DNA, Mutations, the Cell Cycle & Cancer 2026
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

42 Terms
mutation
a change in the nucleotide-base sequence of a gene or DNA molecule
mutagen
something that CAUSES mutations (for example, radiation)
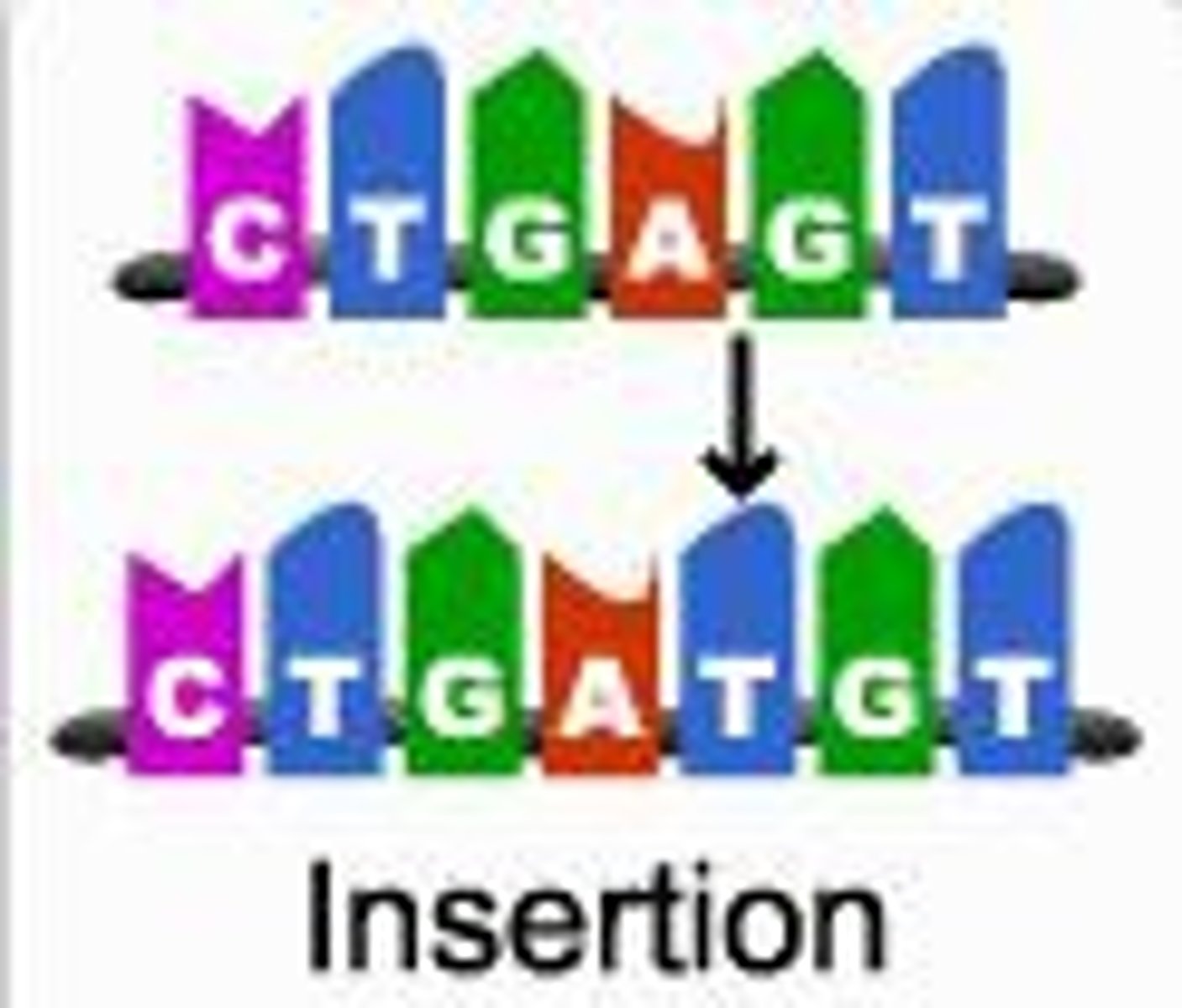
insertion mutation
change in DNA in which a nucleotide is added
deletion mutation
change in DNA in which a nucleotide is lost

substitution mutation
change in DNA in which a single nucleotide is replaced

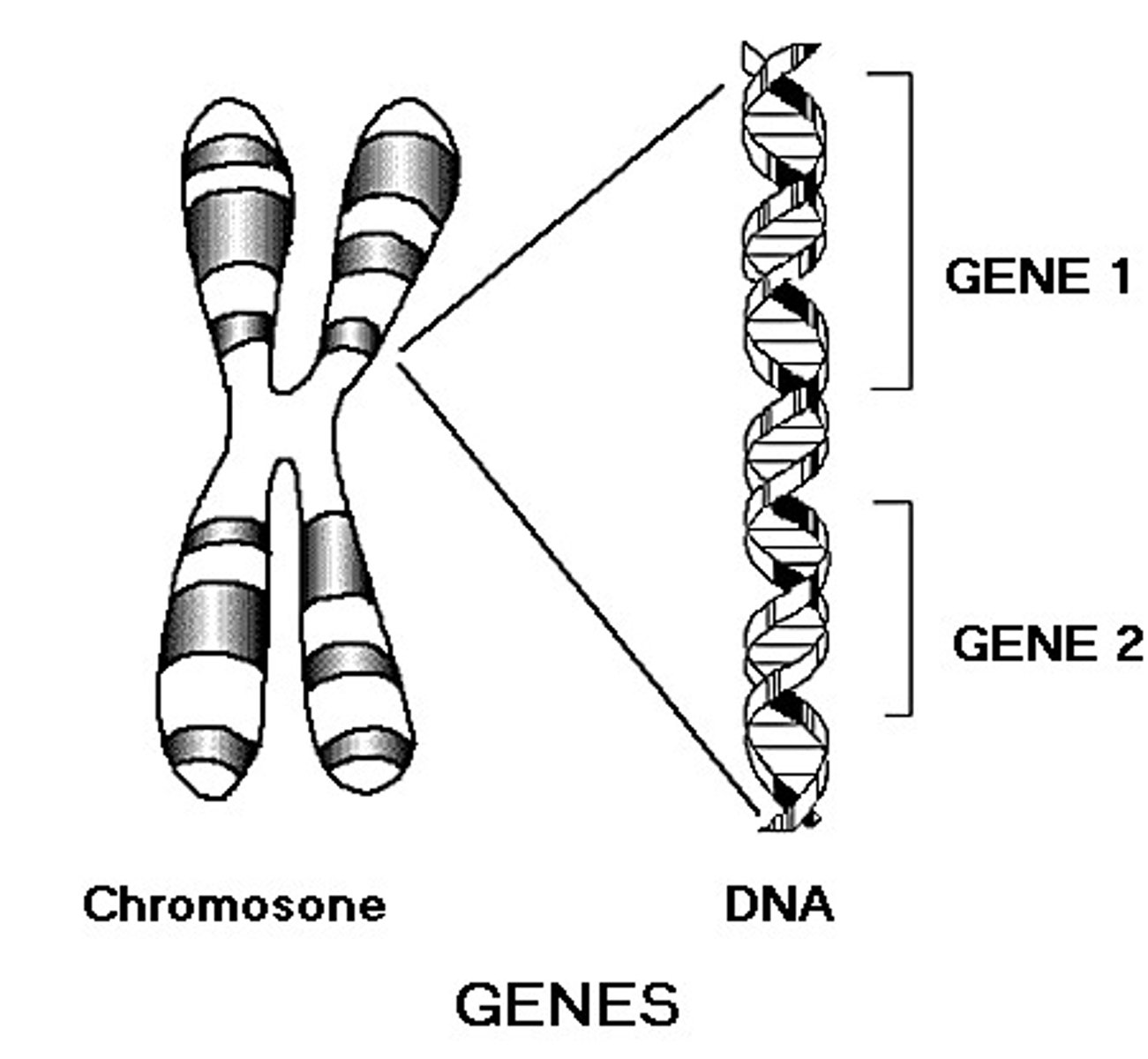
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait
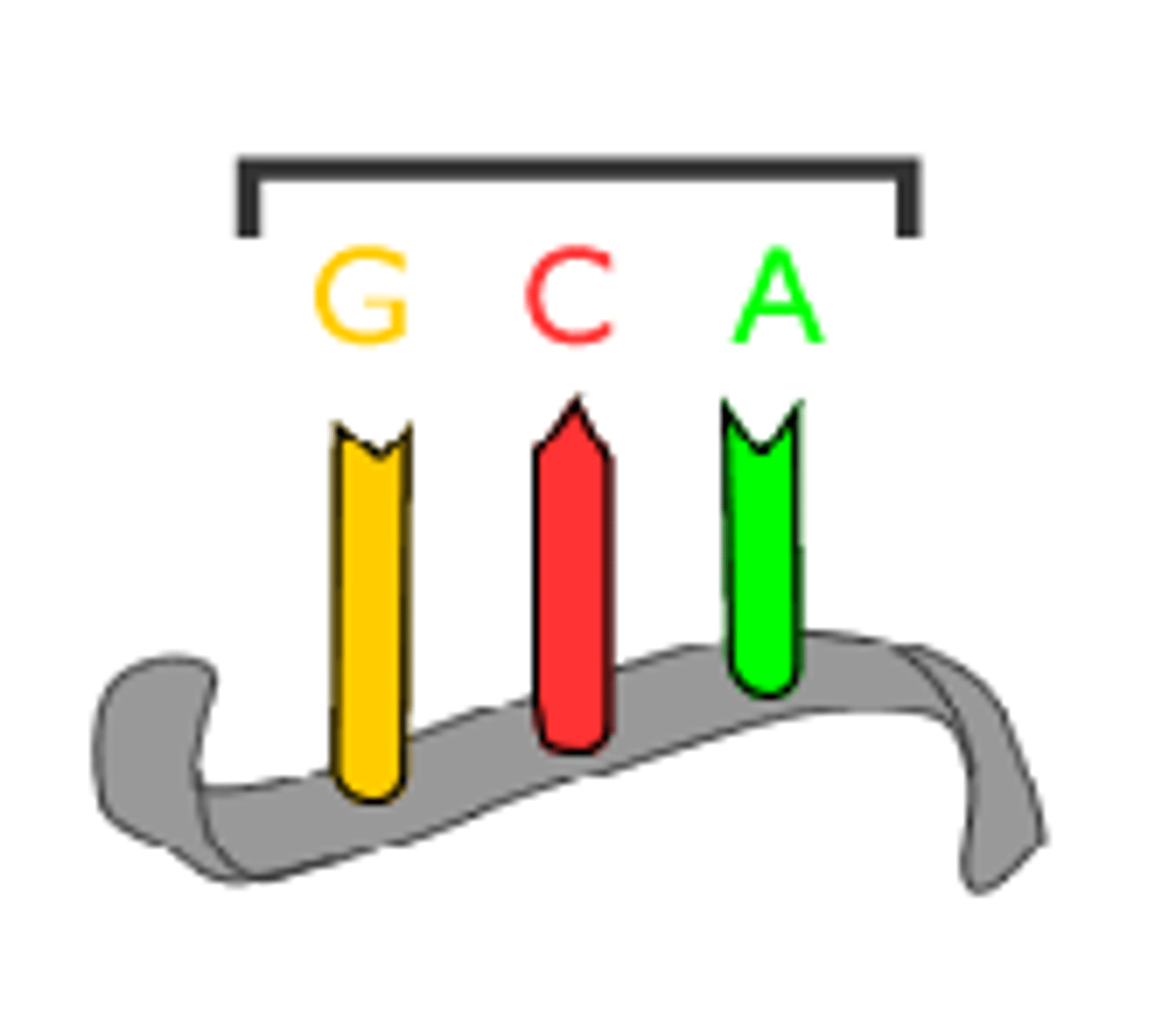
codon
a sequence of 3 nucleotides in DNA (or RNA), like a 'word' that is a code for a specific amino acid, Ex, ATG
carcinogen
A cancer-causing substance
cancer
A disease in which some cells grow and divide uncontrollably (due to mutations), damaging the parts of the body around them.
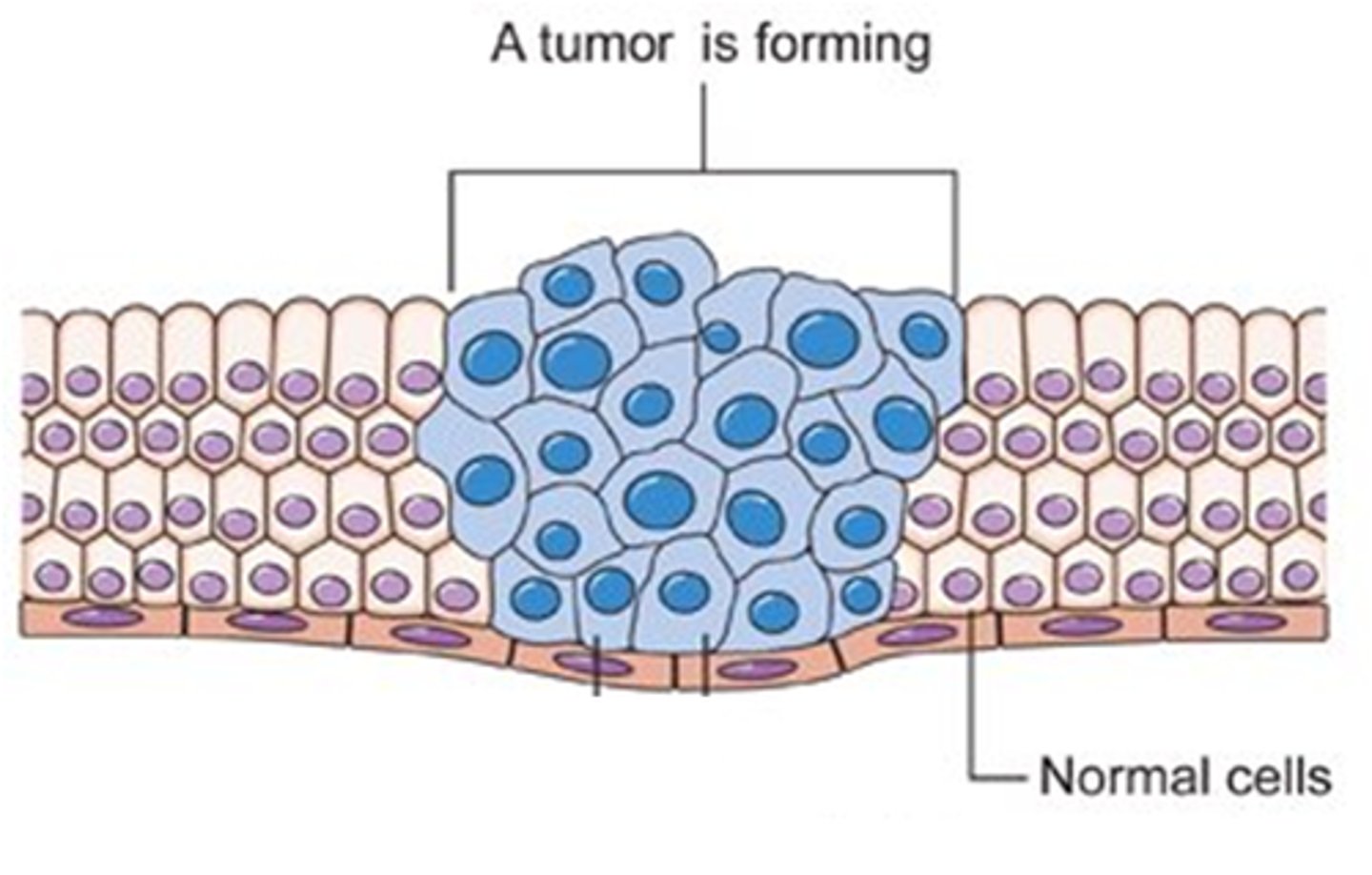
mitosis
cell division - one cell copies all its parts and divides into two cells
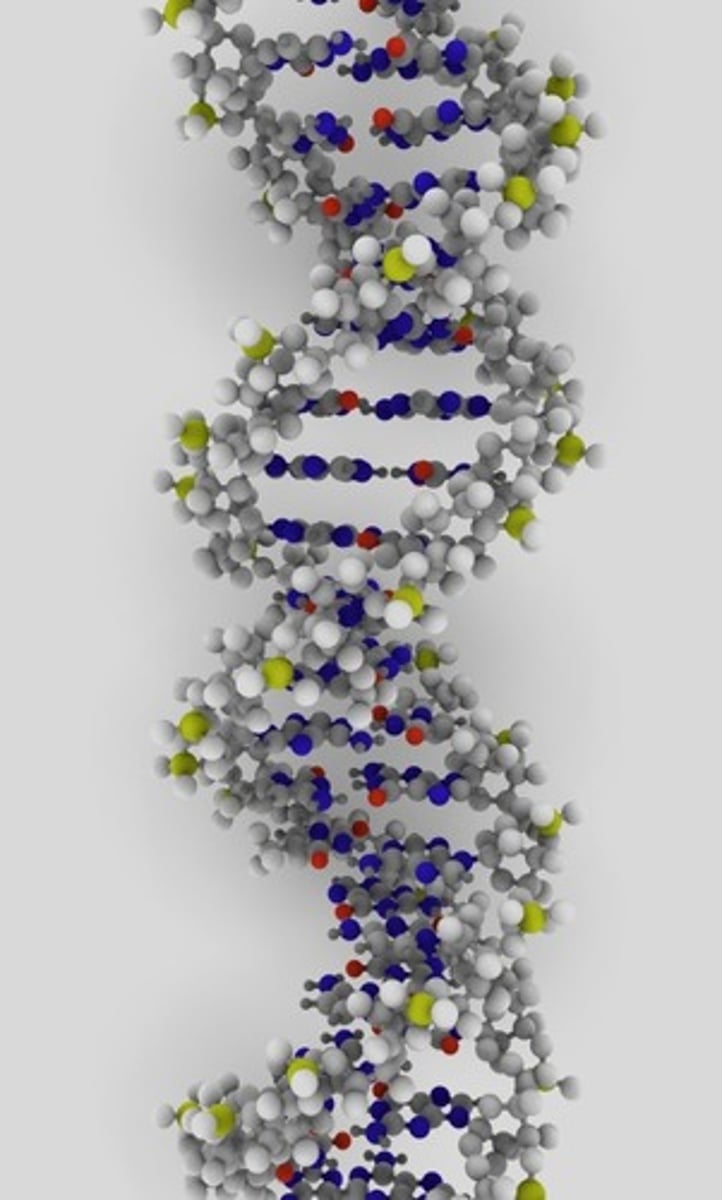
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid, the molecule that contains the information that determines inherited characteristics- used to build molecules that make up your body
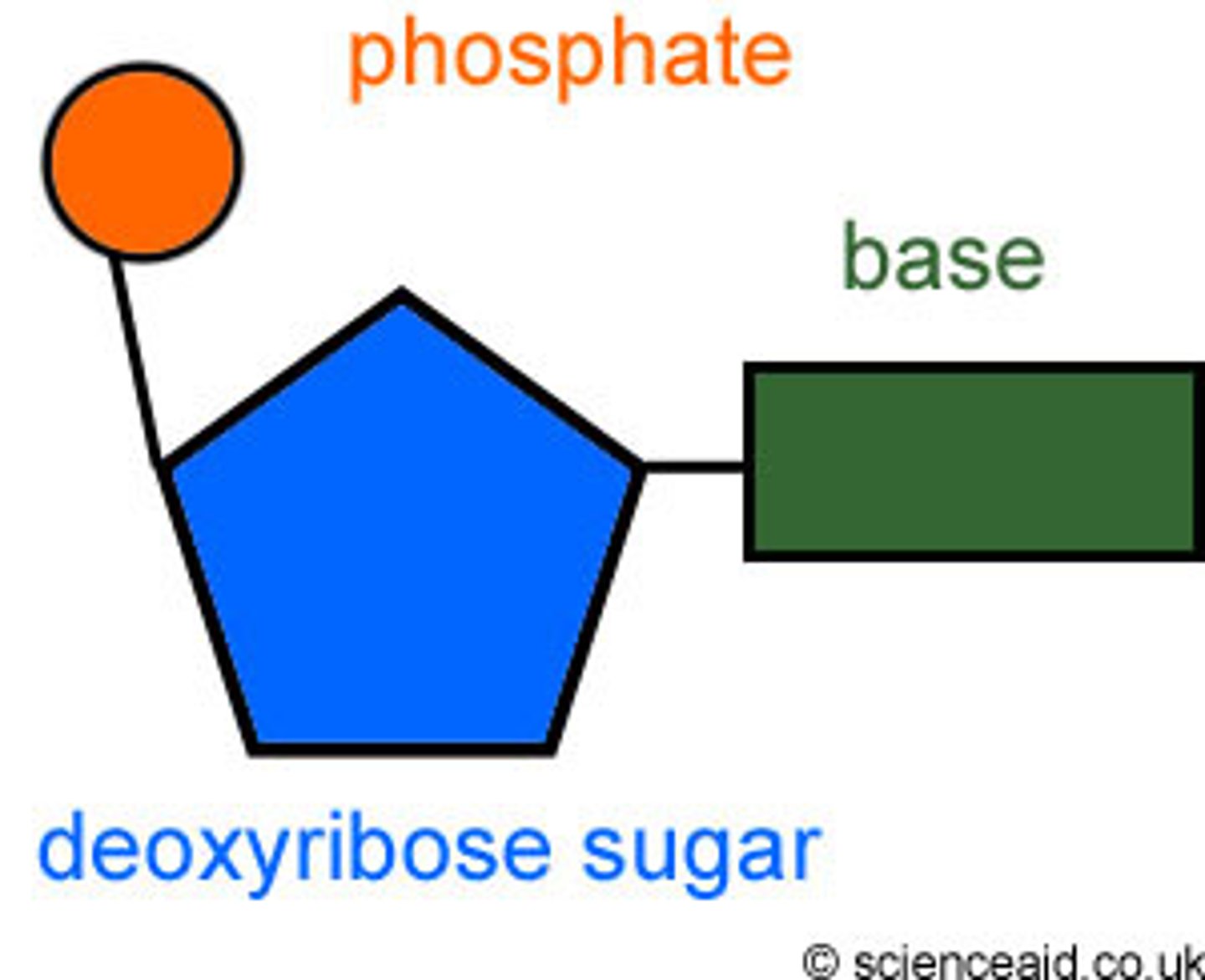
nucleotide
the building block of DNA (has 3 parts: sugar, phosphate and nitrogenous base)
adenine (A)
The nitrogenous base that pairs with Thymine (T) in DNA
thymine (T)
Nitrogenous base that pairs Adenine (A) in DNA
cytosine (C)
Nitrogenous base that pairs with guanine (G).
guanine (G)
Nitrogenous base that pairs with Cytosine (C) in DNA and RNA
mutation
a change in the nucleotide-base sequence of a gene or DNA molecule
mutagen
something that CAUSES mutations (for example, radiation)
deoxyribose
sugar molecule that makes up part of the backbone of DNA
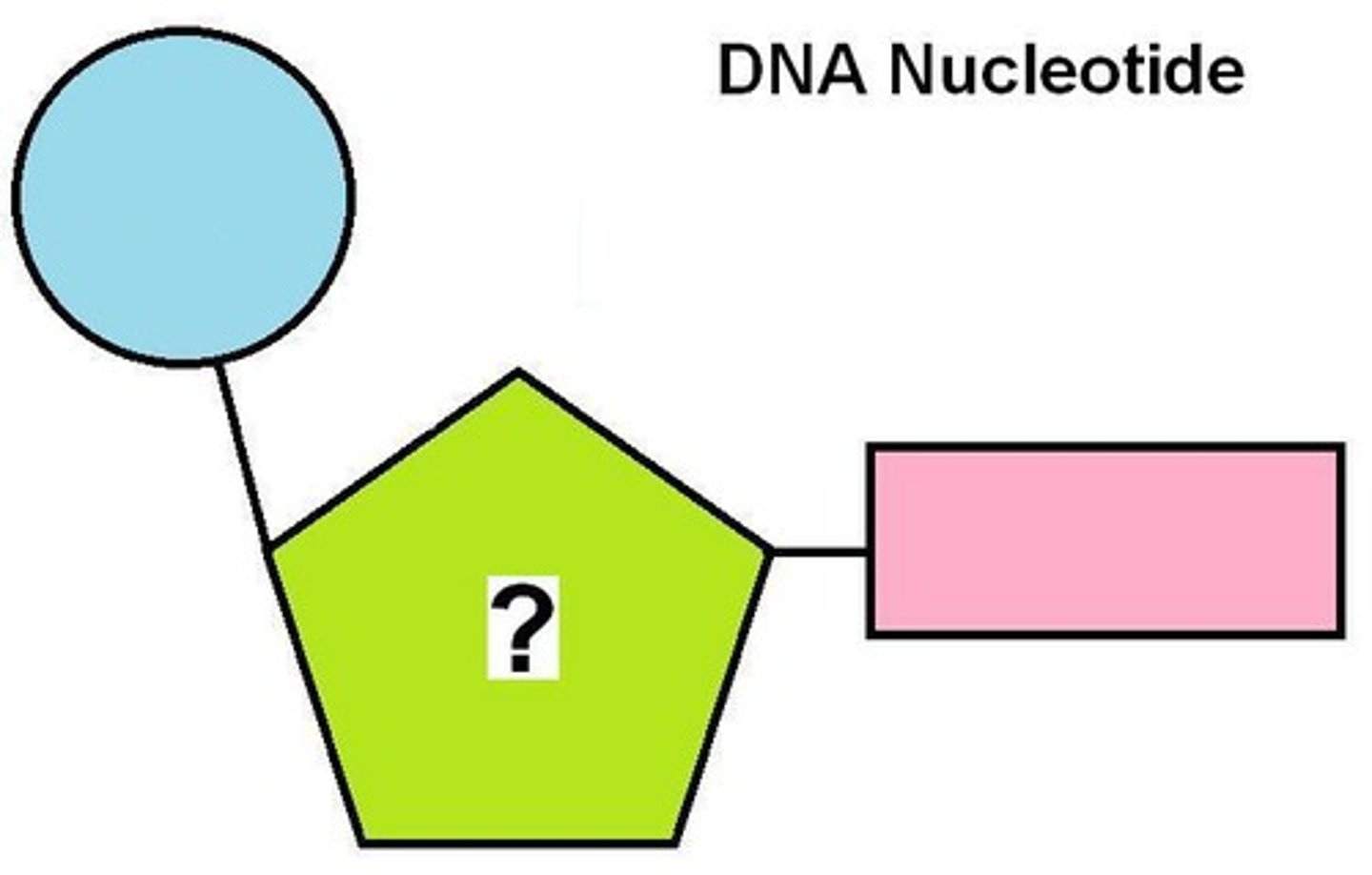
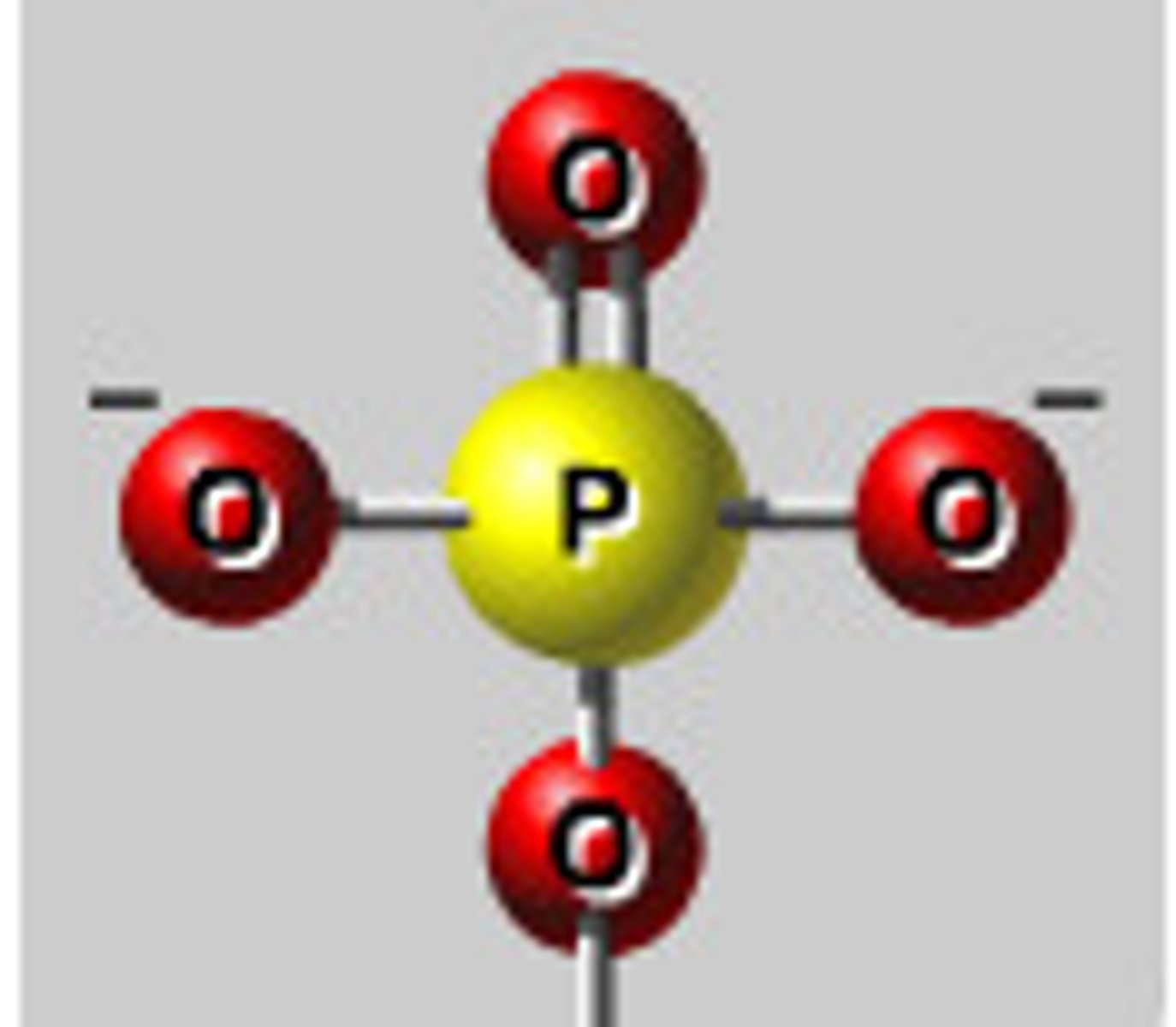
phosphate
molecule (not sugar) that makes up part of the backbone of DNA
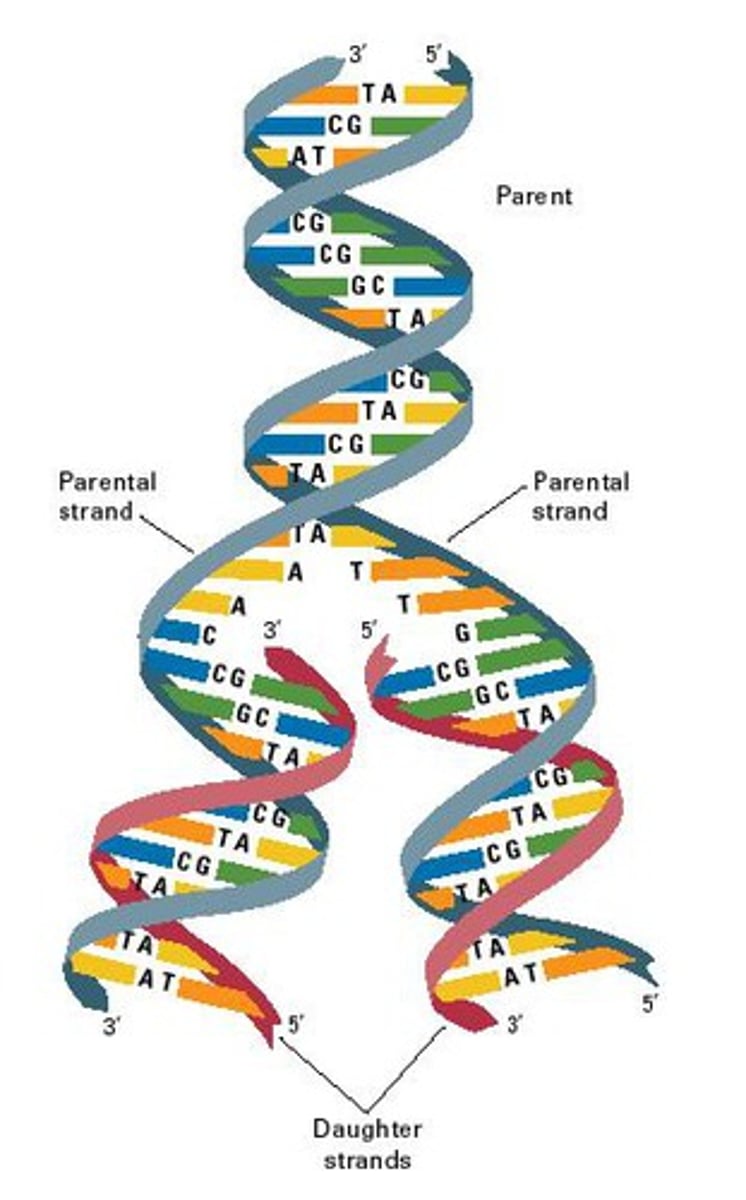
DNA replication
the process of making a copy of DNA, needed in order to make new cells in mitosis
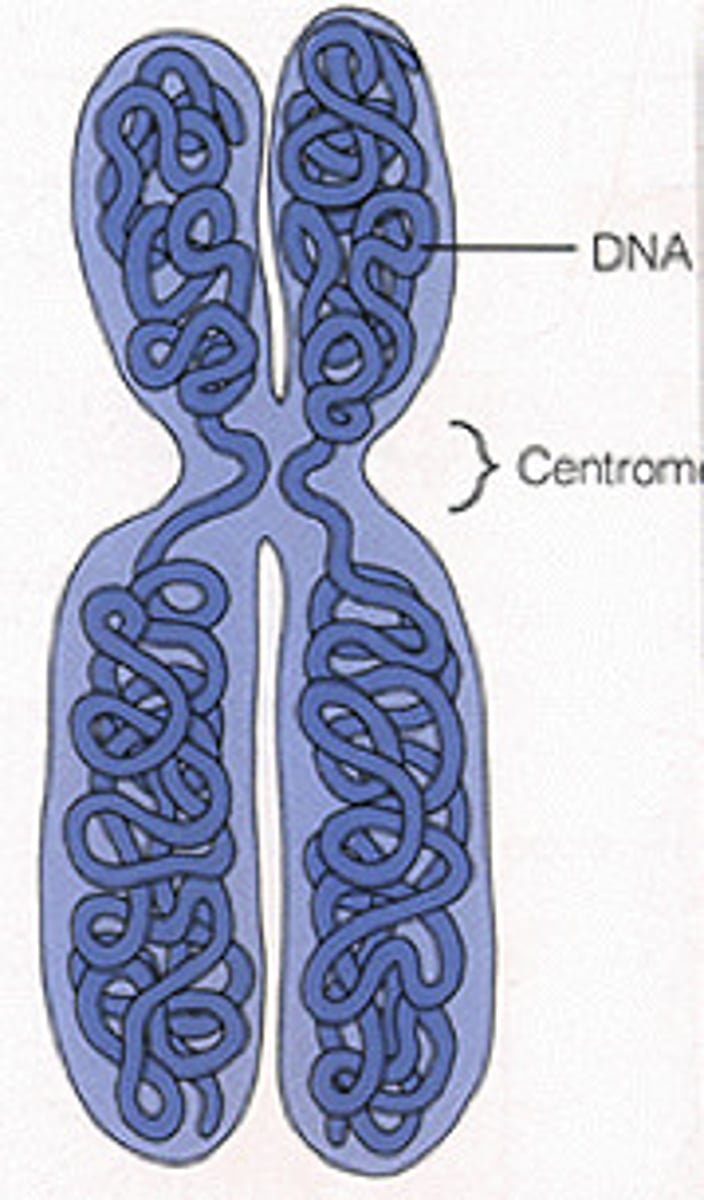
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait
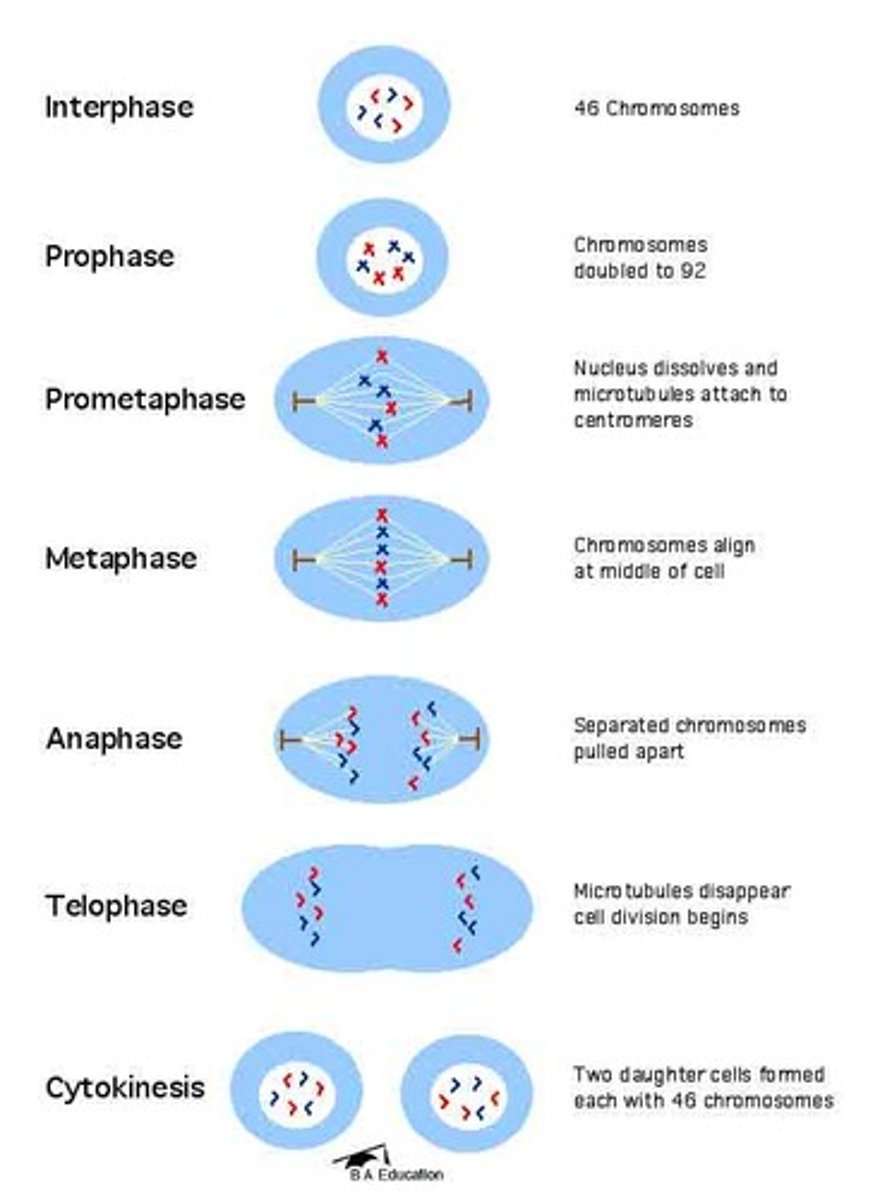
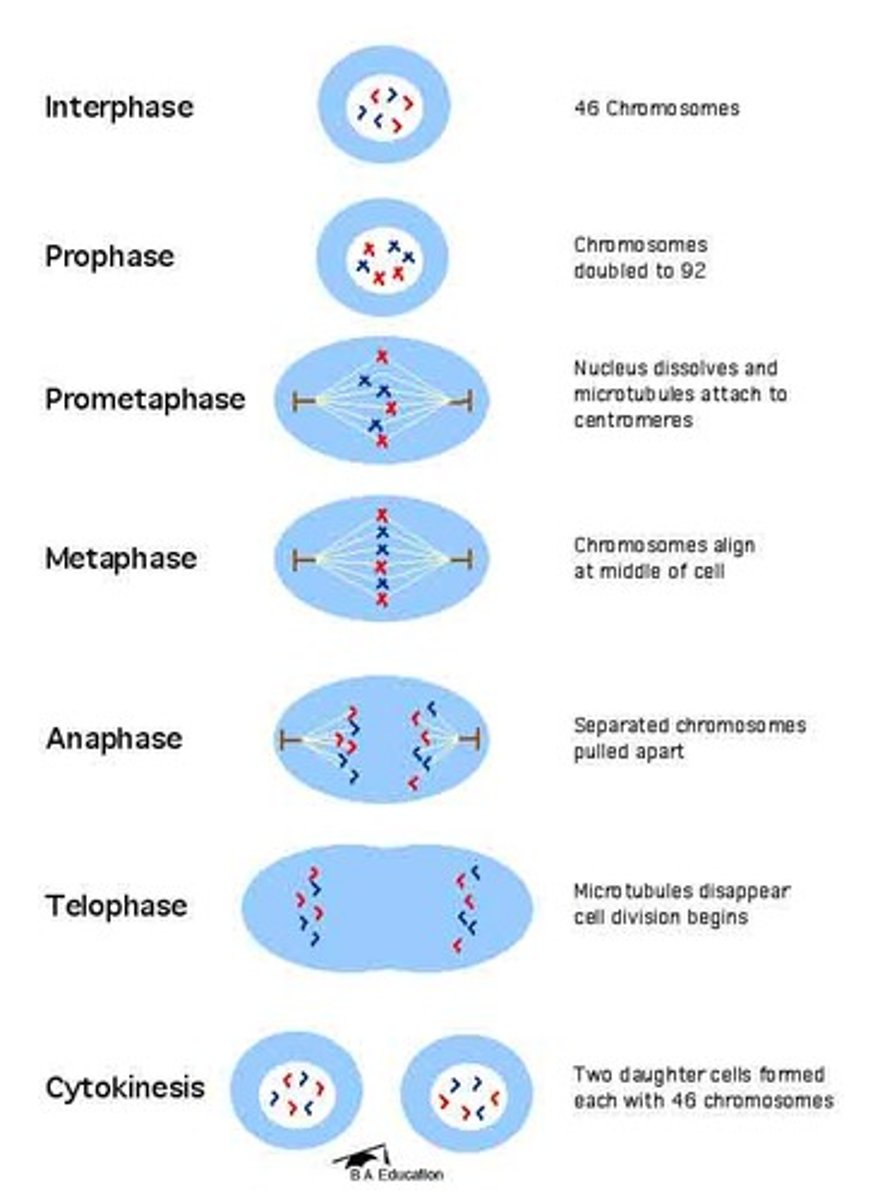
mitosis
cell division - when a cell pulls apart into 2
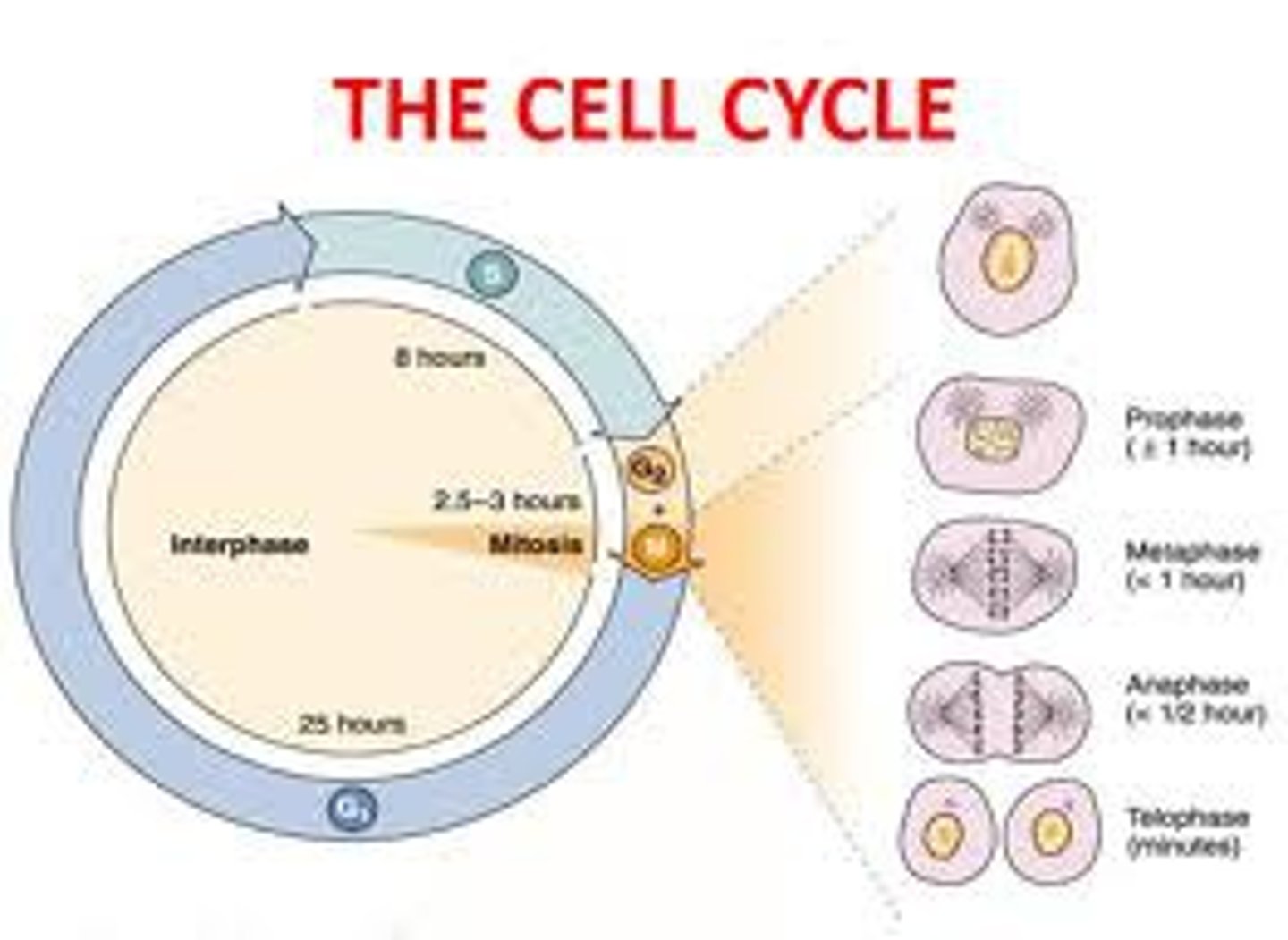
the cell cycle
series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide
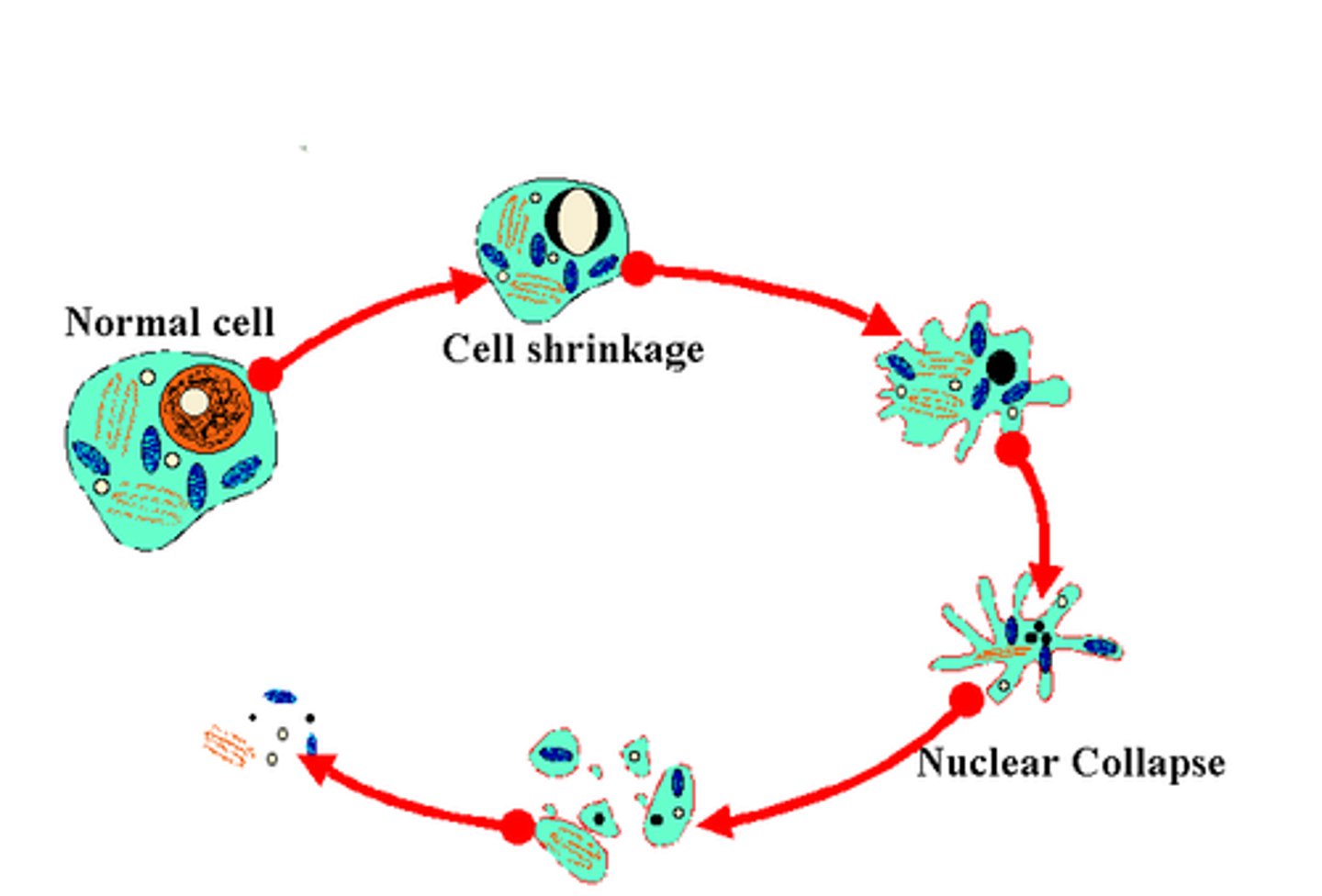
apoptosis
programmed cell death
tumor suppressor genes
make proteins that stop cell division and kill cells

proto-oncogenes
code for proteins that tell normal cells to grow and divide.

oncogenes
mutated genes that cause the cell to grow and divide uncontrollably (like pressing the gas pedal in the car)

G1 phase events
Cell grows, organelles multiply
S phase events
DNA replication
G2 phase events
cell gets organized for division
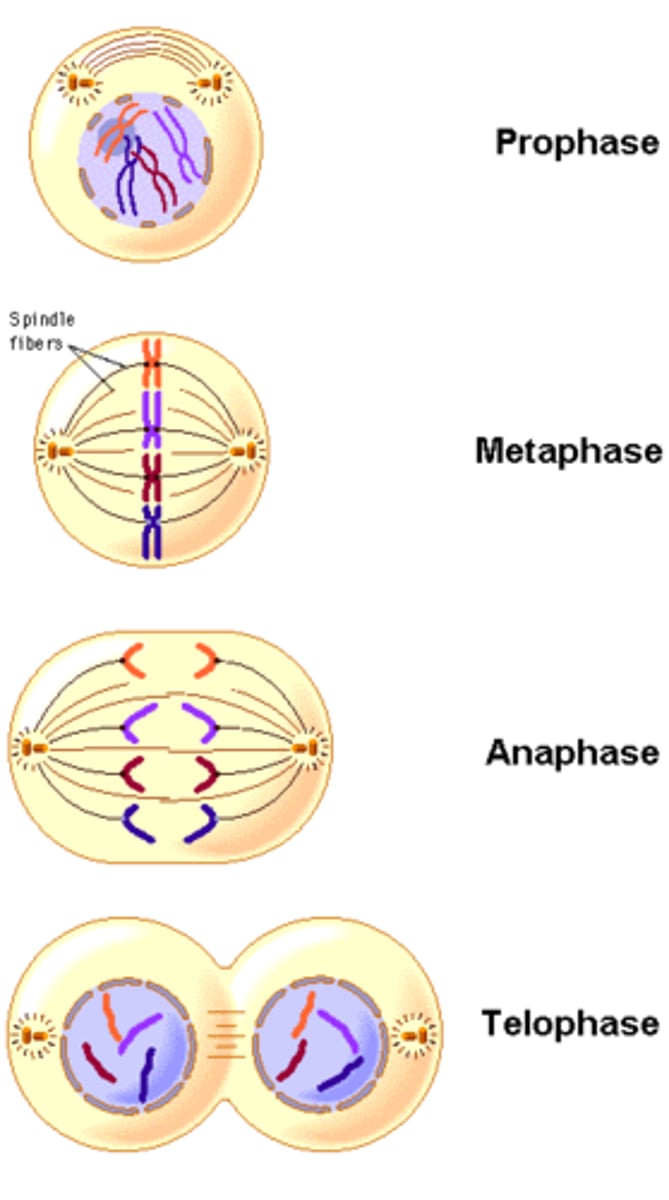
M phase events
cell divides in an organized way (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis)
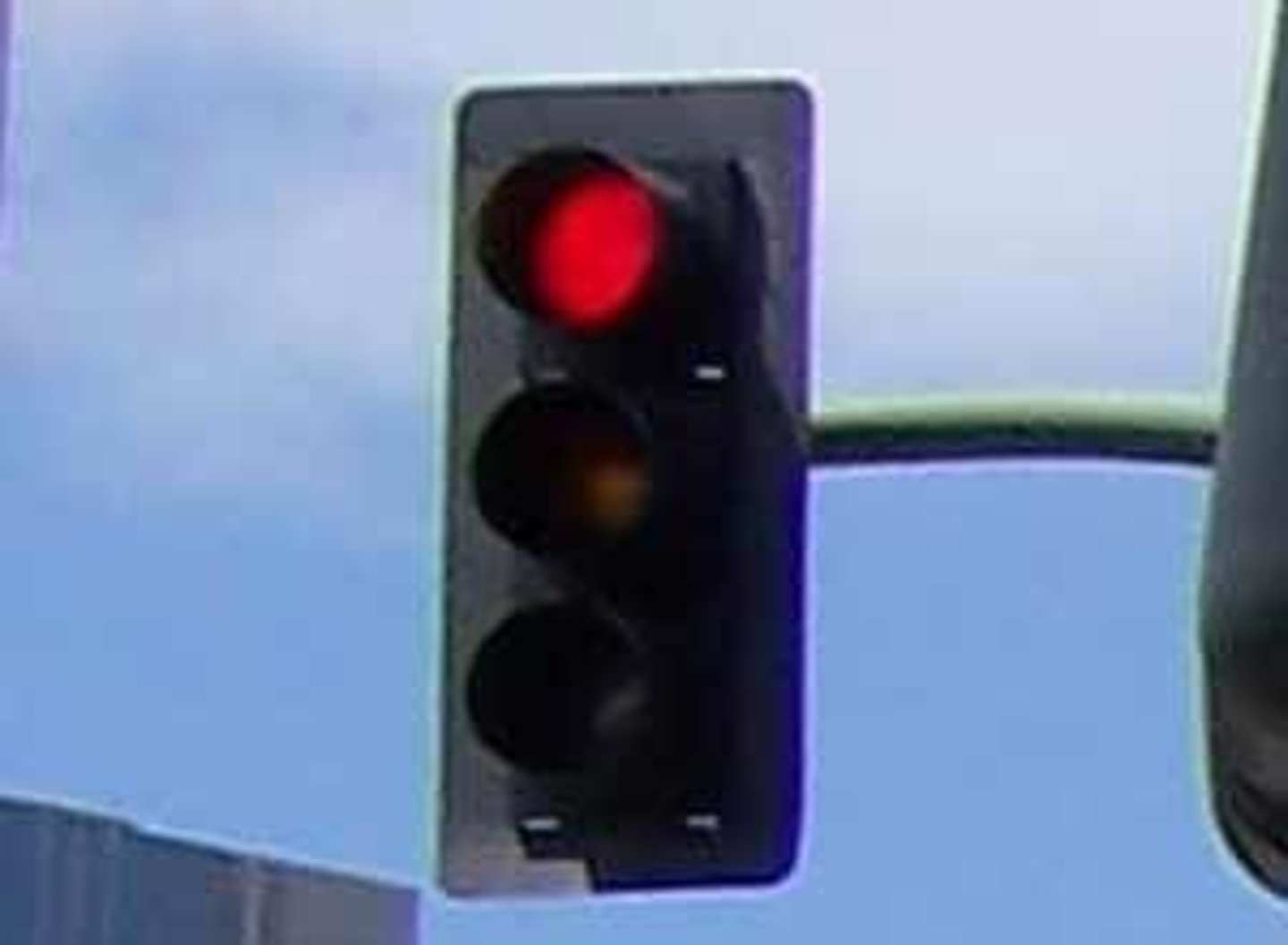
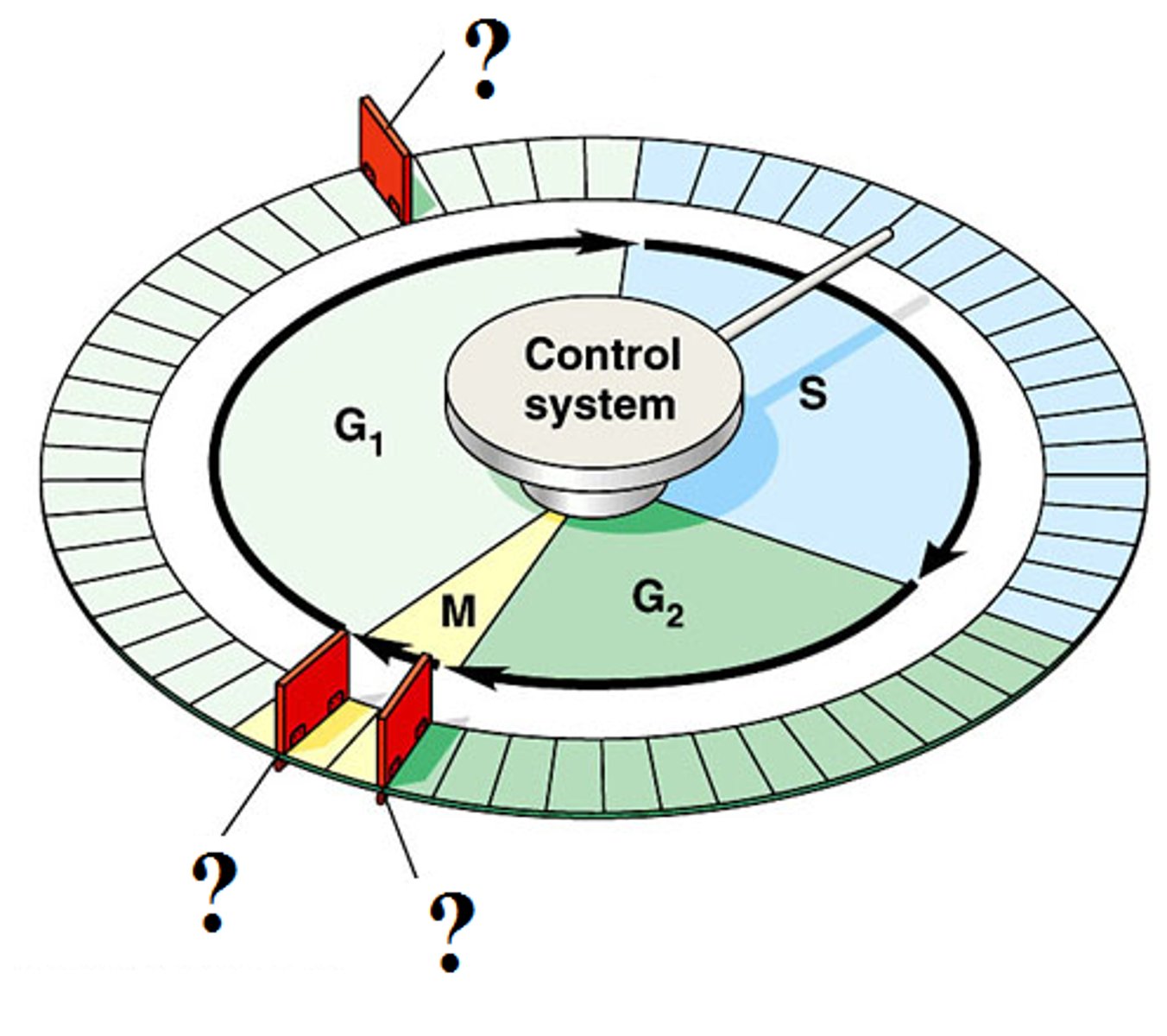
cell cycle checkpoints
'traffic stops' in the cell cycle - making sure everything is healthy and that the DNA is ok
DNA repair genes
code for proteins that correct/repair DNA mutations
p53 gene
codes for proteins that cause the cell cycle to stop, the DNA repair, or apoptosis in cells with bad DNA
melanin
A pigment that gives the skin its color

folate
vitamin needed for healthy fetal development, destroyed by too much UV
Vitamin D
vitamin needed to absorb calcium to build strong bones, made in the epidermis when skin absorbs UV-B rays
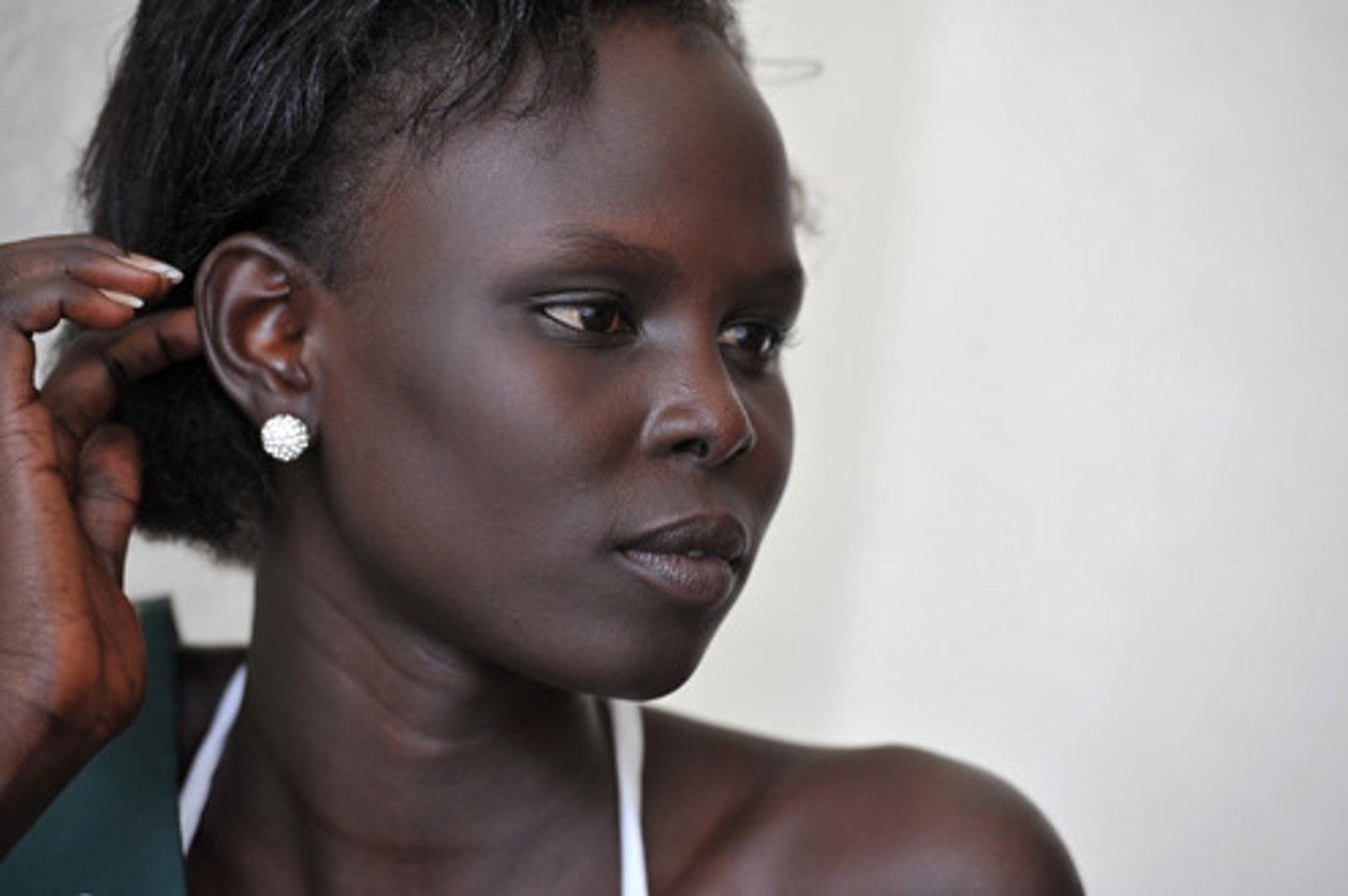
evolutionary advantages for dark skin in high UV intensity areas
protects folate but allows UV-B in enough to produce Vitamin D

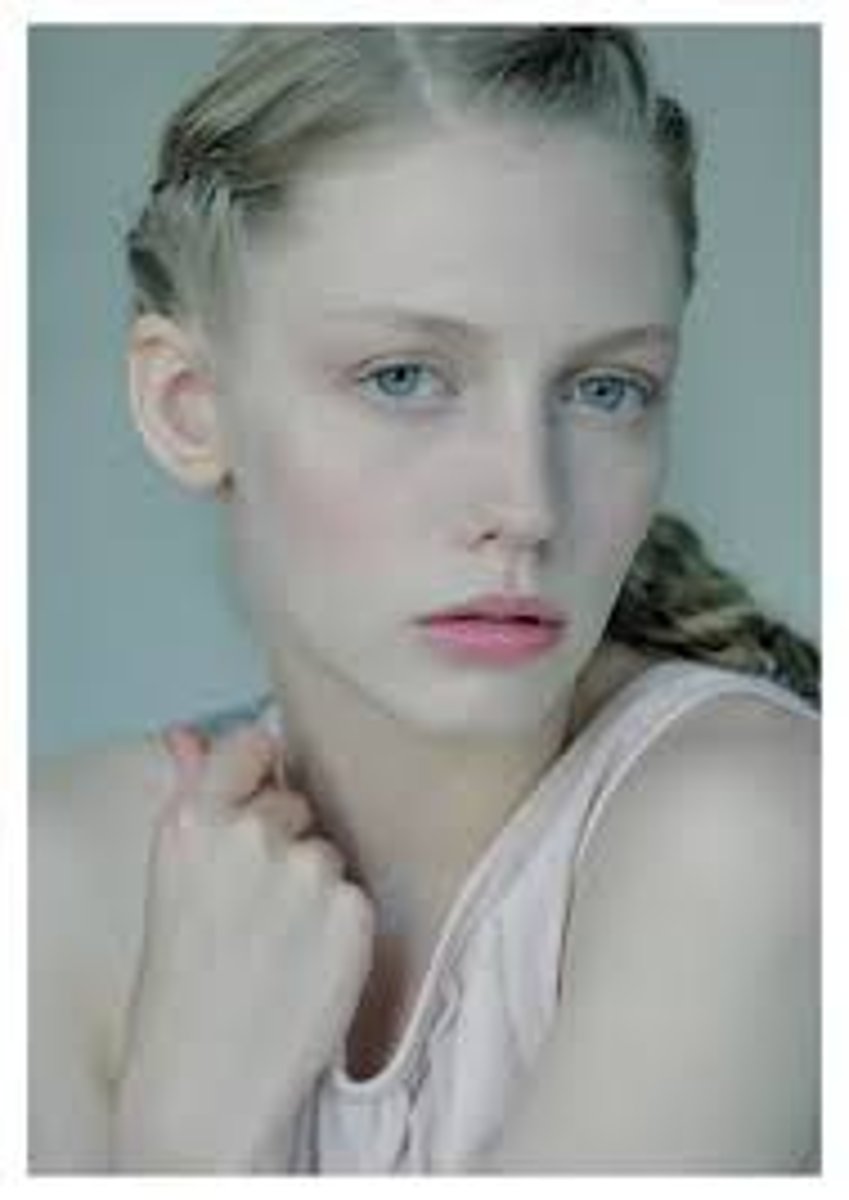
evolutionary advantages for light skin in low UV intensity areas
folate is not at risk, allows UV-B in enough to produce Vitamin D

melanocyte
cell that produces brown pigment in the epidermis