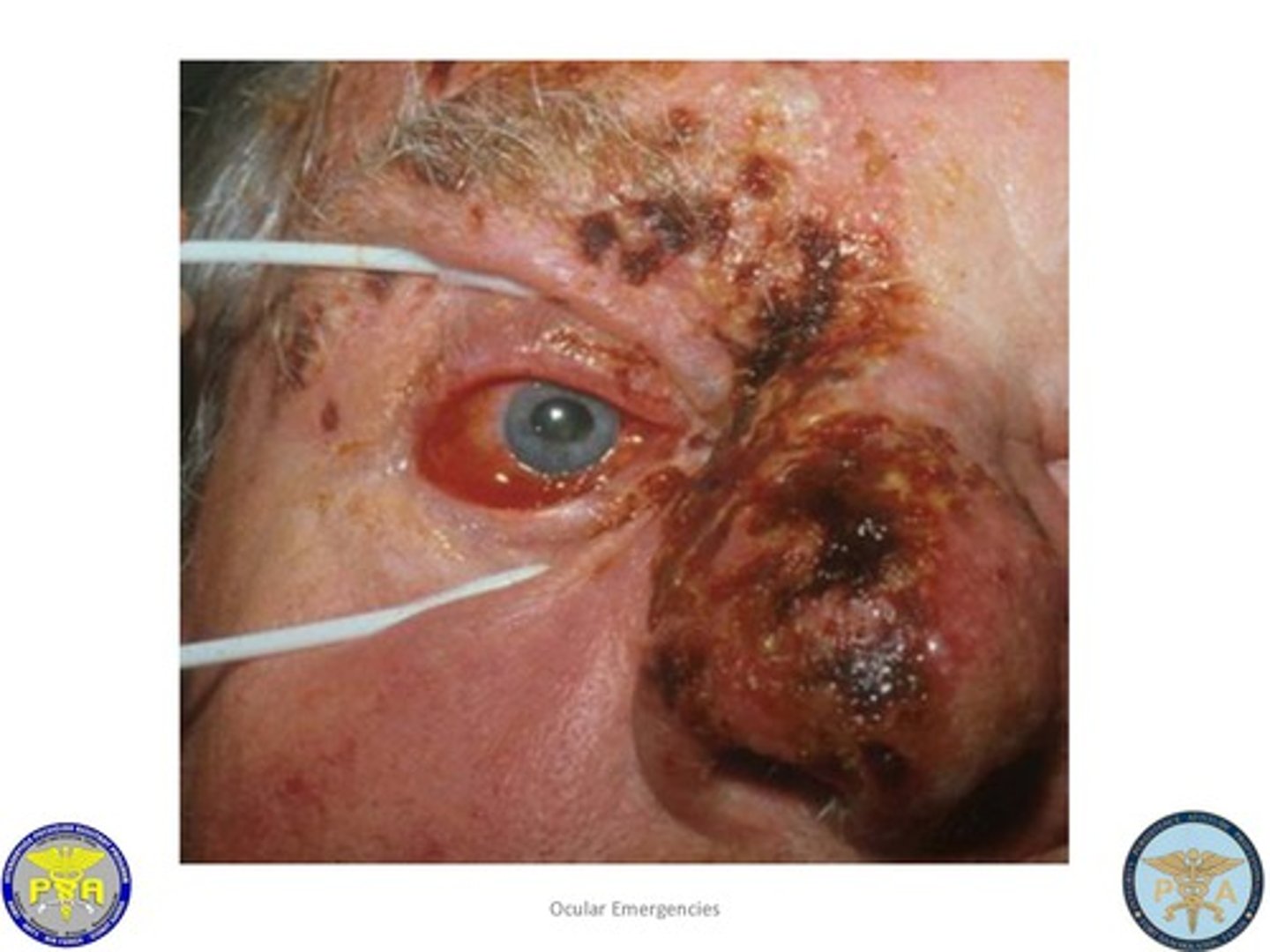
What cranial nerve branch involvement by varicella zoster virus infection can cause herpes zoster ophthalmicus?
Cranial nerve V1 branch involvement by varicella zoster virus infection can cause herpes zoster ophthalmicus.
Varicella zoster virus belongs to what family of viruses?
Varicella-zoster virus belongs to the human herpesvirus family of viruses (HHV-3)
What is the route of transmission of the varicella zoster virus.
Respiratory secretions are the route of transmission of the varicella zoster virus.
Varicella vaccine can be given to HIV patients who have a CD4+ cell count greater than what?
Varicella vaccine, which protects against varicella-zoster virus, is a live-attenuated vaccine that can be given to patients with HIV who have a CD4+ cell count greater than 200 cells/mm3.
Shingles involving CN V, dendritic lesions on slit lamp exam if keratoconjunctivitis is present
Zoster ophthalmicus
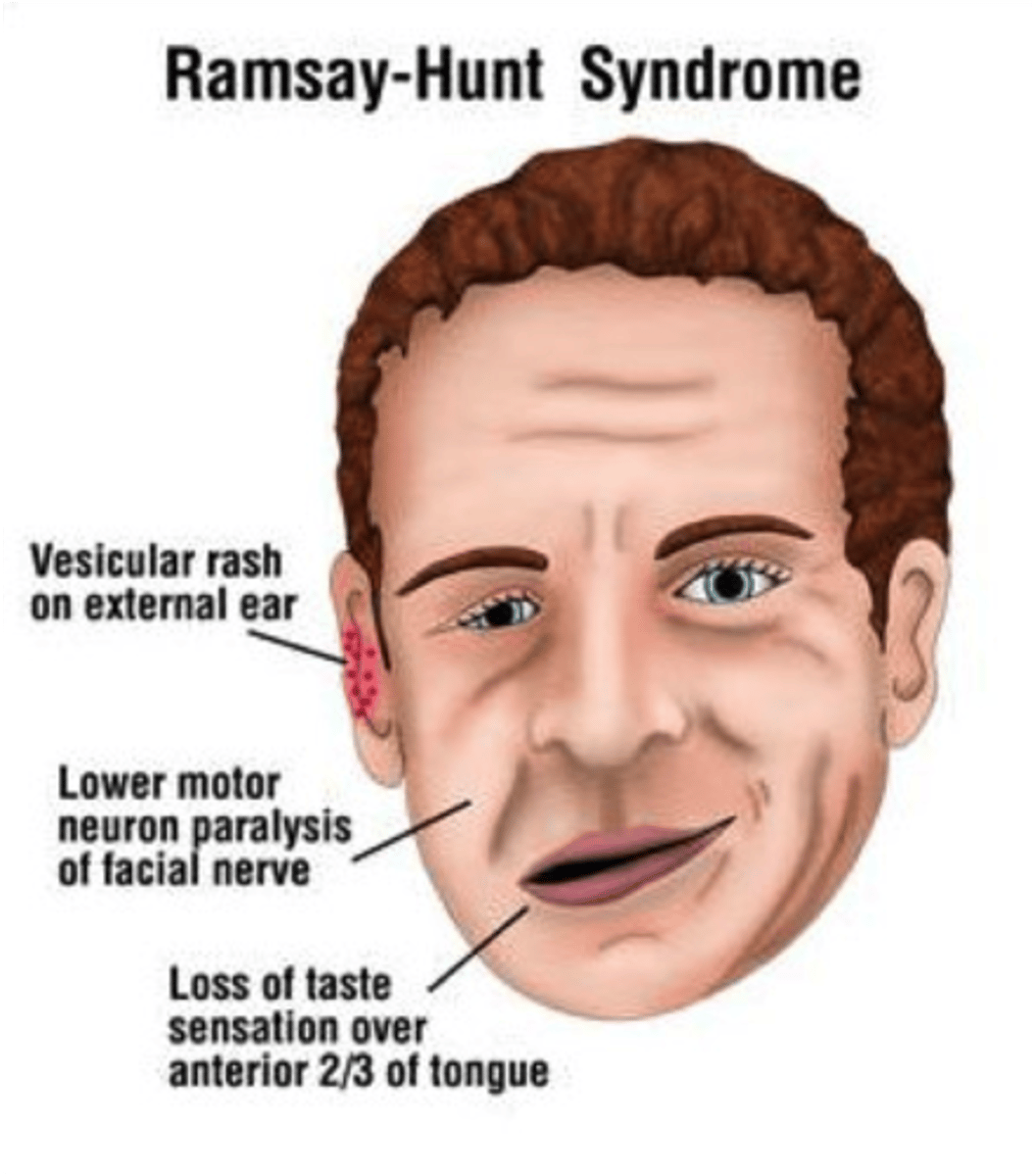
Herpes zoster virus infection of facial nerve (CN VIII) otalgia, lesions on the ear, auditory canal and TM, facial palsy auditory symptoms
Zoster Oticus (Ramsay-Hunt Syndrome)