BPK 241 Week 5
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
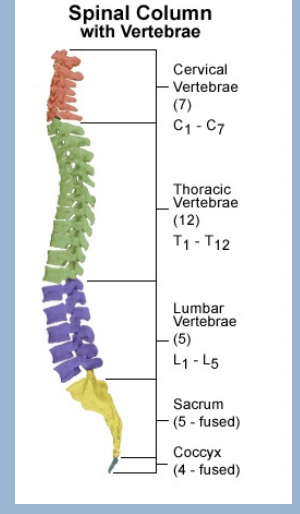
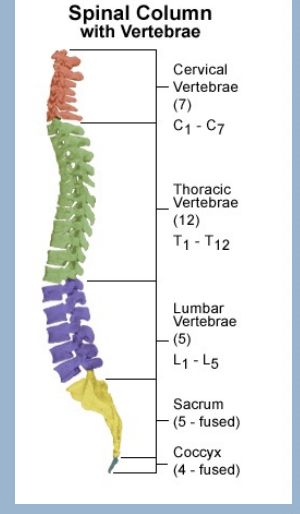
Vertebrae
33 Types - 24 true, 9 false
Kyphodic curve
Distributes forces on spine
Vertebrae types
7 Cervical
12 Thoracic
5 Lumbar
5 Sacral (fused)
Coccyx
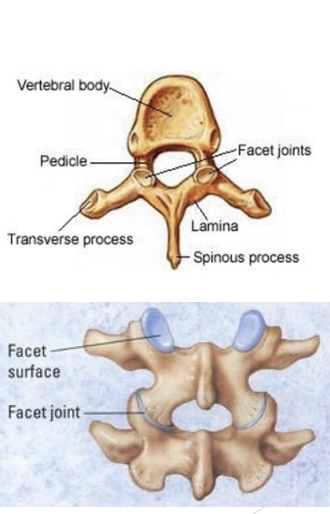
Spine Features
Body (or anterior mass)
Spinous process
Lateral (transverse) process
Articulations with ribs (thoracic spine)
Facet joints (superior & inferior)
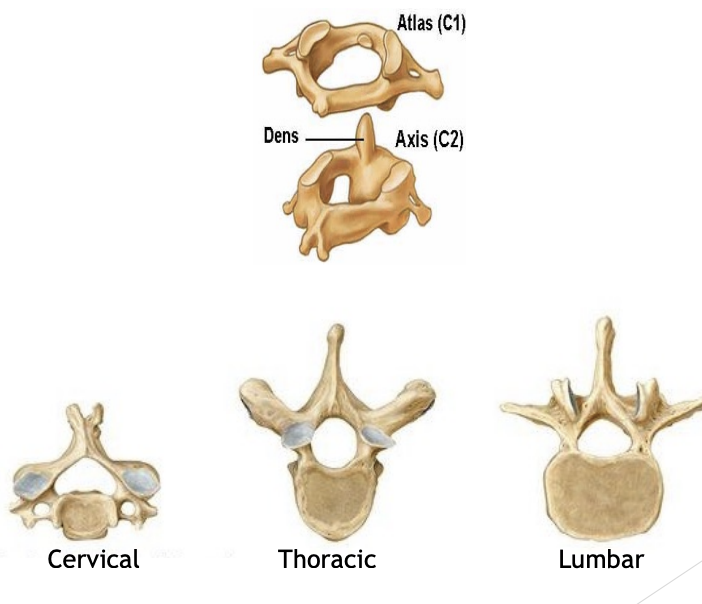
Atlas (C1) & Axis (C2)
Holds your skull
Allows flexion + extension
C1 rotates on C2 - pivot joint
Bone gets bigger downwards as we bear more weight
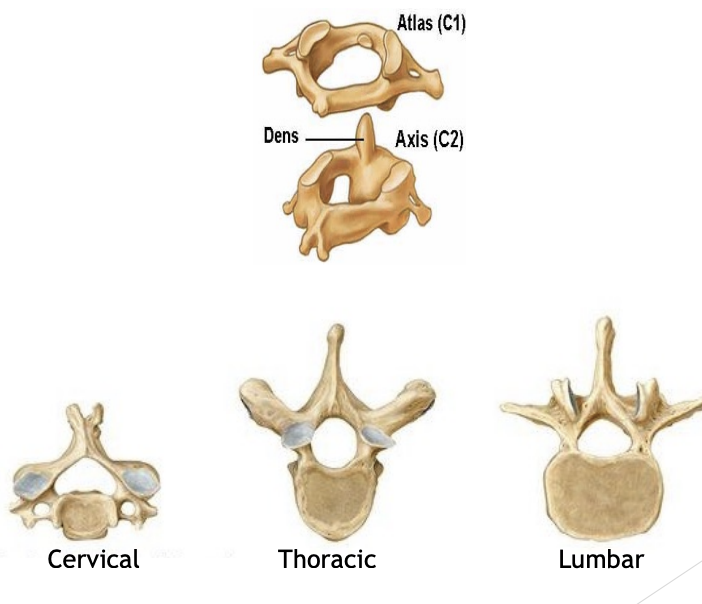
Cervical
High back
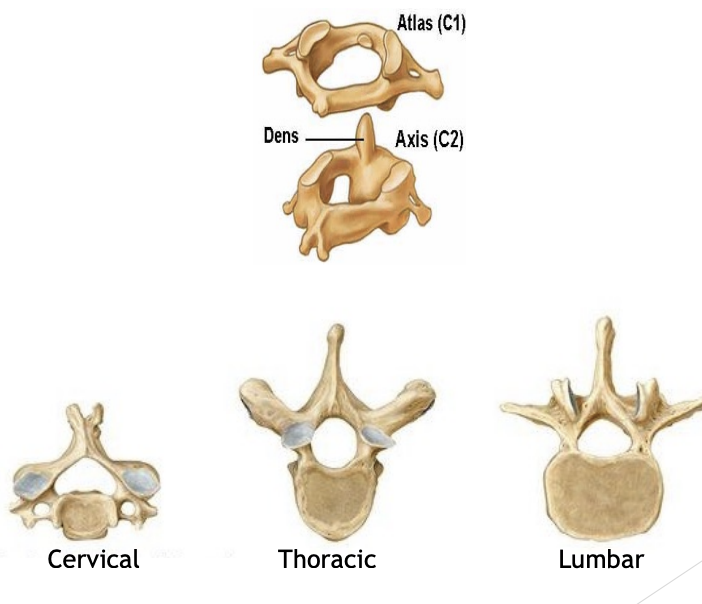
Thoracic
Middle back
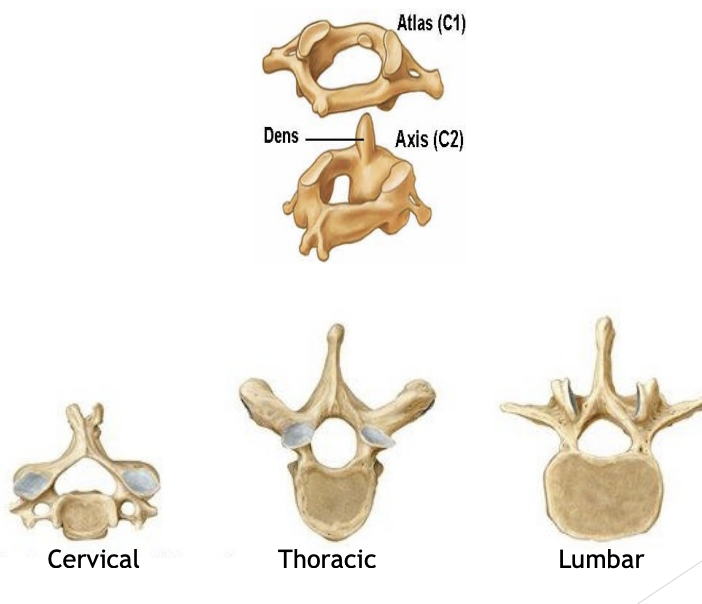
Lumbar
Lower back
Spine ROM
Occipital joint: 50º Flexion-extension, 4º Rotation, 8º Lateral Bend
Atlanto-axial joint: 10º Flexion-extension, 50º Rotation, 0º Lateral Bend
Subaxial Cervical Spine: 50º Flexion-Extension, 50º Rotation, 60º Lateral Bend
Thoracic spine: 75º Flexion-Extension, 70º Rotation, 75º Lateral Bend
Lumbar Spine: 85º Flexion-Extension, 10º Rotation, 30º Lateral Bend
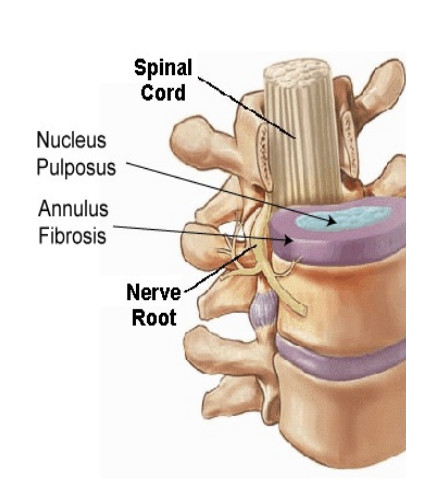
Intervertebral discs
Lie between vertebral bodies
Annulus fibrosus (fibrocartilage)
Nucleus pulposus (gel)
Functions: Stability and Cushioning
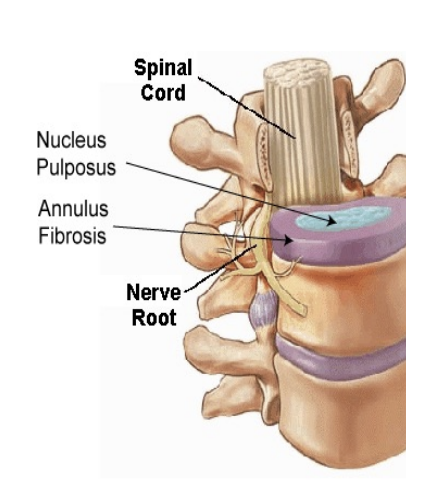
Spine Joints
Fibrocartilaginous
Between discs & vertebral bodies
Synovial
Facets joints (4 per vertebrae)
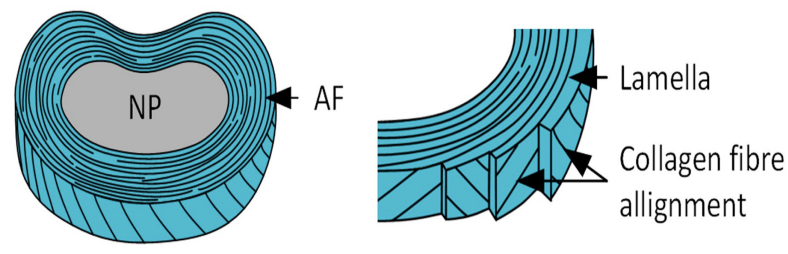
Annulus Fibrosis
Disc Annulus fibres arranged in 15-25 concentric layers
Fibres are angles
Angle changes with alternate layers (a strong configuration)
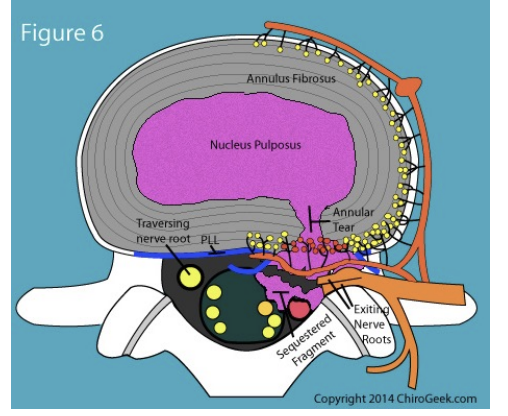
Innervation of Disc
Layers of the annulus fibrosis is thicker at front and thinner at back and collagen is a bit stronger at front and weaker at back. Outer third of disc is innervated
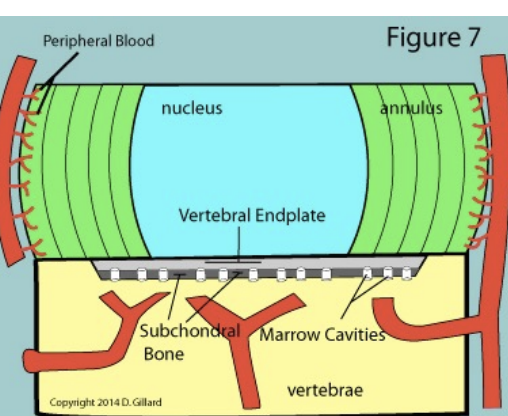
Blood Supply to Disc
Outer third of annulus of annulus fibrosis is the only good area of blood supply
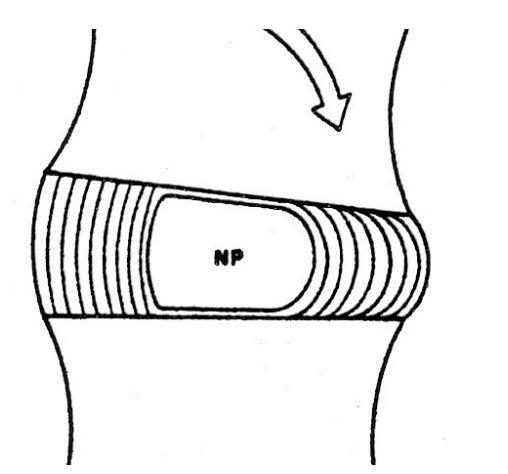
Disc Annulus fibres on bending
Stretch out and compress in on the other side
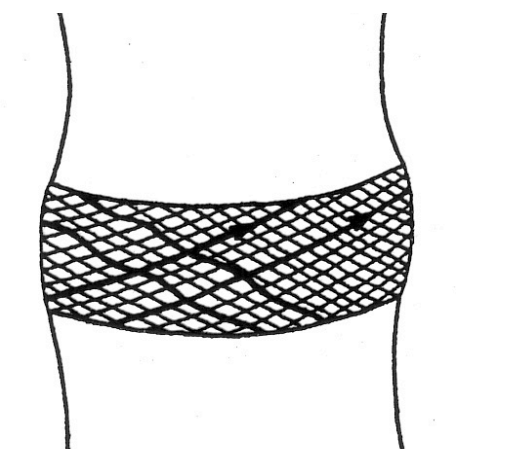
Disc Annulus fibres on rotation
Certain layers are taught and others are squished in
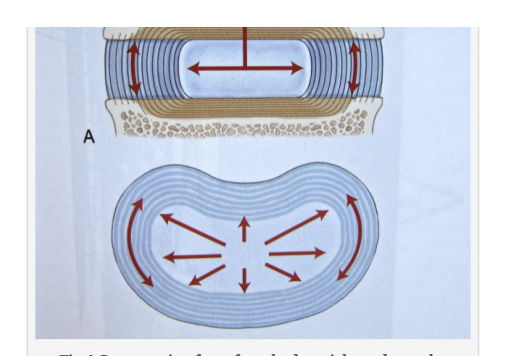
Disc Nucleus Pulposus behaves hydrostatically
Centre of disc (nucleus pulposus) is like a liquid
Liquids are incompressible, so applied load creates outward (radial) pressure in all directions inside the disc
Compressive & Radial Forces
Striped bars show vertical load
White bars show tensile stress in annulus fibrosis
For every posture, compression is << tension
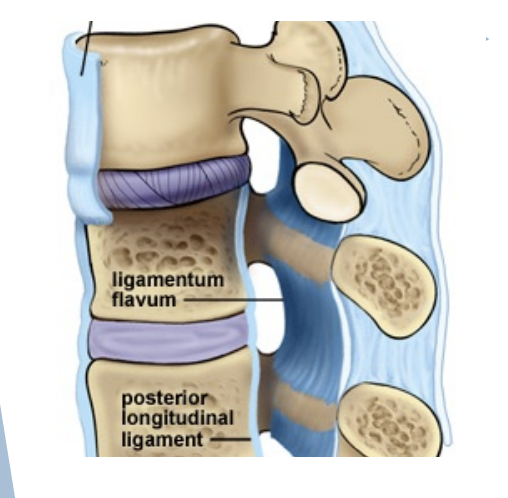
Spine Ligaments
Anterior & posterior longitudinal ligaments
Ligamenta flava
Intertransverse ligaments
Interspinous & supraspinous ligaments
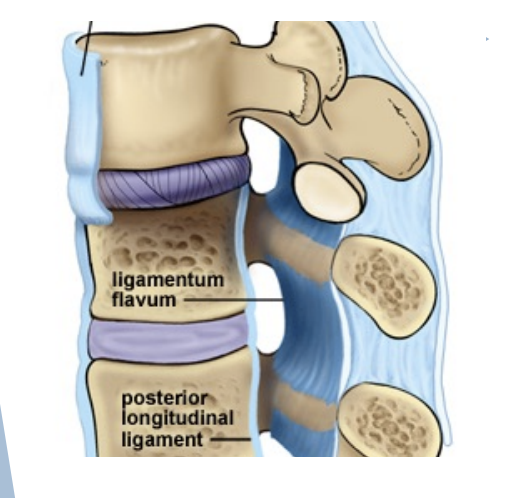
Anterior and Posterior longitudinal ligaments
Connect vertebral bodies
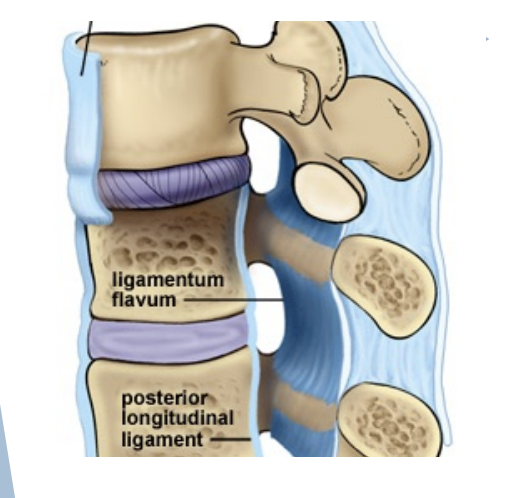
Ligamenta flava
Connect Laminae
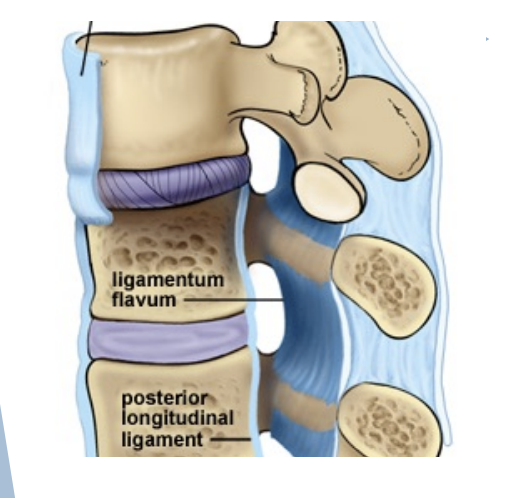
Intertransverse ligaments
Connect transverse process
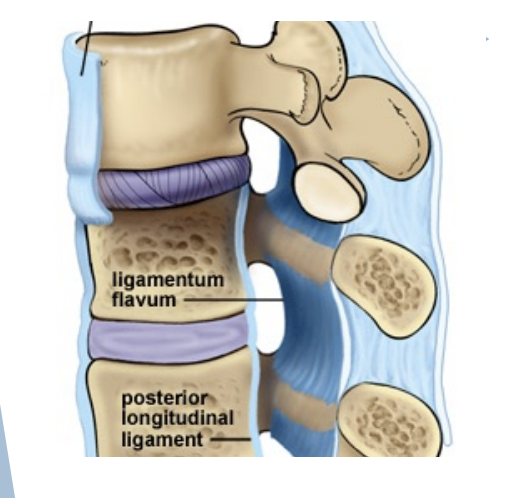
Interspinous & Supraspinous ligaments
Connect spinous processes
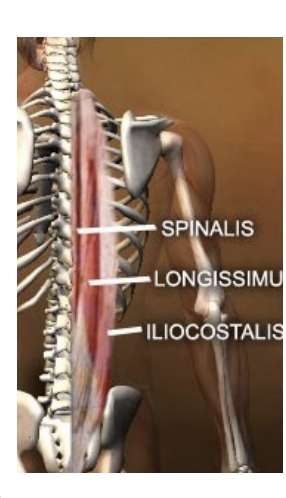
Spine Muscles
Erector spinae - superficial
Transversospinalis - deep
Many others
Spine Movements
Flexion & extension
Cervical, thoracic, lumbar
Lateral flexion (moderate)
Cervical, thoracic (minimal), lumbar
Rotation
Cervical and thoracic only
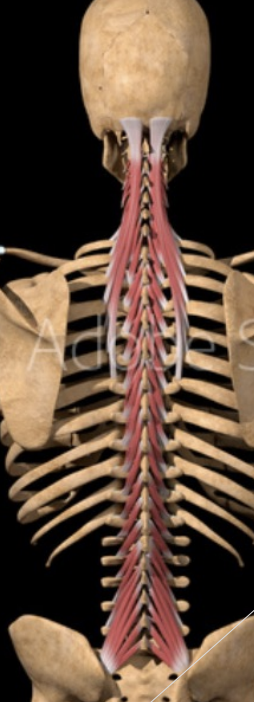
Transversospinalis Muscle Group
Smaller stabilizer muscles
Actions
Uilateral: one side
lateral flexion
turning H & N to the opposite side
Contralaterally - if contract on right, will turn to left
Bilateral: extension of spine
Muscle fibers run superiorly and medially
Spinal Nerves
Cervical nerves
Thoracic nerves
Lumbar nerves
Sacral nerves
Coccygeal nerve
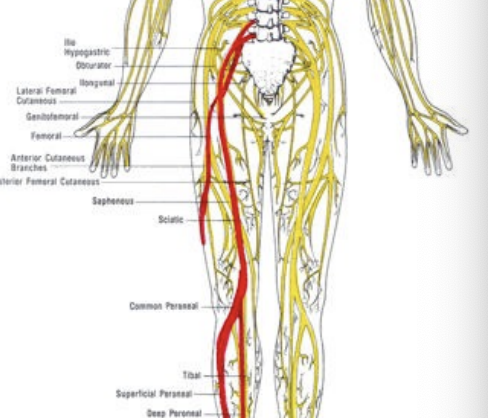
Sciatic Nerve
Arises from the spinal nerves of L4 through S3
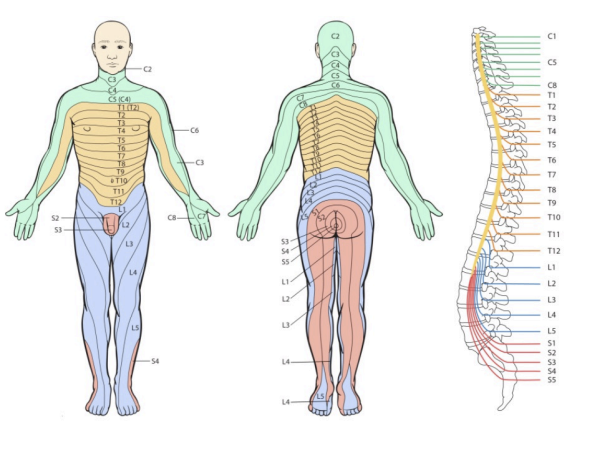
Dermatomes
Sensations + compression areas
Spine Injuries
Cause:
Congenital predispositions
Previous trauma
Mechanical factors
Poor Posture (lifting, bending)
Obesity
Acute or repetitive trauma
Effects:
Pain, tenderness, spasm, restricted ROM
Neurological SSx?
Radiating pain (scaltia)
Weakness, numbness, absent DTR(deep tendon reflexes)
Spine Sprain and Strains
Common (twisting, lifting)
Recurrence is common (lower back pain)
SSx:
Pain & Tenderness
Muscle spasm (delayed onset)
Restricted ROM (early or delayed onset)
Increased warmth towards area
If any neurologic SSx are present, assume fracture (#), dislocation or disc injury - stabilize and transport to hospital
Spine Sprain and Strains Treatment
Rest - supine - no more than 2 days
NSAID/pain medication
Cold therapy at first
Heat therapy later
Physiotherapy or massage Tx
Comprehensive, supervised rehabilitation program
Flexibility (ROM)
Strengthening (the back)
Task specific
Correct predisposing factors
Gradual return to activity
Lumbar DISC Herniation
Nucleus pulposus breaks through annulus fibrosis
Most often occurs at the L4L5 and L5S1 levels
Vulnerable between ages 30 to 50 as elasticity and water content of the nucleus pulposus decreases with age
4 stages
Protusion
Prolasped
Extrusion
Sequestered
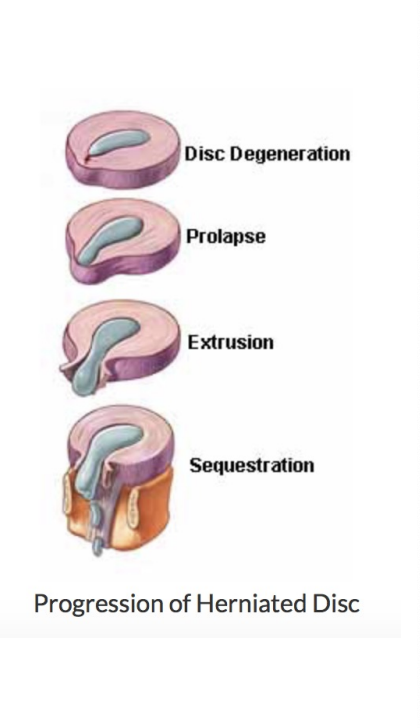
Disc Protrusion
(disc bulge) cracks in annulus fibrosis begin to appear
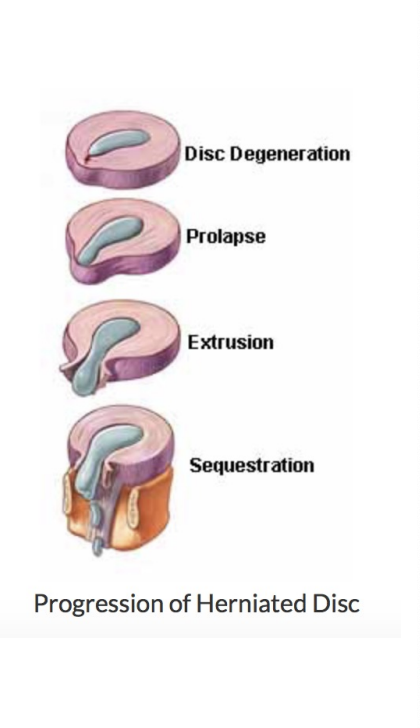
Prolasped Disc
Nucleus pulposus moves completely through annulus fibrosis
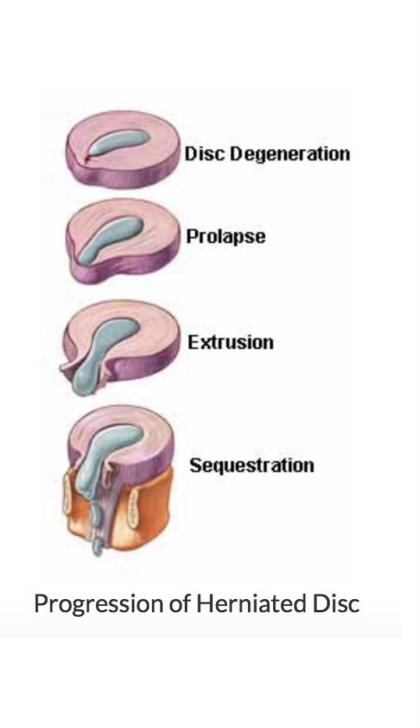
Extruded Disc
Nucleus pulposus moves into spinal canal, comes in contact with a nerve root
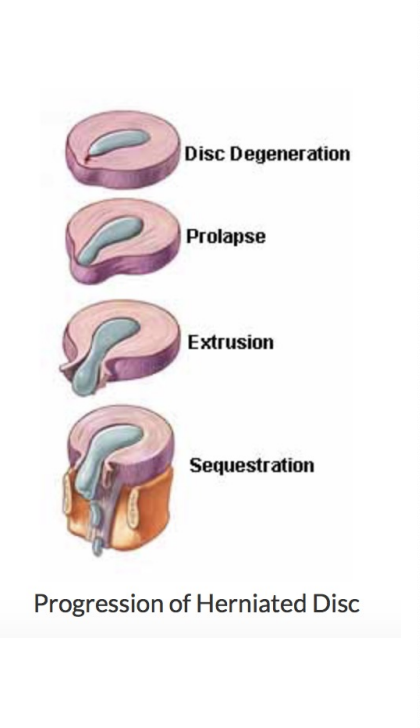
Sequestered Disc
Portion of nucleus pulposus separates from disc and begins to migrate in spinal canal
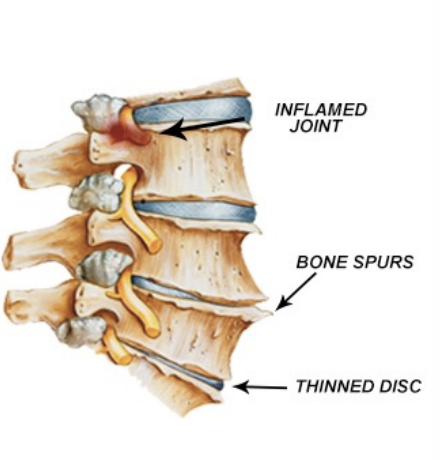
Intervertebral disc disease
As in sprains and strains
Herniation of nucleus pulposus
Compression of nerve root(s) or spinal cord
Effects:
SSx as for sprains & strains plus neurologic (e.g. sciatica)
Instability - muscles need to work harder & bone laying down more calcium
Osteoarthritis (Osteophytes, sterosis)
Tx:
Conservative if possible
Surgical (discectomy, laminectomy, fusion)
Strengthening, ROM
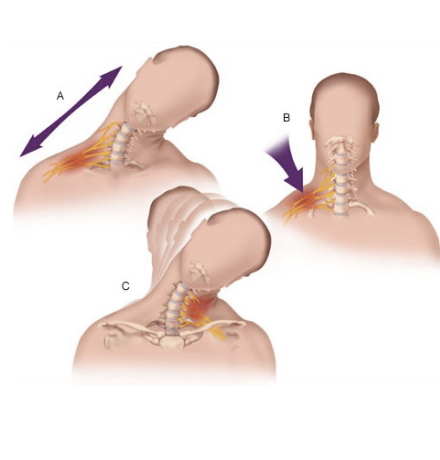
Stinger or Burner
Brachial Plexus Neuropraxia
Hx:
Stretching or compression of brachial plexus
Neck forced laterally
SSx:
Pain/ numbness into fingers, burning, numbness, tingling from shoulder to hand
Athlete may return only symptoms resolve
Tx:
Rest
If symptoms not diminishing or resolving within a few minutes (or worsening) send to hospital
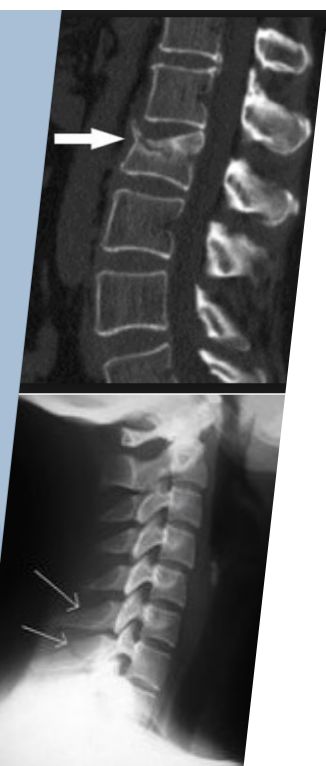
Spine Fracture (Axial Load)
Cervical spine (head into boards at hockey, helmet to helmet in football)
4th, 5th, 6th cervical vert most common
Hyperextension
SSx:
Point tenderness, decreased ROM
Pain in neck, chest, extremities
Numbness/weakness in trunk/limbs
Sore spinal process, sharp pain and very painful at specific spot
Tx:
Stabilize, c-spine collar, spine board
If unconscious, assume c-spine injury
Management of back injuries
Key is balance
Demands with functional capacity(younger players can return)
Expectations with realistic goals
Mainstays
Time! (rest, healing)
Cold, heat, NSAIDs, braces
Physiotherapy, massage therapy, chiropractic
Rehabilitation (indefinite)
Correct predisposing factors
May need to change job or sport
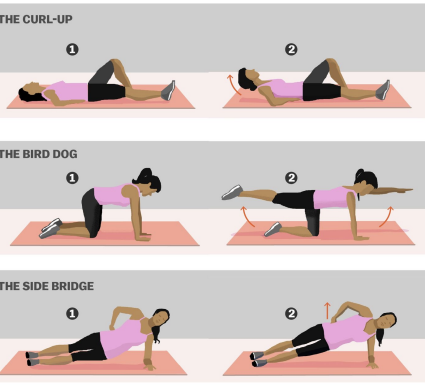
McGill Big 3
Goal is to build endurance in spinal stabilizers
Bird Dog
Trunk Raise
Side Plank
10 seconds of activity
2 seconds rest
Descending pyramid of repetitions (i.e. 8-6-4)
No sit ups
Why don’t we recommend back braces for everyday use or extended periods of time? When might use of back braces be warranted?
Muscles are working harder to resist back brace
Falsehood of belief of good use
No protective benefit → increase of injury