AP Psychology Unit 1 Biological Bases of Behavior - Elrod
1/166
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AP Psychology Elrod Unit 2 Test Study Guide
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
167 Terms
Nature vs. Nurture
Evolutionary Perspective
Central Nervous System
Brain and Spinal cord
Carries messages to the brain
Sends messages from the brain
Pheripheral Nervous System
Nerves not encased in bone
divided into somatic and autonomic
Somatic Nervous System
Controls voluntary muscle movements
recieves messages from motor cortex
Autonomic Nervous System
controls automatic functions of the body (heart, lungs, organs, glands, etc.)
controls our response to stress
divided into 2 (sympathetic and parasympathetic)
Sympathetic Nervous System
Fight or Flight or Freeze Response
mobilizes our body to respond to stress
accelerates some functions but conserves resources needed for a quick response by slowing down some functions
speeds up: heart rate & breathing
dilates: pupils
Slows down: digestion
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Responsible for slowing down our body after a stress response
Homeostasis
The brake pedal that slows down the body’s autonomics nervous system
slows down: breathing, heart rate
constricts: pupils
speeds up: digestion
Reflexes
information is controlled by the spine & does not require the brain to respond
Work differently from the normal nervous system transmission
Brain (matching)
Responsible for transmitting information throughout the body
Central Nervous System (matching)
Responsible for cognitive functioning
Spinal Cord (matching)
Responsible for sending messages to and from the brain
Pheripheral Nervous System (matching)
Responsible for all nervous system functions outside of the brain and spinal cord
Somatic Nervous System (matching)
Responsible for voluntary movement
Autonomic Nervous System (matching)
Regulates heart rate, breathing, digestion, etc.
Sympathetic Nervous System (matching)
spends reserved energy
Parasympathetic Nervous System (matching)
Restores & repairs spent energy
Neurotransmitters
determine what type of signal is being sent
Synapse
space between neurons where neurotransmitters travel through via, receptor sites
Dendrites
where signals are recieved
Neurons
Carry messages using electrical impulses
Glial Cells
Provide physical & chemical support of neurons
Types of Neurons
Afferent (Sensory)
Interneurons
Efferent (Motor)
Afferent (Sensory) Neurons
take infro from the senses and outside world to the brain
Part of PNS
Interneurons
Once information comes from the senses, takes info to different parts of the body
Part of CNS
Efferent Neurons
Take information from the CNS to muscles
Part of PNS
Mnemonic device for Neurons
Think SA/ME (Sensory=Afferent/Motor=Efferent)
Neural Firing
Electrochemical Process
Electrical inside the neuron
chemical outside the neuron (neurotransmitters)
Resting Potential
When a neuron is “charged” but waiting for the next action potential
Threshold
the minimum level of stimulation needed to activate a neuron and create an action potential
Action Potential
All or nothing process
when a neuron sends information down an axon, away from the cell body
Refractory Period
If a neuron fires, it has to go through a resting period before it can fire again
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that move between neurons
Types of Neurotransmitters
Excitatory
Inhibitory
Excitatory Neurotransmitters
make it more likely the next neuron will fire
chemical secreted at terminal button that causes the neuron on the other side of the synapse to generate an action potential (to fire)
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
make it less likely the next neuron will fire
chemical secreted at terminal button that reduces or prevents neural impulses in the postsynaptic neuron
Hormones
can act similarly to neurotransmitters
Types of Outside Influence (Nurture) on Neural Firing
Agonists
Antagonists
Agonists
Blocks re-uptake/excites (SSRIs)
stimulants
Antagonists
Blocks release/inhibits next neuron from firing
pain reliever
depressants
hallucinogens
Divisions of the Brain (vertical-top to bottom)
Forebrain
Midbrain
Hindbrain
Divsions of the Brain (lateral)
Connected by Corpus Collosum
Left Hemisphere
Right Hemisphere
Lateralization
Specialization
Higher up in the the vertical ordering in the brain
= higher function (typically)
Functions controlled by Left Hemisphere
Verbal Memory
Speech
Rational Symbolic Thought
Superior Language Comprehensions
Feeling shapes with right hand
Right hand motor control
Hearing vocal sounds
Vision (right field)
Functions controlled by Right Hemisphere
Musical Ability
Hearing Non-Vocal Sounds
Limited language comprehension
Memory for shapes
Left hand motor control
Feeling shapes with left hand
Intuitive, non-verbal thought
Superior recognition of faces & spatial relationships
Lobes of the Cerebral Cortex
Frontal
Temporal
Parietal
Occipital
Methods of Studying the Brain
Accidents (Case Studies)
Lesions (Lobotomies)
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
Functional MRI
Electroencephalogram
Detects and Investigates brainwaves & consciousness
Functional MRI
Allows us to see the structure of the brain & what parts are active
Split Brain Research (Gazzaniga & Sperry Study)
patients had severed corpus collosum
depending on which side of the brain the word was flashed on, the patient responds by saying or drawing it
Because the 2 sides of the brain aren’t connected or able to work together, the responses are isolated by side (ex. can draw the word but can’t say it)
Brain Plasticity
Developing Neural pathways/networks
Strengthening/weakening neural connections
Lateralization and specialization can change
Depends on age
Sleep
State of consciousness (just less aware)
Part of the natural circadian rhythm
Circadian Rhythm
Awake & sleep cycle
Body naturally changes with the rhythm
Hormones (melatonin) and brain waves
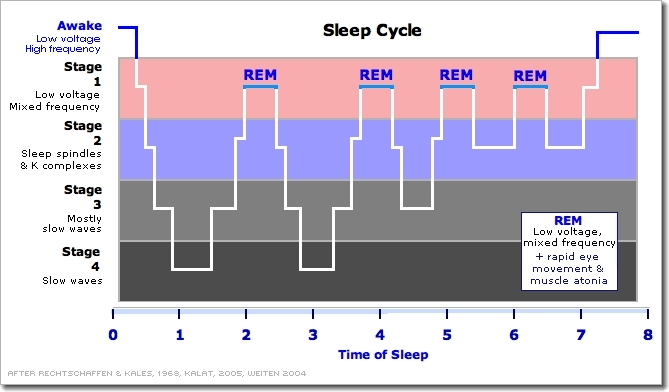
Stages of Sleep
Awake
Awake and Relaxed
Stage 1 (N1)
Stage 2 (N2)
Stages 3 & 4 (N3)
REM Sleep
Awake
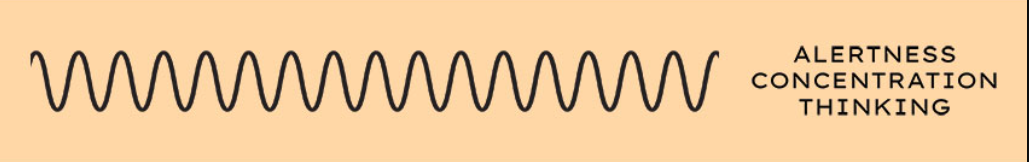
Beta waves
Awake & Relaxed
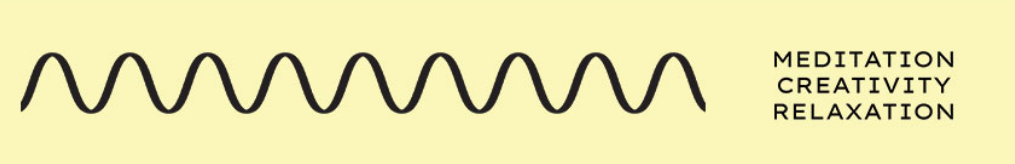
Alpha waves
Stage 1 (N1) - Between Awake & Asleep
Only occurs once
Theta waves
Hypnogogic sleep
Stage 2 (N2)
Theta waves but slower
Sleep spindles & k-complexes
Possibly important for memory consolidation (not 100% sure)
Stages 3 & 4 (N3)
Deepest sleep
Delta waves
Important for physical & hormonal health
REM Sleep
Most Conscious
Most likely to remember dreams
Sleep & Dreams
Dream in different stages
Most likely to remember dreams in REM sleep
Theories of Dreams
Activation-Synthesis theory
Consolidation theory
Activation-Synthesis Theory
Dreams caused by random neural firing
Cerebral cortex tries to make sense of it
Biological theory
explained by biological processes (no real meaning)
Information Processing/Consolidation Theory
Brain is processing information from the day
Information is moved to memory
This neural activity causes dreams
A cognition explanation
How do we know sleep is important?
We sleep
Health problems associated with lack of sleep
How do we know dreams are important?
We dream
REM Rebound
Sleep Cycle Chart
Beta Waves (Image matching)
Theta Waves (Image matching)

Alpha Waves (Image matching)
Delta Waves (Image matching)

Common Sleep Disorders
They interrupt sleep or are symptoms of dysregulated sleep
Insomnia
Narcolepsy
Sleep Apnea
Somnubulism
REM Sleep Behavior Disorder
Insomnia
Inability to fall asleep
Narcolepsy
Inability to stay awake
Sleep Apnea
Condition where you stop breathing in your sleep and wake up
Somnobulism
Sleepwalking
REM Sleep Bahavior Disorder
Keep getting thrown back inot REM sleep - not getting other stages
Sensation
Involves our senses
Collects information from the outside world
Use process of transduction
Senses work together
Synthesia
McGurk Effect
McGurk Effect
Conflicting information presented to eyes & ears and brain can’t comprehend it so it overrides it with vision
Synesthesia
Means joined sensations
neurological condition that causes sensory crossovers, such as tasting colors or seeing shapes when smelling certain scents
Absolute Threshold
Detect stimuli 50% of the time
From nothing to something
Just Noticable Difference/Difference Threshold
Notice a change in stimuli intensity
Weber’s Law
Proportional change in stimuli is necessary
Color Vision Theories
Trichromatic Theory
Opponent Process Theory
Trichromatic Theory
Red, Green, and Blue cones
Explains range of colors
Helps us understand color blindness
Opponent Process Theory
Receptors come in pairs
Blue/Yellow
Red/Green
Black/White
Helps explain afterimages
Vision Deficiencies
Near/Far-Sightedness
Colorblindness
Prosopagnosia
Blindsight
Near/Far-Sightedness
problem with accomodation
refractive eye conditions that affect how light focuses on the retina
near: hard to see objects that are far away; the image is formed in front of the retina, instead of on it.
far: hard to see objects that are close up; the image is focused behind the retina.
Colorblindness
Issues with cones or ganglion cells
dichromatism/monochromatism
dichromatism
partial color blindness that occurs when a person's color vision is based on only two primary colors.
monochromatism
rare form of color blindness in which people can only see shades of gray and are unable to differentiate colors
Prosopagnosia
face-blindness
Blindsight
Sensing things you can’t or don’t visually see
Acetylcholine
Voluntary movement and muscle contraction
Learning
Memory
Sleep
Dopamine
Movement
Attention & alertness
Rewards (related to addictions)
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
inhibits excitation and anxiety (calming)
Endorphins
Pain, relief, and feelings of pleasure
Stress reduction
“natural opiates”
Serotonin
Mood regulation
Hunger/appetite
Sleep
Epinephrine/Norepinephrine
“Fight or Flight” response (increased heart rate, circulation, respiration)
Alertness/Arousal
Norepineprine slows down appetite and digestion during fight or flight
Glutamate
Brain’s major excitatory neurotransmitter
creates links between neurons that form basis of learning, long-term memory