ID 7: Abscessation and UTIs in Livestock: Actinomyces and Corynebacterium
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Describe the Bacterial Properties of Actinomyces and Corynebacterium species in terms of:
1. Bacterial Properties
2. Incubation Period
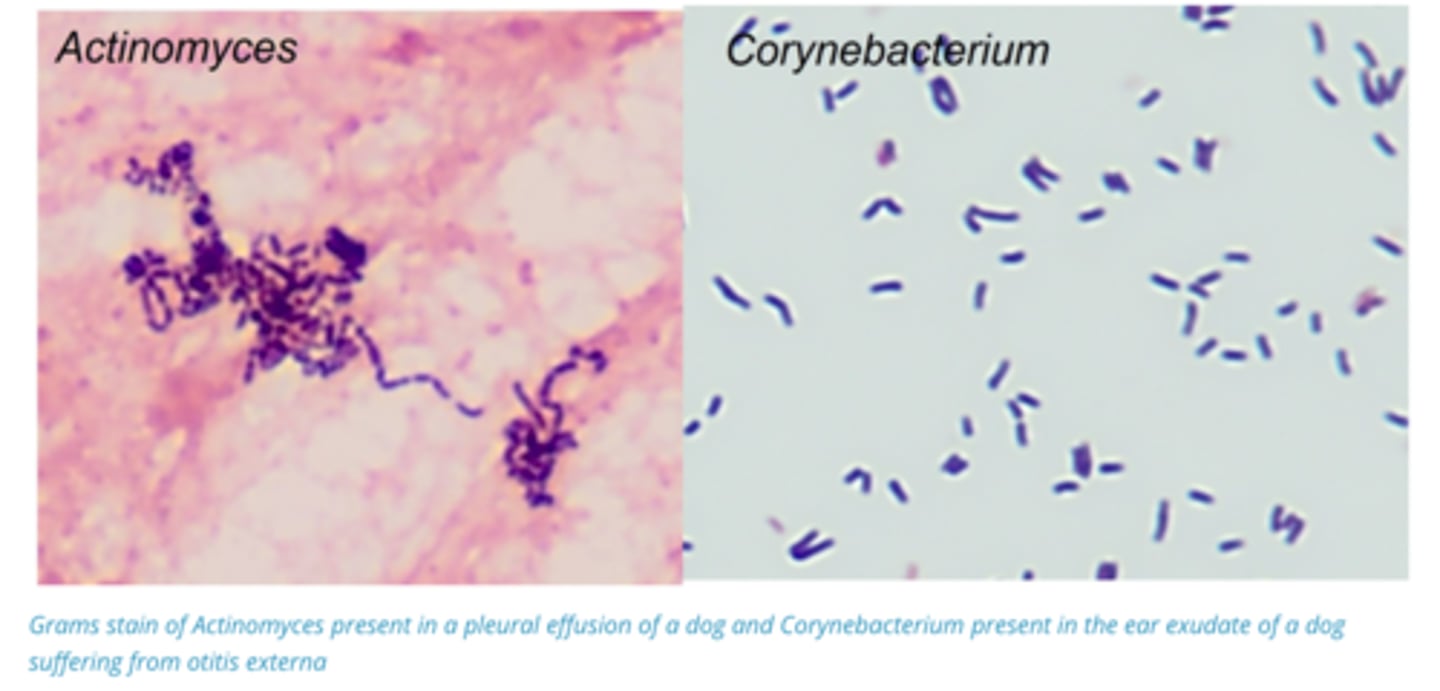
1. Gram +ve pleomorphic rods, non-motile,
- Facultative anaerobes/obligate anaerobes
2. Long Incubation period (Not rapid diseases)
Describe what Disease the following Important Actinomyces and Corynebacterium species cause:
1. Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis
2. Trueperella pyogenes
3. Actinomyces bovis
1. Causes Caseous lymphadenitis/Cheesy Gland in Sheep and Goats
2. Causes Abscessation of skin, sub-cutis and all organs in Ruminants and Pigs
3. Causes Lumpy Jaw in Cattle
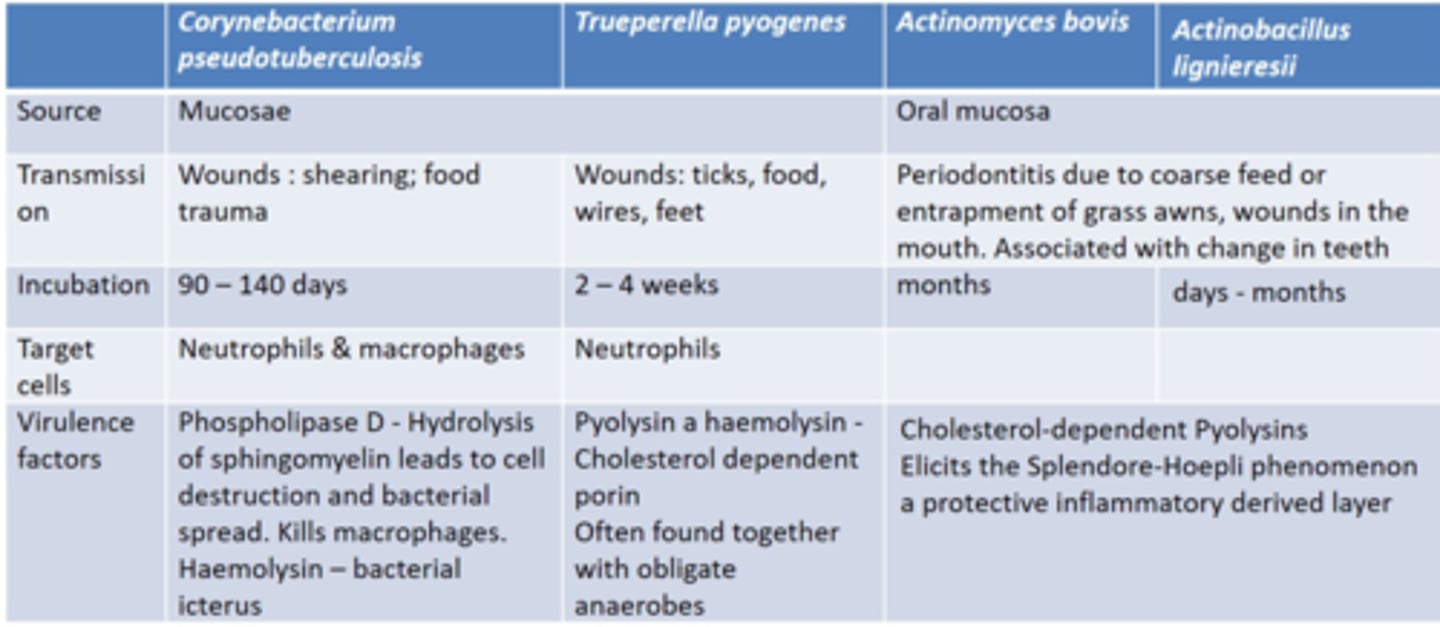
Describe Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis (Caseous lymphadenitis/Cheesy Gland) in terms of:
1. Source of Bacteria
2. Transmission
3. Target Cells
4. Lesions caused by the Bacteria
1. Mucosae
2. Shearing Wounds
3. WBCs
4. Abscessation of regional lymph nodes and internal organs
Describe Trueperella Pyogenes in terms of:
1. Source of Bacteria
2. Transmission
3. Target Cells
4. Lesions caused by the Bacteria
1. Mucosae
2. Tick/Wire/ Feet Wounds
3. WBCs
4. Abscessation of Skin and Internal Organs

Describe Actinomyces bovis (Lumpy Jaw) in terms of:
1. Source of Bacteria
2. Transmission
3. Lesions caused by the Bacteria
1. Oral Mucosa
2. Periodontitis due to coarse feed/wounds in mouth/change in teeth
3. Lesion in the soft tissues and bones of the face
Describe Actinomyces lignieresii in terms of:
1. Source of Bacteria
2. Transmission
3. Lesions caused by the Bacteria
1. Oral Mucosa
2. Periodontitis due to coarse feed/wounds in mouth/change in teeth
3. Wooden tongue, soft tissues of the head
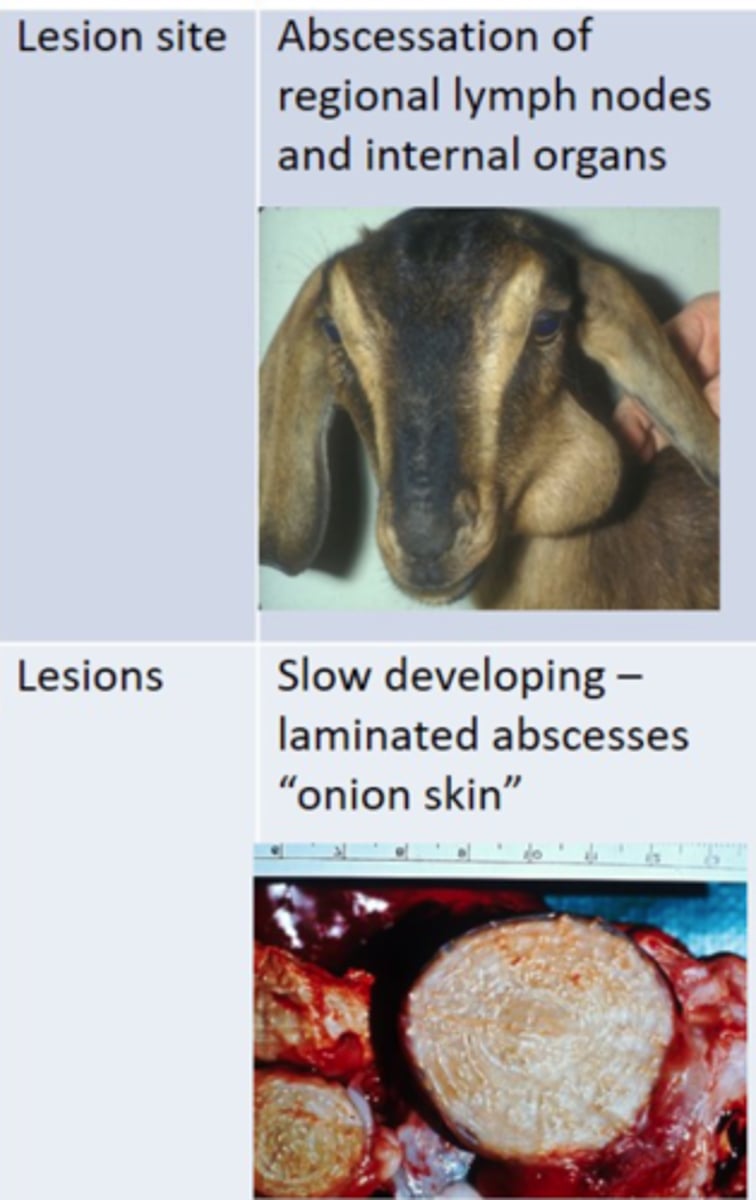
Describe Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis (Cheesy Gland/Caseous Lymphadenitis) in terms of:
1. Source of Bacteria
2. Transmission
3. Lesions
4. Cause of Disease Outbreaks
1. Mucosa of Sheep and Cattle
2. Organism enters wounds and travels to regional lymph nodes + rest of body. As well as Coughing sheep with lung infections
3. Slow developing Onion Skin abscesses in LN and Organs. Internal abscesses are most pathogenic and Cause Chronic Weight Loss
4. Infects and spreads through wounds. Sources of high numbers of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis include ruptured abscesses or those cut open at sheering times in sheep
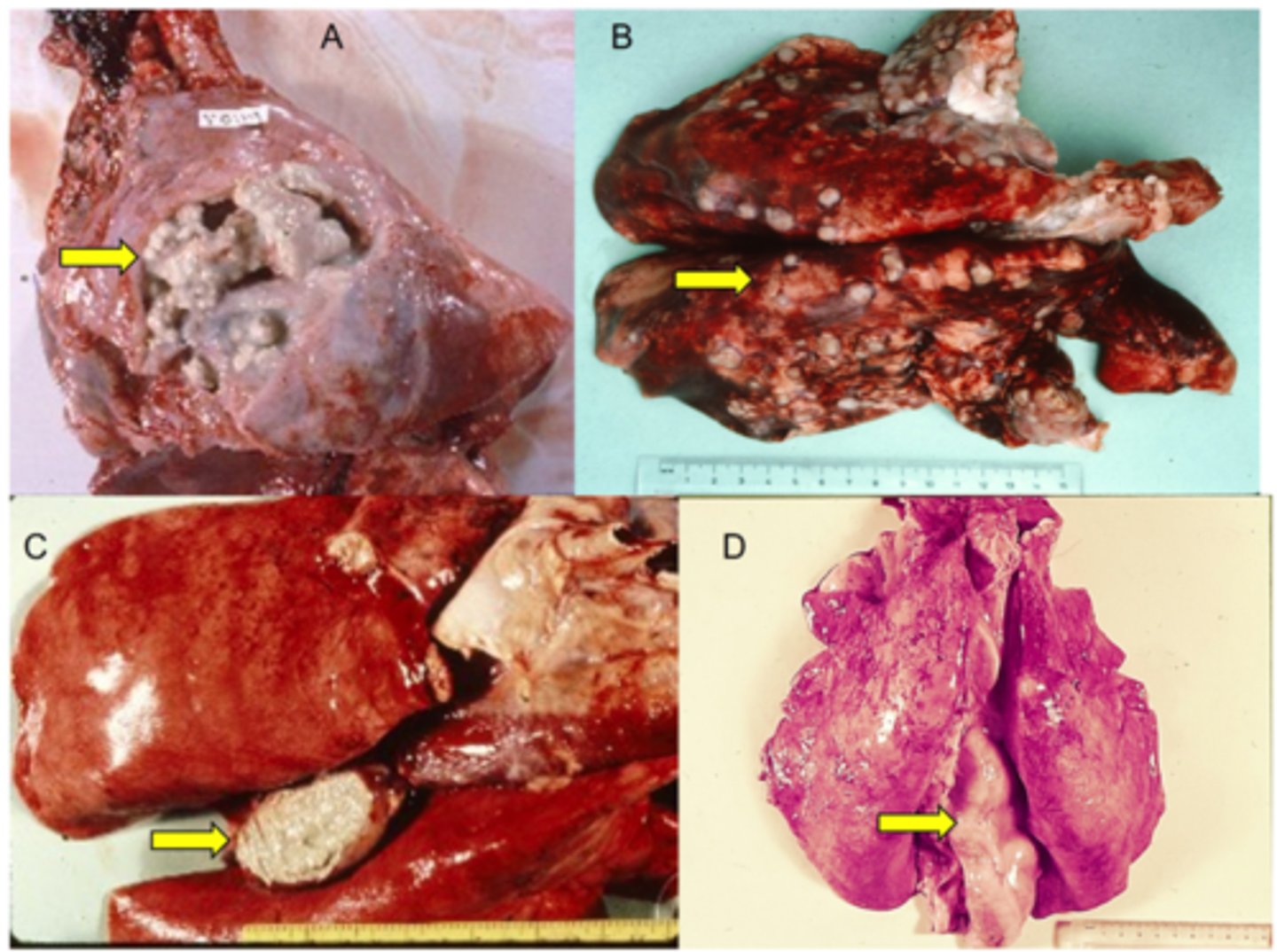
Describe Trueperella pyogenes in terms of:
1. Source of Bacteria
2. Transmission
3. Synergism
1. Found of the Mucosa of Sheep and Cattle
2. Organism enters wounds and localises, Can then spread via the bloodstream and localises in several organs (Lung, Joints, Liver, CNS).
3. Synergistic with many other bacteria (Rarely found alone)
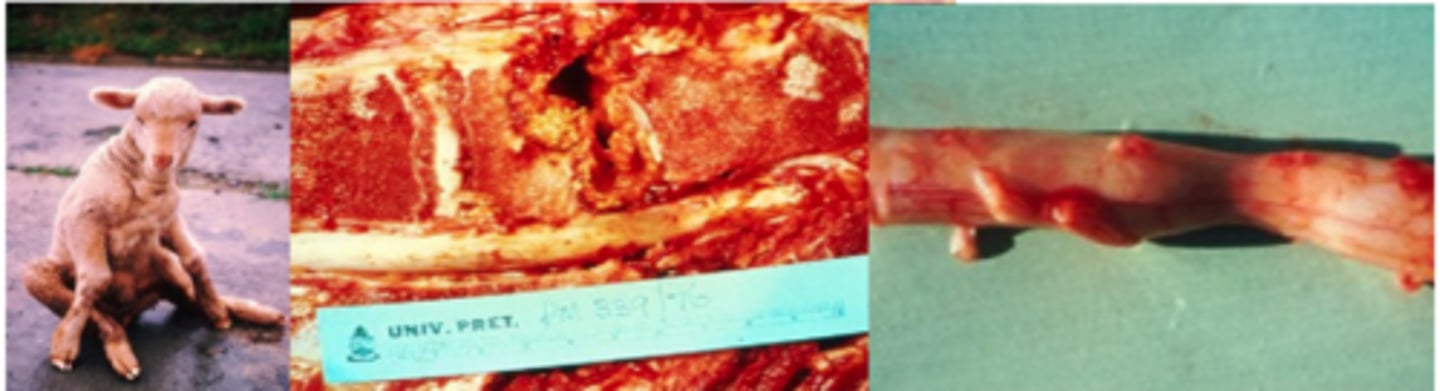
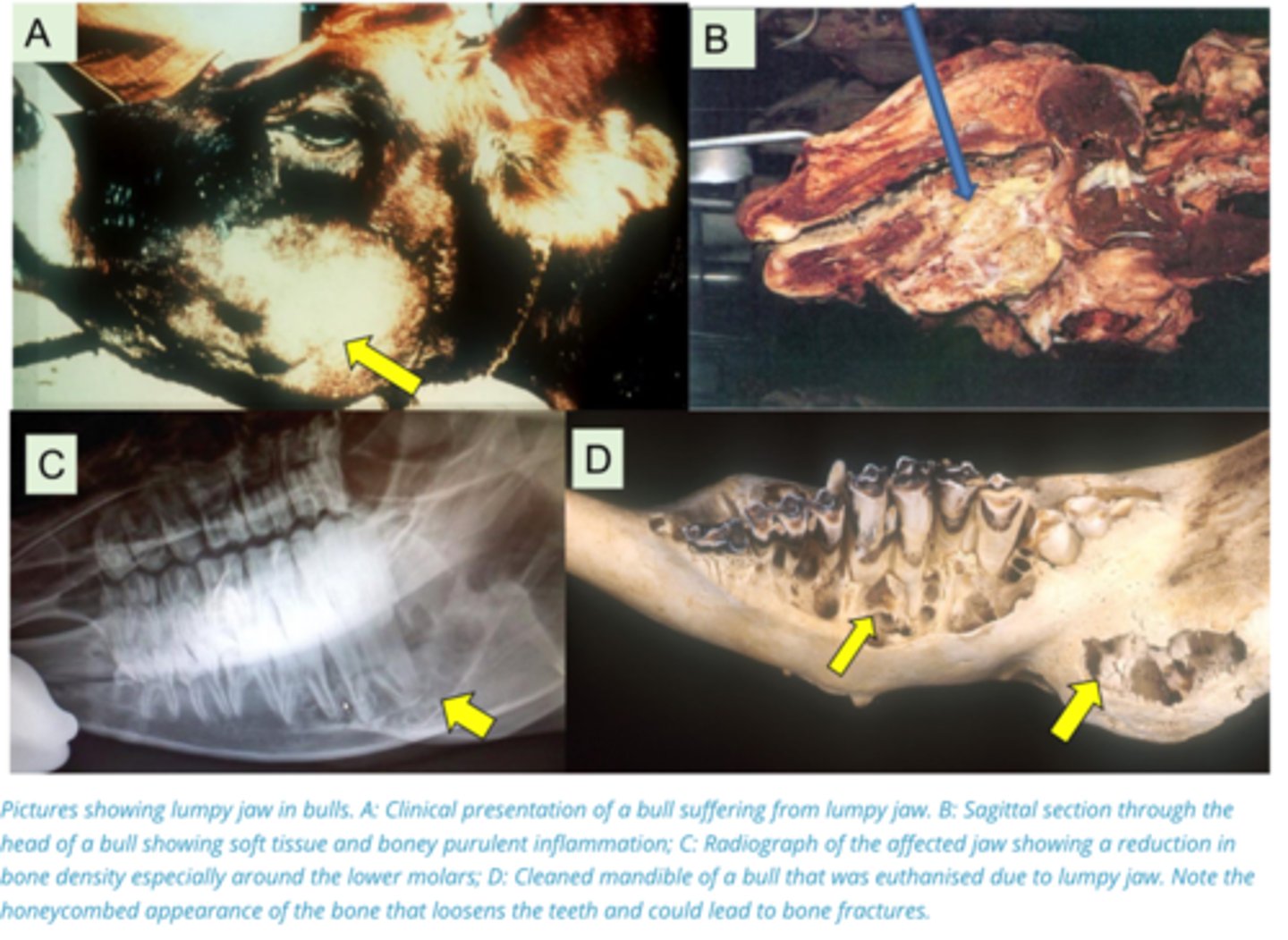
Describe Actinomyces Bovis (Lumpy Jaw) in terms of:
1. Source of Bacteria
2. When Infection Occurs
3. Pathogenesis
1. Commensal of the Oral cavity, causes a slow progressive granulomatous disease of the jaws of 2-5 year-old cattle.
2. Occurs when there is periodontitis during change of teeth, rough feed, or grass entrapment
3. Organism gets under teeth and grows slowly → Infects bone → Bone remodelling around bacteria → Bone becomes expanded, porous, and weak
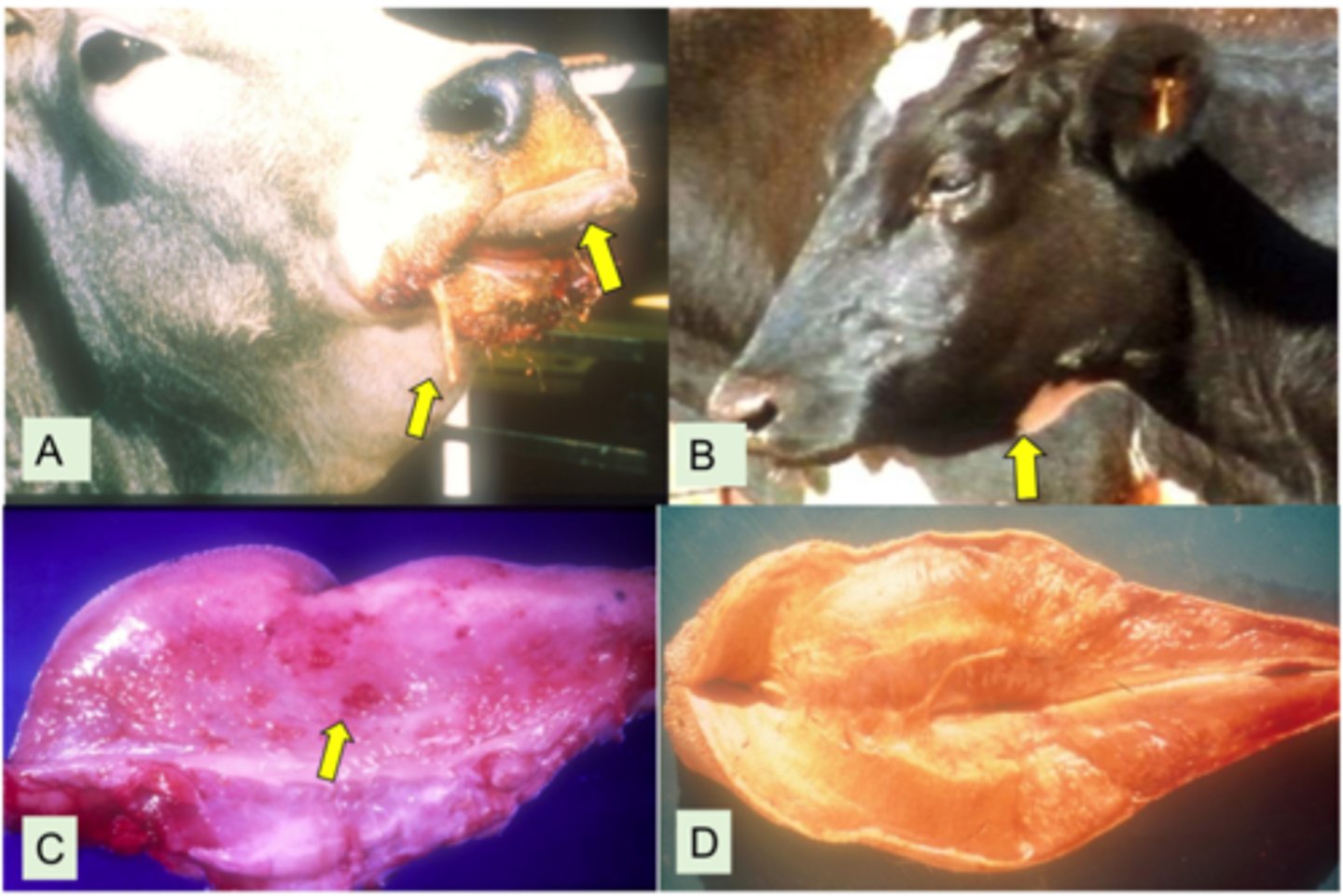
Describe Actinomyces Ligniersie (Wooden Tongue) in terms of:
1. Bacterial Properties
2. Source of Bacteria
3. Pathogenesis
1. Gram -ve coccobacilli
2. Found in oral cavity of ruminants
3. Targets soft tissue, associated with trauma in the oral cavity → Interference with feed intake
Describe the Diagnosis of of Abscessation in animals in terms of:
1. Where to Collect Samples
2. Clinical Examination/Post Mortem
3. Gross Abscess Evaluation
4. Cytological Abscess Evaluation
5. Bacterial Culture
1. Needle aspirate from edge of abscess
2. Examination to check for abscess distribution
3. Pus colour, consistency, and smell. Also look for granules
4. inflammatory cell present, eosinophilic clubbing, Gram +ve/-ve bacterial morphology.
5. Often required as a large variety of bacteria may cause abscessation
Explain the Treatment of Abscessation in terms of:
1. Considerations before Culling
2. Internal Abscesses
3. External Abscesses
4. Antibiotic Treatment
1. Consider Value and Welfare of animals
2. Usually Cull. Expensive and have poor prognosis despite treatment
3. Lance, Drain into a container to reduce environmental contamination, and flush
4. Treat with Macrolides
Explain Methods of Prevention of Abscessation:
- Stopping Injuries
- Isolate animals with Cheesy gland (Contagious), Treat
- Good Wound Care
- Good Shearing Hygiene
- Vaccinate for C. Pseudotuberculosis)
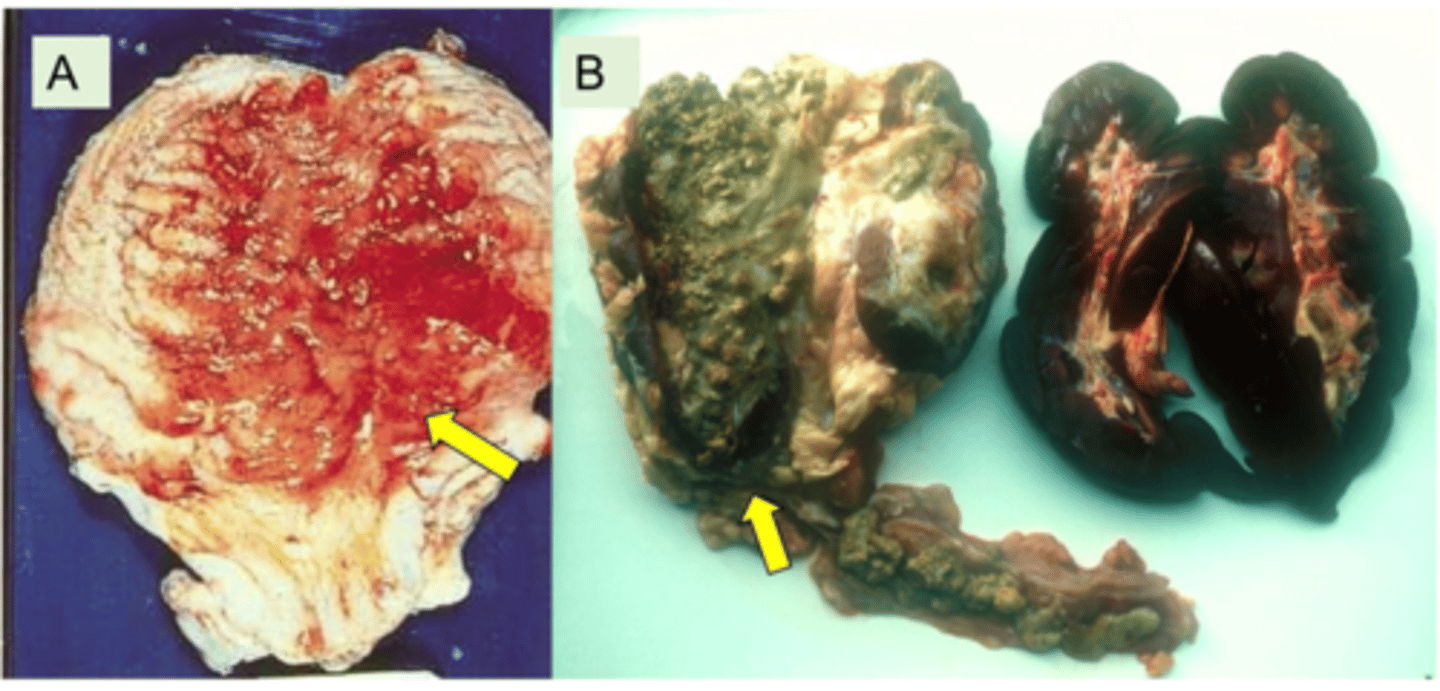
Describe Corynebacterium Renale (Contagious Pyelonephritis) in terms of :
1. Source of Bacteria
2. Animals Disease is most common in
3. Pathogenesis
4. Clinical Signs
5. Diagnosis
6. Treatment
1. Commensals of the vagina + Prepuce, Infectious
2. Most common in multiparous, post parturient cows
3. Bacteria spreads so cattle get infections in bladder → Urinary Tract → Kidneys
4. Causes Uraemia, Renal failure
5. Confirmed by blood biochemistry (High Urea and creatinine Levels)
6. If not in renal failure, treat with penicillins
Define Actinobaculum Suis (Porcine Cystitis-Pyelonephritis Complex in terms of:
1. Animals Most Affected by Disease
2. Transmission
3. Pathogenesis
4. What is Seen on Cytology
1. Affects mainly gilts as the don’t have immune memory,
2. Venereal transmission (Only seen on farms with natural mating). 1 Boar can infect many animals
3. Urinary tract infection within 2 weeks of mating → Frequent Urination + Blood Stained Urine
4. Gram bacteria rods. Obligate anaerobe