ANAPHY 1.1 HUMAN BODY
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:07 PM on 8/30/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
1
New cards
ANATOMY
It is defined as the study of the structure and the shape of the body parts and their relationships to one another
2
New cards
Ana
“apart”
3
New cards
Tomos
“to cut”
4
New cards
Gross Anatomy Microscopic Anatomy
TYPES OF ANATOMY
5
New cards
Gross Anatomy
the study of the form of structures that can be seen with the naked eye
6
New cards
Microscopic Anatomy
the study of the form of normal structures seen under the microscope
7
New cards
PHYSIOLOGY
It is the study of how the body and its parts work and function
8
New cards
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
the study of disorders of functioning • knowledge of normal physiology makes such disorders easier to understand
9
New cards
ORGANISM ORGAN SYSTEM ORGAN TISSUE CELL CHEMICAL
LEVELS OF STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION
10
New cards
Cells
are the basic unit of life, the smallest unit possible of basic life processes like taking in nutrients, expelling waste & reproducing
11
New cards
Tissue
It is a group of similar cells that have a common function
12
New cards
Organ
is a structure composed of two or more tissue types that performs a specific function for the body • At this level, extremely complex functions become possible
13
New cards
Organ System
A group of organs that cooperate to accomplish a common function
14
New cards
Organism
Made up of 11 organ systems & represents the highest level of structural organization
15
New cards
Integumentary, Skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, lymphatic, respiratory,digestive, urinary,reproductive
11 Organ Systems
16
New cards
Integumentary System (system)
Helps regulate body temperature • Protects the body • Eliminates some wastes • Helps make vitamin D • Detects sensations such as touch, pressure, pain, warmth and cold
17
New cards
Skeletal System
Supports & protects the body • Provides a specific area for muscle attachment • Assists with body movements • Stores cells that produce blood cells • Stores mineral and lipids (fats)
18
New cards
Muscular System
Participates in bringing about body movements • Maintains posture • Produces heat
19
New cards
NERVOUS SYSTEM & SPECIAL SENSES
Regulates body activities through nerve impulses by detecting changes in the environment • Interpreting the changes • Responding to the changes by bringing about muscular contractions or glandular secretions
20
New cards
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
• Regulates body activities through hormones transported by the blood to various target organs
21
New cards
Cardiovascular System
Heart pumps blood through blood vessels • Blood carries oxygen & nutrients to cells and carbon dioxide & wastes away from cells & helps regulate acidity, temperature & water content of body fluids • Blood components help defend against disease & mend damaged blood vessels
22
New cards
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM & IMMUNITY
Returns proteins & fluid to blood • Carries lipids from GI tract to blood • Contains sites of maturation & proliferation of B cells & T cells that protect against disease-causing microbes
23
New cards
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Transfers oxygen from inhaled air to blood and carbon dioxide from blood to exhaled air • Helps regulate acidity of body fluids • Air flowing out of lungs through vocal cords produces sounds
24
New cards
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
• Achieves physical and chemical breakdown of food • Absorbs nutrients • Eliminates solid wastes
25
New cards
URINARY SYSTEM
• Produces, stores, & eliminates urine • Eliminates wastes & regulates volume & chemical composition of blood • Helps regulate acidity of body fluids • Maintains body’s mineral balance • Helps regulate red blood cell production
26
New cards
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
• Gonads produce gametes (sperm or oocytes) that unite to form a new organism • Release hormones that regulate reproduction & other body processes • Associated organs transport & store gametes • Mammary glands produce milk
27
New cards
Metabolism, Responsiveness, Movement, Growth Differentiation, Reproduction
6 Important Body Processes
28
New cards
METABOLISM
is all the chemical processes that occur in the body UNIT 1: The Human Body – An Orientation • includes breaking down complex substances into simpler building blocks, or making larger structure from smaller ones or utilizing nutrients & oxygen to produce energy molecules
29
New cards
RESPONSIVENESS
or “irritability” • is the ability to detect and respond to changes that occur both inside and outside of the body
30
New cards
MOVEMENT
includes motion of the whole body, individual organs, single cells, and even tiny structures inside cells.
31
New cards
GROWTH
is an increase in body size due to an increase in the size of existing cells, the number of cells, or the amount of material surrounding cells.
32
New cards
Differentiation
is the process that unspecialized cells undergo to become specialized cells.
33
New cards
Reproduction
refers to either the production of a new individual or the formation of new cells for growth repair or replacement.
34
New cards
HOMEOSTASIS
• A state in which the internal environment of the body remains relatively stable by responding appropriately to changes • A state of “balance” or “equilibrium” which is a result of the proper functioning of each organ and organ system in the body.
35
New cards
DISEASE or DISORDER
results when there is moderate to severe imbalance in homeostasis
36
New cards
Nervous and Endocrine systems
Systems that help maintain Homeostasis
37
New cards
Nervous system
detects changes from the balanced state and sends messages in the form of nerve impulses to organs that can counteract the change
38
New cards
Endocrine System
corrects changes by secreting molecules called hormones into the blood hormones affect specific body cells to restore homeostasis
39
New cards
Feedback mechanism
is a cycle of events in which a controlled condition in the body (e.g. body temp., BP) is continually monitored, evaluated, changed, re- monitored, re-evaluated and so on.
40
New cards
Receptors,Control Center,Effector
Basic Components of a Feedback Mechanism:
41
New cards
1\. Receptor
is a body structure that monitors a change in a controlled condition; this change is called, stimulus • receptor sends information called input to the control center
42
New cards
Control Center
the processing center • evaluates the input it receives from the receptors and generates output commands to appropriate organs when they are needed
43
New cards
Effector
• is a body structure that receives output from the control center and produces a response that changes the controlled condition • any organ of the body can act as an effector
44
New cards
Negative Feedback Mechanism
reverses a change in a controlled condition bringing it back to “normal”. • examples are feedback mechanisms that control: body temperature blood pressure
45
New cards
Positive Feedback System
strengthens a controlled condition • examples are feedback mechanisms that control: childbirth blood clotting
46
New cards
Positive and Negative Feedback Mechanisms
Types of Feedback Mechanisms
47
New cards

Anatomical Position
subject‘s body standing upright; head level with eyes facing observer; arms at the sides with palms forward; and feet flat on the floor • description of the location of the body parts is based on this position
48
New cards
left
• to the left of subject’s body
49
New cards
Right
to the right of subject’s body
50
New cards
Superior
toward the head’s end; upper part of a structure; above or higher • e.g. The forehead is superior to the nose
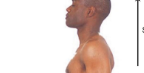
51
New cards
Inferior
away from the head end; toward the lower part of a structure; below or lower • e.g. The navel is inferior to the breastbone
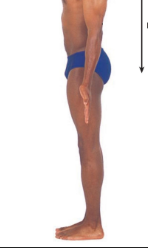
52
New cards
Anterior (or ventral)
• at the front of the body or in front of • e.g., The breast bone is anterior to the spine

53
New cards
Posterior (or dorsal)
• at the backside of the body or behind • e.g., The heart is posterior to the ribs

54
New cards
Medial
• toward or at the midline of the body; inner side of the body • e.g., The heart is midline to the arm
55
New cards
Lateral
• away from the midline of the body; on the outer side of • e.g., The arms are lateral to the chest
56
New cards
Proximal
• close to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk • e.g., The elbow is proximal to the wrist.
57
New cards
Distal
farther from the origin of a body part or point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk • e.g. The knee is distal to the thigh
58
New cards
Superficial
toward or at the body surface • e.g The skin is superficial to the skeleton
59
New cards
Deep
• away from the body surface; more internal • e.g The lungs are deep to the rib cage
60
New cards
Head
skull & face
61
New cards
Neck
supports head & attaches it to trunk
62
New cards
Cephalic
Head
63
New cards
Frontal
Forehead
64
New cards
Otic
Ear
65
New cards
Orbital
Eye Cavity
66
New cards
Oral
Mouth
67
New cards
Nasal
Nose
68
New cards
Buccal
Cheeck
69
New cards
Mental
Chin
70
New cards
Cervical
Neck
71
New cards
Occipital
Back of Head
72
New cards
Trunk
–chest, abdomen & pelvis
73
New cards
Upper Limb
attached to the trunk; consists of the shoulder, armpit, arm, forearm, wrist & hand
74
New cards
Acromial
Point of Shoulder
75
New cards
Sternal
Sternum (center bone)
76
New cards
Pectoral
Chest
77
New cards
Axillary
Armpit
78
New cards
Mammary
Breast
79
New cards
Brachial
Arm
80
New cards
Antecubital
Front of elbow
81
New cards
Cubital
Behind of elbow
82
New cards
Abdominal
Abdomen
83
New cards
Umbilical
Navel
84
New cards
Antebrachial
Forearm
85
New cards
Inguinal
Groin
86
New cards
Carpal
Wrist
87
New cards
Cox
Hip
88
New cards
Palmar
Palm
89
New cards
Digital
Finger
90
New cards
Genital
Reproductive organs
91
New cards
Vertebral
Spinal column
92
New cards
Brachial
Arm
93
New cards
Dorsum
Back
94
New cards
Lumbar
Lower back
95
New cards
Sacral
Between hips
96
New cards
Perineal
In between anus and genitilia
97
New cards
Lower limb
Attached to the trunk;consists of the buttocks,thigh,leg,ankle,and foot
98
New cards
Patellar
Front of knee
99
New cards
Crural
Leg
100
New cards
Tarsal
Instep