HNSC 2170: Unit 4 Protein
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Describe the structure of protein
Strands of amino acids, CHON, sometimes S
What is the structure of an amino acid?
N-containing, 1 C atom (backbone) + amino group (N) + acid group + side group
What are non-essential amino acids?
Body can synthesize
What are essential amino acids?
Body can't synthesize; 9
What is a dipeptide?
2 aas bonded
What is a tripeptide?
3 aas bonded
What is a polypeptide?
>10 aas bonded (dozens → hundreds), oligopeptide = 4-10 aas
What is protein turnover?
Cells → proteins always made & broken down, aas build new proteins & replace old cells
What happens when protein is broken down?
Aas released - recycled, strip N → energy
What happens when aa arrive at a cell?
Used to build growing protein, altered → make needed compound, build different aa, cell dismantles amine group, amine group → energy; converted to glucose/fat → stored, not using amine group → excreted
What is nitrogen balance?
Studies to estimate protein requirements, compare N lost through excretion w/ N eaten in food
What is N equilibrium?
Same amt of protein in body all times; 0, N intake = N output
What is a + N balance?
Protein synthesis = protein degradation, N intake (food) = N excretion (urine, feces, sweat), N intake > N output, ↑protein built than broken down, retaining protein in new tissues (add blood/bone/skin/muscle), ex. growing child, pregnant, recovering from protein def/illness
What is a - N balance?
N intake < N output, ↑protein b.d than building, lose protein by b.d of muscles or other protein tissue, ex. starving, burns, injuries, infection, fever
What are the functions of protein in the body?
Structural components, transport substances around the body, are enzymes, hormones, Abs
What is the role of proteins in maintaining F&E balance?
Maintain distribution between 3 compartments (IC, EC, IF). Can transfer substances (Na, K) & balance. Albumin (protein) prevent imbalance.
What is the role of proteins as a source of energy and glucose?
Provide energy & glucose (sacrificed) in times of starvation or insufficient carbon intake. Limited glucose/FAs → cells forced to use aas for energy/glucose. Amine groups then used elsewhere or added to urea (excreted). Remaining (CHO) build glucose/FA. Protein has no storage. Need → body dismantles proteins → energy. Can lead to deprivation if ↑need prolonged.
What are the structural components of the body?
Muscles, bones, teeth, tendons, cartilage, BV, etc.
What is the role of structural components in the body?
Allow movement.
What substances are transported by proteins?
Lipids, vitamins, minerals, O2.
What are enzymes?
Catalysts. Create disaccharides (sucrose, lactose, maltose) → polysaccharides (glycogen, cellulose, starch). B.d. → energy. Create & b.d. lipids, etc. Puts aas together to make proteins. Food b.d. via digestive enzymes (PROTEINS) → aas → enter cells. Other proteins put aas together → proteins.
What are hormones?
Chemical messengers. Ex. insulin, glucagon.
What are antibodies?
Body makes Abs (proteins) when detecting invading Ags → combat pathogens. Immunity (body remembers Ag → faster Ab production).
What are the consequences of protein deficiency?
↓growth, impaired brain/kidney function, weakened IS, impaired nutrient absorption
What is protein energy malnutrition?
Too little protein or energy (or both)
What is the difference between severe acute malnutrition and chronic malnutrition?
SAM is sudden inadequate food intake, while chronic malnutrition is long-term inadequate food intake
What are the symptoms of severe acute malnutrition?
Rapid weight loss, wasting, edema
What are the consequences of excess protein intake?
Heart disease, kidney disease, obesity
What is the recommended daily allowance for protein?
0.8g/kg body weight
What is the amount of protein supplement recommended after exercise?
10-20g (food/supplement)
What are the food sources of protein?
Meat, legumes, nuts, whole grains
What is the protein quality factor?
A measure of the protein's ability to provide essential amino acids
What are examples of high quality proteins?
Meats, fish, poultry, cheese, eggs, milk, milk products
What are the protein quality factors?
Digestibility and amino acid composition
What happens if there is inadequate essential amino acids?
Limited protein synthesis
What is amino acid adequacy?
Eating foods of high quality proteins or combination of foods with proteins missing from the other
Which amino acids are easily digested and absorbed?
Amino acids from animal products
Which amino acids are less digestible?
Amino acids from plant products
What are high quality proteins?
Contain all essential amino acids
What are plant based foods?
Limited in some essential amino acids
What are complementary proteins?
Eating different protein-rich (plant based) foods supplies missing amino acids
What is a vegetarian diet?
Plant based foods + some (or none) animal foods
What are the potential benefits of a vegetarian diet?
Reduced risk of heart disease, hypertension, diabetes, obesity, some cancers, and cholesterol
What are the protein-based plant foods?
Whole grains, legumes, nuts, and vegetables
What should be limited in a vegetarian diet?
Butter, cream cheese, and sour cream
What are the potential concerns of a vegetarian diet?
Reduced absorbable iron and zinc in plant foods than animal, lack of FAs EPA and DHA, and vitamin D deficiency
What is a partial vegetarian diet?
Plant based foods + poultry, seafood + eggs + milk & milk products, NO certain meats (ex. red meats)
What is a vegan diet?
Plant based foods ONLY (veg, whole grains, legumes, fruit, seeds, nuts), NO animal products
What are the potential concerns of a vegan diet?
May not provide enough food energy, especially in children, affects growth, vitamin D deficiency, and vitamin B12 deficiency
What are the sources of essential FAs for a vegan diet?
Flaxseed, walnuts + oils, soybeans, canola oil
What is the influence of vitamin C on iron and zinc absorption?
Increases absorption
What is calcium?
Mineral for strong bones and teeth
What are some sources of calcium for lacto-ovo vegetarians?
Dark leafy greens, legumes, cereals, soy milk, almonds, sesame seeds
What is a lacto-ovo vegetarian diet?
Plant-based foods + milk & milk products + eggs, NO meat, poultry, seafood
What is a lacto-vegetarian diet?
Plant-based foods + milk & milk products, NO eggs, meat, poultry, seafood
What is an ovo vegetarian diet?
Plant-based foods + eggs, NO milk & milk products, meat, poultry, seafood
What is a macrobiotic diet?
Whole grains, legumes, some vegetables + small amounts of fish, fruit, nuts, seeds
What is celiac disease?
Immune disorder to wheat gluten & related proteins
What are the symptoms of celiac disease?
GI disturbances, diarrhea, steatorrhea, flatulence
What is non-celiac gluten sensitivity?
Gluten causes intestinal mucosa inflammation & malabsorption but not genetic/autoimmune
What is dermatitis herpetiformis?
Celiac disease of the skin, severe, itchy rash
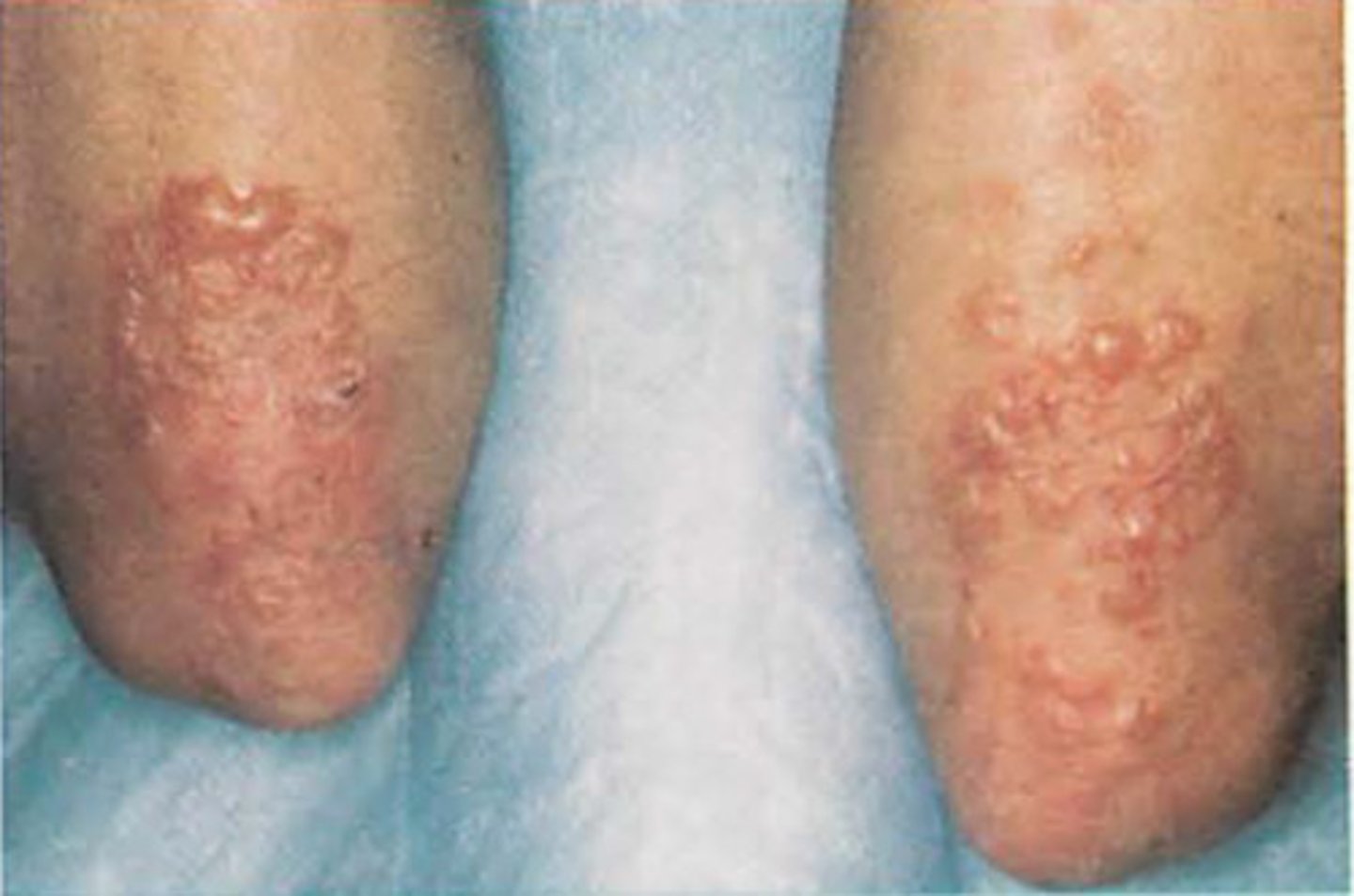
What are the health conditions related to celiac disease?
Anemia, bone disorders, neuro symptoms, fertility problems, risk for developing T1DM, autoimmune thyroid diseases, IBD, intestinal cancers
What are the nutritional complications of celiac disease?
Malabsorption, low body weight, muscle wasting, lactose deficiency
What are the sources of gluten that need to be avoided on a gluten-free diet?
Wheat, barley, rye, oats, beer, ale, gravy, potatoes, salad dressings, imitation seafood/meat, peanut butter
What is the definitive means of diagnosing celiac disease?
Intestinal biopsy
What happens to proteins in the body after eating?
Enzymes break them down into tripeptides, dipeptides, and amino acids.
What is the role of the mouth and salivary glands in protein digestion?
Chewing and crushing moisten protein-rich foods and mix them with saliva.
What is the role of the stomach in protein digestion?
Hydrochloric acid uncoils protein strands and activates stomach enzymes.
What enzymes are involved in protein digestion in the stomach?
Pepsin and HCl.
What is the role of the small intestine and pancreas in protein digestion?
Pancreatic and small intestinal enzymes further split polypeptides.
What enzymes are involved in protein digestion in the small intestine?
Pancreatic and intestinal proteases.
What happens to peptides in the small intestine?
Enzymes on the surface of small intestinal cells hydrolyze them and the cells absorb the amino acids.
What is the Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range (AMDR) for protein?
10-35% of total energy.
What are tripeptides and dipeptides?
Short chains of amino acids.
What is lysine?
An amino acid promoted to prevent or relieve herpes sores.
What is the role of tryptophan?
It acts as a precursor for serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates sleep, mood, and appetite.
What can happen with an excess of one amino acid?
It can limit the absorption of another amino acid, causing a temporary imbalance.
What are the benefits of creatine supplementation?
Increased lean muscle and improved performance in short burst sports.
What is the loading dose for creatine supplementation?
15-25g per day for 5-7 days, followed by smaller daily doses of 2-5g.
Can lysine cure herpes?
No, it does not cure herpes but may help prevent or relieve sores.
What does tryptophan advertise to relieve?
Pain, depression, and insomnia.
What type of sports can creatine improve performance in?
Sports that use intense short bursts of energy, like sprinting or weight lifting.
What type of sports should creatine not be used for?
Longer endurance sports like long distance running or swimming.