Bio Unit 4-5
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Look at cell pogil, surace area:volume pogil, and diffusion pogil Look at organelle function quizlet Look at cell drawing
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
what is the cell theory
1- all life is composed of cells
2- all cells come from other cells
what is a theory
something in science that has been constantly tested and proved correct
cell size range
100µm to 1µm (µm being micrometer)
which are smaller prokaryotes or eukaryotes
prokaryotes
cells are surrounded by
plasma (cell) membrane
what is the plasma (cell) membrane made of
phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins
what does the cell membrane let in
small uncharged molecules (ex: water)
what can proteins let in
they are like doors and can let in larger charged molecules (ex: C6H12O6)
HOWEVER each doorway can only let in certain things
every cell has
ribosomes, DNA, cell/plasma membrane, cytosol
eukaryotic cells have
nucleus and membrane bond organelles
why are membrane bond organelles so important
allows for compartmentalization of cell activities which separates organelles from the rest of the cell (lysosomes destroys stuff but doesn’t destroy everything because of membrane)
4 groups of organelles
1 - controls genes and proteins
2 - control production, modification, and breakdown of cellular products
3 - energy
4 - structure, movement, signalling
controls genes and proteins
nucleus, ribosomes
control production, modification, and breakdown of cellular products
endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus (body), lysosome, peroxsisome, vacuole
energy
mitochondria, chloroplast
structure, movement, signalling
cell membrane, cell wall, cytoskeleton
differences between animal and plant cells
animal - centrioles, cilia, vesicle, flagella, lysosome, gap junctions
plant - cell wall, chloroplast, plasmodesmata
what is the endosymbiotic theory
an ancestral eukaryotic dell engulfed an aerobic bacterium but did not digest the potential food item
eukaryotic cells engulfed mitochondria and chloroplast (they used to be prokaryotes)
why would a cell want a smaller volume to surface ratio (2:1 vs. 1:8)
smaller cells make it easier for the things in the cell to move to where they need to be but if they are bigger it makes it harder to maintain homeostasis
what are the 2 ways a cell can move huge molecules both ways across membranes
exocytosis and enodcytosis
what is exocytosis
used to export bulky molecules (ex: proteins or polysaccharides) requires energy and can with with or against the concentration gradient
what is endocytosis
used to take in large molecules requires energy and can go with or against the concentration gradient
in both exo and endo -cytosis the materials being transported…
are packaged ina vesicle with fuses with the membrane
what are the 2 types of endocytosis
phagocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis
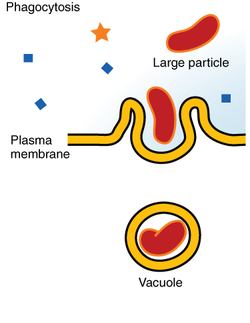
what is phagocytosis
the englufment of a particle by the cell wrapping the cell membrane around it, forming a vacuole
the pseudopodium strecth to let it in
what is receptor-mediated endocytosis
it uses membrane receptors for specific solutes
basically it needs something to say let me in
the molecule needs to bind to the receptor
in both phagocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis the material being transported…
is packaged in a vesicle which fuses with the membrane
what is energy
capacity to cause change
what is kinetic energy
energy of motion
what is potential energy
energy stored in a location or structure of matter (including chemical energy)
what is chemical energy
potential energy stored in the bonds between atoms
what is the law of thermodynamics
energy can change form but cannot be created or destroyed
energy transfers or transformations increase disorder, or entropy, with some energy being lost as heat
what are exergonic reactions
ones that release energy
what are endergonic reactions
ones that require energy and yield products rich in potential energy
what is metabolism
the sum of reactions in your body
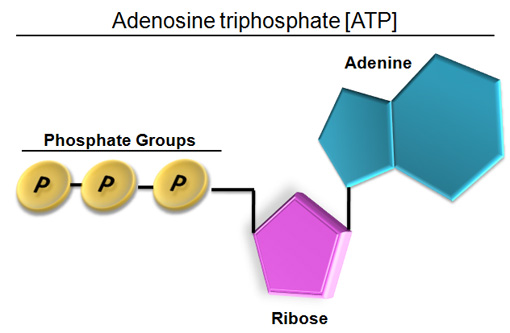
what is ATP
it powers nearly all forms of cellular work
just ignore the ribose for now
has 3 phospate groups (triphosphate) with enrgy between the bonds and a adenosine
The transfer of a phosphate group from A T P is involved in
chemical, transport, and mechanical work
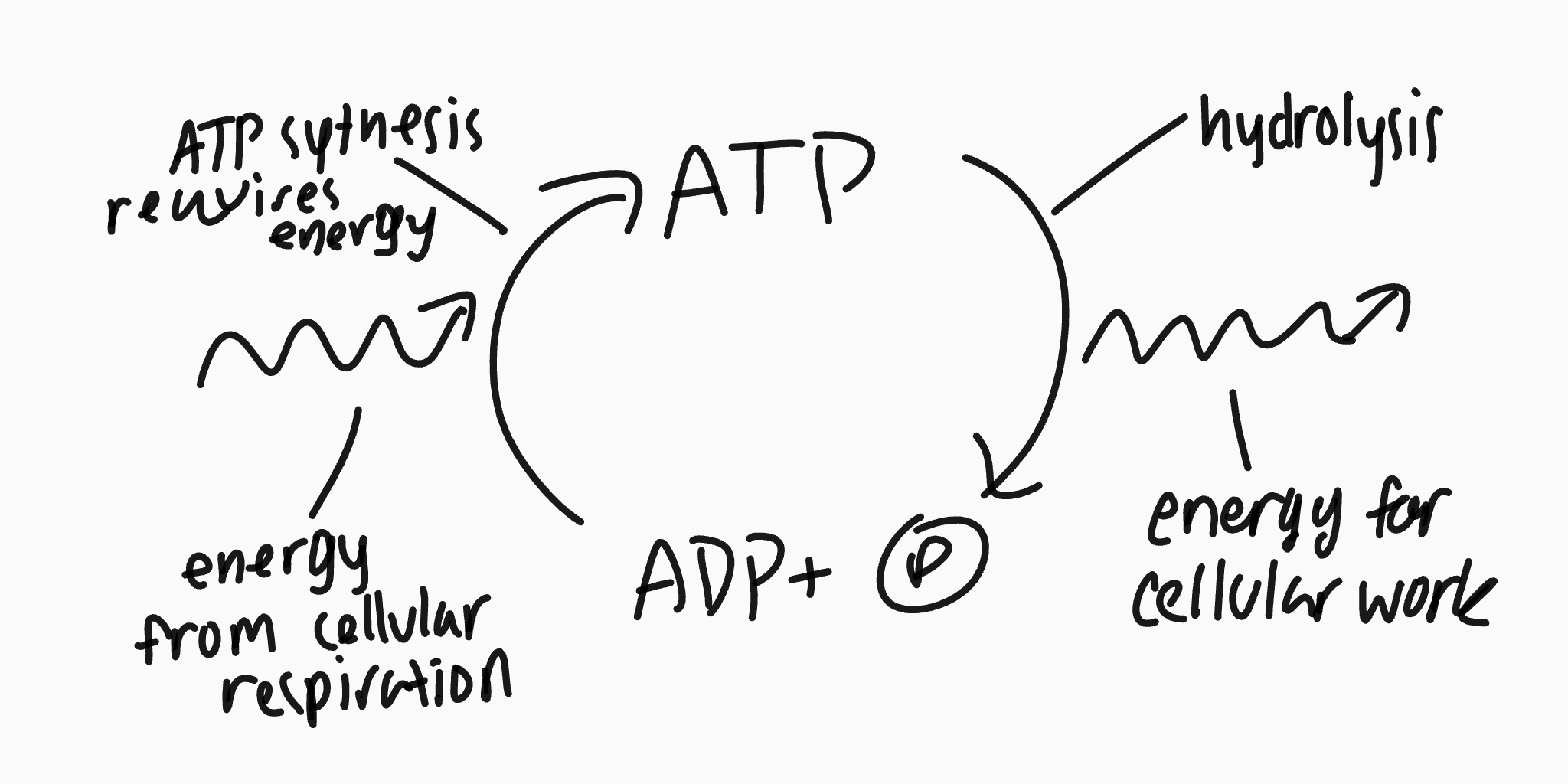
when the body needs the energy how does it get it
it adds water to get the energy between the bonds making it a diphosphate (ADP)
what are enzymes
catalysts (speed up chemical reactions) they decrease the reaction energy needed for a reaction to begin without being consumed by the reaction
what is the relationship between substrates and active sites
an enzymes substrate fits specifically in a region of the enzyme called the active site (every reaction has a different shape and reaction)
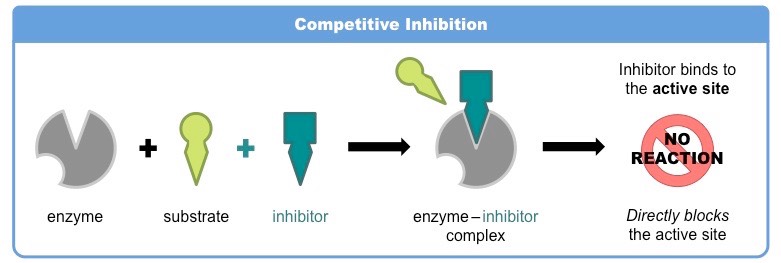
what is a competitive inhibitor
reduces enzymes productivity by blocking the substrate molecule from entering the active site
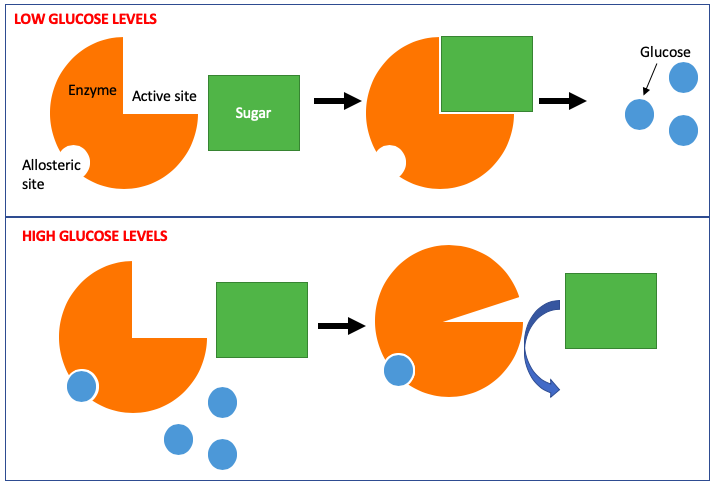
what is a noncompetitive inhibitor
it doesn’t enter the active site, instead it binds to a site elsewhere on the enzyme and its binding changes the shape so the active site no longer fits the substrate
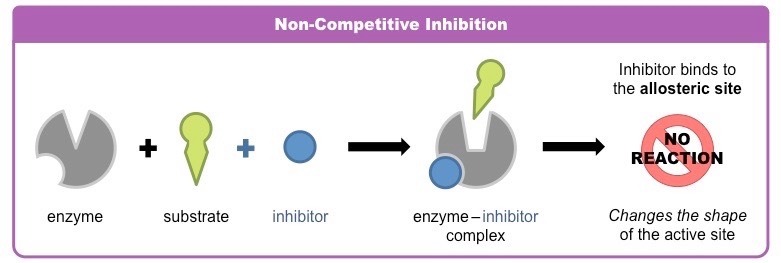
what is feedback inhibition
it helps regulate metabolism
so the product of a reaction is a noncompetitive inhibitor for the same reaction
because it already happened so it doesn’t need to happen again
most beneficial drugs…
act as enzyme inhibitors (ex: pesticides and deadly poisons used for warfare)
is it better to have many small cells or few larger ones
many smaller cells because it offers more surface area and in smaller cells it is easier for things to get around within the cell
what r the 2 main things that make up the cell membrane
phospholipids and membrane spanning proteins and some small surface proteins
what is the structure called when a carbohydrate chain is attached to a protein
glycoprotein
what is the structure called when a carbohydrate is attached to a phospholipid
glycolipid
what type of transport requires energy (ATP)
active transport
in which types of transportation do molecules move along (down) the concentration gradient
passive transport - diffusion and facilitated diffusion
in which types of transport do molecules move against (up) the concentration gradient
active transport
which type of transport involves channel (membrane-spanning) proteins
active transport and facilitated diffusion
in which type of transport do molecules pass between the phospholipids
diffusion
which type of transportation moves large, charged molecules or ions
active transport and facilitated diffusion
which type of transport moves small nonpolar and polar molecules
diffusion
when there is a difference in concentration of a particular particle on either side of a membrane a _______ exists
concentration gradient
when do the particles stop moving back and forth across the cell membrane
when they reach equilibrium
at that point there is no _________ but the particles continue to move randomly across the membrane called _____
net movement
dynamic equilibrium
what is the gap for facilitated diffusion between the proteins called
gated channels
what type of molecules attached to the membrane spanning protein allowing it to open
hormones
explain (in detail) active transport
it happens between the membrane spanning proteins and there is an ATP binding site because it requires energy and the ion binding site which is the thing passing though, it goes from the low to high concentration after the process is done the ATP becomes ADP as it lost a phosphate
if the net movement of water is out will the solution inside the cell become more or less concentrated
more as it is loses water making it have more solute than solvent
what is the diffusion of water through a membrane
osmosis
what is going on a hypertonic cell
the water is leaving it making it shrivel
what is going on in a isotonic cell
the amount of water going in and out is equal
what is going on a hypotonic cell
more water is going into it making it get larger and sometimes burst (only animal cells)
what is the name for a hypertonic animal and plant cell
crenated
plasmolysed
what is the name for a hypotonic animal and plant cell
lysed
turgid
what allows the plant cell to not shrivel or get as large as the animal cell
its cell wall
WHY in a hypertonic cell is the water leaving
the water is leaving because water moves from a place of high concentration to low concentration
inside the cell has plenty of water to balance out the solute but the outside has lots of solute and not as much water so it leaves to try to even it out
this means the outside of the cell has a higher concentration (more solute and less water)
WHY in a hypotonic cell is more water coming in
the water is coming in because water moves from a place of high concentration to low concentration
outside the cell has plenty of water to balance out the solute but the inside has lots of solute and not as much water so it comes into the cell to try to even it out
this means the outside of the cell has a lower concentration (less solute and more water)
what does cholesterol do for the cell membrane
cholesterol makes up a small part of the cell membrane and helps it to maintain its fluidity
the cell membrane is mostly made up of lipids and if it was only lipids when it got cold the cell membrane would freeze but it doesn’t because of the cholesterol
imagine you put a cell that is 40% water into a solution that is 80% water what will happen (if it is an animal and if its a plant)
animal - it'll hypotonic and will be lysed
plant - it’ll be hypotonic and turgid
what is the difference between an exergonic reaction and exocytosis
exergonic reaction - one that releases energy
exocytosis - used to export bulky molecules out of a cell
what is the active site
the place where the substrate bonds
when a cell gets bigger what increase faster (volume or surface area)
volume
what does the nucuelous do
make ribosomes
ATP is broken down by what
hydrolysis
what is rough ER and what does it do
Ribosomes are on the surface and involved in protein synthesis
what is smooth ER and what does it do
Contain enzymes for synthesis lipids and detoxication of drugs
what are peroxisomes and what do they do
detoxify and lipid metabolism and the processing of reactive oxygen species, convert hydrogen peroxide to water in both animal and plant cells