Flip-flops and Registers
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Flip-flops
Store 1 bit - limitation as computers usually use 32 or 64 bit numbers
Synchronous digital circuits
Registers
Comprised of flip-flops
Store data being used in CPU
Fastest type of storage
Usually large enough to hold a word
-ve expensive to make so use RAM for main memory
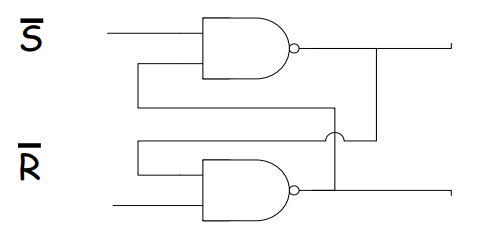
Set-rest flip-flops
A high voltage to S sets the top output to 1 and that cannot be undone lowering voltage at S - essentially storing the bit
A high voltage to R switches the output to 1 at the bottom and 0 at the top
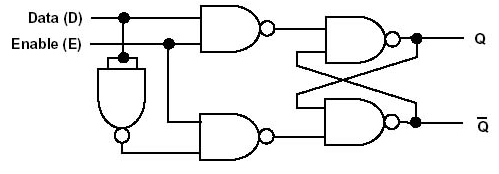
D-type flip-flop
No set/reset - just a data input
Acts like a delay or 1 bit store
State changes only when clock is high
It is an RS latch with additonal NAND gates that make it simple to control. When Enable is 0, both control NAND gates will have a 1 output, and the RS latch will remain stable. When Enable = 1, Q will become equal to Data. If Data changes while Enable = 1, Q will also change. When Enable goes back to 0, the most recent value of D will remain on the Q output.
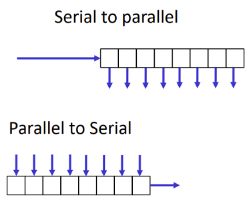
Shift register
Shifts output every clock cycle
Can be used to convert between serial and parallel
User visible registers
General purpose
Usually 16 in modern CPUs
Data
Address only (less common)
DO not store data
Only a memory address
Condition codes in status register
Sets of individual bits
Can be read by programs but not usually set by them
Code examples: carry, overflow, interrupt
Control registers
Usually hidden from user
E.g. MAR, MBR
Supervisor mode
Status controlled by status register
Allows privileged instructions to execute
Used by OS