Vanegas Exam 1: 1.1 OT Process
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
steps of the OT process
1. Referral
2. Screening
3. Evaluation
4. Intervention Planning
5. Implementation of intervention
6. Intervention review - is the client meeting their goals?
7. Outcomes - successful or not? discharge ready?
difference between screening and evaluation
screening - quick and easy; formal or informal; further assessment needed?
evaluation - always formal; need for OT services?
the ot process is
not linear! its resembles a cycle
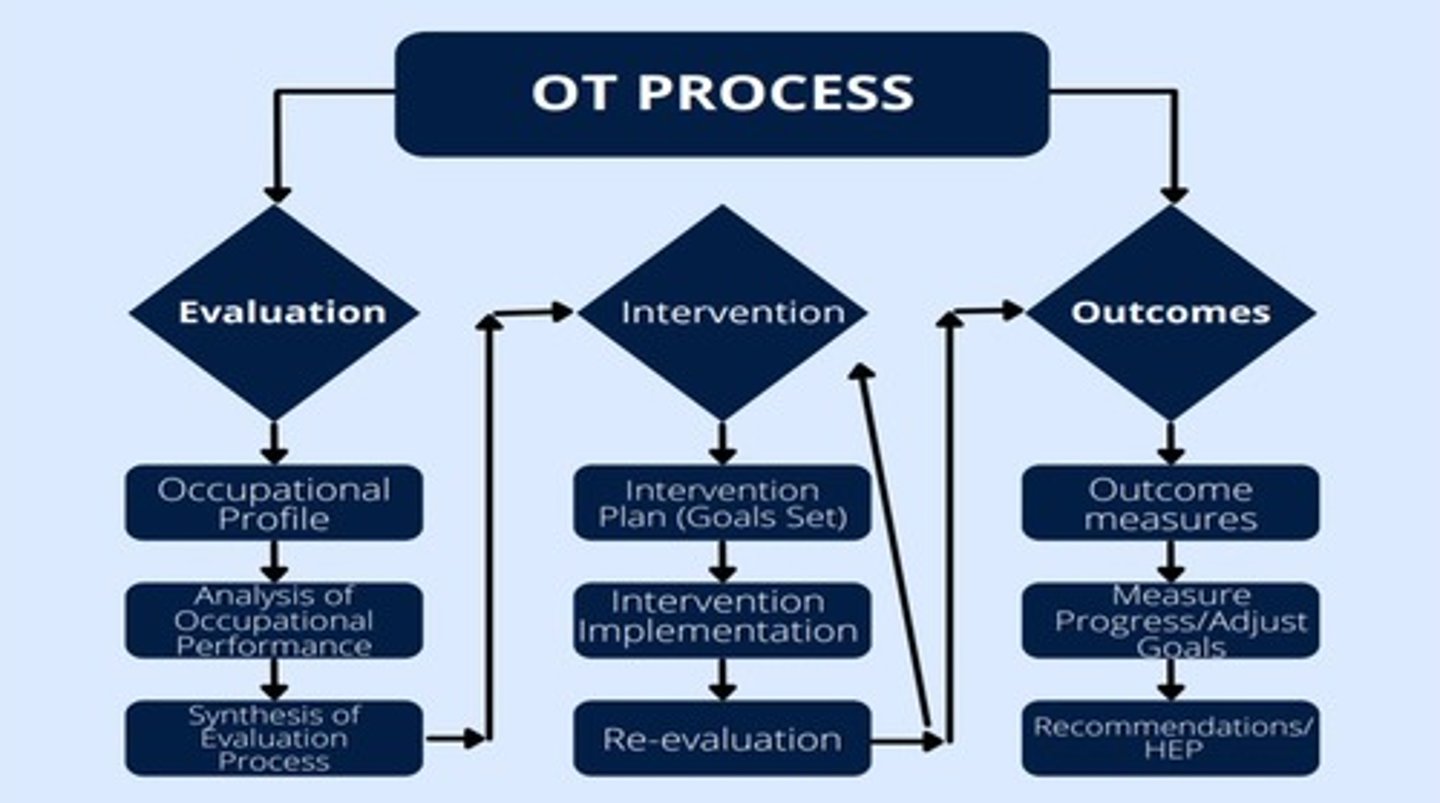
what initiates the OT process?
a referral
who can refer patients to OT?
-physicians
- other legally qualified professional (PT, SLP, neuro, nurse practitioner)
professionals qualified to refer clients to OT vary by
state
can you treat a patient without a referral?
not when OT is needed formally!
referrals can be either
oral or written (mostly written)
when can OTs treat without a referral?
when individuals, group and/or populations may seek OT services informally
ex: what does ot do? --> clients seek info
OT is responsible for compliance! Where can they seek resources?
state regulatory boards
licensure requirements
determines whether further evaluation is needed
screening
does not cover all areas of occupation:
a) screening
b) evaluation
a) screening
identifies need for OT services
a) screening
b) evaluation
screening
can be formal or informal
a) screening
b) evaluation
screening
does not cover all areas of occupation
a) screening
b) evaluation
screening
process of obtaining and interpreting data necessary for intervention
a) screening
b) evaluation
evaluation
includes planing for and documenting the evaluation process and its results
a) screening
b) evaluation
evaluation
uses formal assessments
a) screening
b) evaluation
evaluation
the evaluation process consists of:
1) generation of occupational profile
2) analysis of occupational performance
occupational profile
Summary of the client's occupational history and experiences, patterns of daily living, interests, values, and needs
is assessment part of the evaluation process?
yes!
specific tools or instruments that are used during the evaluation process
assessments
aka outcome measures
outcome measures
are standardized instruments that measure an individuals actual or perceived activity limitations and participations restrictions and an individuals quality of life or health status.
contribute data to the comprehensive evaluation
assessments
the occupational profile consist of
1) occupational history
2) current needs and priorities
3) contexts
4) performance patterns and performance skills
5) current needs and priorities
6) review of available records
7) client interview - formal or informal
8) interviewing caregivers and family members
occupational profile sample questions
Who is the client?
Why is the client seeking service?
What are the client's currentconcerns relative to engaging inoccupations and daily lifeactivities?
What occupations and activities are successful or are problematic for the client?
What aspects of the client's contexts (environment & personal factors) influence engagement in occupation and desired outcomes?
What is the client's occupational history?
What are the client's values and interests?
What are the client's patterns of engagement in occupation and how have these changed over time?
What are the client's priorities and targeted outcomes?
analysis of occupational performance can occur simultaneously with
the development of occupational profile
data gathered while evaluation of occupational performance...
can contribute to the client's profile
what helps guide the assessment process?
the clients performance!
select assessment tools that match their performance level
who develops the intervention plan?
the OT and the CLIENT
one purpose of OT intervention:
enhance the client's ability to participate in occupational performance
five approaches to intervention planning
1) create or promote healthy occupational engagement
2) establish or restore a skill or ability
3) maintain current functional abilities
4) modify, adapt, compensate
5) prevention
what approach: fall prevention program for well, elderly adults
prevent
what approach: healthy transition from work to retirement
create/promote health
what approach: restoring motor control for ADL/IADL following CVA
establish restore
what approach: energy conservation for individuals with dyspnea 2° to COPD
modify/adapt
what approach:habit training for individuals with early stage Parkinson's
maintain
who directs, monitors and supervises at intervention
OT
what does an intervention review consist of?
evaluation of the intervention plan; are we on target?
completed on a regular basis to determine if goals are being met
intervention methods
-therapeutic use of self
-occ based interventions -> activities
- tasks that SUPPORT OCCUPATIONS (preparatory methods and tasks -> hot pack, massage, beads --> catheter)
- group interventions
- education training
-virtual interventions
- advocacy
what does the intervention review process consist of?
1) OT evaluates the intervention plan (may be formal or ongoing)
2) determination if client goals are being met
3) may include a formal re evaluation to determine changes since previous evaluation
formal intervention review
review every 10th visit
team conferences
when should an intervention review be done?
completed on a regular basis to determine whether the client's goals are being met - revise goals constantly
ongoing intervention review
always!
asses skills and any hw given
is the intervention working? do we see improvements?
who is responsible for determining the need to continue, modify, or discontinue OT services?
the OT
... measurement of the outcomes of intervention is critical! why?
objective --> outcome measures
to determine the effectiveness of the intervention
during an intervention review, the plan might be
changed
continued
discontinued
what is used to measure progress or adjust tx?
outcomes
outcomes/results of tx are a collaboration between
client
significant others --> may either hinder or help
intervention team
subjective outcomes example
the client perceives that they improved, even though they might have not physically improved
"client was not able to regain strength but OT helped with adaptation and rehab" - "now I can do it!" --> I achieved ;)
outcomes focus on many factors:
1) occupational performance (optimal not independent)
2) client's perception of goals/process of meeting goals
3) well being of caregiver (we are not only limited to treated the patient!) - educate about respite, burnout
when the client has reached the established goals what comes next?
discharge
when do we discharge a client?
1) when the client has reached the established goals
2) when the client has achieved maximum benefit from OT services
what does the OT do during discharge?
1) formally discontinues services
- conversation with client and family members
2) create a discharge plan
- follow-up recommendations and arrangements (what next?)
3) provide summary statement about changes in client status from initial evaluation through end of services
- impact?
-before? now?
- include outcome measures! be objective ;)
OT process diagram
1) referral
2) evaluation
- occ profile
-analysis of performance
3) intervention
- plan
- implementation
- review
4) outcomes
- engagement in occupation to support participation
what forms a continuum of care?
a variety of settings
available services ... across settings
vary
progress is not always...
sequential
ups and downs
continuum of care - types
• Acute care hospitalization (ICU)
• Acute rehab
• Subacute rehab (IRF)
• SNF (LTACH/DOC)
• Home health care
• Residential care and assisting living units
• Home and community based setting
• Outpatient care
• Day treatment
• Worksite
Clients in an ... setting typically have either a new medical condition (eg, heart attack, burn, cerebrovascular accident, or traumatic brain injury) that led to hospitalization or an exacerbation of a chronic condition (eg, multiple sclerosis).
acute care inpatient
in what setting might the client require life support because of the severity of the condition
acute care inpatient
Three general roles have been identified for the occupational therapist working in the acute care setting
education, initiation of the rehabilitation process, and consultation
T/F Acute hospitalization is frequently stressful and frustrating for clients.
TRUE
Providing OT intervention services in an acute care setting may be challenging for therapists because ... (environment)
it is often necessary to perform assessments in a client's room rather than in more natural environments designed for ADLs.
To partially replicate the home environment during the intervention session, the therapist might
position the client's bed flat, eliminate the bed rails, and lower the bed.
Clients may be admitted to an inpatient rehabilitation unit when they are able to tolerate
several hours (usually 3) of therapy per day and are deemed capable of benefiting from rehabilitation.
Rehabilitation settings may be classified as
acute or subacute (IRF- inpatient rehabilitation facilities)
Clients are generally medically stable in this setting and require less acute medical care compared to services provided in an acute care hospital
inpatient rehab
What setting provides a social element that is not present in the acute care hospital?
inpatient rehabilitation
-normal clothes
-eat at dinner table
-socialize
Clients may still require some level of acute medical care in this setting.
acute rehab
In what setting do interventions focus on resuming the roles and occupations deemed important to the client's life?
acute rehab
Although bedrooms in acute inpatient rehabilitation settings are similar to those found in acute care hospitals, clients are often encouraged to
personalize their room by having family and friends bring in pictures, comforters, and other items from home.
what do clients wear in acute inpatient rehab settings?
clients are expected to wear street clothes rather than pajamas.
The culture of rehabilitation facilities focuses on the client's
performance and goal attainment.
Upon completion of the acute inpatient rehabilitation program, where are clients discharged?
some clients return home and receive home health services
some clients are referred to a subacute rehabilitation setting for continued services
subacute rehab is also know an
IRF
short term SNF
Focus of tx in subacute ?
The focus of intervention continues to be restoring functional abilities; however, because of the slower rate of change, the occupational therapist must also consider the need to adapt or modify the environment.
The pace of intervention services varies, and engaging in 3 hours of therapy per day is not mandatory.
subacute rehab
skilled nursing facility (SNF)
is an institution that meets Medicare or Medicaid criteria for skilled nursing care, including rehabilitation services.
slow paced therapy
LTACH/DOC
Discharge at SNF
Many residents will stay in an SNF for the remainder of their lives; others will be discharged home.
SNF goals of TX
Goals should be directed toward:
- independence and meaningful occupational pursuits
- may include fostering engagement in occupations through environmental modifications and adaptations
Goal at what facility: reading materials and playing cards with enlarged print to foster leisure pursuits for clients with macular degeneration.
SNF
what kind of service might be offered at SNFs?
hospice care
The physical and social environments in skilled nursing facilities may impede ... why?
the natural performance of ADLs.
Clients often receive assistance with self-care tasks to expedite task completion, but this assistance is not focused on fostering engagement in occupational performance.
T/F Extreme variations in disability status are present in SNFs
TRUE
Age and disability gaps at SNFs may cause...
- Observing residents who are severely and permanently disabled may lead newly disabled individuals to form negative expectations of their own performance
- Younger adults placed in SNFs (where most residents are older adults) may feel isolated and abandoned, which can adversely affect performance.
provides services within the client's home and affords the most natural context for intervention
home health
The desired outcome for services provided within the home could include
supported completion of ADLs or IADLs such as bathing, dressing, and meal preparation.
An alternative to an acute inpatient rehabilitation program for clients with traumatic injuries (eg, head or spinal cord injuries) is a
home and community-based therapy program.
This type of program provides intensive rehabilitation in the client's own home and community
home and community based setting
In home- and community-based settings, the client is performing in her natural physical, social, and cultural environment.
what setting more closely resemble home situations; clients may reside there on a permanent or transitional basis, depending on their prognosis?
residential care
Although clients do not require ongoing intensive medical care, the facilities are staffed with care providers 24 hours a day because of the clients' need for safety and supervision
residential care
provides health services in a cooperative living setting
assisting living unit
A client may live in an apartment or a cottage where one or more meals are provided on a daily basis; medication management is provided as needed; and 24-hour support is available
ALU
services provided in hospitals and freestanding clinics to clients who reside elsewhere.
outpatient
Clients receiving services in this setting are medically stable and able to tolerate a few hours of therapy and travel to an outpatient clinic.
outpatient
To evaluate a client's performance of ADLs or IADLs in an outpatient setting ...
the therapist must extrapolate how task performance would occur at home
day treatment centers
allow people to obtain treatment during the day, along with occupational and rehabilitative therapies, but live at home at night
Work Site Therapy Settings
address employee's therapy needs related to work injury