Observation and Cognition
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
skin
what is the largest organ in the body?
edema
observation of skin gives preliminary data about:
CV and pulmonary systems
inflammation and ____
infection (redness/swelling)
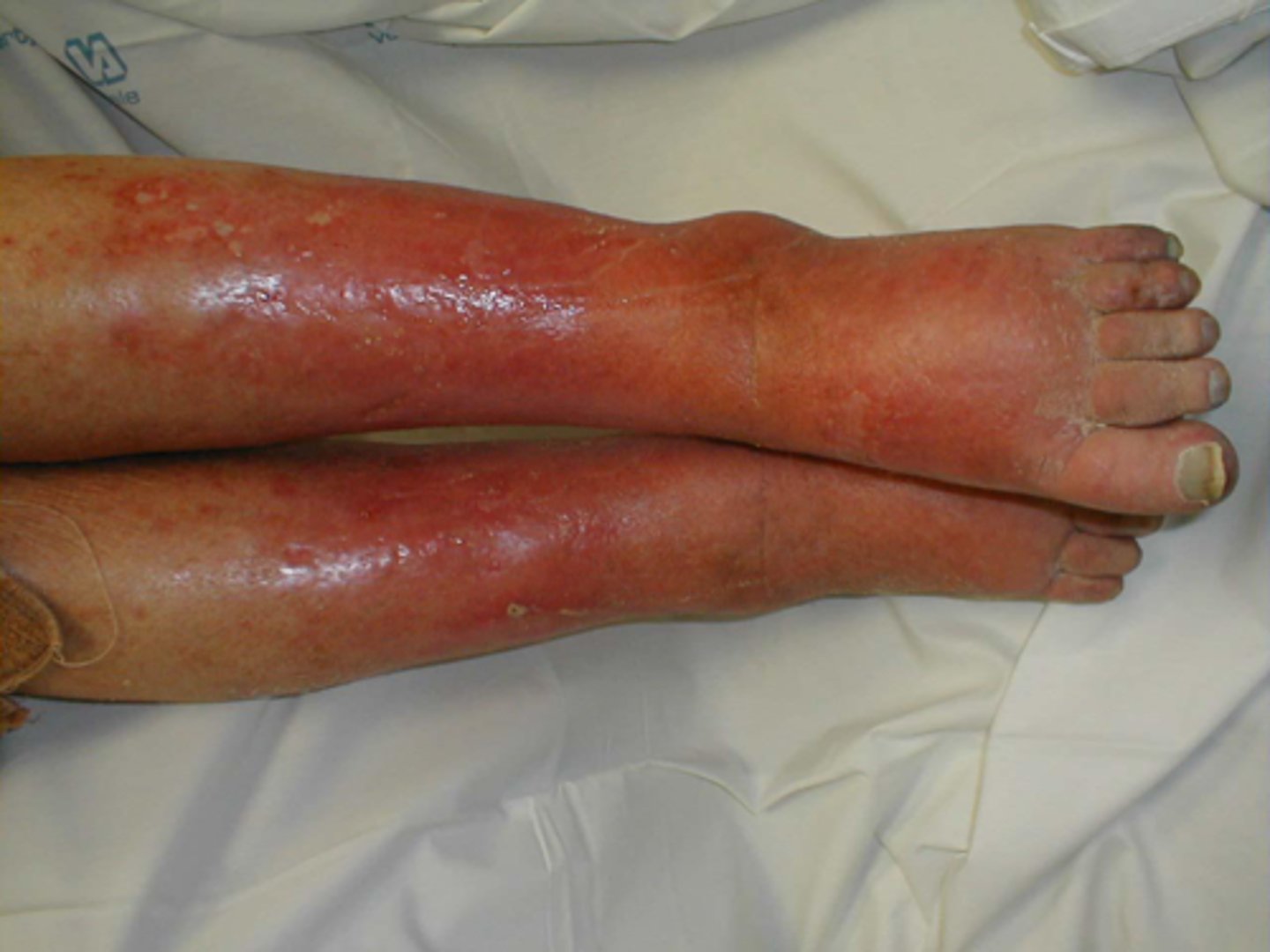
Cellulitis
a common bacterial infection of the skin and underlying tissues.
It causes redness, swelling, pain, and warmth in the affected area.
typically occurs when bacteria enter the skin through a cut, scratch, or other break in the skin.
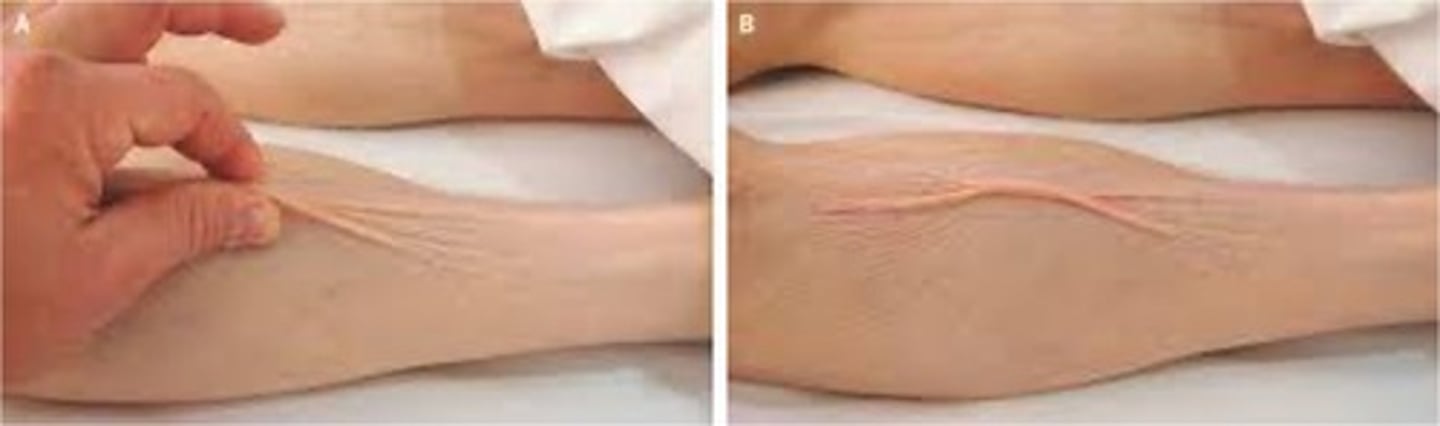
extensibility
ability to be stretched
dehydration
tenting of the skin on the hand can signify ____
soles; palms
hair is normally found over the entire body except on the ____ of the feet, ____ or the hands and portions of the genitalia
alopecia
hair loss
can be associated with disease or medication side effect
can be associated with aging, but typically only in the frontoparietal scalp (any other areas are a concern)
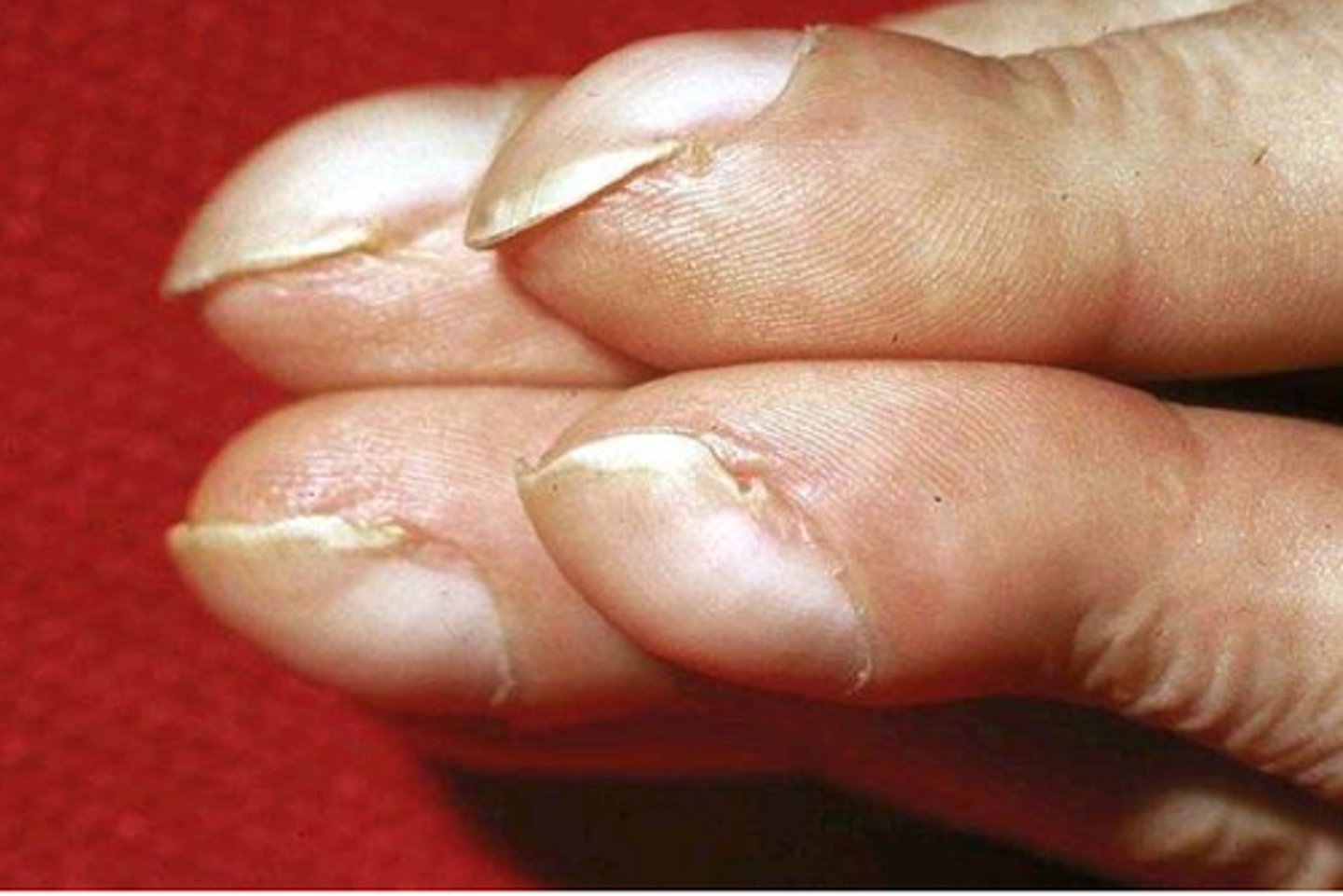
clubbing
bulbous fingertips with loss of normal nail plate angle
nails may be cyanotic and spongy
caused by long term hypoxia due to CP diseases such as congenital heart defects and CF
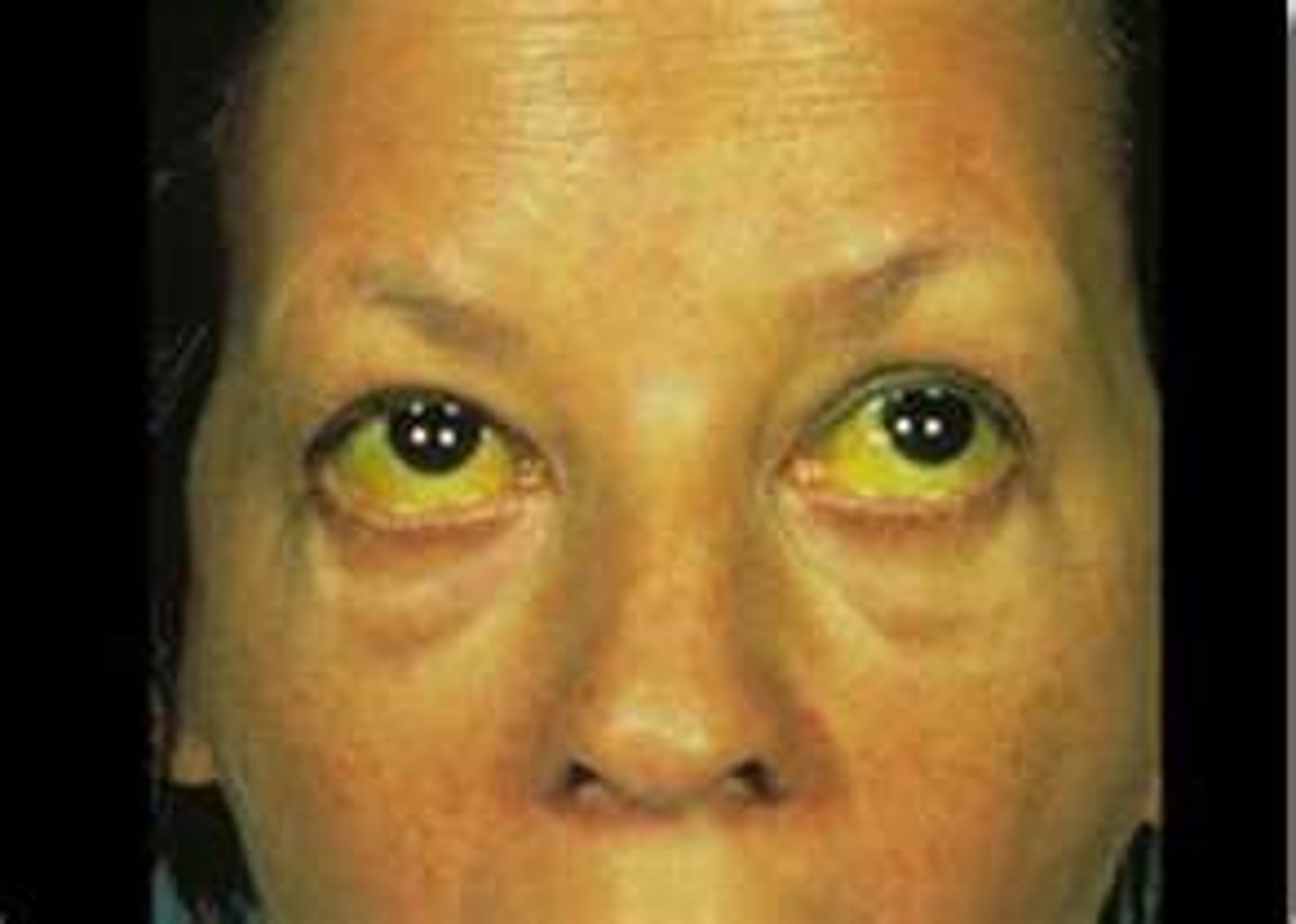
jaundice
yellow discoloration of sclera, skin, and mucous membranes
associated with excessive levels of bilirubin
pallor
paleness associated with decreased levels of oxyhemoglobin and local blood flow
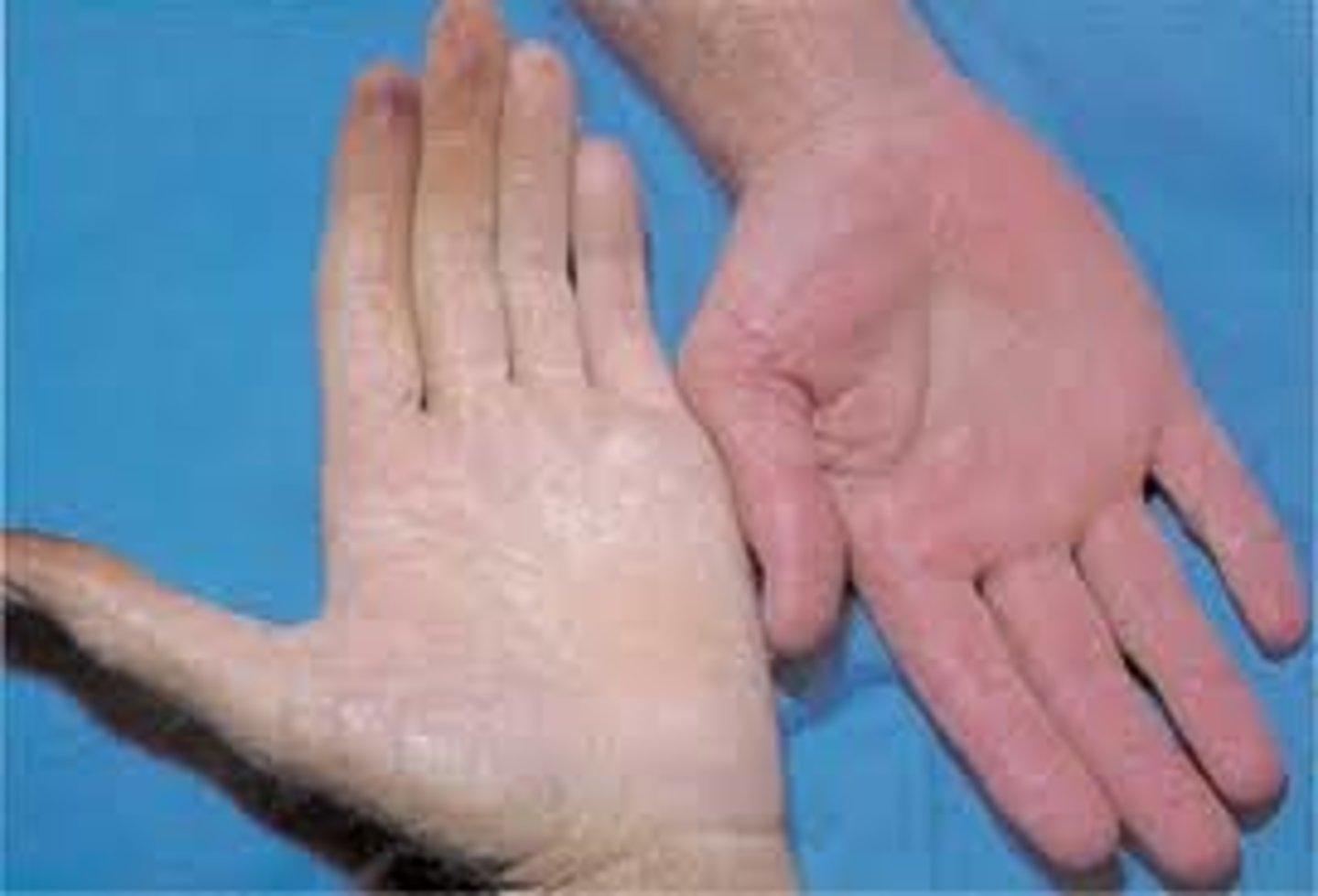
ecchymosis
a discoloration of the skin resulting from bleeding underneath, typically caused by bruising.
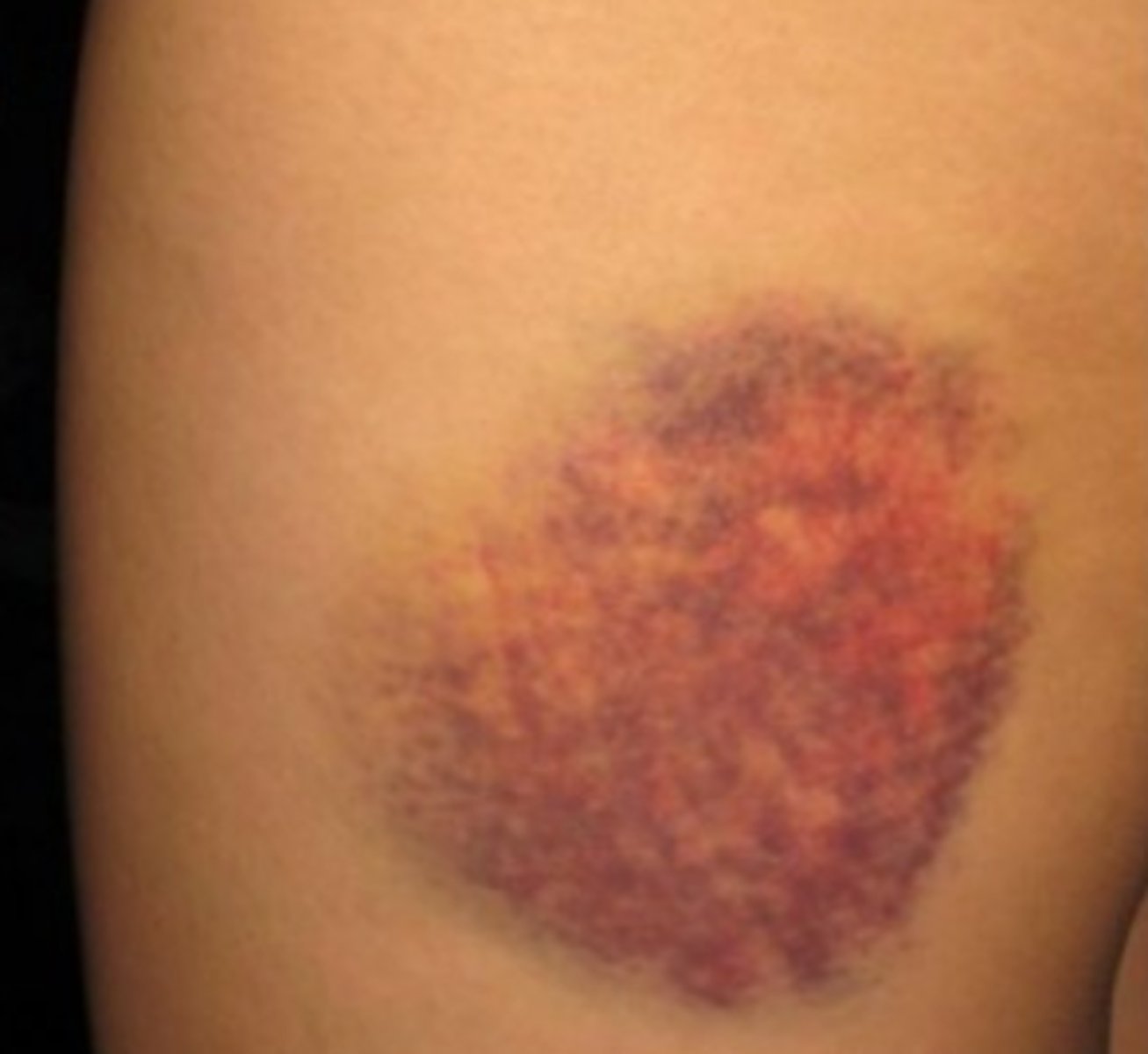
erythema
reddened area of the skin caused by increased blood flow
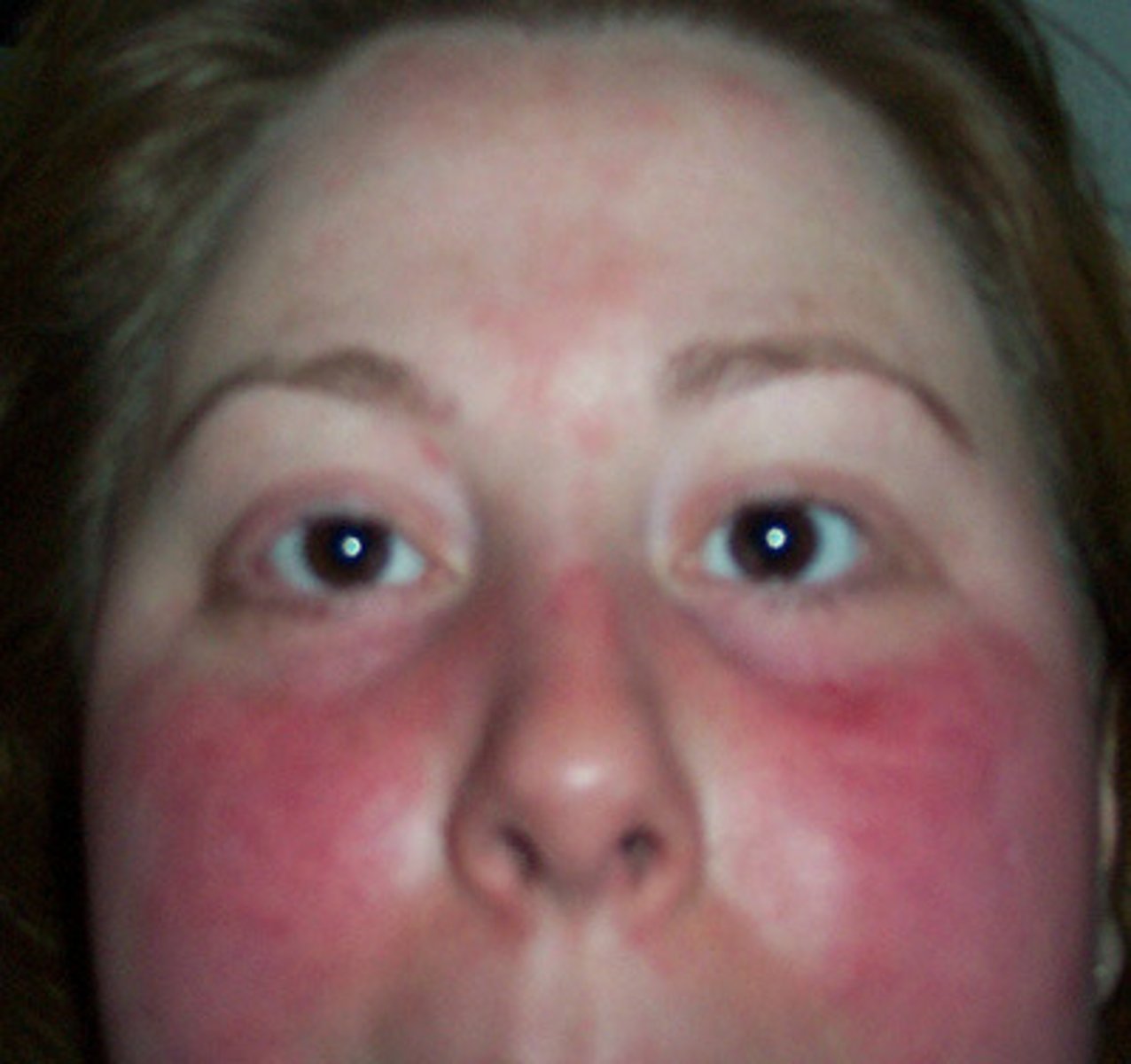
flushing
diffuse redness of the face or another area of the body
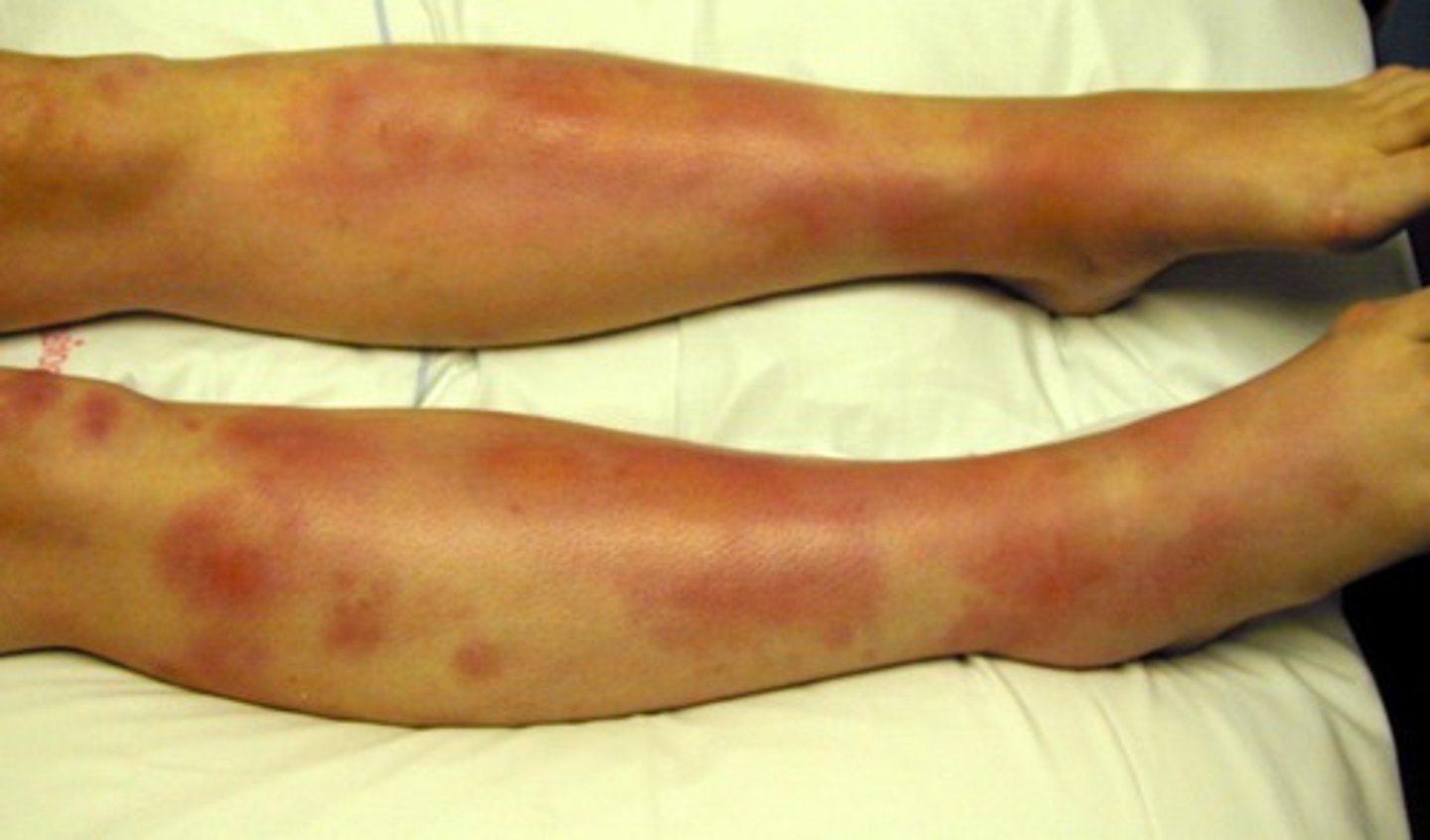
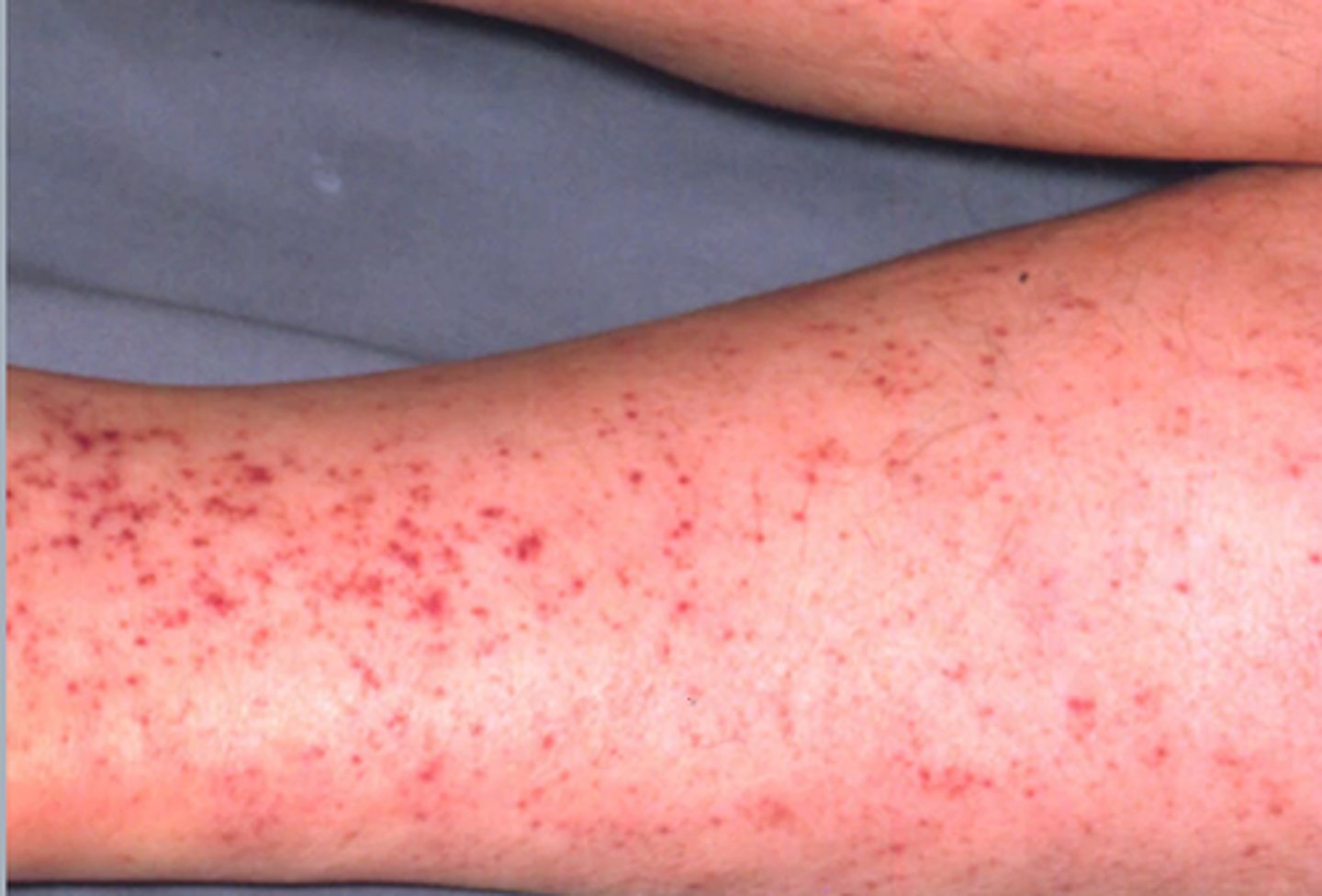
petechiae
tiny red or purple hemorrhagic spots caused by capillary bleeding with subsequent leakage of blood into the skin
can be the sign of something minor or major or a reaction to a medication
central cyanosis
diffuse skin color changes in central aspects of the body (head, trunk) as well as color changes in mucous membranes
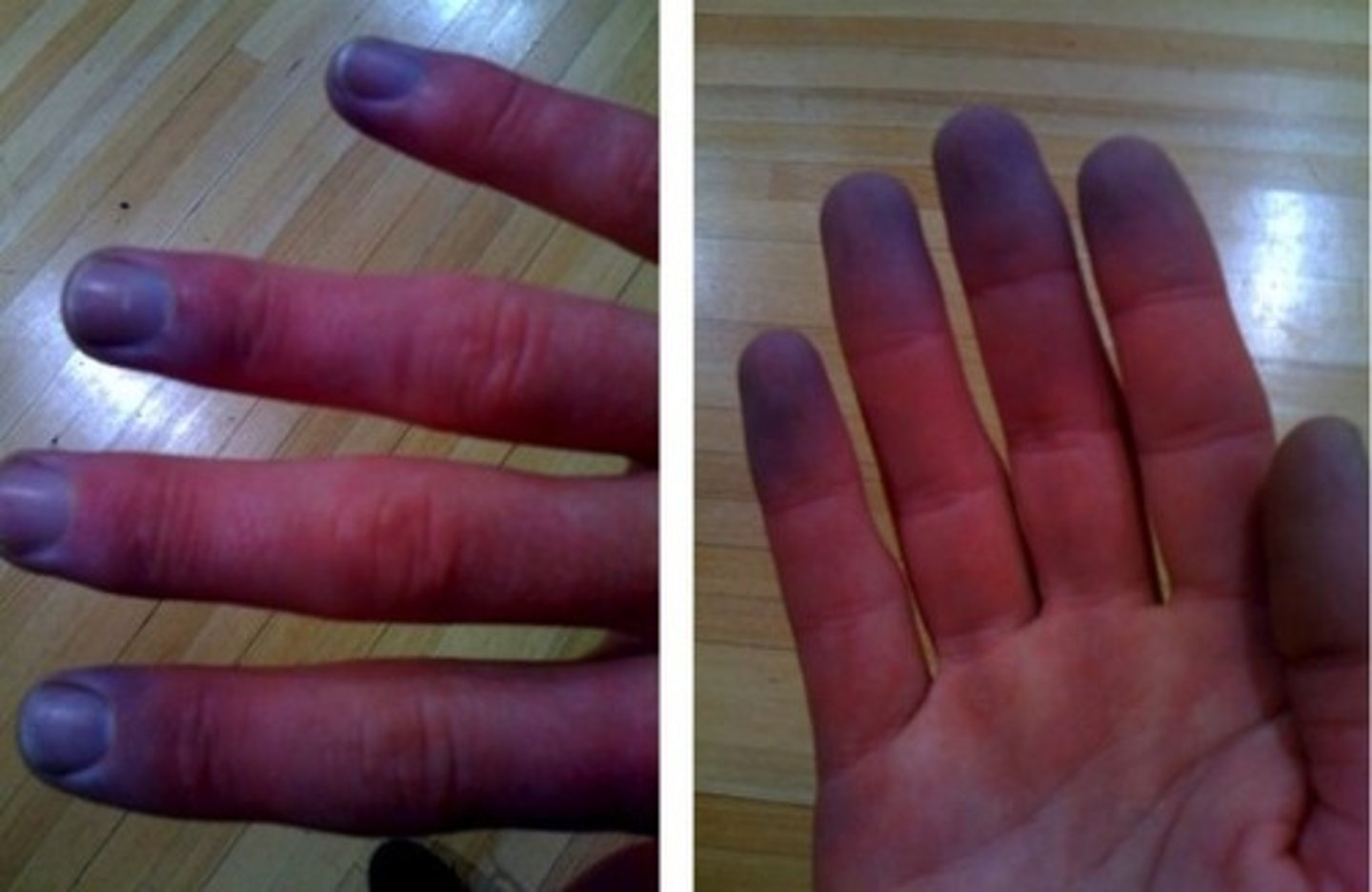
peripheral cyanosis
color changes in nail beds and lips owing to decreased cardiac output, exposure to cold, or arterial/venous obstruction

infectious reasons for petechiae
- endocarditis
- meningococcemia
- mononucleosis
- rocky mountain spotted fever
- scarlet fever
- sepsis strep throat
- viral hemorrhagic fevers
- other medical conditions
noninfectious reasons for petechiae
- leukemia
- vasculitis
- thrombocytopenia
- scurvy (vitamin C deficiency)
- vitamin K deficiency
UMN lesions
MORE (unregulated innervation)
spasticity
hyperreflexia
positive babinski (toes point up)
clonus
weakness and atrophy (disuse)
>
with an UMN lesion the flexors ___ the extensors in the LEs
>
with an UMN lesion the extensors ___ the flexors in the UEs
LMN lesions
LESS
hypotonia or flaccidity
hyporeflexia
weakness and atrophy (denervation)
fasciculations
negative babinski (toes point down)