Linear Midterm 1 Theorems and Definitions
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Elementary Row Operations
1. Replacement: Replace one row by the sum of itself and a multiple of another row
2. Interchange: Switch any two rows
3. Scaling: Multiply all entries in a row by a nonzero constant
A rectangular matrix is in echelon form (or row echelon form) if it has the following three properties
1. All nonzero rows are above any rows of all zeros.
2. Each leading entry of a row is in a column to the right of the leading entry of the row above it.
3. All entries in a column below a leading entry are zeros.
If a matrix in echelon form satisfies the following additional conditions, then it is in reduced echelon form (or reduced row echelon form)
1. The leading entry in each nonzero row is 1.
2. Each leading 1 is the only nonzero entry in its column.
What is a pivot position?
A location (entry) of matrix A that corresponds to a leading entry in reduced echelon form
What is a linear combination?

Definition of Span
Conceptually, everywhere we can get to in Rn by traveling in the directions of v1, v2, … vp

Ax = b
The linear combination of matrix A, with columns a1…an, and vector x in Rn is Ax = b
Let A be an M x N matrix. Then the following statements are logically equivalent. That is, for a particular A, either they are all true statements or they are all false.
1. Ax = b has a solution for any b
2. Each b in Rn is a linear combination of the columns of A
3. The columns of A span Rn
4. The matrix A has a pivot position in every row
Properties of Matrix Multiplication
A(u+v) = A(u) + A(v)
A(cu) = cA(u)
Homogeneous
Ax = 0
Nonhomogeneous
Ax = b for nonzero b
Linear Independence
An indexed set of vectors {v1...vp} in R^n is said to be linearly independent if the vector equation x1v1 +...+ xpvp= 0 has only the trivial solution x1 = x2 = xp = 0
Linear Dependence
An indexed set of vectors {v1...vp} in R^n is said to be linearly dependent if the vector equation x1v1 +...+ xpvp= 0 has at least one nontrivial solution (at least one xi =/ 0)
Linearly Dependent Sets
1. A set of vectors S = {v1,v2, … vp} is linearly dependent if and only if one of the vectors in the set is a linear combination of the others.
1. If a set has more columns than rows, then the set is linearly dependent. That is, any set S = {v1,...,vp} in R^n is linearly dependent if p>n
2. If a set S = {v1,...,vp} in Rn contains the zero vector, then the set is linearly dependent
Matrix Tranformation
A transformation (or function or mapping) T from Rn to Rm is a rule that assigns to each vector x in Rn a vector T (x) in Rm
Domain of T
The set Rn
Codomain of T
The set Rm
Range of T
The set of all images T(x)
T: Rk → Rm is a Linear Transformation if:
T(x+y) = T(x) + T(y) for all x,y in Rk
T(cx) = cT(x) for all x in Rk, c in R
Image
For x in R^n, the vector T(x) in R^m
If T is a linear transformation, then what is true?
T(0) = 0
T(cu+dv) = cT(u) + dT(v)
The Matrix of a Linear Transformation
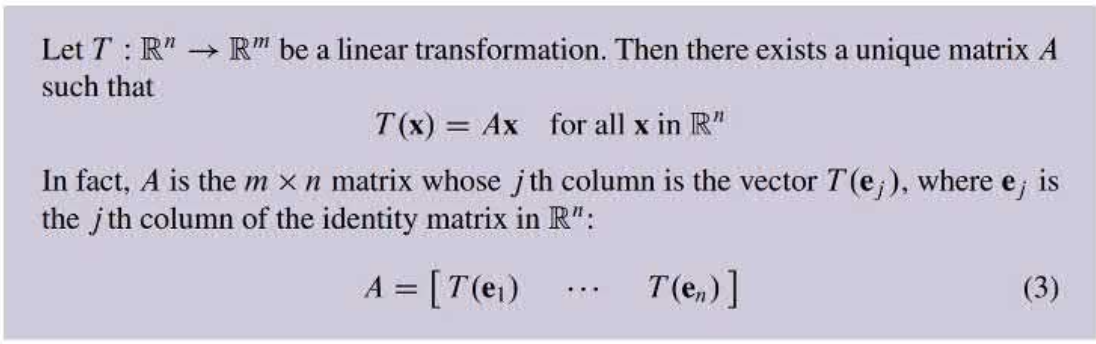
A matrix transformation T: Rn → Rm is one to one if:
T(a) = T(b) → a = b
“No target is hit more than once”
A matrix transformation T: Rn → Rm is onto if:
If each b in Rm is the image of at least one x in Rn. A transformation is not onto when there is some b in Rm for which T(x) = b has no solution.
“Every target is hit at least once”
Properties of a one to one transformation T: Rk → Rn
MT = [T(e1) … T(ek) ] = 0 has 0 free variables
MT has a pivot in every column
n >= k
Properties of an onto transformation T: Rk → Rn
T(x) = b is always solvable
MTx = b is always consistent
Augmented matrix of MT and b has no pivot in the last column for any b
MT has a pivot in every row
n <= k