Week 10 pt. 2
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
Two types of error-prone repair systems
SOS system in bacteria
- used at replication forks that stalled because of unrepaired DNA damage.
- Sloppy DNA polymerase used instead of normal polymerase.
- Adds random nucleotides opposite damaged bases.
Microhomology-mediated end-joining (MMEJ)
- Similar to NHEJ, but nucleotides are removed at dsDNA breaks to produce short complementary regions, leading to small deletions.
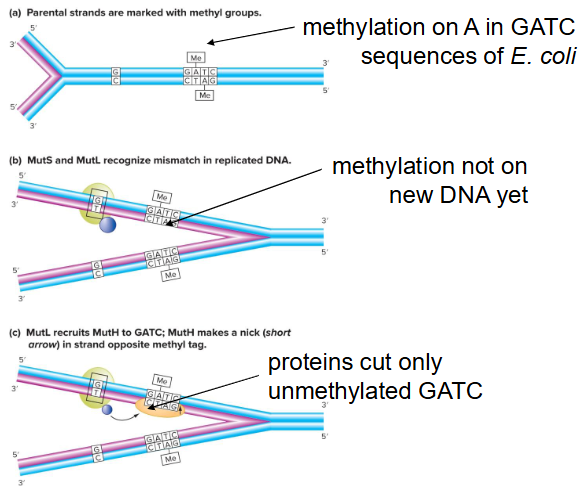
How do repair enzymes know which strand is wrong?
Methyl-directed mismatch repair
- Bacterial recognition and repair system mutations after DNA replication. Relies on tagging parental groups with methyl groups.
- Eukaryotic cells also have mismatch repair system, but tag not yet known.
What if there is too much damage all at once? + example
Apoptosis - programmed cell death.
E.g. epidermal cells die all at once (peeling) after too much UV exposure.
Some mutations derail apoptosis, so some damaged cells don’t die. (Cancer!!)
What if DNA repair genes are inactive? + example
Many hereditary human diseases are due to defects in DNA repair genes.
Xeroderma pigmentosum - autosomal recessive diseases.
Mutation in any one of the seven genes involved in nucleotide excision repair.
Colorectal cancer - mutations in mismatch repair genes.
Breast cancer - mutations in BCRA1 and BCRA2 involved in dsDNA break repair by homologous recombination.