Gravitational fields
1/31
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What is a gravitational field?
A field created around any object with mass, extending all the way to infinity, but diminishing as the distance from the centre of mass of the object increases
What is a radial field?
A symmetrical field that diminishes with distance2 from its centre, such as the gravitational field around a spherical mass or the electrical field around a spherical charged object
What is a uniform field?
A gravitational field in which the field lines are parallel and the value for g remains constant
What is a point mass?
A mass with negligible volume
Define gravitaional field strength
The gravitational force exerted per unit mass on a small object placed at that point within the field.
What are gravitational field lines?
Lines of force used to map the gravitational field pattern around an object having mass
What is Newton’s laws of gravitation (in words)
The force bewtween two point masses is:
Directly proportional to the product of the masses, F ∝ Mm
Inversely proportional to the square of their separation, F ∝ 1/r2
What is Newton’s laws of gravitation (equation)
F = -GMm/r2
A minus sign is required to show that gravitational force is an attractive force.
What is the gravitational constant?
The constant in Newton's law of gravitation, with a value determined from experiment of 6.67 x 10-11 Nkg-2m2
Kepler’s 1st law
Each planet moves in an elliptical orbit with the sun at one of the two foci
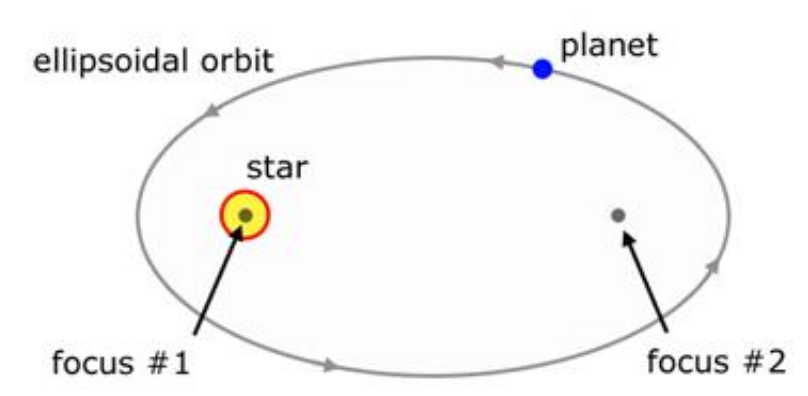
Kepler’s 2nd law
A line segment joining a planet and the sun sweeps out equal areas during equal intervals of time
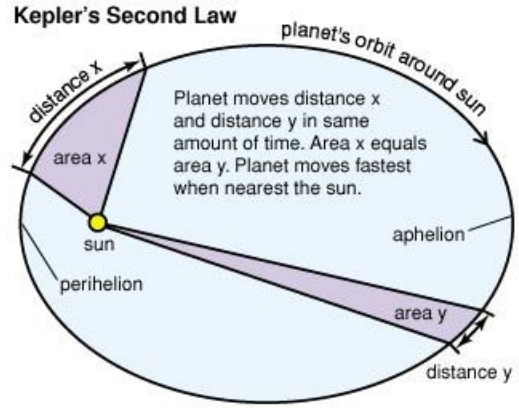
Kepler’s 3rd law
The square of the orbital period of a planet, T, is directly proportional to the cube of its average distance, r, from the sun (can also be applied to satellite orbits) i.e. T2 ∝ r3 or T2/r3 = k
How do you derive Kepler’s 3rd law?
Assume that the planetary orbit is circular.
Centripetal force required to keep planet in orbit is provided by gravitational force between the sun and the planet (or planet and satellite).
The mass of the orbiting planet (or satellite) cancels so the relationship is INDEPENDENT of this.
You can substitute linear velocity with v = 2πr/T
All things in the equation (apart from T and r) are constants so you can rearrange.
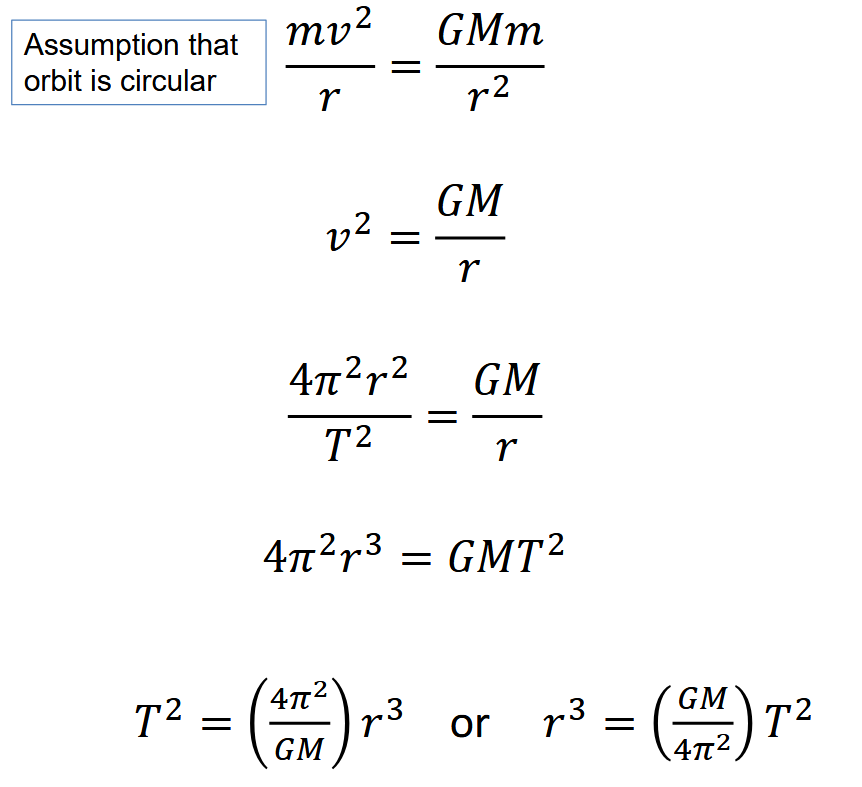
What is the equation for the time period of an object in orbit, and what do the terms mean?
T2 = (4π2 / GM) r3
T is the time period of the orbit
G is the gravitational constant
M is the mass of the object creating the gravitational field
r is the (average) radius of the orbit
What are the two equations for linear velocity of an object in orbit, and what do the terms mean?
v = √( GM / r )
v = 2πr / T
v is the linear velocity
G is the gravitational constant
M is the mass of the object creating the gravitational field
r is the (average) radius of the orbit
T is the time period of the orbit
How do you derive the equation involving M for the speed of an object in orbit?
The centripetal force required to keep planet in orbit is provided by gravitational force between the planet (or sun) and object, so mv2 / r = GMm/ r2
Rearrange and cancel out m to get v2 = GM / r
As such v = √(GM / r)
How do you derive the equation involving T for the speed of an object in orbit?
Assuming the object is circular, it will have a constant speed.
This means speed = distance travelled / time taken
The circumference of one full orbit is 2πr, and this takes one time period (T) to complete
As such v = 2πr / T
What is gravitational potential?
The work done per unit mass to bring an object from infinity to a point in the gravitational field, unit J kg-1
How does the gravitational potential vary between the Earth and Moon?
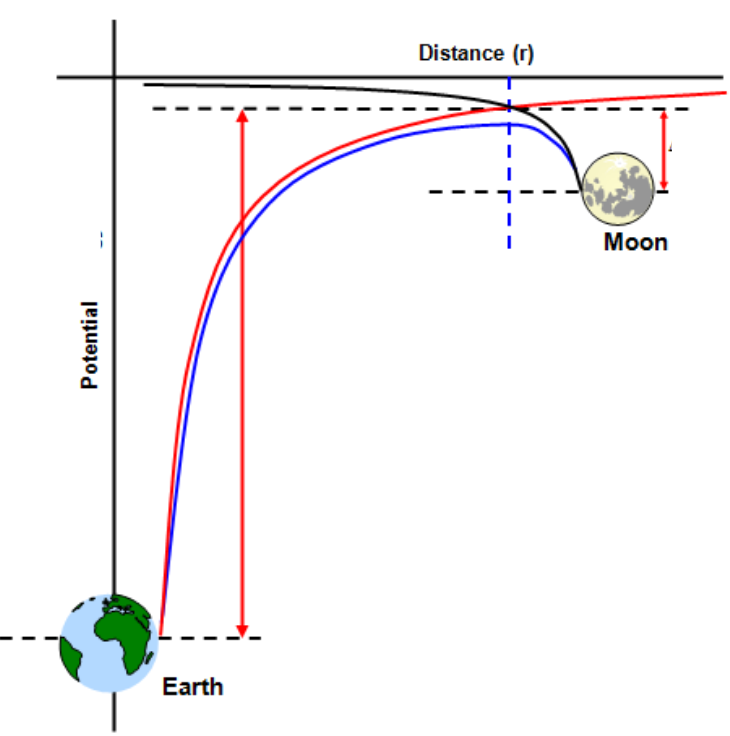
Define gravitational potential energy
The work done (by the gravitational field) to move a mass/object from infinity to a point in a gravitational field.
What is the equation for escape velocity, and what do the terms mean?
𝑣 = √ ( 2𝐺𝑀 / 𝑟)
v is the escape velocitys
G is the gravitational constant
M is the mass of the planet/object creating the gravitational field
r is the radius of the planet
How do you derive the equation for escape velocity?
If a mass is given kinetic energy greater than the GPE it has on a planet’s surface then it can be moved to infinity (i.e. it can completely escape the gravitational field). As such:
½𝑚𝑣2 = 𝐺𝑀𝑚 / r
Rearrange to get escape velocity, 𝑣 = √( 2𝐺𝑀 / r)
Since the m (mass of the object) cancels out, the escape velocity is the same for ANY mass on a given planet.
What is the eqaution for gravitational field strength in terms of F?
g = F / m
g is gravitational field strength at the point
F is the graviational force that would act on an object of mass m at that point
m is the mass of the object that the graviational force acts on
What is the eqaution for gravitational field strength in terms of r, and what do the terms mean?
g = - GM / r2
g is gravitational field strength at the point
G is the graviational constant
M is the mass of the object creating the gravitational field
r is the radius of the point from the object’s centre.
What is the equation for graviational force acting on an object, and what do the terms mean?
F = - GMm / r2
F is the graviational force acting on the object
G is the graviational constant
M is the mass of the object creating the gravitational field
m is the mass of the object in the gravitational field
r is the distance from the object in the gravitational field to the centre of the object creating the gravitational field
What is the equation for graviational potential, and what do the terms mean?
Vg = - GM / r
Vg is the gravitational potential at a specific point in a gravitational field
G is the gravitational constant
M is the mass of the object creating the gravitational field
r is the distance from the centre of the objecrt creating the gravitational field
What is the equation for graviational potential energy, and what do the terms mean?
energy = - GMm / r
energy is the gravitational potential energy
G is the gravitational constant
M is the mass of the object creating the gravitational field
m is the mass of the object in the gravitational field. This equation finds the GPE of this object
r is the distance from the object in the gravitational field (mass m) to the centre of the object creating the gravitational field (mass M)
What is a satellite?
A body orbiting around planet
What is a geostationary satellite?
A satellite that remains in the same position relative to a spot on the Earth's surface, by orbiting in the direction of the Earth's rotation over the equator with a period of 24 hours
What is an advantage of a geostationary satellite?
You always know where the satellite is in the sky so antennae receiving a signal (e.g. satellite TV) can be positioned and receive a constant signal
How do you find the total energy of a satellite?
Total Energy = KE + GPE
It is important to keep GPE as a negative value when adding to KE
How do the total energy, GPE and KE of a satellite vary with respect to each other?
The total energy of a satellite remains constant (providing no rocket boosters are used)
As the GPE increases, the KE decreases and vice versa