CH 26 DENSITY IR EXPOSURE PHYSICS EXAM 5
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
________ exposure is one of 2 IR EXPOSURE properties that compromise of visibility detail
Image receptor ( IR exposure)
Visibility of detail refers to
Visibility of detail refers to the fact that the image is visible to the human eye only because sufficient exposure & contrast was received by the IR
Density refers to
Was the term used to reflect exposure to the RADIOGRAPHIC film. Since 1920 was defined as the degreee. the overall blackening of the image Black metallic silver deposited on the emulsion of radiographic film.
•Density was the visible result of the radiographic exposure
Density is now expressed as
IR EXPOSURE
Brightness refers to
Monitor control function that can changing the lightness and darkness of image. Represents the luminous intensity of the monitors light emission
–ctrlled by LUT
Window level refers to
Describes digital post processing that produces changes in brightness,does not change the IRexposure or the dose given to the patient
The key to visible image is
proper IR exposure
Overexposed IR REFERS TO
Overexposed IR has received too many photons therefore has recorded too much information
–Digital post processing can eliminate excess information on overexposed image
Underexposed IR REFERS TO
Underexposed image has not received the information in the first place has is not capable of being manipulated if details were never recorded.
Relationship between mAs and IR exposure is a direct proportional one T or false
True
Quantum noise refers to
refers to a lack of insufficient incoming data for processing.
the word quantum means counted or measured, and the term has been used in photography to indicate an insufficient number of x-ray photons.
Quantum noise results in
Results in a modeled image, which is why it’s also called quantum mottle
The solution to this problem is to increase number of (quantum) of incoming signals by an increasing mAs of the X-ray beam
System noise occurs
Occurs when the digital image of system adds noise to the image
Background radiation contributes to
Also contributes to image and results in ambient noise.
Ambient and System noise are lower than quantum noise.
Responsibility of radiographer to provide the digital IR with appropriate exposure is to ?
Provide Minimum 30% change in MAs for visible density change
•Make changes in doubles or halves
kVp controls
average energy and strength of x-ray photons at anode target
Changes in Kvp
Change in kilovoltage alters the intensity of the beam when mAs and other factors remain the same
–kVp affects production of scatter
–Change in kVp varies quantity and quality
•Therefore, has tremendous impact on density/IR exposure
30-50 kvp
4-5 percent change
50-60kvp range
8-9% range
90-130 kvp range
10-12%
As mAs increases x-ray exposure________and film density also
Increases, increases because there is a direct relationship
Kilovoltage alters the_________ Of the beam, reaching the IR two ways?
Alters the intensity of beam.
-Voltage controls the energy, and the strength of the electron strike in the target with the x-ray tube.
Controls the average energy of the x-ray photons produce at the anode target
Kilovoltage
____ alters both quantity and quality
Kvp
How can you adjust contrast.
MAs
Increasing Kvp does what?
produce more scatter
Secondary radiation
Reduce radiographic contrast
Generator Configuration Affects
Affects average energy of beam
•Total # of higher energy photons in the x-ray tube emission spectrum is controlled by the amount of ripple in the wave-form
–Only consider when changing from single phase to high-frequency multi-phase
–Might be more accurate to change kVp to maintain density/IR exposure
Larger focal spots utilize greater _______
incident electron stream than small
•Manufacturers adjust mAs at the filament for dual focus tubes
•Will not affect density/IR exposure in properly calibrated equipment
Blooming occurs when
Blooming occurs with large milliamperes because the incident electron beam is not easily focused by the focusing cup. It is Rare for blooming to cause visible density/IR exposure difference
•Large focal spots tend to bloom more at higher milliamperes
•If occurs, replacement of tube may be indicated
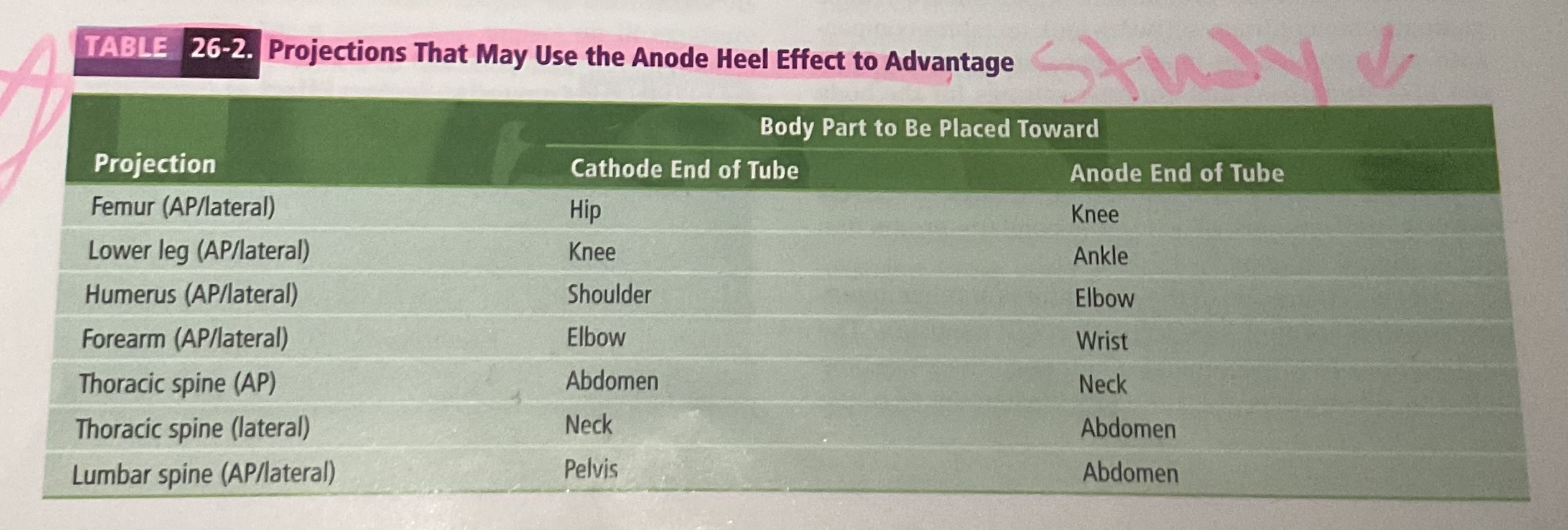
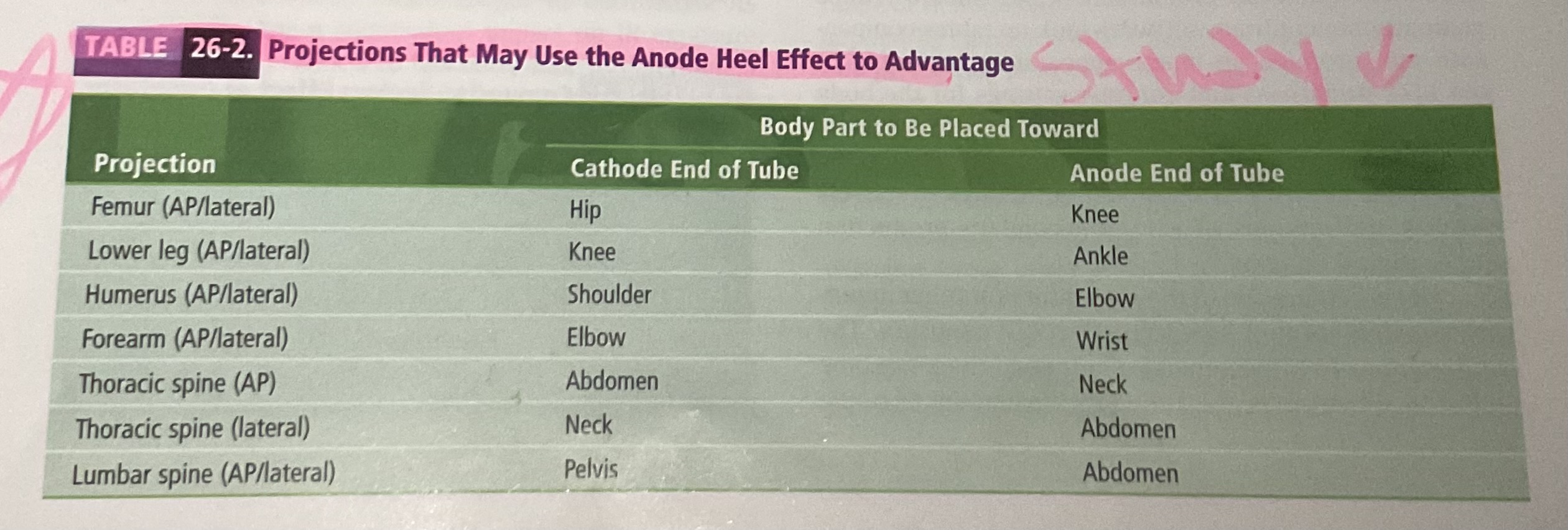
anode heel effect alters…
Alters the intensity of radiation and therefore IR exposure can cause higher exposure up to 45% between an and cathode end of the image because IR exposure is always greater at the cathode end.
Anode heel effect is more pronounced when
More pronounced when the collimationis open wide, then when it is closed
when you see an extremely small angle to the anode 12° or less
Anode heel effect can be minimized when
Can be minimized by collimation or a greater SID
Anode heel effect can be an advantage when
Converted to an advantage when placing the portion of the object with greatest subject density toward the cathode end of the tube.
Utilizes the greater intensity for the greater subject density and leaves a lesser intensity of the anode end of the tube for the letter density.
Study
Study
SID alters the
•OID prevents
SID alters the intensity of beam reaching IR according to inverse square law
(The inverse square law affects the exposure inverse proportion to the square of the distance) ex : as distance increases radiation, intensity, and IR exposure decreases.
•OID prevents scatter from reaching
Inverse square law refers to?
Expresses the change in intensity when the distance changes for example. as distance increases radiation, intensity, and IR exposure decreases.
Filtration Has ability to
Ability to alter beam intensity and affect IR exposure
•What are the types of filtration?
Inherent filtration, added, and total
IR exposure decreases when Filtration is_______
Increased
Because they are inversely proportional
Beam Restriction refers to
Restriction of the beam, Collimation or reducing primary beam field size reduces the total number of photons available
•Reduces scatter
•Reduces overall IR exposure/density
Large anatomic part size And high Kvp levels dramatically increase?
Dramatically increase, scatter production
Because the amount of attenuation is dependent on
Depending on thickness and type of tissue being imaged .
tissue type = is dependent on atomic number and the density of the tissue. Pathology can also alter tissue thickness or type.
( there is a inverserelationship between tissue thickness/type and IR exposure, As tissue thickness, Average is a number of tissue and or tissue density increases than IR exposure decreases)
Pathology can either have an attitude or destructive effect
Additive Condition; decrease it exposure
Destructive conditions; Increase IR exposure
Grids purpose
is to absorb scatter, the more the efficient grid, the less will be density/IR exposure. Improves image contrast
•High Grid ratio, low freq.,dense interspace material, moving grids, grid errors all reduce density/IR exposure
Grids primary purpose is
Reduce scatter
Improve image contrast
Increase grid ratio decreases ……
density/IR exposure, Inversely related
Compensation for varying grid ratios is accomplished by ______ mAs?
Increasing MAs