Biogeochemical cycles
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
1
New cards
Energy flow
Sun → autotrophs→ heterotroph→ heat
2
New cards
Biotic
Relating to or resulting from living things
3
New cards
Abiotic
Not derived from living organisms
4
New cards
Reservoir for carbon, oxygen, nitrogen and water
The atmosphere
5
New cards
Reservoir for phosphorus, sulfur and potassium
Soil
6
New cards
How are oxygen and carbon dioxide cycles between abiotic and biotic components
Photosynthesis and cell resp
7
New cards
How much carbon in organic matter comes from CO2
Over half
8
New cards
How does phytoplankton take in CO2
Dissolved (HCO3)
9
New cards
Describe the carbon and oxygen cycle
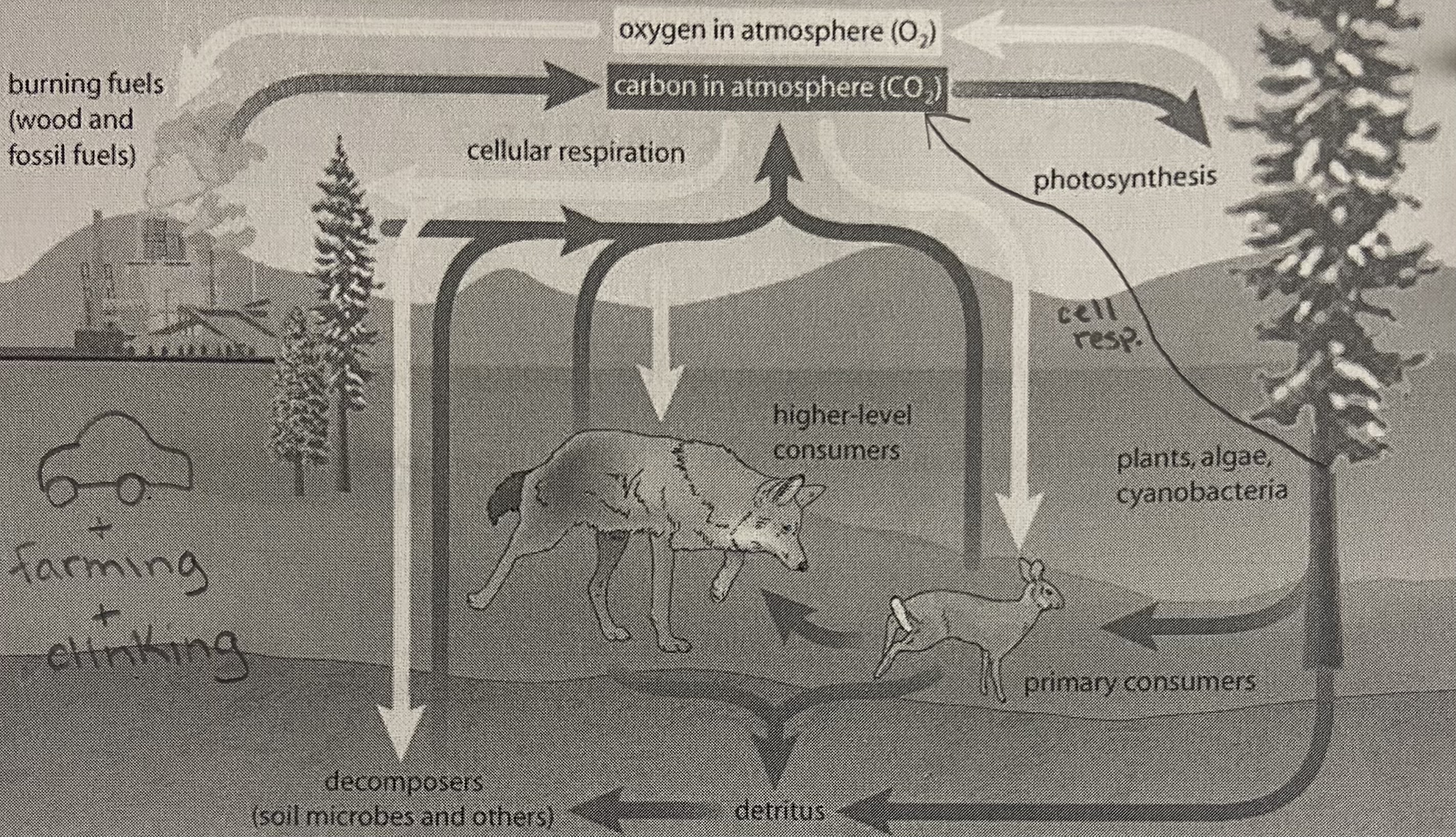
10
New cards
Examples of carbon long term cycle
Formation of oil and gas: burning recycles this carbon
11
New cards
How is the carbon in shells returned to the atmosphere
Volcanic activity and geologic uplift and erosion
12
New cards
Rapid cycling of carbon
CO2 in the atmosphere goes into photosynthesis for biotic environments and through respiration, it is returned. It is also dissolved in water in the surface ocean and is returned through evaporation
13
New cards
Slow cycling of carbon
Dead organisms go to the deep ocean and either: go back to the surface ocean or continue to the earths crust. Here, due to weathering, they will go back to the surface ocean or be formed into petroleum deposits. Photosynthesis in biotic environments can also form fossil fuels. The fossil fuels are combusted and return to the atmosphere
14
New cards
Where is most of carbon located
Aquatic systems (50 times as much as the atmosphere) the ocean is a carbon sink
15
New cards
Human impact on CO2
* burning of fossil fuels
* Deforestation: decreases the amount of carbon that is removed from the atmosphere
* Ozone depletion: increases UV light which is harmful to phytoplankton, less carbon removed from oceans
* Deforestation: decreases the amount of carbon that is removed from the atmosphere
* Ozone depletion: increases UV light which is harmful to phytoplankton, less carbon removed from oceans
16
New cards
Climate Change and CO2
* higher CO2 levels increase global average temperature
* Higher levels of greenhouse gases traps low energy long wave thermal radiation: warming the earth
* Higher levels of greenhouse gases traps low energy long wave thermal radiation: warming the earth
17
New cards
Do organisms need nitrogen?
Yes. It is an element in genetic material
18
New cards
The nitrogen cycle
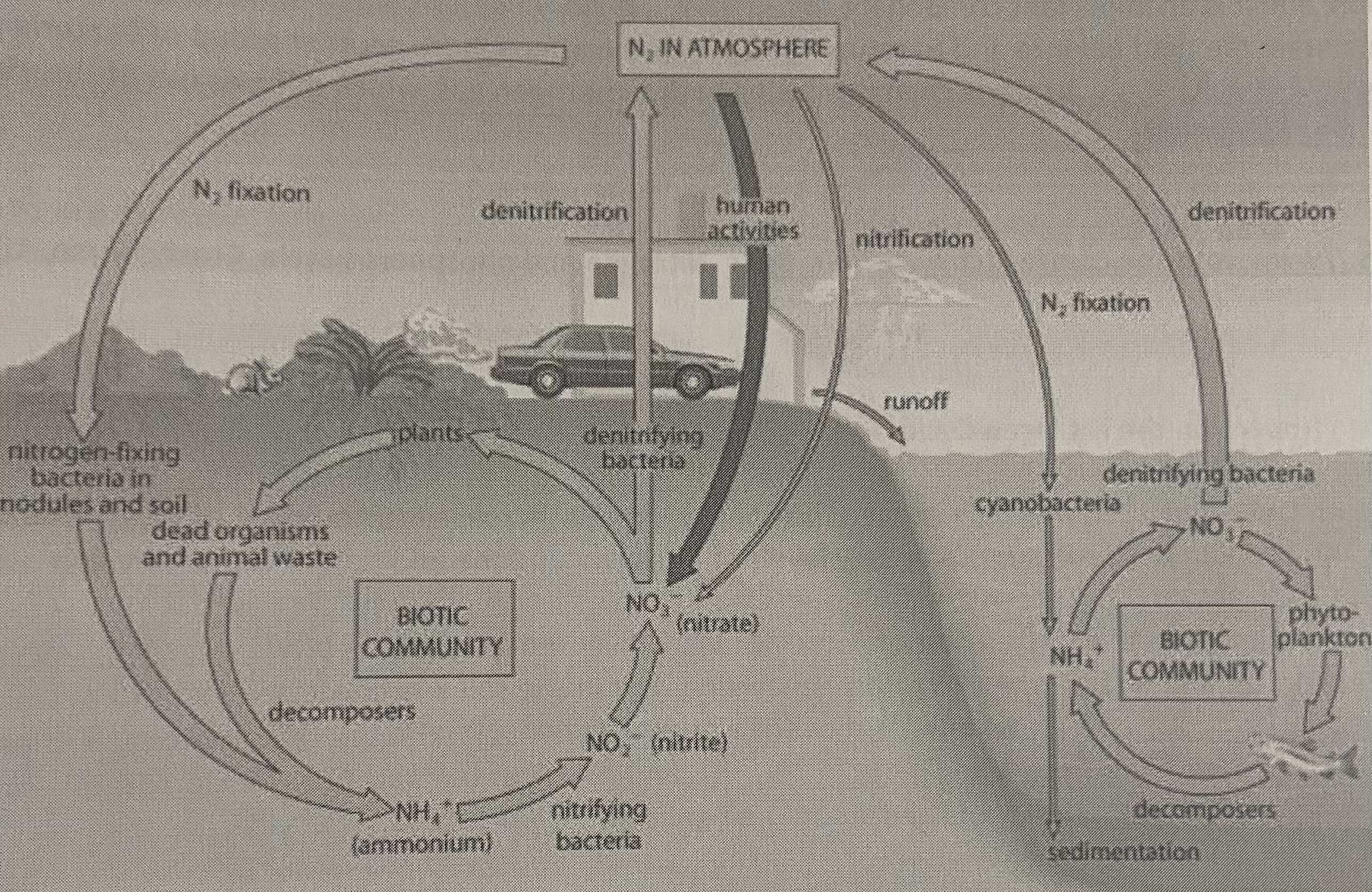
19
New cards
How is can plants use nitrogen
It has to be reduced ( or fixed ) into ammonium by lightning or prokaryotes
20
New cards
Prokaryotes
Nitrogen fixing bacteria like rhizobium, soil bacteria and Cyanobacteria in oceans are important because not enough nitrogen can be fixed by lightning alone
21
New cards
Nitrification
* occurs when ammonium is converted to nitrites and then nitrates
* The nitrates are soluble and can be absorbed by plants to make proteins
* NH4→NO2→ NO3
* The nitrates are soluble and can be absorbed by plants to make proteins
* NH4→NO2→ NO3
22
New cards
Denitrification
* a build up of nitrogen is detrimental to plant growth
* Denitrifying bacteria change nitrates back into nitrogen gas which diffuses out of the ground into the atmosphere to maintain balance
* Denitrifying bacteria change nitrates back into nitrogen gas which diffuses out of the ground into the atmosphere to maintain balance
23
New cards
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle
* nitrogen overload: the addition of nitrogen to plants increases growth, extra nitrogen collects in streams and lakes, it affects tree roots and stints tree growth
* Combustion: burning fossil fuels results in nitrogen containing compounds to be released. They can combine with oxygen to cause acid deposition. This damages trees by dissolving the waxy layer on leaves, making trees more prone to acid rain
* Agriculture run off: with phosphorus, nitrates result in the eutrophication of nutrients in aquatic ecosystems
* Combustion: burning fossil fuels results in nitrogen containing compounds to be released. They can combine with oxygen to cause acid deposition. This damages trees by dissolving the waxy layer on leaves, making trees more prone to acid rain
* Agriculture run off: with phosphorus, nitrates result in the eutrophication of nutrients in aquatic ecosystems
24
New cards
Why is phosphorous important to organisms
Needed to make atp and dna. Found in bones, teeth and shells
25
New cards
The main reservoirs for phosphorus
Soil and rocks
26
New cards
How can plants absorb phosphorus
Rock weathering: adds phosphorous to soil in the form of phosphate
27
New cards
How is phosphorus returned to soil
Animal excretion and decomposers
28
New cards
How is ocean bottom phosphorus returned to the surface
Geological uplift
29
New cards
Phosphorus cycle
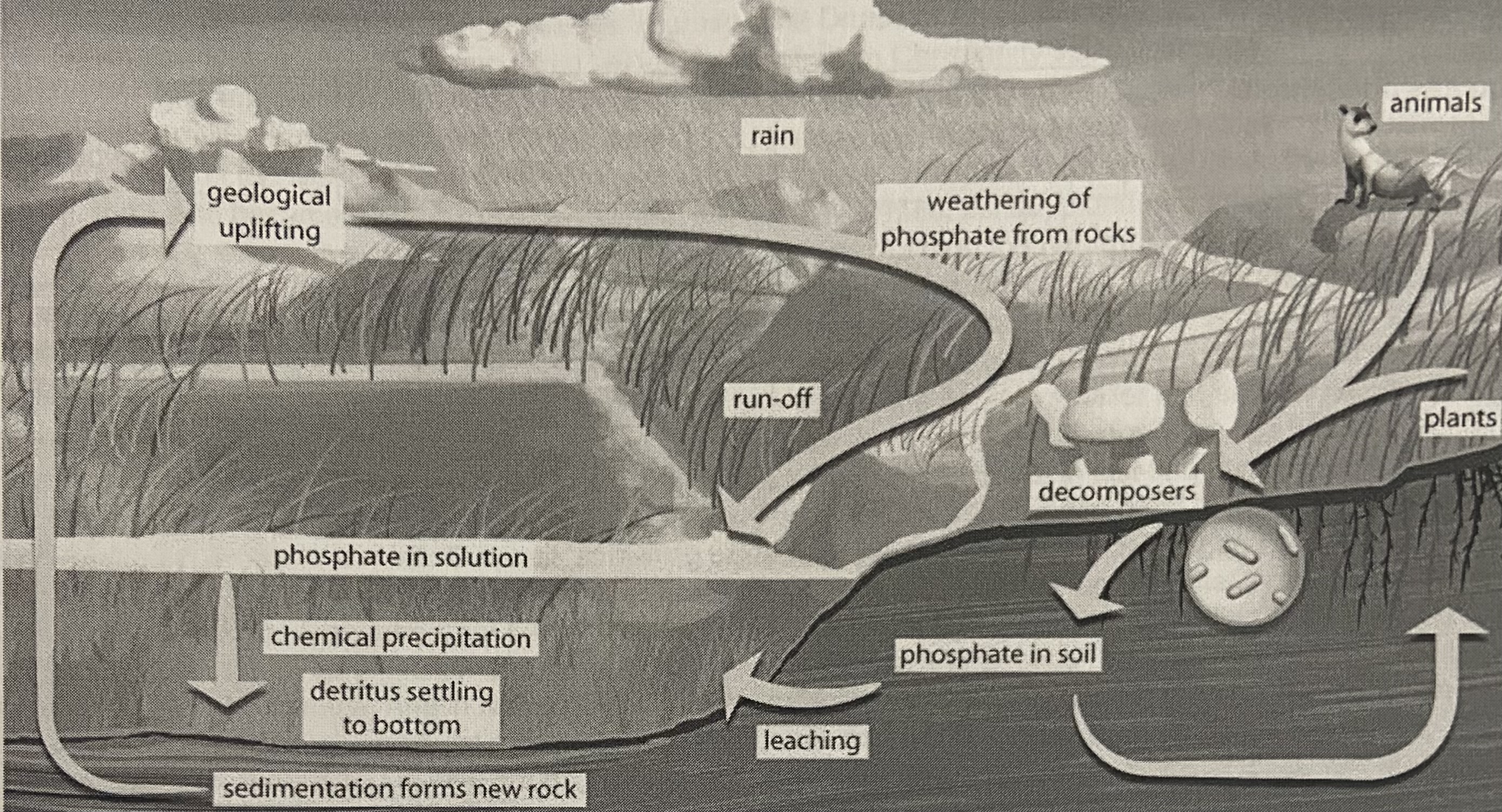
30
New cards
Human impact on the phosphorus cycle m
Eutrophication: part of agal growth in lakes. Phosphates provide nutrients for agal growth but fertilizer run off, organic matter wastes, animal waste and mining contribute to an acceleration of eutrophication. Excessive amounts of phosphorus results in an increase of photosynthetic organisms. When large amounts of algae die, decomposers use up all the oxygen available to other organisms