Life 320 exam 3
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
commensalism
one species benefits the other is unaffected
ex:hermit crab and shell
amensalism
one species is harmed and the other is unaffected
ex: penicillium
mutalism
both species benefit
ex:aphids and ants
exploitation
one organism benefits at a cost to another
communities
interactions of populations
predation
A biological interaction where one organism, the predator, hunts, kills, and consumes another organism, the prey, for food.
ex:seal and shark
parasitism
organism feeds on host, many times till death
ectoparasitism
live on or adjacent to host
ex:bed bugs
endoparasitism
live in host
ex: cymothoa exigua
herbivory
animal consuming primary producer
Grazing
under herbivory, consuming part of grasses herbs and algae
Browsing
under herbivory, consuming wood vegetation
Parasatoids
consume host, but does not kill until ready to mature
detritvores
consume dead organisms
coprophagy
eating feces or dung
competition
two or more species interact for one or more resources -/-
indirect competition
indirectly competing over resource
ex: lion vs hyena over zebra
adaptions to avoid consumption
chemically: spray fluid
Physically: spines
Psychologically
hide
run
become unpalatable
Adaptions for consumption
find:visual and chemical
herbivores: eyes side head horizontal aligned pupils
capture: chase
Eat: tear apart, swallow, digest
herbivore
what digestive system longer, herbivore or carnivore
tannis
released during chewing, bind to proteins and inhibitt digestion
terpenoids
Terpenoids are a diverse group of organic compounds found in plants. They are responsible for the distinct aromas and flavors in fruits, flowers, and herbs. OILS, LATEX, RESIN
Nitrogen compounds
morphine, nicotine, lignin, cyanogenic glycosides
constant herbivory
affects the distribution and abundance of plants
ex:elk grazing without wolves
insect outbreaks
can cause defoliations
ex:pine beatle
biocontrol
using organisms to control other species (can introduce species that take over)
ex:cactus as a fence→ bugs to eat cactus
coevolution
The reciprocal evolutionary influence between two or more species, where changes in one species lead to adaptations in the other species over time.
Pairwise coevolution
between species or populations
diffuse coevolution
between guilds or trophic levels
guild
group of species that exploit the same resource in the same way
Charles Mode
Mathematical ecologist that predicted genetic oscillations like predator-prey
red queen hypothesis
evolutionary arms race, evolutionary responses go back and forth, no one really gets an advantage
Host-virus coevolution
European rabbits and myxoma virus, 90% mortality, explosive
David Pinmentel host-parasitoid system
limited by intraspecific competition. The rapid rate of evolution which occurred was the most important aspect of the experimental parasite-host populations. Within eight generations in a 16-cell system, reproductive capacity of the parasite declined 40 per cent. In 20 generations in a 30-cell system, reproductive capacity of the parasite declined 68 per cent. Such important qualitative changes in the parasite and host populations influenced the population characteristics of the systems to some degree.
plant-insect coevolution
herbivorous insects drive natural selection for plant defenses
Plant defenses select for behaviors or detoxification mechanisms
sympatric/Sympatry
Living in the same region (SAME)
allopatry/ allopatric
living separated from each other (OTHER)
Character displacement
coevolution among competitors
trophic mutualism
partners specialized in complementary ways to obtain energy and nutrients
Defensive mutualism
one partner receives food while the other protects against herbivores/predators/parasties
dispersive mutualism
pollination and seed dispersal
ruminants
bacteria live in rumen in digestive tract and decompose cellulase
Aposematism
warning coloration denoting noxious chemicals. Accumulate chemicals from external sources
Crypsis
mimicking some part of the environment
coloration
structure
movement
chromatophores
color changing
ambush predator
blend into the environment to get prey
Batesian Mimic
non harmful modeling as harmful
~octopus playing as lion fish
Mullerian Mimic
group of unpalatable species that resemble each other
ex:stripes of bee
Wasmannian mimic
mimic organism it lives with
ex: mimic social insect species to live in their space and protection
~common in insect species
agressive mimic
mimic has characteristics of prey model
ex: flashes mating pattern of other species to attract
Vavilovian mimic
weeds that mimic crop species
Poop mimic
mimicing poop
ex: dung beatle and seed that looks like poop
brood parasitism
eggs laid in other nests where nesting bird accepts them and cares for their upbringing, often kicking out other baby birds
ex: brown headed cowbirds
Lynx-Hare
classic example of predation
Ex in class questionable because two data sets are used from different locations
really affected by:
hare populations oscillate areas where no lynx
hare pop influenced by available food and predators
Hare fecundity affected by stress
Hunting pressure
Gause Culture butterflies
bottles with refuge and no refuge for prey + immigration
=absence of refuges and immigration, both prey and predator extinct
=two could only coexist with complex dynamics of immigration
Huffaker mites and oranges
rubber balls and oranges
most arrangements= extinction
needed complex arrangement with special barriers to predators so two coexist= spatial mosaic of suitable habitats enables coexistance
Sustained oscillations

Lotka-Volterra Model
R=prey pop size
r=exponential growth rate
P= pred pop size
RP=# pred-prey interactions
c=capture efficiency
cRP= overall capture rate
a=assimilation efficience
acRP=predator birth rate
dP= externally imposed death rate
equilibrium pred: r/c equilibrium prey: d/ac
Oscillation time=2pi sqrt rd
prey isocline
know pred isocline and put together circle
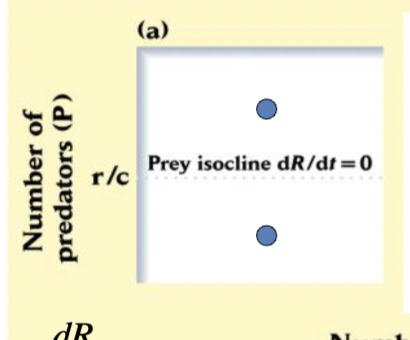
Lotka Volterra model dynamics
CYCLES natural part of model
extinction possible for high rates of capture
equilibrium are UNSTABLE=no constant population size
Cycle is neutrally stable
Predator-Prey Stability
stability in these =reduced oscillation
Reduce amplitude
reduced predator efficiency/prey escape
External density-dependent constraints on either predator or prey
Alternate food sources for predator
Refuge for prey at low densities
Reduced lag between prey abundance and predator response
L-V model more realistic
Spatial realism (metapopulation, immigration to predator free)
More sophisticated ways to think about feeding (multiple prey items)
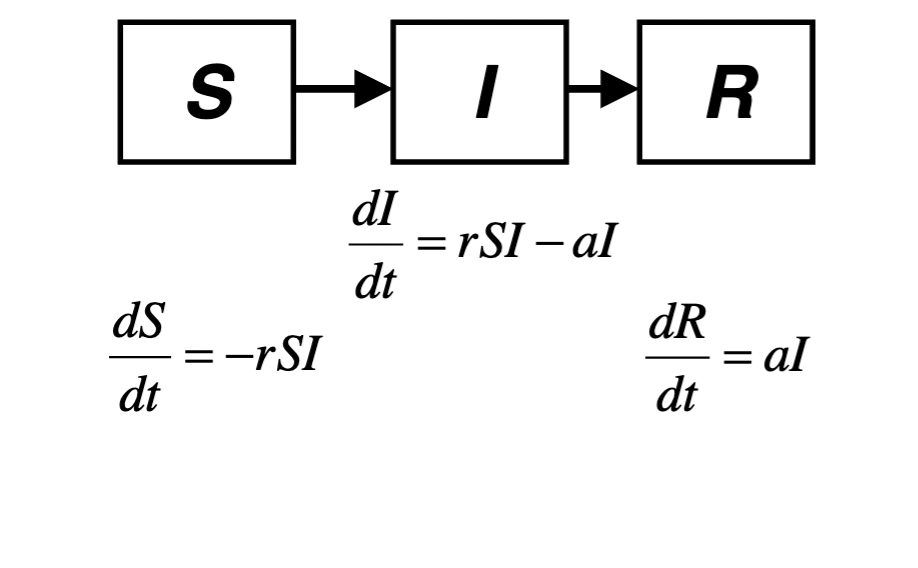
SIR model
Susceptible, infected recovered
r= transmission rate
a=recovery rate
S initial<a/r = epidemic die out
small a/r = slow recover, fast transmission
threshold phenomenon: virulence/persistence tradeoff
S (SIR)
Susceptible individuals: capable of contraction
vaccination can reduce # of susceptible
I (SIR)
Infected: have the disease and can give it to other S individuals
R (SIR)
Resistant: can non longer acquire the disease
Competition
use or defense of a resource by one individual that reduces that availability of that resource to other individuals
intraspecific competition
comp among the same species
interspecific competition
comp among different species
lower resource levels
Superior species survive at ____
David Tilman
author defines resources as
something that can be consumed and have its amount reduced (food)
consumers use resources for maintenance & growth
when its availability is reduced, biological processes are affected, reducing population growth
Nonrenewable
Can’t regenerate. Space
renewable
regenerate.
external: sunlight
direct internal: prey
indirect internal regeneration: nutrients released during decomp. important in nature
limiting resource
resource that restricts growth. Often co-limitation by multiple resources
Competition exclusion principle
two species can’t coexist indefinitely on the same limiting resource
(same space for same resource)
ex: separate from each other grow similar in space, but together one outcompete in a space
logistic growth
intraspecific competition
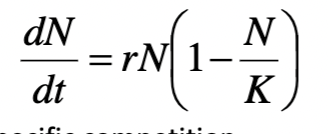
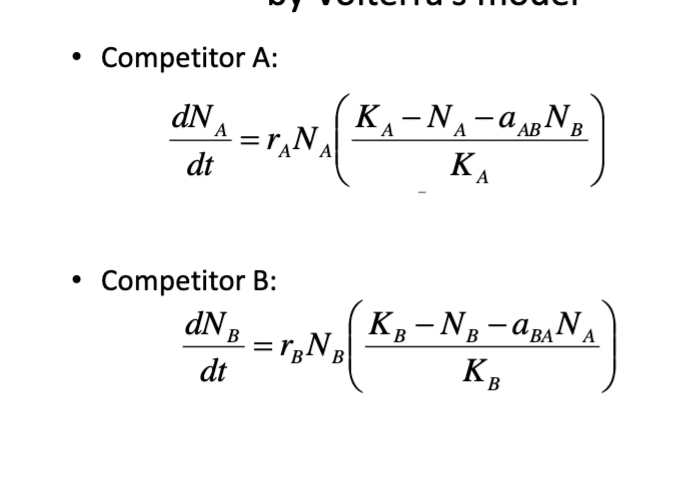
Volterra’s Competition model
coexistence occurs when a<1 (inter weaker than intra)
when species not competing for resource at the same time/place/way
a=interspecific
COMPETITION VARIES DEPENDING ON THE SYSTEM
Evidence for light competition
forest canopies
tall growth
broad leaves
vertical leaf orientation
nutrient competition
deep roots
symbiotic fungi
nutrient storage
exploitation competition
indirect competition through mutual effects on shared resources
interference competition
consumers profitable defend resources through antagonistic behaviors
Allelopathy
release of chemicals to affect the outcome of competition
ex:sage brush release compounds reducing seed growth and germination
Muller shrub
small animals live under shrubs and forage close yielding ring around (not allelopathy)
Connell barnacles
two compete for same space. Removing one allows other to grow there, but with the other there can’t grow
Sea stars lower tide predator (Paine)
asymmetric competition
competitors co-exist locally, but on different microhabitats
superior competitor for resources is almost always limited by some other factor
environmental stress
predators
Organism absent or rare
competition
who the comp is
what is resource
removal of competition
adding resources
Community ecology
study of a unit that arises from the interaction of populations
community
assemblage of species that live in the same place
close community
coevolution among members is prominent
Clements
holistic concept
community is a super organism whose functioning can only be appreciated when it is considered as an entire entity
Clements
Clements Community Vegetation grows in community groups
Vegetation grows in community groups that are cohesive and distinct
“Holistic concept” a community is a superorganism whose functioning can only be appreciated when it is considered as an entire entity.
The functions of various species are connected like parts of the body, and have evolved to enhance interdependent functioning.
“Closed community” where coevolution among members is prominent
Gleason Community
Community is a fortuitous association of species whose adaptations and requirements enable them to live together under the physical and biological conditions that characterize a particular place.
“Individualistic concept” that organization is absent above the species level
“Open community” where coevolution is uncommon & diffuse
individual concept
organization is absent above the species level
Gleason
Open community
coevolution is uncommon and diffuse
Gleason
ecotone
Transition zone between two different ecosystems where species from both ecosystems coexist and interact. Ecotones have higher biodiversity and unique species adapted to the unique conditions found in this zone. They play a crucial role in supporting ecological resilience and facilitating the movement of species.
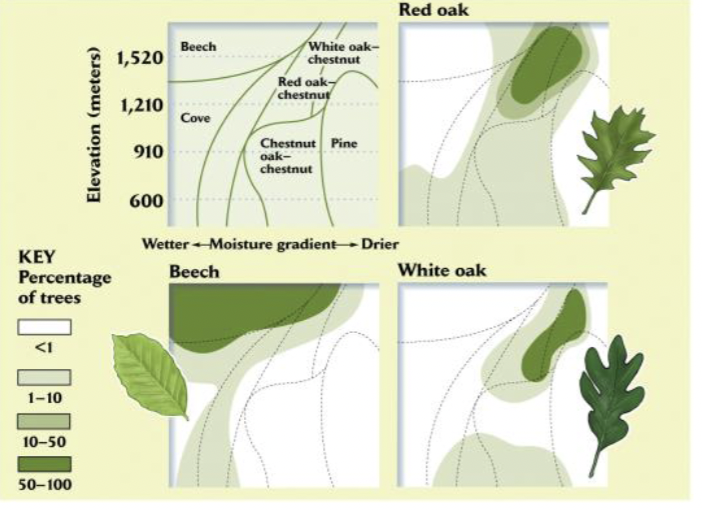
Whittaker
PUTS CLEMENTS VIEWS to REST
species are independently distributed, not in groups as predicted by Clements
Ecotones
We still name communities by their dominant vegetation, but recognize that plants and animals are widely, independently distributed
Graph Theory
set of nodes and edges that connect nodes
each species=node
interactions=edges
Simple graph no loops (like cannibalism or decomposers of own species)
path=sequence of nodes connected by edges that do not have a node appear more than once
Food Chain
path in the food web that has as its end nodes one that is a producer and one that is a consumer that is not prey to another node
keystone species
exert strong control on community composition and function
ex: sea urchin, sea otter, kelp forest
HSS hypothesis
earth is green because carnivores depress the populations of herbivores that would otherwise eat all the plants
ex:lakes ~ sea algae daphnia fish bigger fish
Top-down
ARGUE AGAINST: food webs much more complex
Top-down control
predators exert control on levels below
ex:zooplankton+chlorophyll+ w/ w/out fish