Unit 2: Molecular and Ionic Structure and Properties
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
"I think I did well on that test" I got a 76 :/
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
intramolecular forces
attractions within a molecule
intermolecular forces
attractions between molecules
ionic bonding
transfer of electrons from a metal to a nonmetal
coulomb’s law
an increase in charge or decrease in size = increased bond energy
covalent bonding
sharing of electrons between non metals
polar molecule
electrons are not shared equally; large change in electronegativity
nonpolar molecule
electrons shared equally; small change in electronegativity
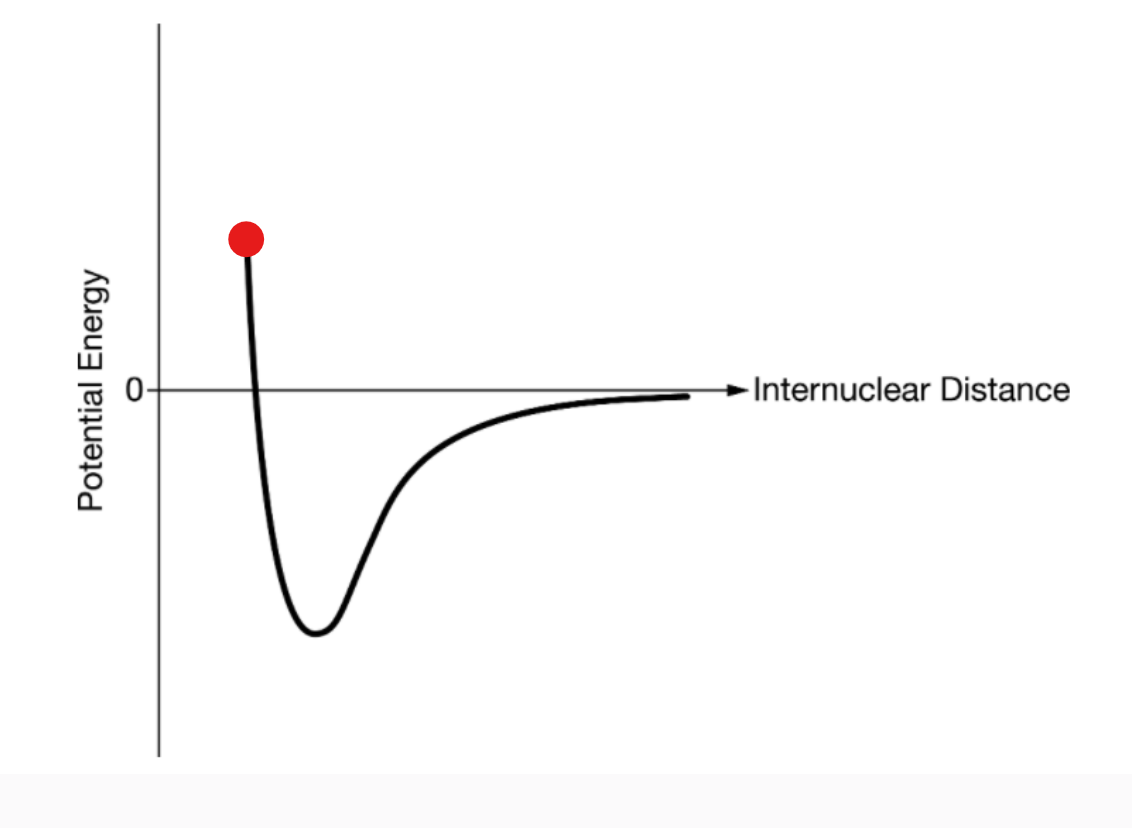
repulsion; the molecules are too close to form a bond
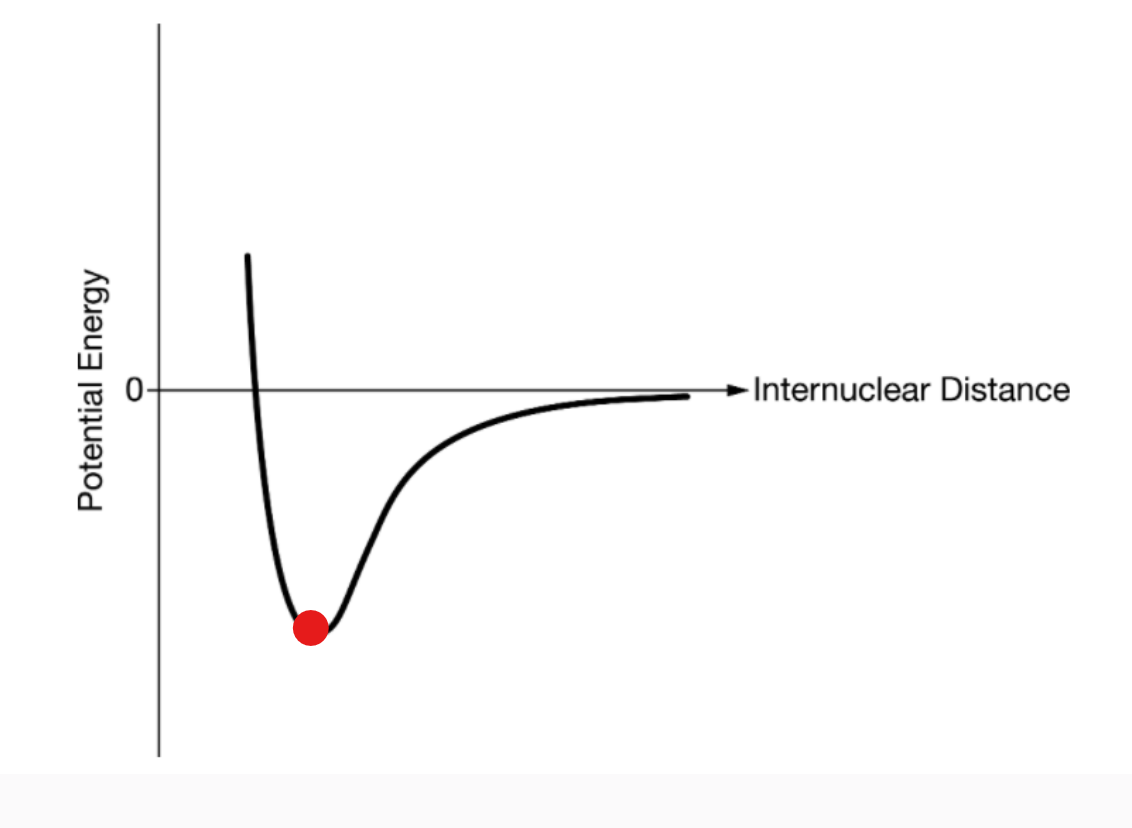
where the molecules are actually bonded together (internuclear distance at this point = bond length)
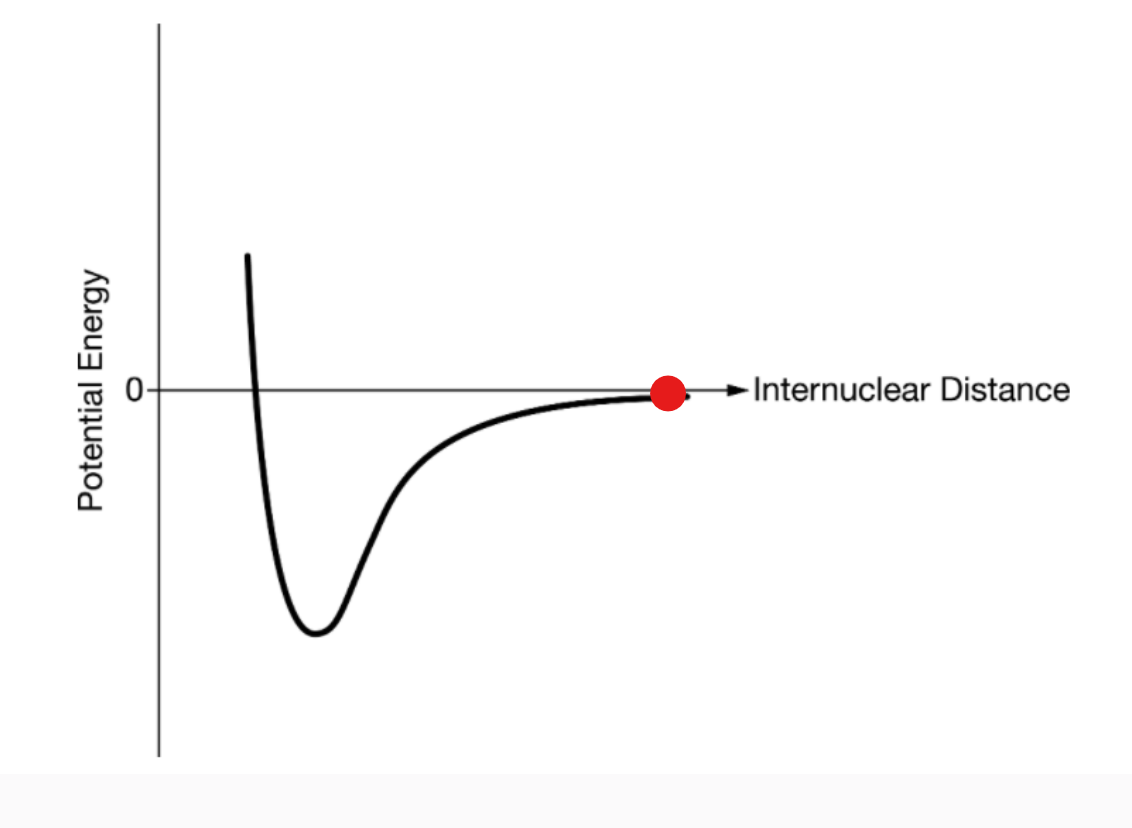
where the molecules are too far apart to form a bond
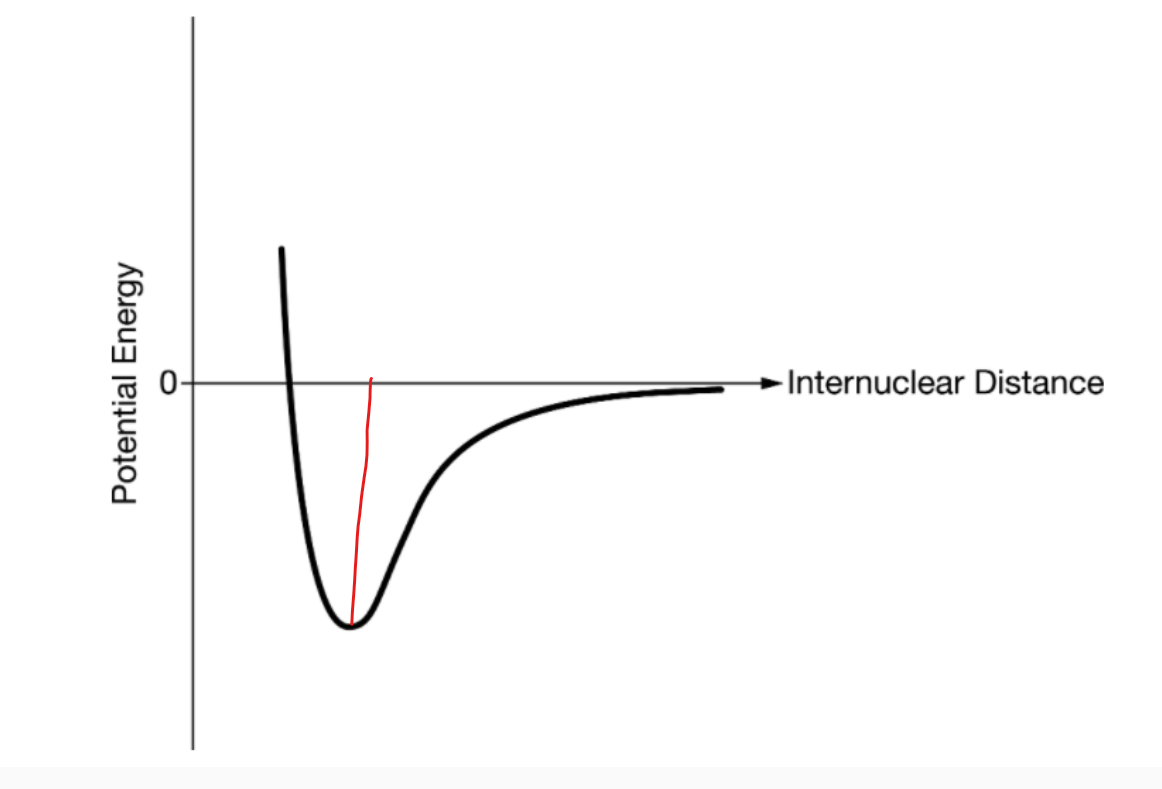
bond energy
bond energy
strongest bond
lowest potential energy = ?
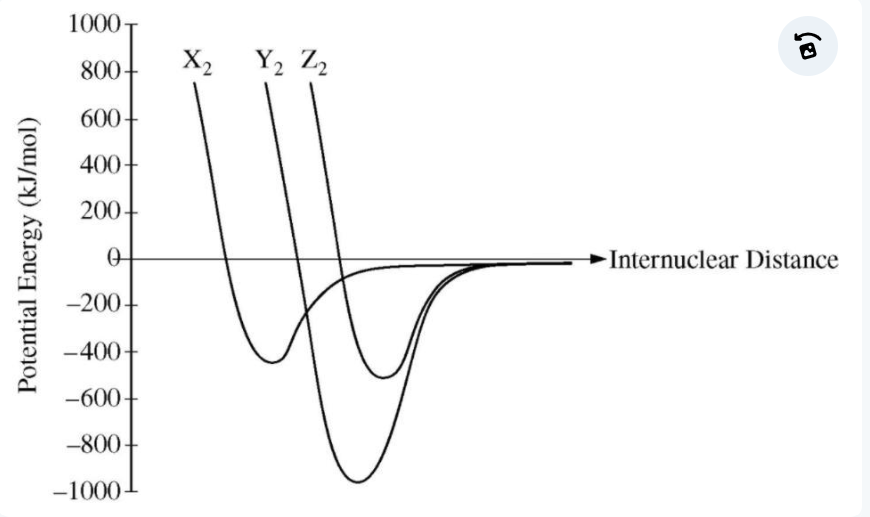
smaller
bond length is shorter for _______ molecules
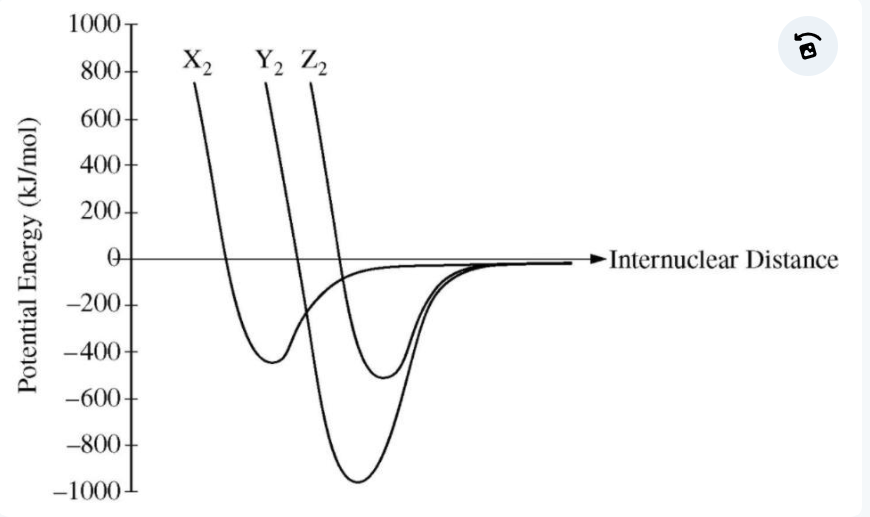
increased bond energy, decreased bond length
increased bond order = ?
bond order
the number of bonding pairs of electrons between two atoms
from sp to sp³
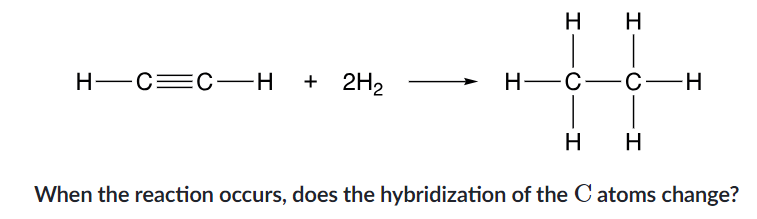
sp³
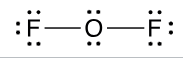
what is the hybridization of oxygen?
pi bonds
formed by the lateral overlap of two atomic orbitals; e-shared around atoms
sigma bonds
a result of the head-to-head overlapping of atomic orbitals; e- shared between atoms
8 sigma, 3 pi
sigma bonds and pi bonds?
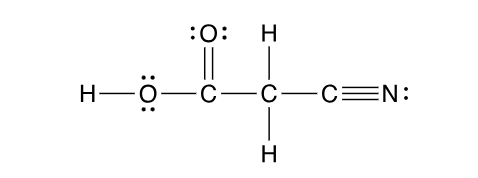
2 sp³ orbitals
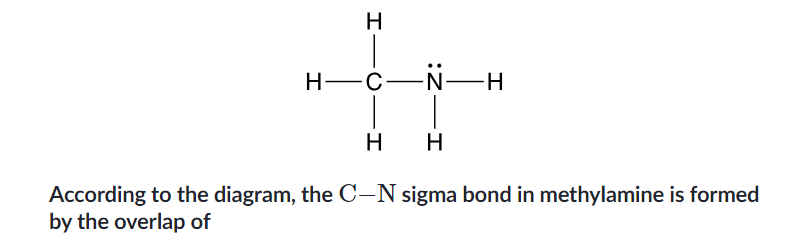
yes, from sp to sp²
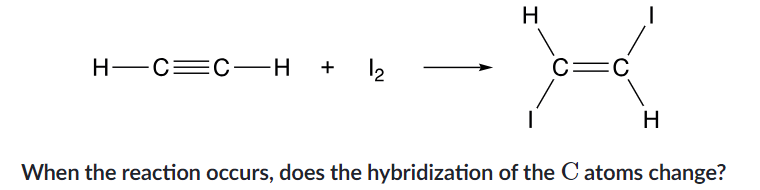
bond polarity
difference in electronegativity of two elements
more electronegative atom
dipole arrow points towards ______
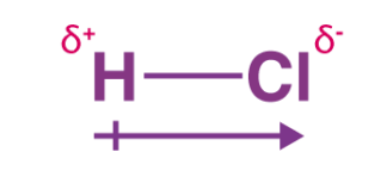
increased bond energy
delocalized electrons = ____________
single bond
sigma bond
double bond
sigma bond + pi bond
triple bond
sigma bond + 2 pi bonds
Octet rule
All atoms end up with 8 electrons around them (except for hydrogen and boron)
Steps to draw Lewis Structures
count the valence electrons of all the atoms
determine the central atom
remove an electron from each atom for a bond (S—O bond removes one electron from S and one from O)
add the remaining electrons as lone pairs to create an octet around each atom
if octet has not been achieved add multiple bonds
if all atoms have achieved an octet and not all valence electrons have been assigned, add the remaining electrons to the central atom
most electronegative
the central atom is the ______
expanded octet
when a atom has more than 8 electrons
the electrons of pi bonds are delocalized
in resonance structures
formal charge
a hypothetical charge assigned to an atom in a molecule. It's based on the assumption that electrons in all chemical bonds are shared equally between atoms, regardless of their relative electronegativity.
= valence electrons - (lone electrons + ½ bond electrons)
better structures
molecules with lower formal charges are _____
negative
a more electronegative atom will have a more _______ formal charge
sign
adjacent atoms should not have formal charges with the same ________
charge on chemical species
sum of formal charges =
closer to 0
a more favorable Lewis Structure will have a formal charge ___________
0
6 valence electrons - (4 unbonded electrons + 4 bond electrons / 2) = 0
formal charge of oxygen in H2O
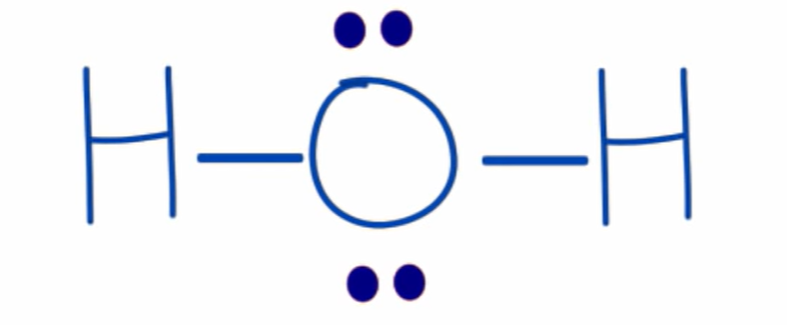
0
6 valence electrons - (4 unbonded electrons + 4 bond electrons/2) = 0
formal charge of oxygen in CO2
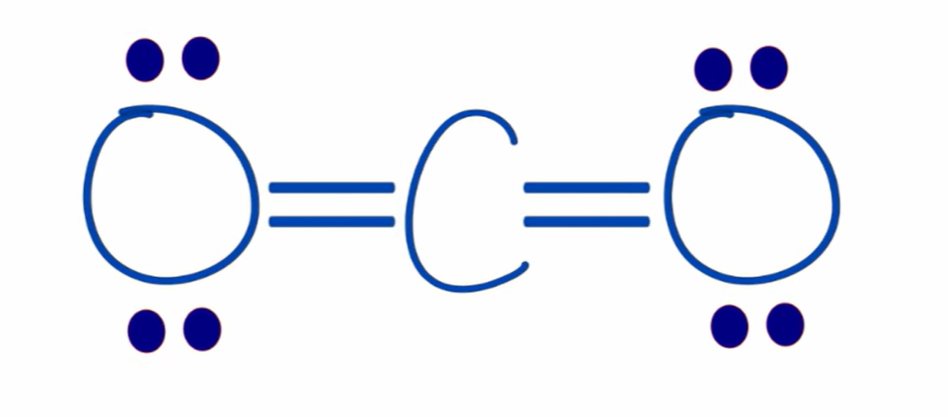
0
4 valence electrons - (0 unbonded electrons + 8 bond electrons/2) = 0
formal charge of carbon in CO2
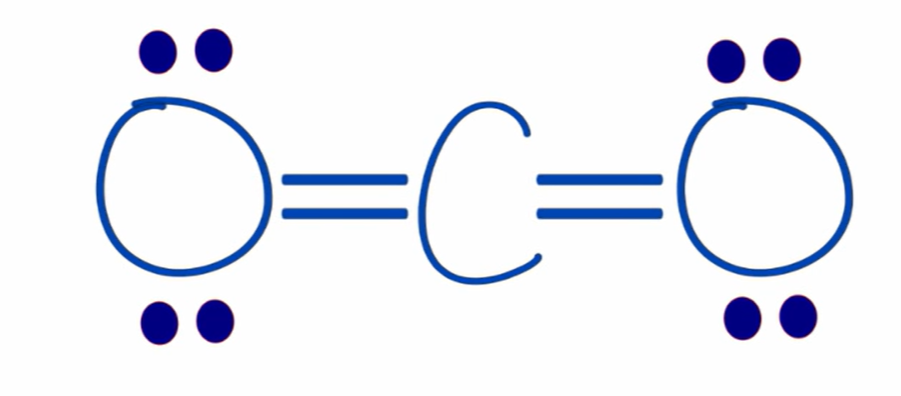
0
1 valence electron - (0 unbonded electrons + 1 bond electron/2) = 0
formal charge of hydrogen in H2O
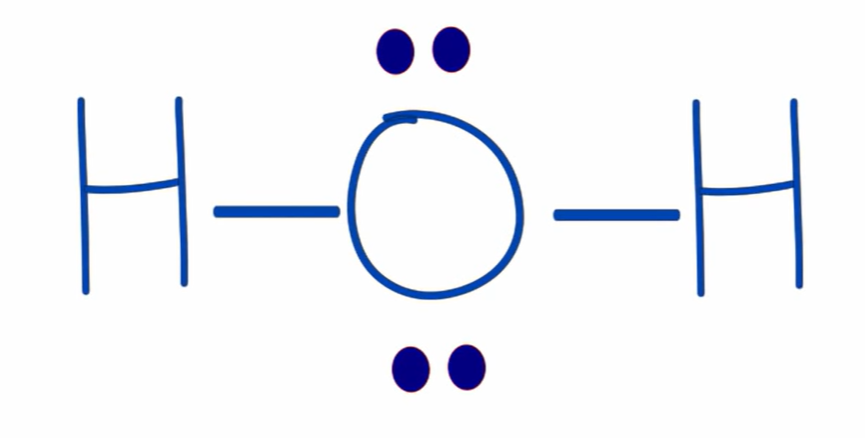
-1
6 valence electrons - (6 unbonded electrons + 2 bond electrons/2) = -1
formal charge of oxygen furthest to the left in NO3
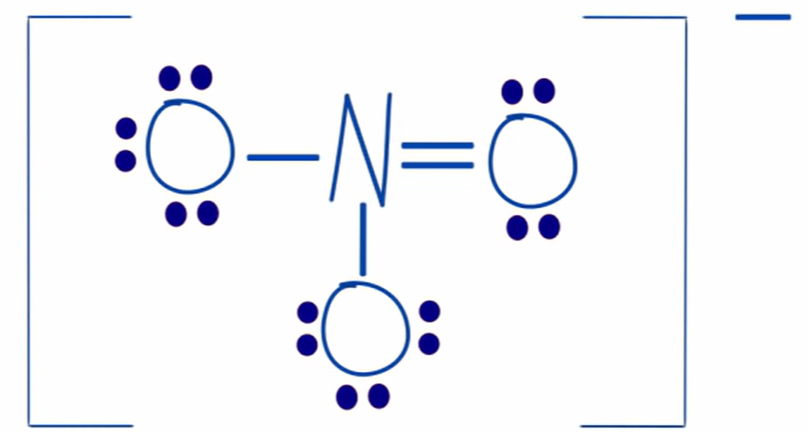
-1
charge of resonance structure
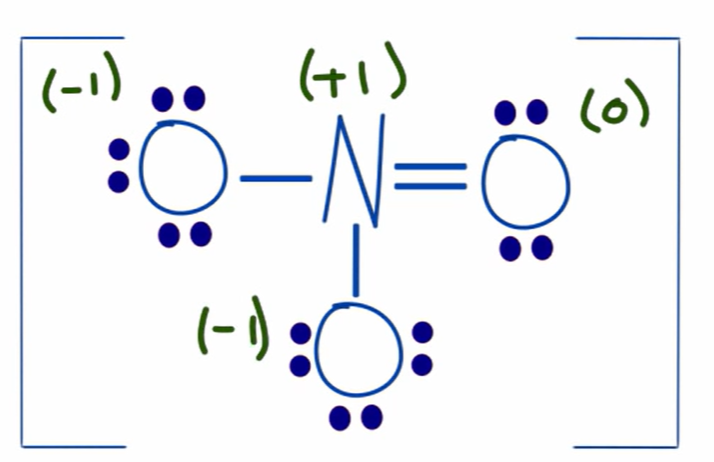
the one on the left, because it has a charge of 0
which resonance structure is more favorable?
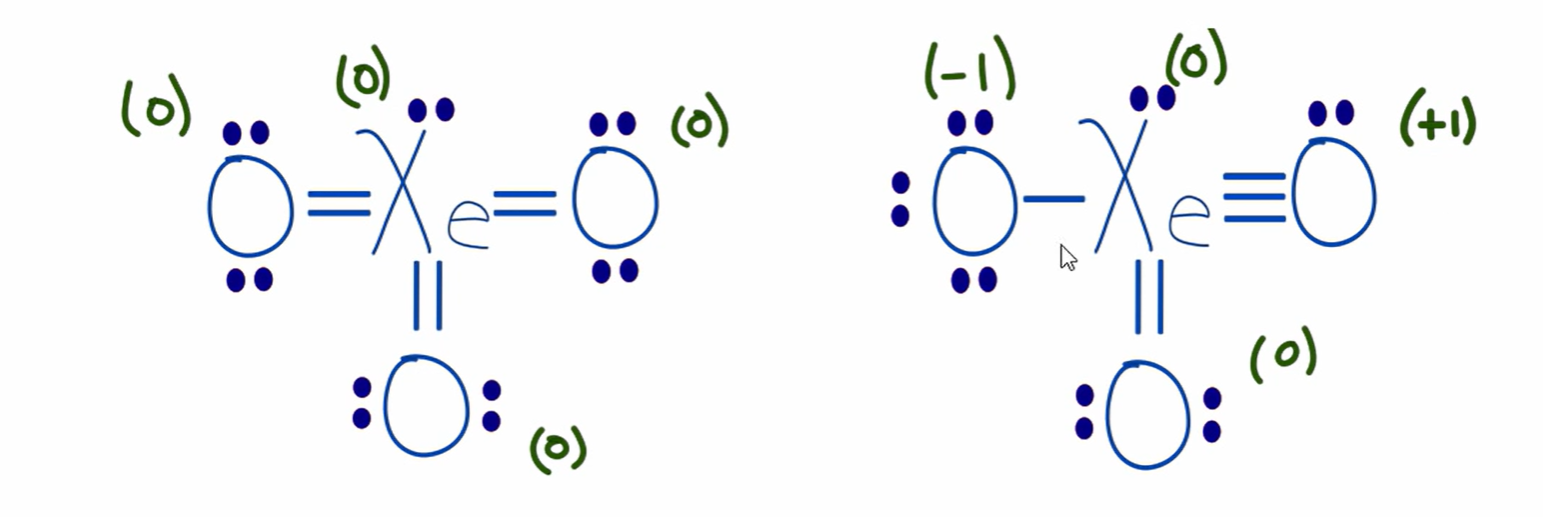
negative
bonds and lone pairs are ________
repel
electrons (-) ____ each other
minimize repulsion
because bonds and lone pairs are negative, they arrange themselves to ________________
steric number
number of electron domains
2
sp steric number
3
sp² steric number
4
sp³ steric number
Linear
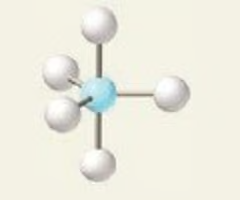
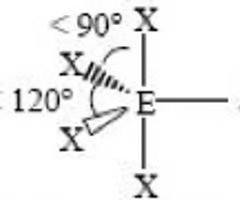
< 90, < 120
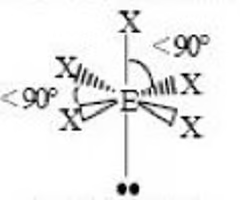
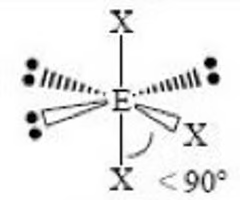
Sawhorse or Seesaw (trigonal bipyramidal) bond angle
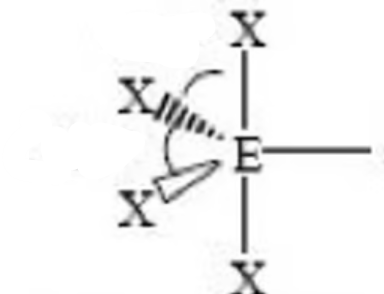
< 90, < 90
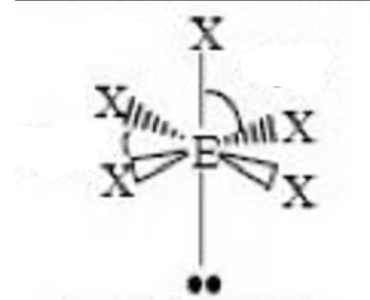
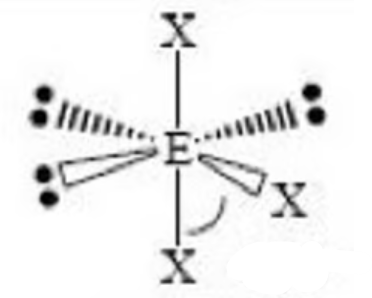
square pyramidal bond angle
< 90
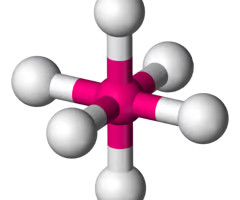
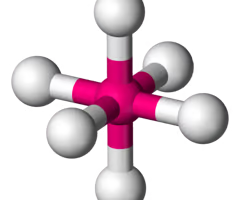
T shape (octahedral) bond angle
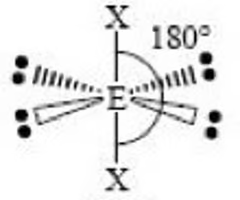
180
linear octahedral bond angle
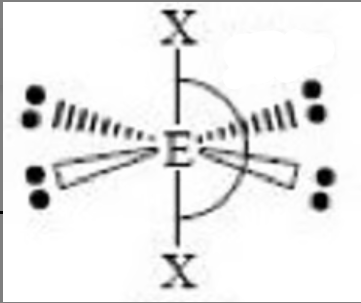
polar molecule
a molecule with an uneven distribution of charges; asymmetrical; bonds don’t cancel out; lone pairs of electrons disrupt electrical symmetry
nonpolar molecule
a compound with an even distribution of charges; symmetrical; identical atoms
polar; the lone pairs on the oxygen atom make the molecule asymmetrical
polar or nonpolar?
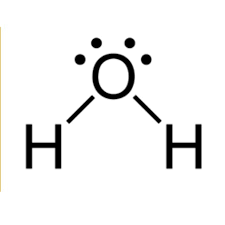
nonpolar, because it has an even distribution of electron density, and its dipoles cancel each other out.
polar or nonpolar?
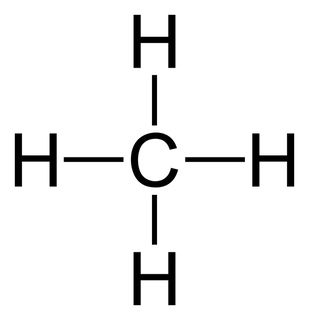
polar
any molecule with lone pairs of electrons on the central atom