Unit 1: Thinking Geographically
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Absolute Direction
Corresponds to the direction on a compass: north, south, east, west, and combinations such as northeast and southwest
Ex - Milwaukee is NORTH of Chicago

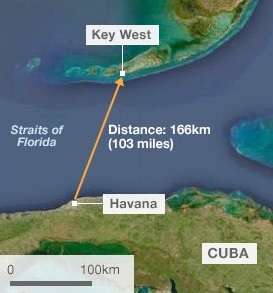
Absolute Distance
Exact, measurable physical space between two locations, usually expressed in units like miles or kilometers
Ex - Cuba is 100 miles from Florida
Absolute Location
The precise, fixed position of a place on Earth, typically expressed using latitude and longitude coordinates
Ex - Chicago is 41.8781° N, 87.6298° W
Census Data
Comprehensive collection of demographic and economic information about the population of a region, conducted by a government agency used to allocate resources and inform policy decisions
Data included - gender, age, Hispanic (y/n), race, # of people in home

Cultural Landscape
Built forms that cultural groups create inhabiting Earth and the meaning, values, representations, and experiences associated with those forms
Geographical area shaped by human activity and reflecting cultural practices, beliefs, and values
ANYTHING on earth modified/created by humans

Elevation
Height of a geographical location or feature above a fixed reference point, usually mean sea level - crucial aspect of topography
Affects climate and vegetation zones, settlement patterns, agricultural and economic activities, and transportation and infrastructure
Environmental Determinism
Belief that a region's physical environment, including climate, landforms, and natural resources, determines the development and cultural patterns of the people who live there
Was used to justify racism, colonialism, and imperialism suggesting certain groups were inherently “inferior” due to their environment
Ex - Development of Inuit culture in response to the Arctic conditions in which they live - Use what you have!

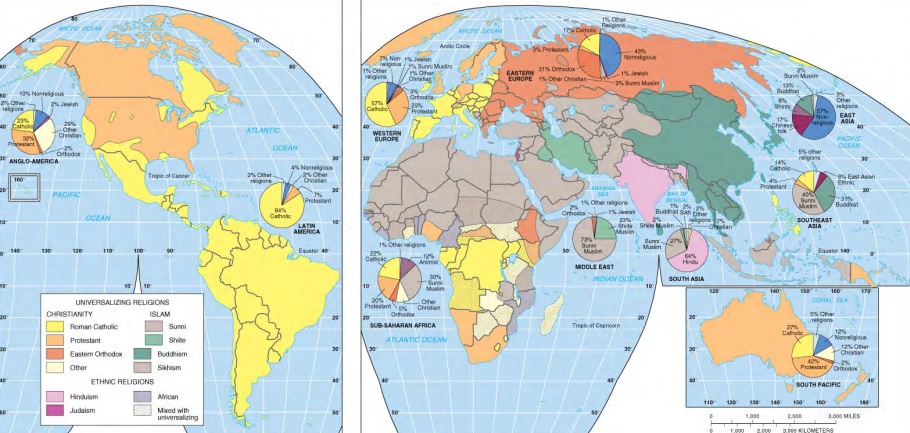
Formal Region
Area that shares one or more common characteristics, such as language, climate, or economic activity, throughout its boundaries
Political - any country, state, or city
Cultural - language or religious area
Economic - area where there is one dominant economic activity
Agriculture/Climate - area where one climate or type of agriculture is practiced
Functional Region
Area organized around a central point, or “node” with surrounding areas that are linked by these interactions. Distance decay occurs with movement away from the center (node)
A geographic area that has been organized to function politically, socially, culturally, or economically as one unit (connected by transportation, communication, or economic activities
Metropolitan Area - typically liked by transportation network
Business - stores, restaurants, radio/tv
Geographic Information System (GIS)
Computer-based system that captures, stores, analyzes, and displays geographically referenced data used for mapping and spatial analysis
Information stored in “thematic layers”
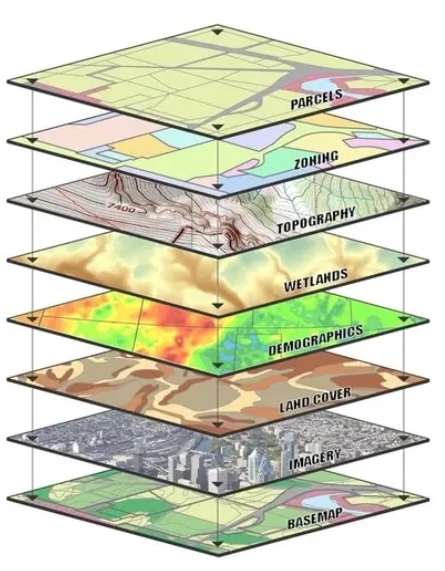
Global Positioning System (GPS)
Satellite-based navigation system that provides precise location and time information anywhere on Earth
Network of satellites to transmit signals to GPS receivers, allowing for the accurate determination of geographical coordinates
Natural Resources
Something found within the natural environment that is accessible and economically valuable to humans including food, water, soil, plants, animals, and minerals
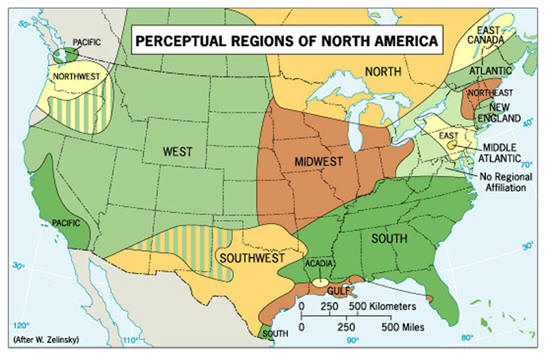
Perceptual/Vernacular region
Geographic area defined by people's beliefs, feelings, and attitudes about a place, rather than by physical or official boundaries
Place
A location on Earth that is distinguished by its physical and human characteristics
Possibilism
The belief that any physical environment offers a number of possible ways for a society to develop and that humans can find ways to overcome environmental challenges

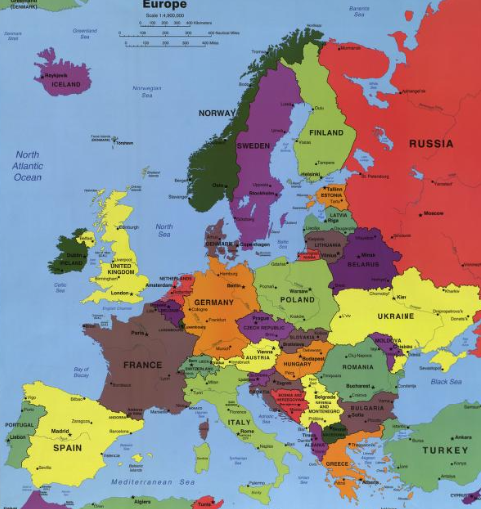
Reference map
Map that shows the location of geographic features and political boundaries
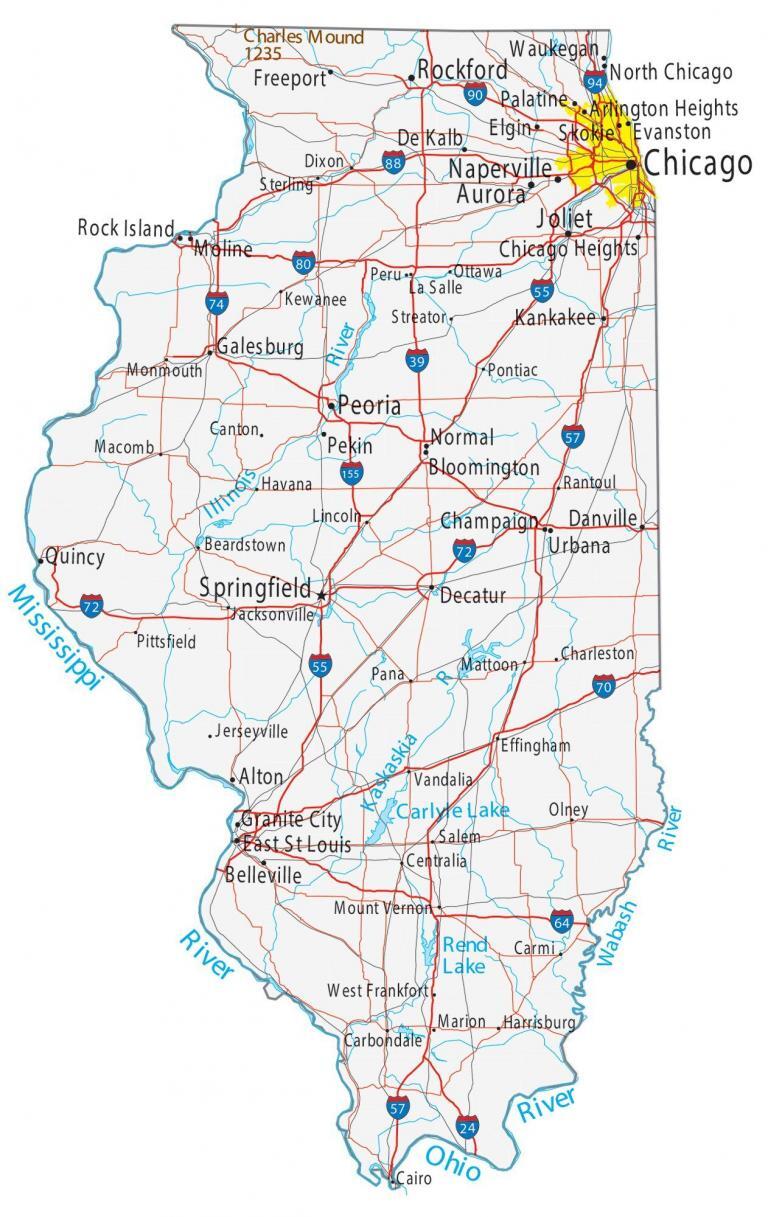
Region
Geographical area defined by shared characteristics, which can be physical, human, or both
Relative Direction
A direction that can be described as position, such as in front of or behind, to the left or to the right; describes the general relationship between places
Store is just past the big oak tree
Other side of the railroad tracks
Behind the school
Relative Distance
A measurement of the level of social, cultural, or economic similarity between places despite their absolute distance from each other
Shipping goods from China to U.S. make these places seem “closer” economically even though the distance is far
Approximate measurement of the physical space between two places, considering factors like time, cost, and difficulty of travel
New York City is 2 hours away from Washington D.C. by train - focuses on travel time
Relative Location
Describes a place's position in relation to other places, landmarks, or geographical features - uses TWO or more locations
Grocery store is across the street from the post office
Chicago being located on Lake Michigan as a railroad transportation hub
Remote Sensing
Process of collecting information about the Earth's surface from a distance, typically using satellites, aircraft, or drones

Satellite Imagery
Images of Earth taken by artificial satellites orbiting the planet

Scale
Refers to both the relationship between Earth's surface and the portion being studied, and the different scales of analysis), which are hierarchical levels of observation (global, national, regional, local)
Sense of Place
The emotional and psychological connection individuals have with specific locations, shaping their perceptions and experiences of those places
Thematic Map
Type of map that visually represents a specific subject or theme related to human activity and spatial patterns - DATA!!!
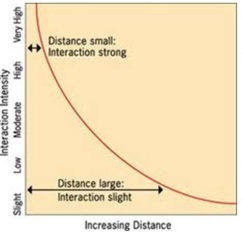
Distance Decay
Interactions between places weaken as the distance between them increases; things that are close to each other are more likely to be related or have interactions than things that are further apart. Essentially, the further you are from something, the less likely you are to interact with it.
Time-Space Compression
The shrinking of distance and time through advancements in technology, particularly in transportation and communication, leading to greater global interconnectedness and a feeling that the world is smaller
Wagon, car, train, airplane
Hand-delivered mail, dial-up internet, high-speed internet
Flow
The movement and connections between places and people, including the flow of resources, information, ideas, and even cultural elements (SPEED)
Globalization
The increasing interconnectedness and interdependence of countries and cultures, primarily driven by advancements in technology, communication, transportation, and trade
Human Geography
The study of the processes that have shaped how humans understand, use, and alter Earth
Pattern
The observable arrangement or distribution of people, objects, or phenomena across space
Linear, centralized, random
Sustainability
The use of Earth's land and natural resources in ways that ensure they will continue to be available in the future; Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
Scale of Analysis
The geographical area or level of organization used to study and analyze data:
Global: Encompasses the entire world and ignores borders of countries
Regional: Focuses on large geographic areas or regions (e.g., West Africa, North America)
National: Focuses on a single country (France, Japan, Botswana)
Local: Focuses on a specific location within a country (e.g., a city, state, province).
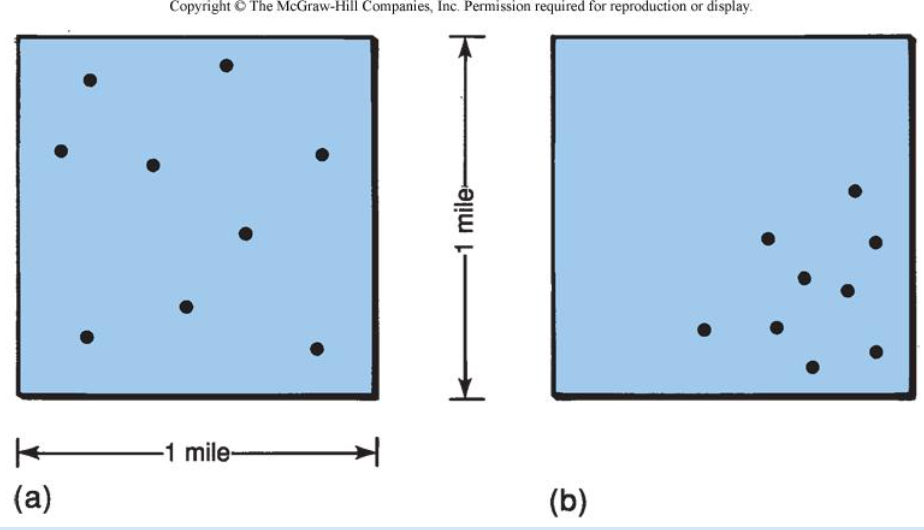
Clustering
Spatial pattern where people or objects are closely grouped together in specific areas of a population. This suggests that the concentrated regions have a higher density than the surrounding areas
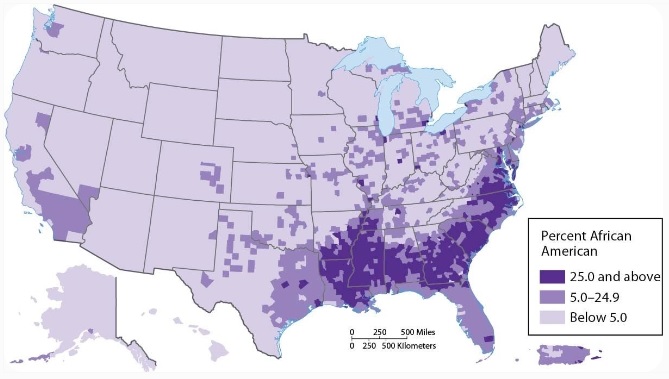
Dispersal
Spatial pattern where objects are spread out from one another
The way in which a phenomenon, like a population or cultural trait, is spread out over a geographic area

Map Distortion
Inaccuracies that occur when representing the Earth's three-dimensional surface on a two-dimensional map; distorts spatial relationships in shape, area, distance, and direction
Online Mapping and Visualization
Using digital tools and techniques to create and display maps and geographic information online, often through Web Geographic Information Systems (Web GIS)
Google maps - showing real-time information (traffic, stores, restaurants)
Spatial Relationships (Distribution)
Arrangement or spread of phenomena across space
Regional Analysis
The study of a specific area or region to understand its unique characteristics, patterns, and how its parts interact; examining physical, social, economic, and cultural factors to explain the region's functioning
Density
Frequency of something within a given space, often measured per unit of land (e.g., people per square mile);
HOW MANY - focus on high/low
Concentration
Extent of a feature's spread over a given space (clustered/dispersed)
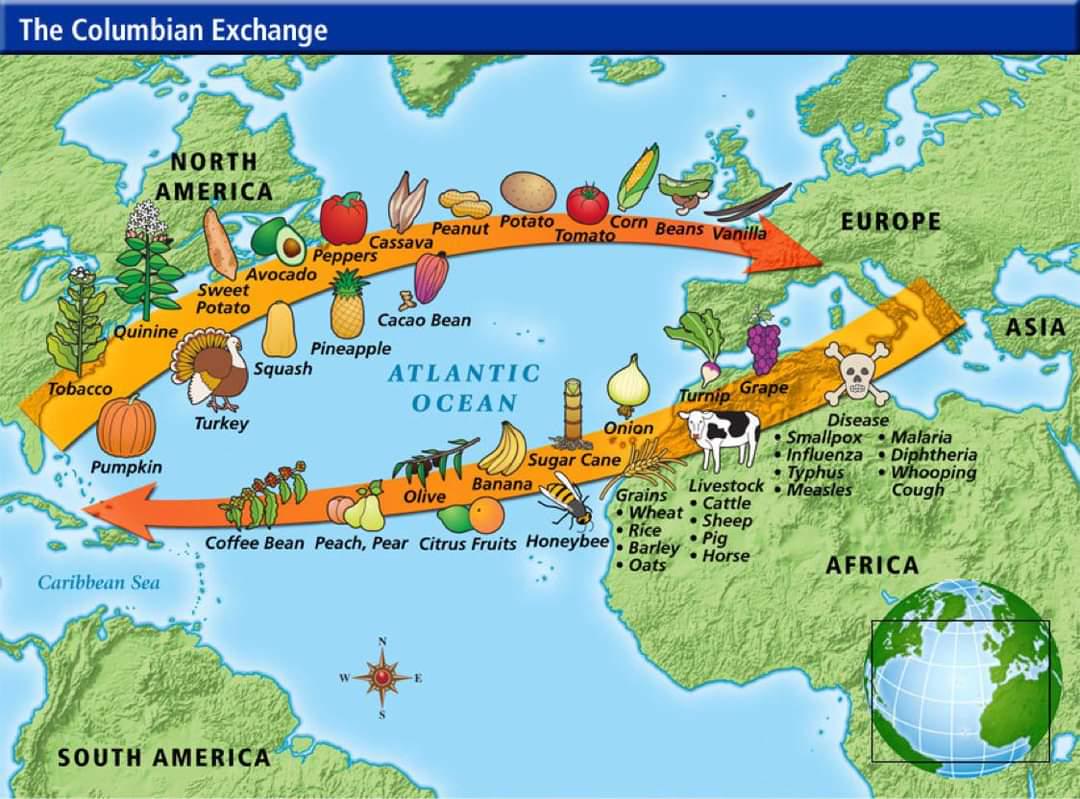
Relocation Diffusion
The spread of a cultural trait or idea from one place to another due to the physical movement of people, like migration
(eg. Columbian Exchange)
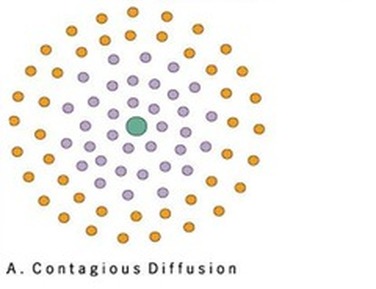
Contagious Diffusion
Process where a cultural trait or innovation spreads rapidly and widely through a population, typically through direct contact and interaction
Rapid, widespread diffusion of a characteristic throughout the population (diseases or viral internet trends)
Hierarchical Diffusion
Spread of an idea from larger city or urban area, to smaller cities or urban areas, and possibly rural areas (leapfrog)
Spread of an idea from persons or nodes of authority or power to other persons or places
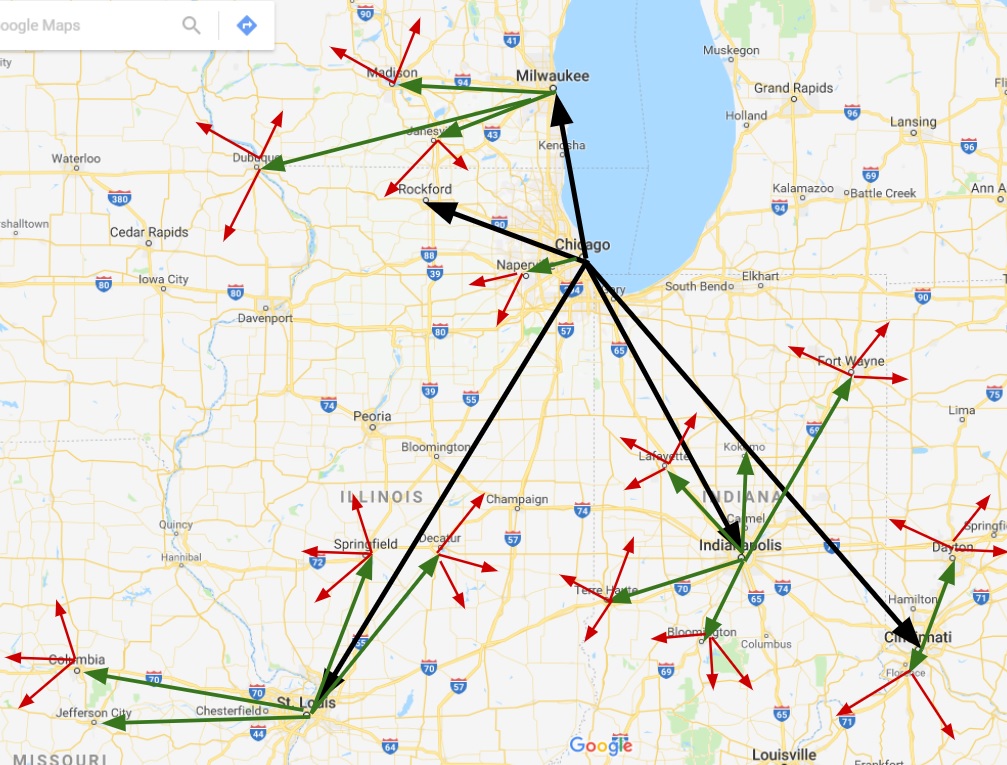
Stimulus Diffusion
Occurs when a cultural trait diffuses and is modified or adapted as it's adopted in a new location, rather than being adopted in its original form (underlying principle is diffused)

Cultural Ecology
Theory that examines the relationship between human cultures and their environment
Study of the interactions and results between society (humans) and their environment
Interdependence
Mutual reliance between nations, regions, or systems, where the actions or decisions of one significantly impact others; interconnectedness of the world and how globalization has increased the need for collective action and cooperation on various issues
Hearth
Region where a particular cultural innovation or practice, such as agriculture or religion, first originated and then spread to other areas
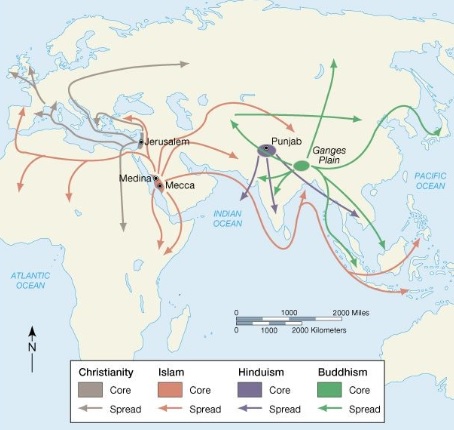
Transnational (Multinational) Corporation
Company that conducts business, operates factories, and sells products in many countries, not just its headquarters or where its shareholders are located

Spatial Approach
Studying the arrangement and relationships of things within a given space, looking at how they are located and how they interact with each other and their environment
Land Use
Specific functions for which humans utilize land, including agriculture, residential, commercial, industrial, and recreational areas
Regional Boundary
Edge or limit of a region, marking where the dominant characteristics or features of that region change or diverge; transitional and often contested and overlapping and can reflect cultural, political, or environmental differences