Coastal landforms
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What are the coastal landforms that are caused by erosion?
cliffs and wave cut platforms
headlands and bays
caves arches stacks
What are coastal landforms caused by deposition?
beaches
spits
offshore bars and tombolos
barrier islands
sand dunes
estuarine mudflats and salt marshes
How are cliffs formed?
As the sea erodes the land
overtime, they retreat due to the action of the waves and weathering
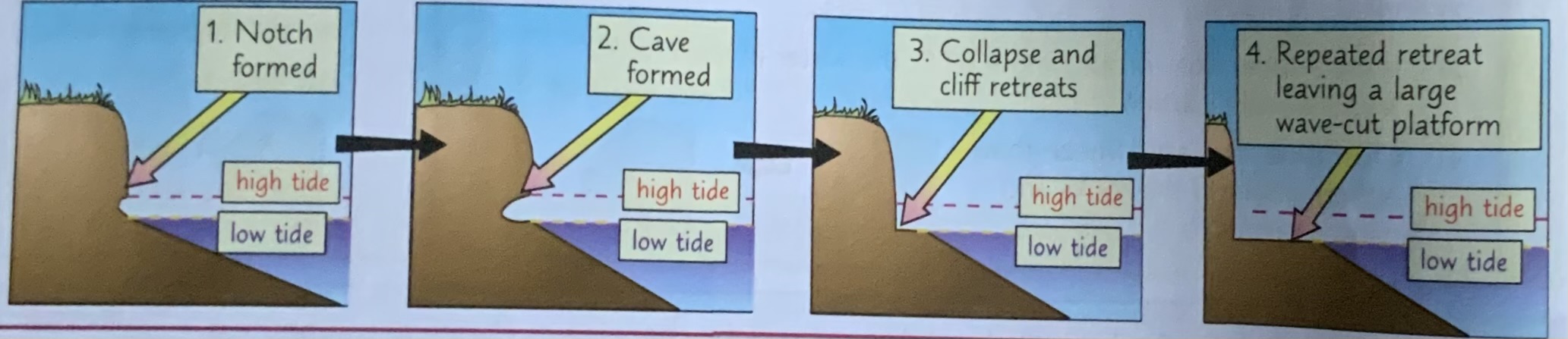
How are wave cut platforms formed?
1) At high-energy coastlines, hydraulic action + abrasion can cause formation of wave-cut platforms
2) Powerful destructive waves attack base of cliff at high tide
3) The hydraulic action + abrasion creates wave-cut notch which over time increases in size - this is called undercutting
4) Eventually overhang created by undercutting collapses due to weathering + gravity
5) The cliff retreats, leaving a wave cut platform that is exposed at low tide
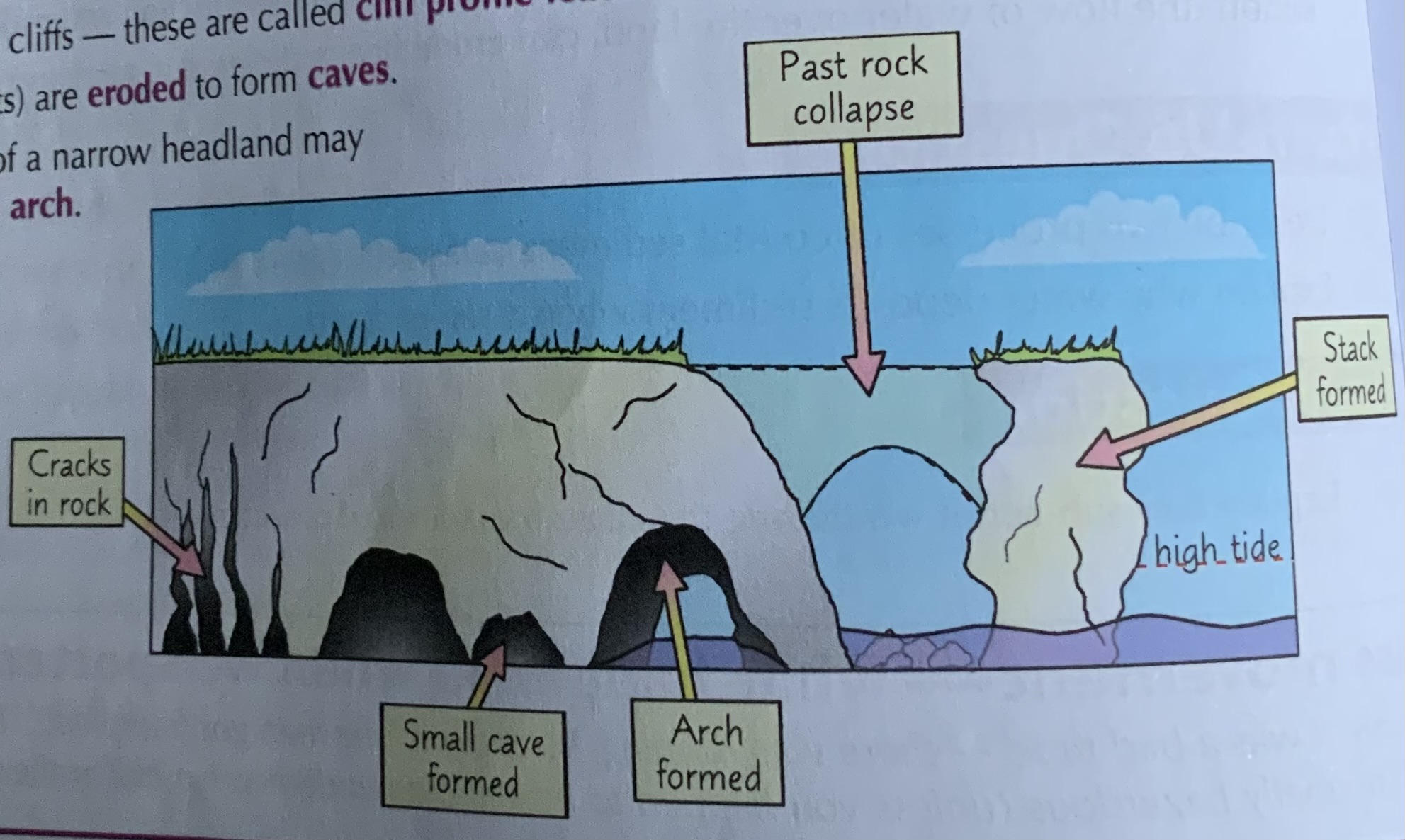
How are caves, arches and stacks formed?
1) At a headland, where rock is hard, erosion is slow, can lead to a variety of landforms
2) Wave refraction concentrates wave energy onto the headland, can contribute to the formation of caves, arches, stacks and stumps
3) Joints in headland are susceptible to erosion by hydraulic action
4) Over time joints widen, forming cave which is enlarged by hydraulic action + abrasion
5) Eventually erosion cuts through the headland forming an arch
6) roof of cave will eventually collapse due to gravity + lack of support
7) This leaves a stack which will over time be eroded by weathering, abrasion and hydraulic action to form a stump
What coastal landforms are made by deposition?
beaches
spits
offshore bars or tombolos
barrier islands
sand dunes
estuarine mudflats and saltmarshes
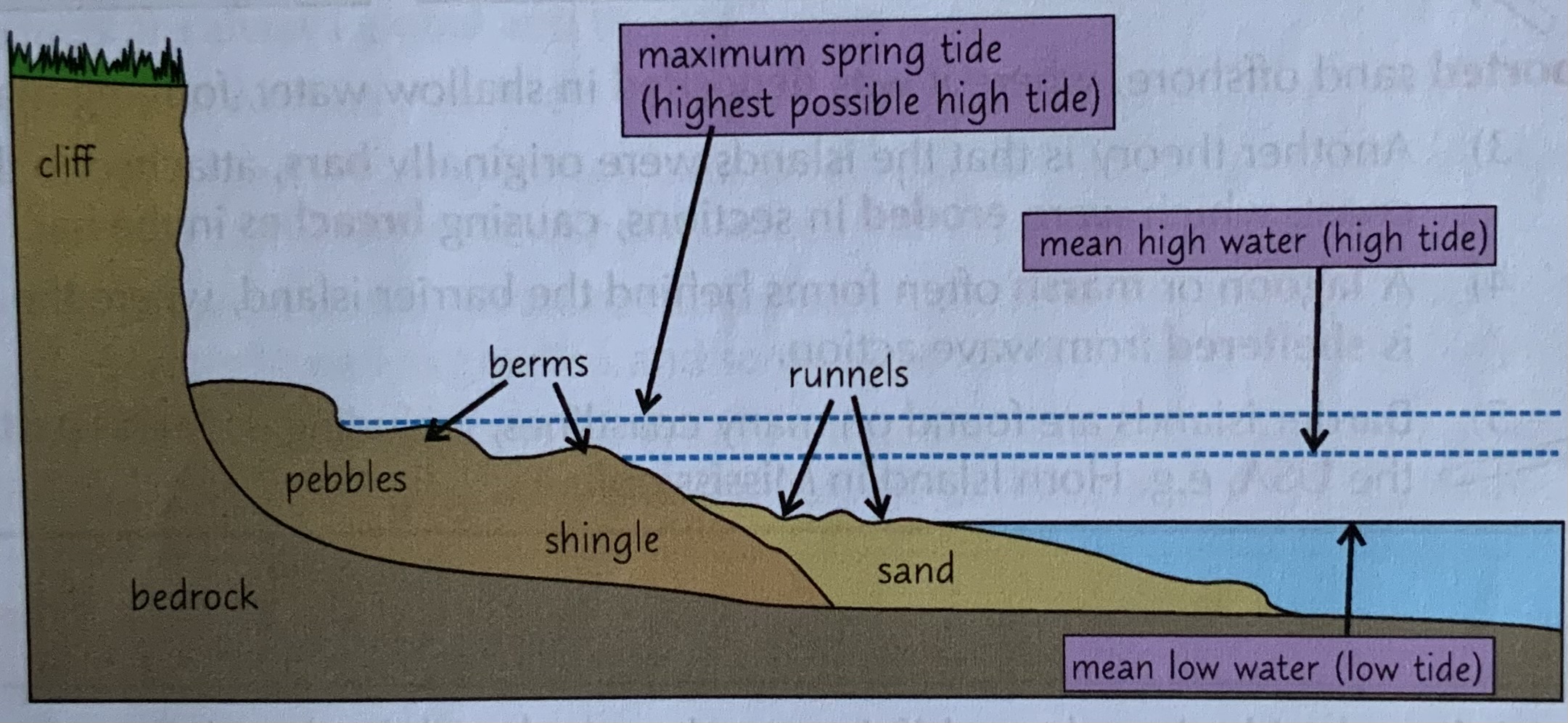
beaches
Beaches form when constructive waves deposit sediment on the shore
Shingle beaches are steep and narrow. made up of larger particles, which pile up at steep angles
Sand beaches, formed from smaller particles, are wide and flat
Beaches have distinctive features
Berms: ridges of sand and pebbles found at high tide marks
Runnels: grooves in the sand running parallel to the shore, formed by backwash draining to the sea
Cusps: crescent-shaped indentations that form on beaches of mixed sand and
how are spits formed?
Spits tend to form where the coast suddenly changes direction,e.g. across river mouths.
1) Longshore drift continues to deposit material across the river mouth, leaving a bank of sand and shingle sticking out into the sea. A straight spit that grows out roughly parallel to the coast is called a simple spit
2) Occasional changes to the dominant wind and wave direction may lead to a spit having a recurved end
3) Over time, several recurved ends may be abandoned as the waves return to their original direction.A spit that has multiple recurved ends resulting from several periods of growth is called a compound spit.
4) The area behind the spit is sheltered from the waves and often develops into mudflats + saltmarshes

How is a offshore bar formed?
Bars are formed when a spit joins two headlands together.
This can occur across a bay or across a river mouth
1) A lagoon forms behind the bar
2) Bars can also form off the coast when material moves towards the coast(normally as sea level rises). These may remain partly submerged by the sea - offshore bars
4) A bar that connects the shore to an Island (often a stack) is called a tombolo.
How are barrier islands formed?
it is not clear exactly how barrier islands form but scientists think that they probably formed after the last ice age ended when ice melt caused rapid sea level rise
The rising waters flooded the land behind beaches and transported sand offshore where it was deposited in shallow water forming islands
Another theory is that the islands were originally bar attached to the coast which were eroded in sections causing breaches in the bar
A lagoon/marsh often forms behind the barrier island where the coast is sheltered from wave action
How is a sand dune formed?
1) when sun deposited by longshore drift is moved up the beach by the wind
2) Sun by driftwood or berms is colonised by plants and grasses. The vegetation stabilises the sand and encourages more sand accumulate there forming embryo dunes
3) overtime the oldest dunes migrate inland as newer embryo dunes are formed
How are estuarine mudflats and saltmarshes formed?
1) mudflats and saltmarshes form in sheltered, low energy environments
2) as silt and mud are deposited by river or tide, mud plants develop
3) the mud flats are colonised by vegetation that can survive the high salt levels and long periods of submergence by the tide
4) the plants trap more mud and silt and gradually they build upwards to create an area of saltmarsh that remains exposed for longer and longer between tides
5) erosion by tidal currents/streams forms channels in the surface of mudflats and saltmarshes. These may be permanently flooded or dry at low tide