MP3: Managing Offering-Based SCA
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is innovation in a marketing context
the creation of substantial new value for customers and the firm by creatively changing one or more dimensions of the business
captures both tangible products and intangible services
relatively easy for competitors to copy offerings
Key Aspects of Innovation
Broader than product of technology innovation
Must generate new value for customer and seller
Involves change leading to differentiation and SCA
How can firms innovate
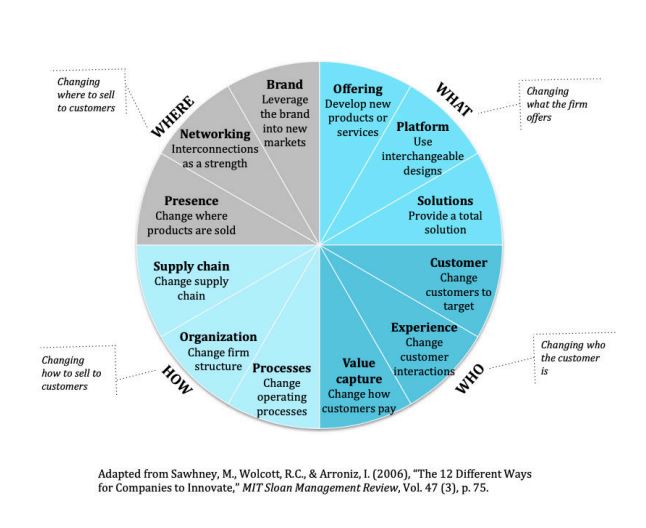
Change WHAT the firm offers
Change WHO the customer is
Change HOW you sell
Change WHERE you sell
Innovation Radar
captures different ways a firm can innovate and helps define the innovation space
What are the 2 main ways marketing supports innovation strategies
Launch new offerings to customer => generate sale with acceptable profit levels → Many good products fail to achieve financial goal due to poor launches
Develop innovative offerings by collecting customer input and forecasting trends → Extensive efforts go into test marketing and understanding the factors that will influence customers to adopt the new offering
why 75% product launches fail
Lack of perceived benefit
No differential advantage
Price vs performance mismatch
Poor launch execution
Poor positioning of new product
Competitive response
Give an example of a failed innovation and why it failed
Kellogg’s Breakfast Mates failed because parents didn’t want their children eating breakfast in the car, despite being a “solution for harried parents
What’s the difference between Sustaining and Disruptive Innovation
Sustaining Innovation: Improves performance of existing products incrementally (lower risk). → market leaders often win
Disruptive Innovation: Offers a new value proposition, often with worse short-term performance, but cheaper, smaller, simpler, and grows over time → market entrants usually win
Why do market leaders struggle with disruptive innovation
Can lose their leadership position due to failing to manage disruptive innovatioin
Bias toward larger markets
Difficulty in quantifying new markets
Oversupplying features beyond customer needs
What’s a Red Ocean Strategy
Competes in existing markets, with known rules, incremental innovations. Often account for the majority of sales but low profits and high rivalry. (close to shore where sharks fight → red)
Can be managed, tested and analysed
What’s a Blue Ocean Strategy
Creates new market space and demand with less competition, higher profits level , and disruptive positioning.
Less competitive rivalry, transforms the image of competitor’s brand features such that they become a negative attribute in the new market.
Hard to test, often requires intuition, high risk
Blue Ocean initiatives characteristic
Don’t use competitors as the benchmark
Reject trade-off value vs cost
Redefines value proposition
Often the first mover develops barrier to imitation
Drivers of Adoption
People (adoption lifecycle)
Psychology (social proof, authority, scarcity, prospect theory)
Products (relative advantage, compatibility, complexity, trialability, observability)
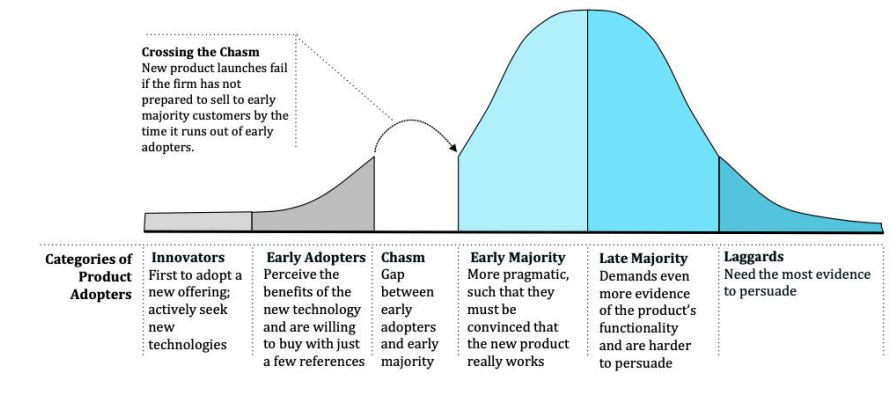
5 adopter categories in the innovation lifecycle
Innovators
Early adopters
→ Crossing the chasm: new products fail if the firm not prepared to sell early majority
Early majority
Late majority
Laggards
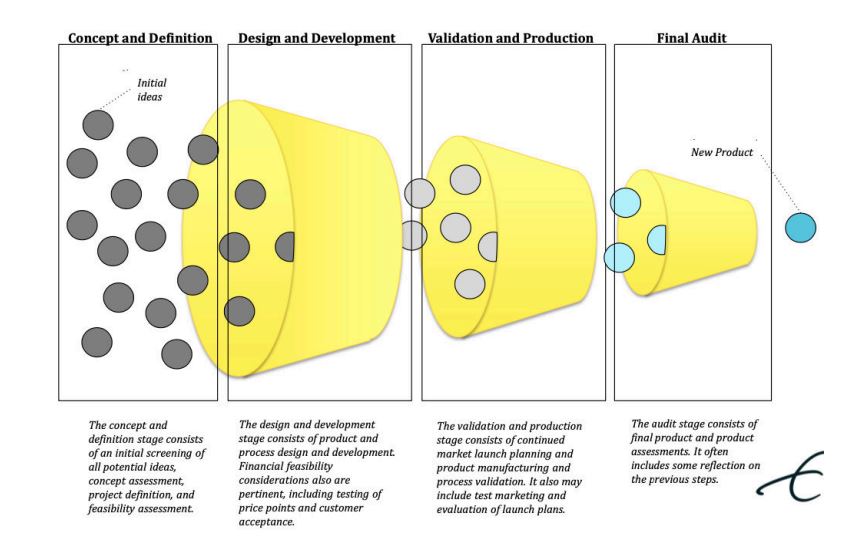
What is the Stage-Gate Design Review Process
A product development process that divides innovation into phases, with evaluations at each stage to ensure effectiveness.
Concept & definition (initial ideas) → Design & development → validation & production → final audit → new product
What is Conjoint Analysis used for
To understand customer value by modeling how they trade off attributes, and to predict preferences, WTP, and market share &impact of a proposed new product
What are the two main stages of Conjoint Analysis
Design: Define attributes/levels, choose profile sets
Analysis: Use regression to estimate part-worth utilities
How do you calculate WTP, attribute importance
part-worth difference*value of one unit
Importance = Attribute utility range / Sum of all attribute ranges