Section 25 - Semen Analysis
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Instruct a patient in the correct method for collecting a semen specimen
Instructions:
Abstain from ejaculation for 2–7 days before collection.
Avoid using lubricants or regular condoms (use only medically approved non-toxic condoms if needed).
Collect the entire specimen in a provided sterile container.
Keep the specimen at 20–37°C and deliver it to the lab within 1 hour
List the procedure included in semen analysis
Macroscopic Analysis: Liquefaction, appearance, volume, viscosity, and pH.
Microscopic Analysis: Sperm count, motility, morphology, and viability.
Other Tests: Round cell count, sperm agglutination, and post-vasectomy verification.
Describe the method used to evaluate sperm motility
Method:
Use a wet mount at 400× magnification.
Assess motility categories:
Rapid progressive: ≥25 µm/s.
Slow progressive: 5–25 µm/s.
Non-progressive: <5 µm/s.
Immotile: No movement.
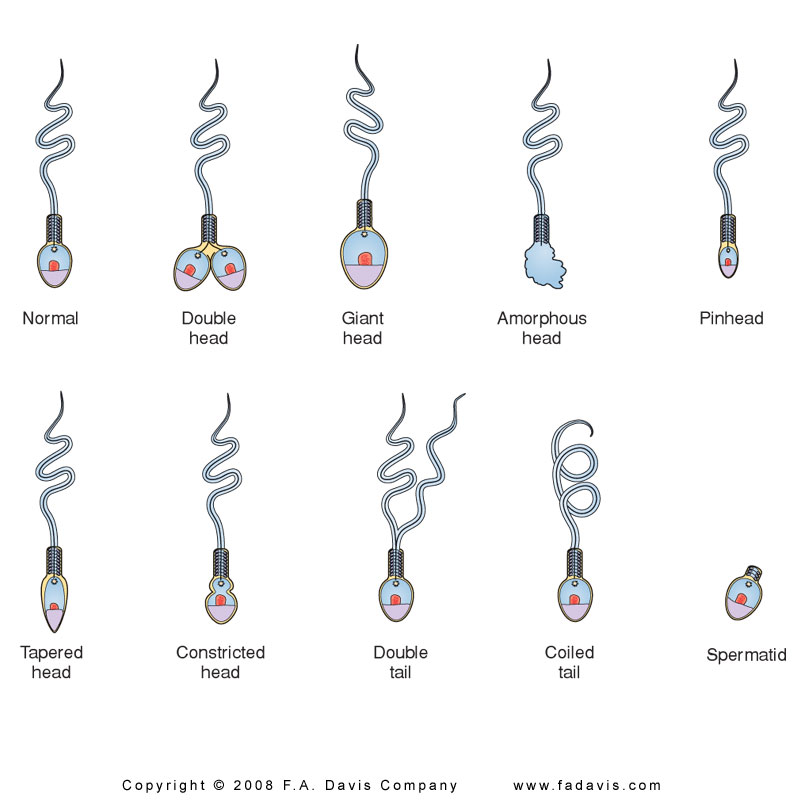
Describe abnormal Sperm morphology
Abnormal Forms:
Heads: Double, round, pinhead, tapered, constricted.
Midpiece: Distended, thin.
Tails: Short, coiled, multiple, broken.
List methods for identifying a questionable fluid as semen.
Detect acid phosphatase activity.
Identify spermatozoa microscopically.
Rape cases – better to test for acid phosphatase than presence of sperm
Only body fluid with high levels of acid phos
Detection of seminal plasma glycoprotein, p30
DNA analysis
Reference Values for Semen Analysis
Volume and Viscosity:
Normal: 2 – 5 mL
pH:
7.2–8.0
Sperm Count
>40 million per ejaculate (20 million/ mL x 2 mL)
Sperm Motility
Need to have sperm with forward, progressive movement
Examine within 1 hour; evaluate undiluted on glass slide with cover slip
Estimate percentage with progressive, forward motion in 20 fields
0 to 4
4: rapid straight line motility
3: slower speed, some lateral movement
2: slow forward movement, more lateral
1: no forward progression
0: no movement
Normal: 50%; rated as 2
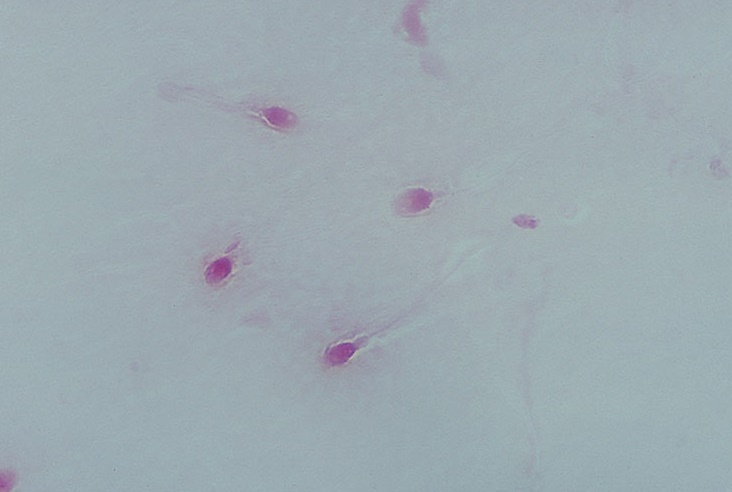
Sperm Viability
Dead cells stain red; normal are blue-white
Count number/100 cells
Normal: 75% living
Postvasectomy Analysis
Only concern is presence of sperm
Takes several months for all sperm to be gone, based on time and ejaculations
Begin in 2 months; continue until 2 months are negative
Wet preparation under phase; if negative, centrifuge for 10 minutes, examine again
Routine Laboratory Analysis
Viscosity - highly viscous, liquefies in 60 min
Color - opaque white - grayish white
Volume - 3.5 mL (range 1.5 - 5.0 mL)
pH = 7.2 - 8.0
Turbidity - somewhat turbid, increased with elevated WBC
Fructose – 315 mg/dL
Microscopic Exam
Sperm concentration > 20 million/ mL
Sperm count >40 million/ejaculate
Motility > 50% within 1 hour
Morphology
Normal criteria: >30% normal Strict criteria: > 14% normal
Seminal Fluid
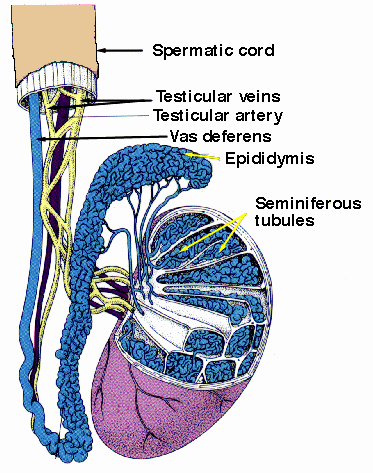
•Sperm are produced in the seminiferous tubules.
•During their passage through the epidiymis, the sperm will continue to mature and develop.
•Fluid is added to the sperm in the vas deferens.
•During a vasectomy, the vas deferens is cut to block the escape of sperm into the ejaculate
Appearance of Sperm Specimen
Normal = gray-white, translucent
White turbidity = infection: culture
Red = blood cells, abnormal
Yellow = urine, prolonged abstinence, medications
Urine is toxic to sperm: no motility
Clots remaining after 1 hour: wait for liquefaction before analyzing
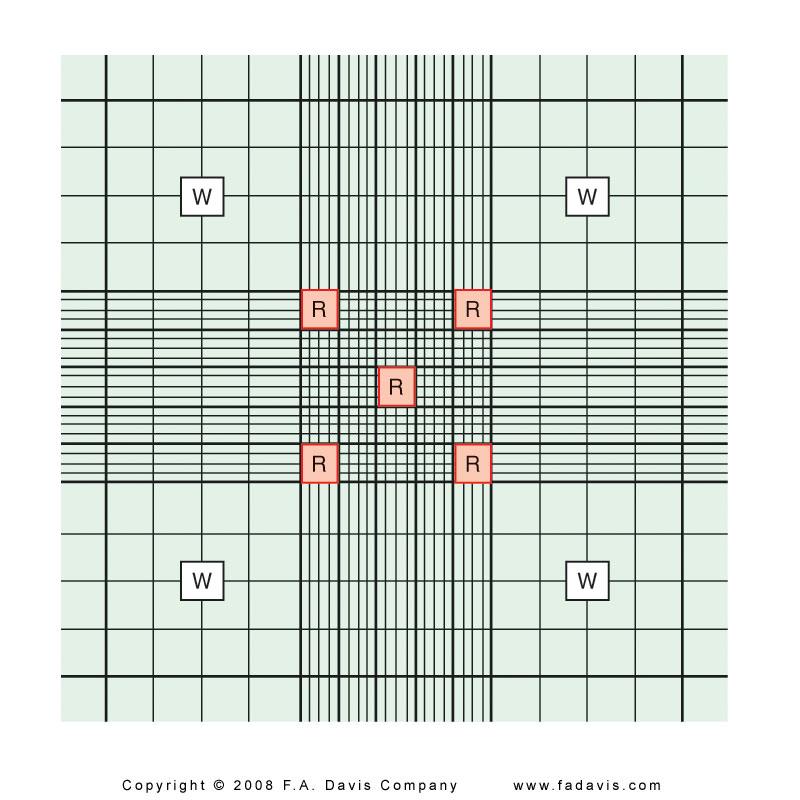
Sperm Concentration
Number sperm/mL
Normal
> 20 million/ mL
20-250 million/mL
10-20 million borderline
Automated or Neubauer chamber,
same as RBC - 5 20squares
Dilution: 1 to 20
Count both sides of chamber, sides must agree within 10%; use the average
Appearance of clumped sperm may indicate anti-sperm antibodies