Intro to thermodynamics and kinetics
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is internal energy
The total of the contributions of all the energies. It is impossible to calculate precisely due to the immense number of interactions occurring in a molecule. Energy is hence described in terms of energy changes - i.e. enthalpy is measured as ∆H not just H
Kinetic theory of gases
Gas consists of molecules with mass m and diameter d in constant random motion.
The molecules’ sizes are negligible compared to the distances they move
There are no interactions between molecules besides perfectly elastic collisions
What is temperature
A measure of the amount of energy the particles in a material have
In a gas this is translational, in a solid it is vibrational
Although the velocity of a particle may change due to collisions, the conservation of energy means that the distribution of velocities of all the gas particles is conserved at a given temperature.
What is heat
It is related to temperature. It is a form of energy that can flow between two objects with different temperatures. Heat will flow from the object with the higher temperature to the lower temperature
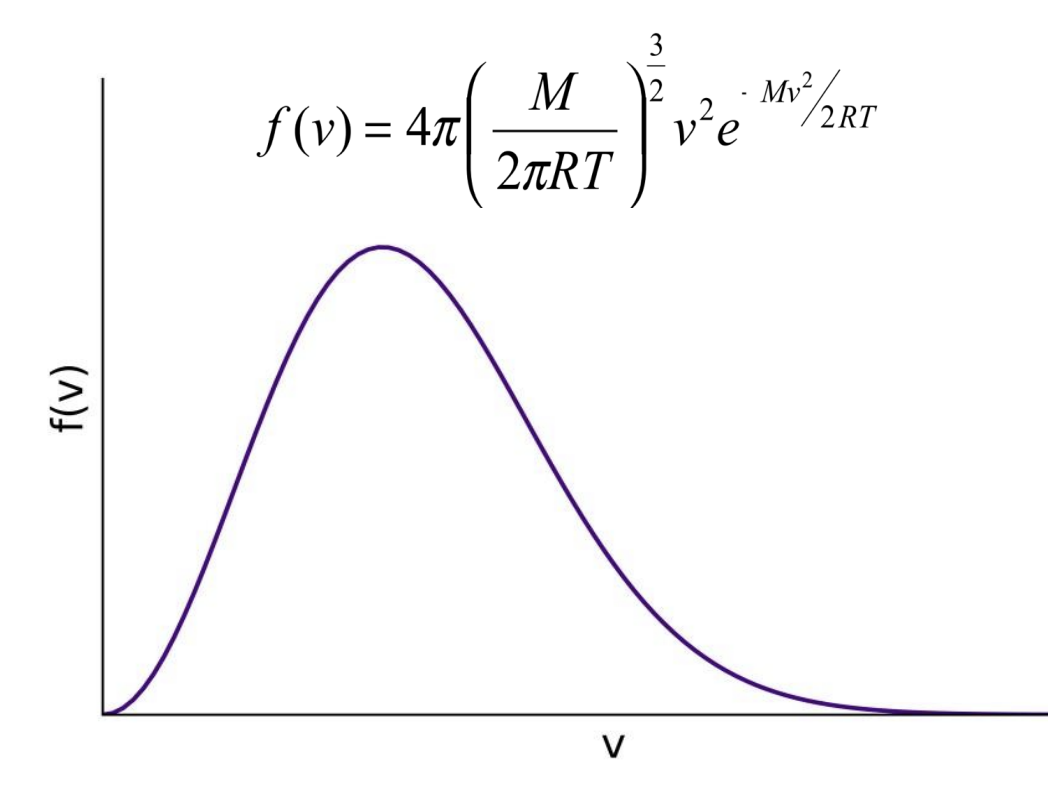
How is the speed of molecules in a gaseous system distributed
Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution of speeds. The area corresponds to the number of molecules.
(don’t need to remember the equation)
Work
A form of energy. Mechanical work is done when a force moves through a distance.
Work = Force x distance (w = Fd)
distance needs to be in the same direction as force
Work done compressing a gas

Bimolecular vs unimolecular reaction

3 types of system

What restrictions can you put on a closed system
Isobaric - constant pressure
Isothermal - constant temperature
Isochoric - constant volume
Adiabatic - No heat flows between system and surroundings
Letter for internal energy
and heat energy
U
q
Is doing work a positive or negative work energy exchange (w)
Negative.
The work energy change is the change in potential to do work.
What can ∆U be simplified to
∆U = q + w
Reversible processes key concepts

What does dU mean
and d bar
A very small change in internal energy

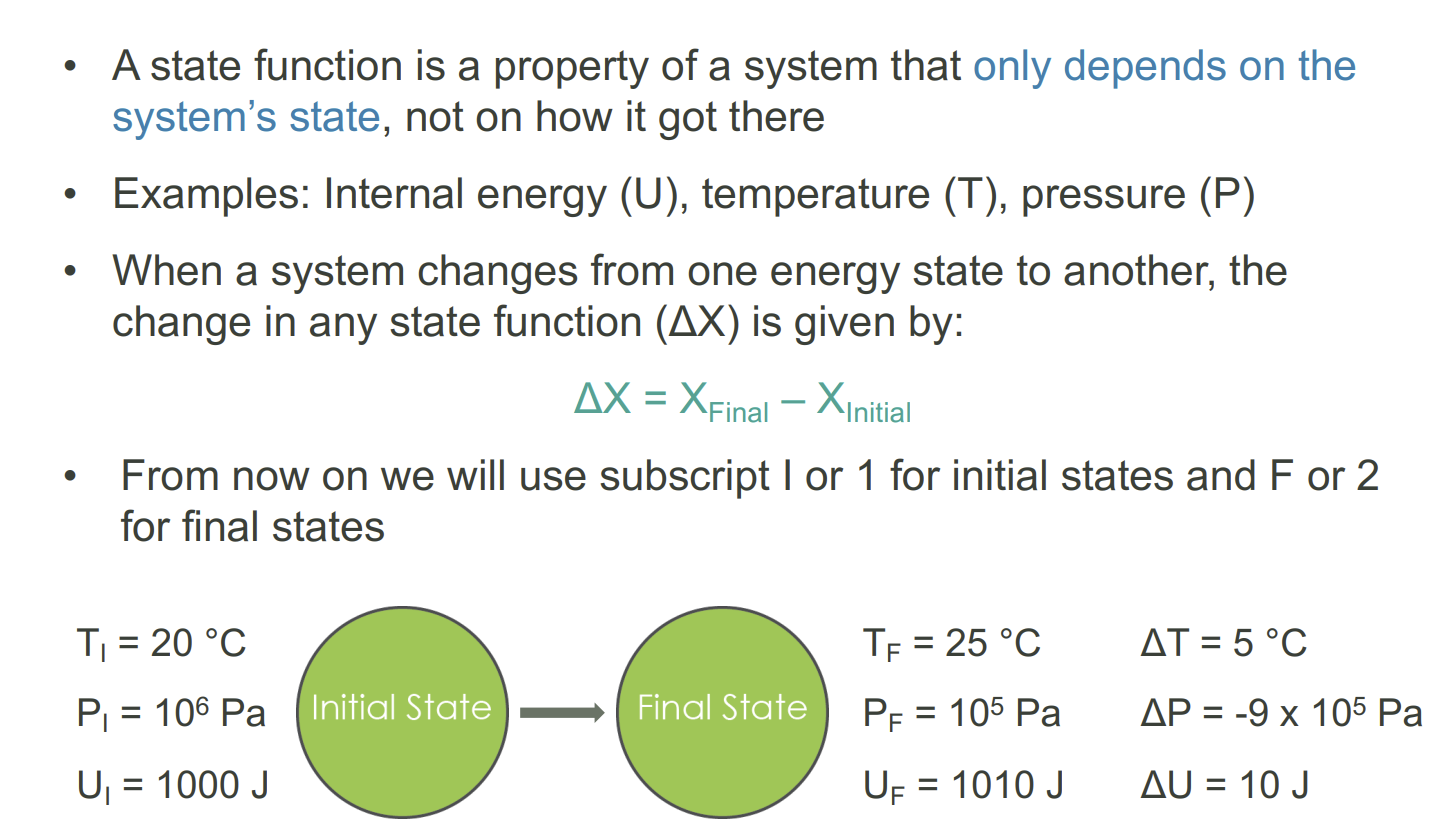
What is a state function
Can be determined from an instantaneous snapshot of a system.
It does not matter what the initial energetic state was or where the state is going
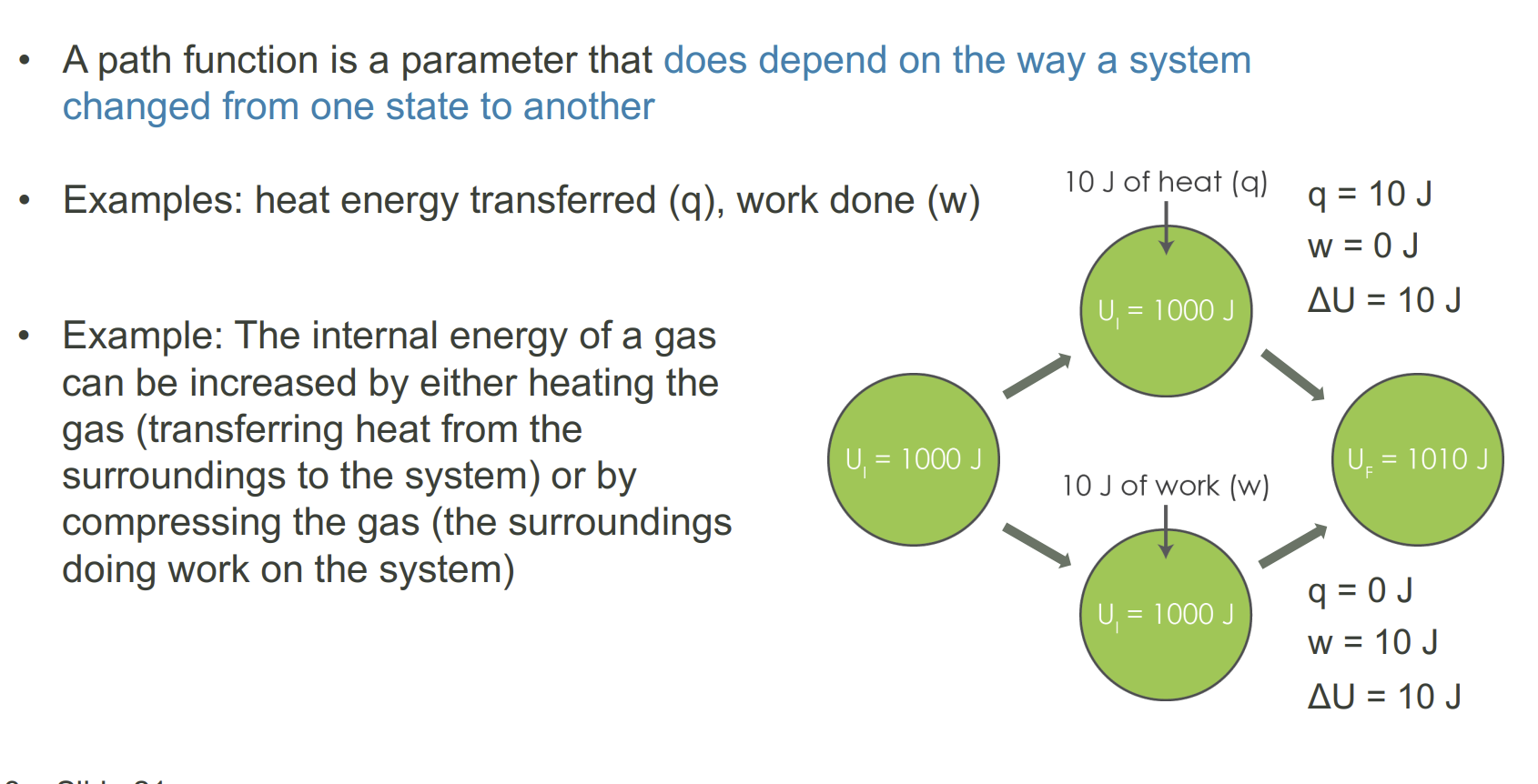
What is a path function
A parameter tied to a process - heat and work. These are flows of energy and not intrinsic properties of a system so cannot be instantaneously measured.