Topic 5A.1: The Importance of ATP
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pg. 14
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What are autotrophic organisms?
Autotrophic organisms are organisms that make complex organic compounds from simple compounds in the environment
Most of them do this by photosynthesis
What is photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the process by which living organisms (particularly plants and algae) capture the energy of the Sun using chlorophyll and use it to convert carbon dioxide and water into simple sugars such as glucose and starch
What are the glucose and starch molecules used as?
The glucose and starch molecules are used as an energy source by the organism, and as the building blocks of other important molecules such as proteins.
There are a few autotrophic bacteria that are not photosynthetic. How do their synthesise their food?
They use energy from chemical reactions to synthesise their food
What does heterotopic mean ?
Heterotrophic organisms are organisms that obtain complex organic molecules by feeding on other living organisms or their dead remains
They use the products of photosynthesis indirectly for making necessary molecules, and as fuels to supply energy for activities
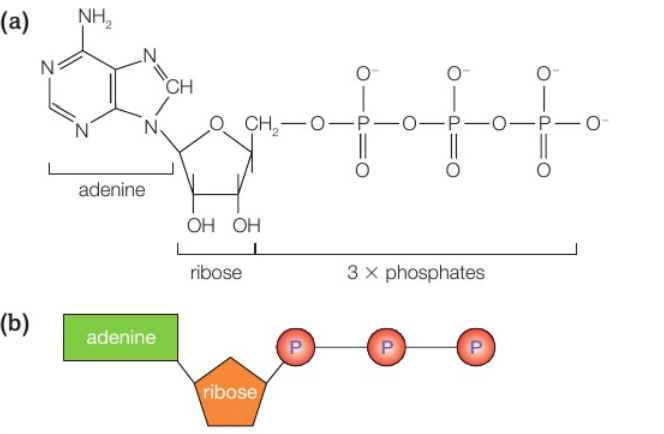
What is adenosine triphosphate (ATP)?
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleotide that acts as the universal energy supply in cells.
It is made up of the base adenine, the pentose sugar ribose and three phosphate groups
What occurs if anything interferes with the production or breakdown of ATP?
Anything that interferes with its production or breakdown is fatalto the cell and, ultimately, the organism
What occurs when energy is needed?
When energy is needed, the third phosphate bond can be broken by a hydrolysis reaction
This is catalysed by the enzyme ATPase.
What is ATPase?
ATPase is the enzyme which catalyses the formation and breakdown of ATP, depending on the conditions
What is adenosine diphosphate (ADP)?
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP), is a nucleotide formed when a phosphate group is removed from ATP, releasing energy to drive reactions in the cell
ADP is the result of the hydrolysis of ATP
What are the three results of the hydrolysis of ATP?
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP)
A free inorganic phosphate group (Pi)
Energy
About 34kJ of energy is released per mole of ATP hydrolysed
Some of this energy is lost as heat and is wasted.
The rest is used for any biological activity in the cell which requires energy
EXAM HINT
Synthesising (making) ATP is a condensation reaction
Breaking down ATP is a hydrolysis reaction.
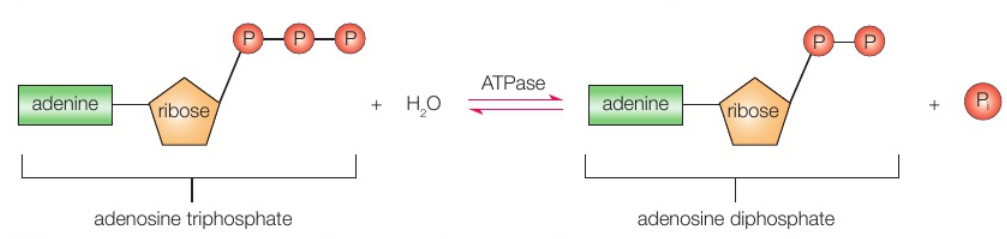
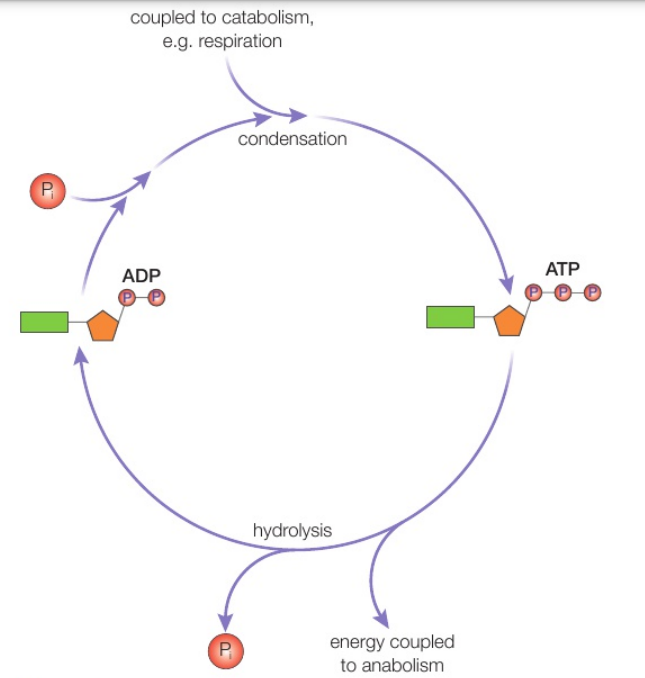
The breakdown of ATP into ADP and phosphate is a reversible reaction.
The breakdown of ATP into ADP and phosphate is a reversible reaction. This means
ATP can be synthesised (made) from ADP and a phosphate group
PAGW 15??????
Where does the energy needed to drive the synthesis of ATP usually come from?
The energy needed to drive the synthesis of ATP usually comes from catabolic (breakdown) reactions or reduction/ oxidation reactions (redox reactions)
As a result, an ATP molecule provides an immediate supply of energy for your cells, ready for use when needed
What are reduction/oxidation reactions (redox reaction)?
Reduction/oxidation reactions (redox reactions) are reactions in which one reactant loses electrons (is oxidised) and another gains electrons (is reduced)
There are two main ways in which ATP is formed from ADP and inorganic phosphate in the cell. Explain both
By using energy released from the catabolic reactions which take place, for example, in cellular respiration.
By by the removal of hydrogen atoms from several of the intermediate compounds in a metabolic pathway
What is the main way in which ATP is synthesised?
The main way in which ATP is synthesised is by the removal of hydrogen atoms from several of the intermediate compounds in a metabolic pathway
What happens when two hydrogen atoms are removed from a compound?
When two hydrogen atoms are removed from a compound, they are collected by a hydrogen carrier/acceptor
The acceptor is reduced
Electrons from the hydrogen atoms are then transferred along a series of carriers known as an electron transport chain
The components of the chain are reduced when they receive the electrons, and oxidised again when they transfer the electrons to the next part of the chain.
These redox reactions each release a small amount of energy which is used to drive the synthesis of a molecule of ATP. In this way, the energy is readily available for use when it is needed in the cell
What is the electron transport chain?
The electron transport chain is a series of electron-carrying compounds along which electrons are transferred in a series of oxidation/reduction reactions, driving the production of ATP