GCSE Homeostasis and response
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:36 AM on 11/25/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
1
New cards
Define homeostasis
The maintenance of a constant internal environment
2
New cards
Define negative feedback
when a change from normal conditions is detected and prompts a response to return to normal
3
New cards
Give three procedures that homeostasis maintains
Temperature, blood glucose levels (BGL), water balance
4
New cards
What are the two communication systems in the body
hormonal and nervous system
5
New cards
How does the hormonal system send signals
via hormones in the bloodstream
6
New cards
How does the nervous system send signals
via electrical impulses in neurones
7
New cards
define stimulus
a signal to which an organism responds
8
New cards
give the stimulus for smell
chemicals
9
New cards
describe the coordination pathway
stimulus - receptor (PNS) - coordinator (CNS) - effector
10
New cards
give examples of stimuli
pressure, temperature, sound, light, chemical
11
New cards
give examples of receptors
skin, eyes, ears, nose, tongue
12
New cards
give examples of coordinators
brain + spinal cord
13
New cards
give examples of effectors
muscles and glands
14
New cards
what are glands?
organs that secrete hormones or fluids such as tears and sweat
15
New cards
what are nerves?
bundles of neurons in the PNS
16
New cards
where are electrical impulses generated?
receptor
17
New cards
what are the three types of neurones?
sensory, relay and motor
18
New cards
where are sensory neurones found?
receptors to CNS
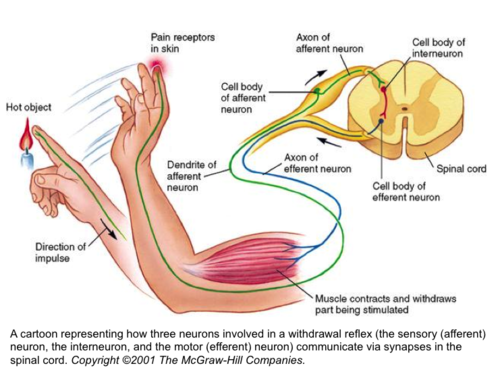
19
New cards
Where are relay neurones found?
CNS
20
New cards
where are motor neurones found?
CNS to effectors
21
New cards
What does the reflex arc do?
rapid automatic response to stimuli to protect the body
22
New cards
what part of the CNS do reflexes go through?
the spinal cord (usually closer than brain)
23
New cards
what is a synapse?
the gap between neurons
24
New cards
how do synapses work?
The nerve signal is transferred by neurotransmitters which diffuse across the gap and set off a new electrical signal in the next neuron.
25
New cards
describe how electrical impulses are transmitted across synapses
when the electrical impulse reaches the end of a neuron, vesicles move to the join to the cell membrane to release neurotransmitters into the synapse, which *diffuse* across the synapse, binding to receptors on the next neurons membrane and begins a new impulse.
26
New cards
give an identifying feature of a sensory neuron
cell body sticking out of the axon
27
New cards
give an identifying feature of a relay neuron
short
28
New cards
give an identifying feature of a motor neuron
cell body attached to the dendrites + effector on the end
29
New cards
what is the eye?
a sensory organ that detects light and converts light energy into electrical impulses.
30
New cards
what are rods responsible for?
black and white vision in low light
31
New cards
what are cones responsible for?
coloured vision in high light
32
New cards
what do radial and circular muscles do?
radial muscles contract, circular muscles relax
33
New cards
What is accommodation?
the process by which the eye's lens changes shape to focus near or far objects on the retina
34
New cards
how does accommodation work for distant images?
Ciliary muscles relax, suspensory ligaments contract, lens is long and thin (less refraction needed)
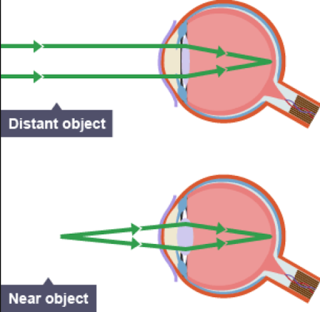
35
New cards
how does accommodation work for close images?
Ciliary muscles contract (bulge), suspensory ligaments relax, lens is short and fat (more refraction needed)
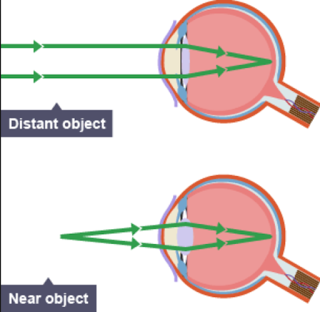
36
New cards
Why does the lens become fatter to see close objects?
the divergent rays are shining on the ends of the lens, so it makes it bulgy to focus the rays into the retina.
37
New cards
What is myopia?
short sightedness - unable to see distant objects - eye is too long / lens is too convex - image forms in front of retina
38
New cards
What is hyperopia?
long sightedness - unable to see close objects - eye is too short / lens is too concave - image forms behind the retina
39
New cards
what are the treatments for myopia and hyperopia?
concave for myopia, convex lens for hyperopia
40
New cards
What part of the brain controls homeostasis?
hypothalamus
41
New cards
What is the thermoregulatory system made up of?
receptors that monitor body (blood) temperature
42
New cards
What is negative feedback?
A response to a change in the body that reverses the change
43
New cards
What effectors do the thermoregulatory system use?
sweat glands, blood vessels in skin and skeletal muscles
44
New cards
What is the body's negative feedback loop to being too cold?
stimulus - too cold / receptor - thermoreceptors in the skin / coordinator - hypothalamus (brain) / effector - sweat glands, skeletal muscles, blood vessels, erector muscles / response - vasoconstriction, shivering, sweat glands stop, piloerection / core body temperature rises
45
New cards
Why does the body use vasoconstriction/dialation?
vasodialation allows heat to be lost by radiation. vasoconstriction stops heat from being radiated.
46
New cards
Why does the body shiver?
rapid skeletal muscle contraction - high rates of respiration, which is an exothermic reaction.
47
New cards
Why does the body use piloerection when cold?
to trap warm air between hairs.
48
New cards
Why does the body sweat?
cool skin through evaporation
49
New cards
What is the endocrine system?
a group of glands that secrete hormones directly into the blood
50
New cards
What are hormones and what do they do?
Hormones are messenger proteins that travel to their target organ in the blood. They create a response in the target organ
51
New cards
What is different about hormones?
They are slower than the nervous system but have longer-lasting effects.
52
New cards
What is the pituitary gland?
The master gland - it loosely controls other glands
53
New cards
What is thyroxine action an example of?
Negative feedback
54
New cards
What is thyroxine?
A hormone secreted by the thyroid when it detects TSH. It controls metabolic rate and targets almost all cells. It has nearly constant levels due to negative feedback
55
New cards
What is used to make thyroxine?
Iodine
56
New cards
How does thyroxine link to temperature regulation?
Because thyroxine controls metabolic rate, including respiration (an exothermic reaction), thyroxine production will be inhibited in high temperatures to reduce metabolic rate and slightly cool the blood. The reverse is also true.
57
New cards
What is adrenaline?
A hormone secreted by the adrenal gland that is stimulated by the nervous system at times of excitement/distress. It prepares the body for fight or flight.
58
New cards
What are adrenaline's target organs?
Vital organs like the heart and lungs
59
New cards
Describe the fight or flight response
Increased heart rate, increased breathing rate, dilation of airways, increased blood glucose levels, dilation of pupils
60
New cards
Describe the journey of glucose in the blood
glucose is eaten as sugar/starch/carb - digestive system uses carbohydrases to break down into glucose - glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream by the SI (villi)
61
New cards
Why can't blood glucose levels get too high?
The water concentration of the blood would fall. Water would leave the cells via osmosis and shrivel up.
62
New cards
Why can't blood glucose levels get too low?
The water concentration in the blood would rise. Water would enter the cells via osmosis and burst.
63
New cards
What would cause peaks in blood glucose levels?
Eating
64
New cards
Why might blood glucose levels peak at different rates?
Differences in food: simple and complex carbohydrates
65
New cards
What evidence might be in a graph to show that there's a mechanism to prevent blood glucose from falling too low?
Blood glucose levels never fall beyond a certain point - negative feedback might activate a mechanism to raise blood glucose levels like glucagon secretion or hunger
66
New cards
What is the function of the pancreas in the endocrine system?
Detects and controls blood glucose levels with insulin and glucagon.
67
New cards
What are the target organs for insulin and glucagon?
Liver and muscles
68
New cards
How does the pancreas respond to high blood glucose?
Secretes insulin
69
New cards
How does the pancreas respond to low blood glucose levels?
Secretes glucagon
70
New cards
What does insulin do?
Makes glucose into glycogen to be stored in the liver, reduced blood glucose levels.
71
New cards
What does glucagon do?
Breaks glycogen in the liver down to be released into the blood, increases blood glucose levels.
72
New cards
Define excretion
The removal of metabolic waste from the body.
73
New cards
How is carbon dioxide produced and how is it excreted?
Produced by the aerobic respiration of cells, diffuses from bloodstream into lungs to be exhaled
74
New cards
How is lactic acid produced and how is it excreted?
Produced by anaerobic respiration in muscles, oxidised in the liver
75
New cards
How is excess water produced and how is it excreted?
Produced by drink/food/respiration, urination through the kidneys
76
New cards
How are excess ions/salts produced and how are they excreted?
Produced by food/drink/chemical reactions, urination through the kidneys
77
New cards
From what source is the most water gained?
Drinking water
78
New cards
How is the most water lost?
Urination
79
New cards
Why must the body remain isotonic?
Cells will shrivel or burst if blood is too concentrated or dilute
80
New cards
What do the kidneys control?
How much urea, salt ions and water are released in urine
81
New cards
Which blood vessels carry blood to the kidneys?
The renal arteries off the aorta
82
New cards
Which blood vessels carry cleaned blood away from the kidney?
The renal vein off the vena cava
83
New cards
Name the tube that carries urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
The ureter
84
New cards
Where does ultrafiltration occur?
The capsule
85
New cards
How does ultrafiltration work?
The pores in capillaries seep tissue fluid etc into the gap between it and the capsule. Particles small enough to diffuse across the nephron's wall (water, glucose, salts, urea) into the nephron. Bigger particles like RBC's, WBC's and proteins cannot fit and don't get filtered out.
86
New cards
What is a nephron?
The small capillary-like tubules that filter metabolic waste out of blood.
87
New cards
What does the nephron reabsorb?
The glucose lost by ultrafiltration
88
New cards
What are the three main processes in the nephron?
Filtration, reabsorption, urine production
89
New cards
How does reabsorption work and what does it reabsorb?
Capillaries wound around the nephron diffuse all glucose particles back into the blood. It also diffuses some water back into the blood.
90
New cards
How does urine production work?
Controlled by ADH, contains urea, some water and some salt ions.
91
New cards
What is the problem with urea? How is it produced?
Proteins consumed in the diet will be broke down into amino acids to be turned into different proteins. Excess amino acids can't be stored, so they are deaminated into ammonia, and then urea. Urea is toxic.
92
New cards
What does deaminated mean?
Breaking down excess amino acids into ammonia and then urea.
93
New cards
Define osmoregulation
the control of the water and salt levels in the body. The correct water balance between the cell and the surrounding fluid must be maintained to prevent problems with osmosis.