The Asexual Cycle
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Define clones
Population of genetically identical single-celled organisms derived from a single ancestral cell.
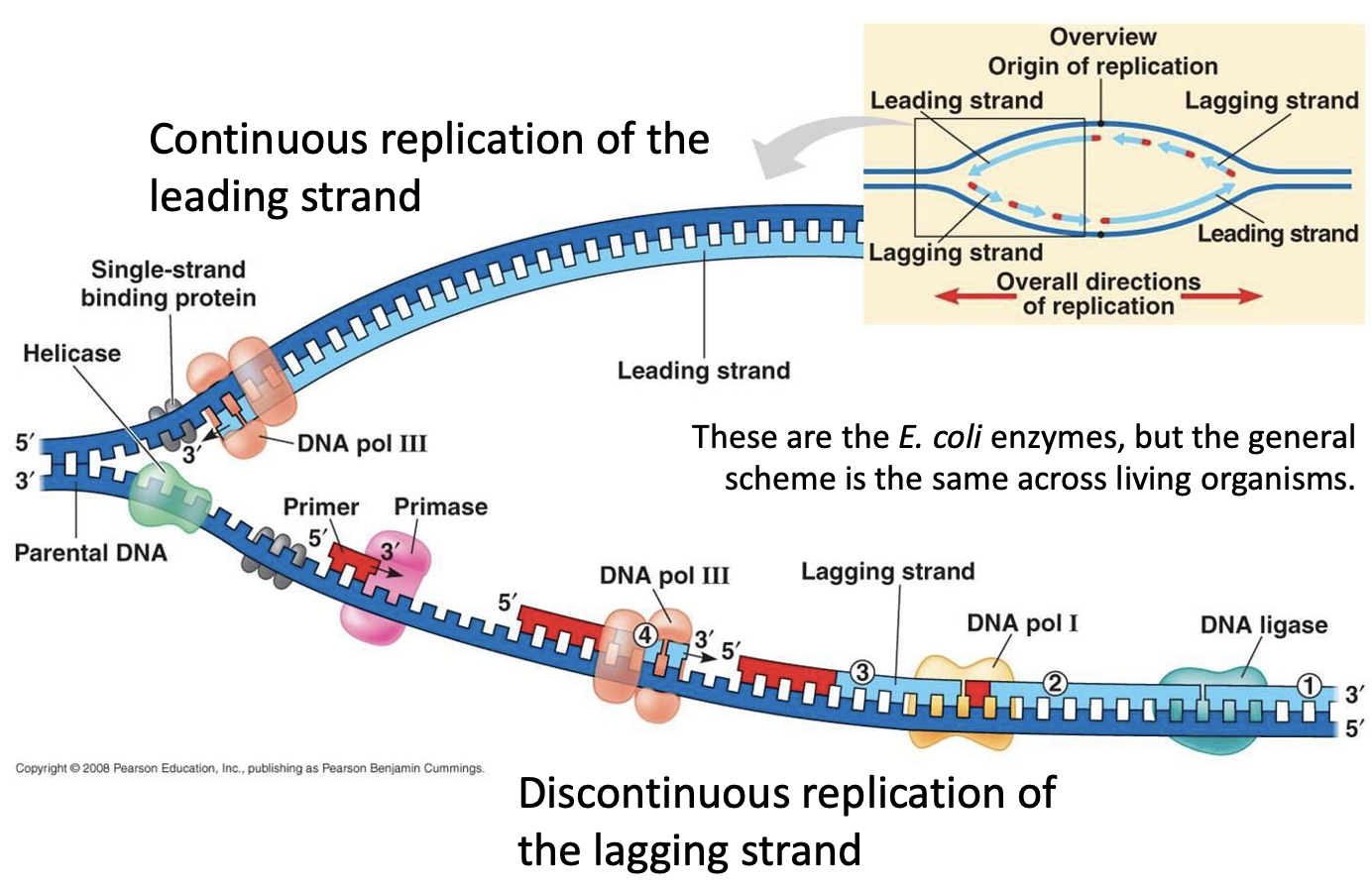
Define semidiscontinuous DNA replication
Model of DNA replication where one new strand is synthesised continuously while the other is synthesised discontinuously with Okazaki fragments.
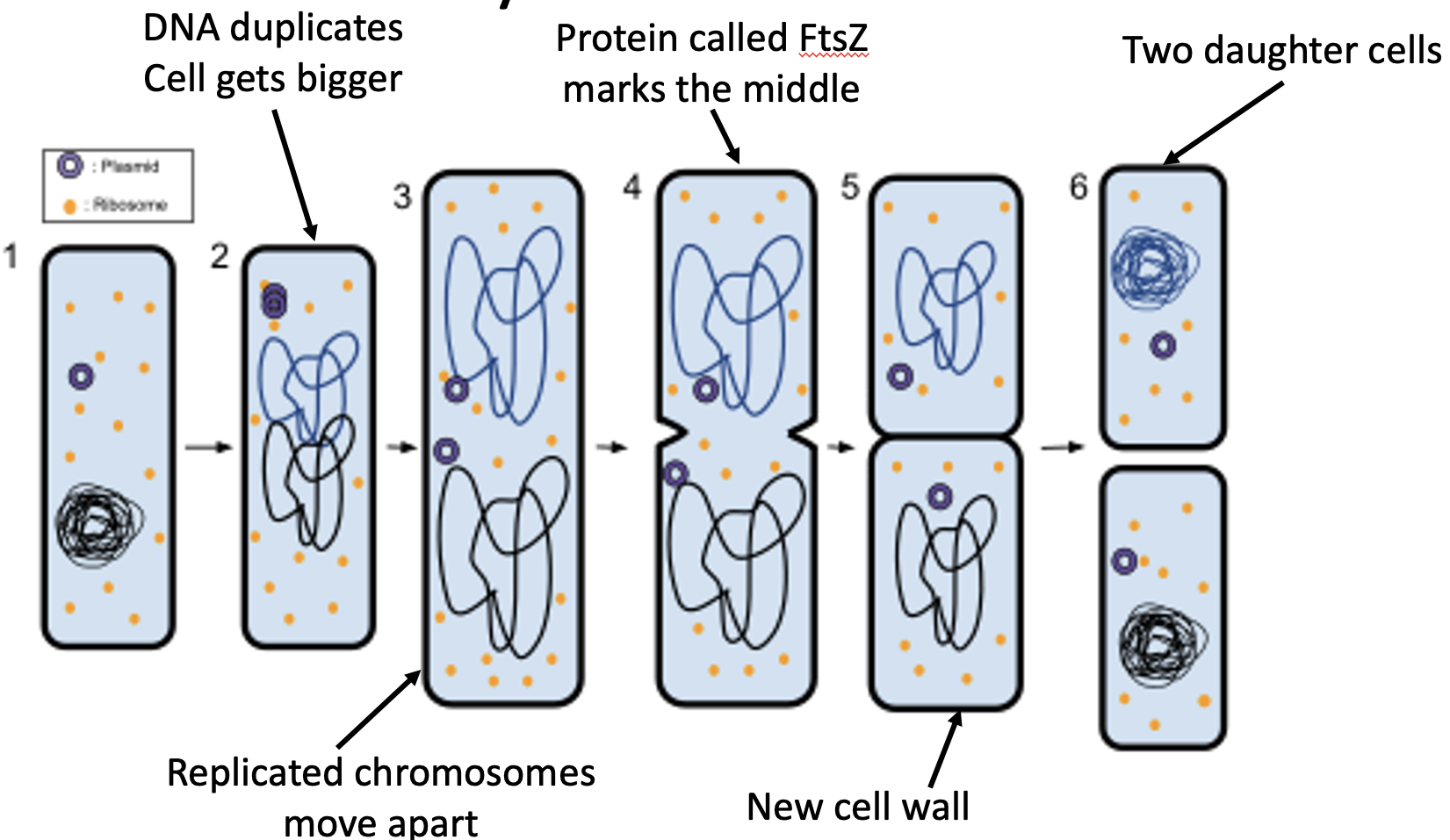
Describe the process of binary fission in bacteria
DNA duplicates, cell gets bigger. Replicated chromosomes move apart. Protein called FtsZ marks the middle. New cell wall forms. 2 daughter cells are produced.
Describe the stages of the cell cycle
Interphase (main part of the cell cycle). G1 (cell size increases, ribosomes + RNA produced, preparation for DNA synthesis). S (DNA synthesised (chromosomes duplicated)). G2 (cell checks fidelity of DNA, preparation for nuclear division). Mitosis (cell division (PMAT)).
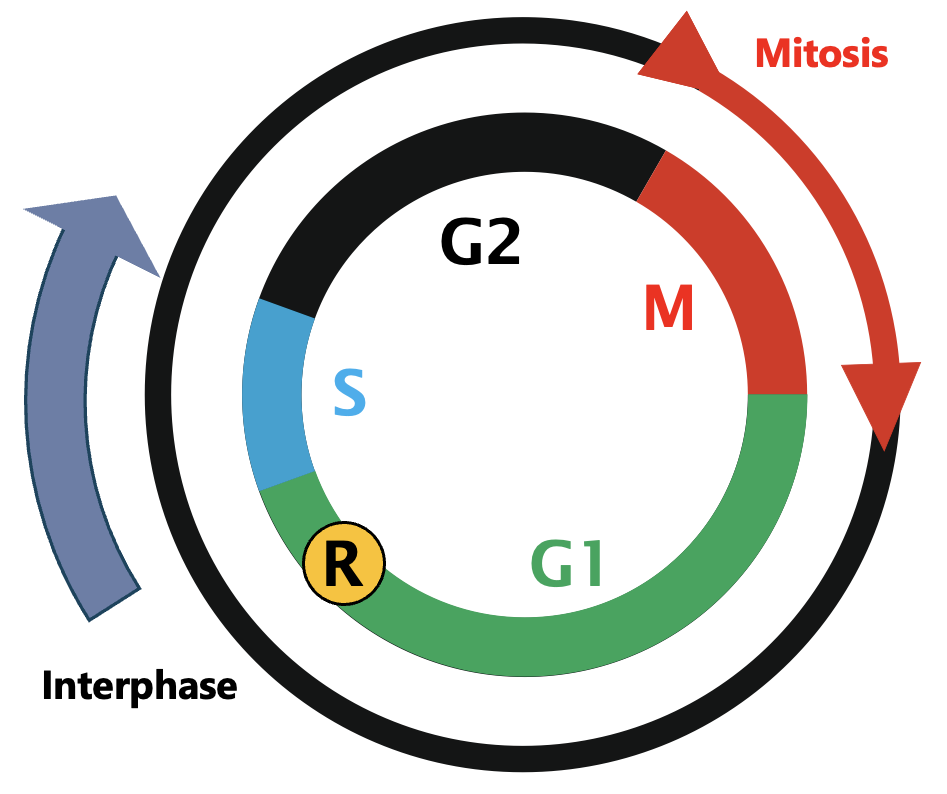
Describe interphase
Includes G1 + S + G2.
Describe prophase
Chromosomes condense so they are now visible. Each chromosome comprises 2 chromatids + a single centromere. Sister chromatids are held together by a protein called cohesion. Later in this stage the nuclear membrane breaks down (prometaphase).
What is the mitotic spindle’s job?
To separate sister chromatids to diff daughter cells. Happens because microtubules get shorter = pull chromosomes towards the poles.
Define microtubules
Polymers of small tubule protein subunits.
Define centromeres
Specialised chromosomes regions that direct the equal segregation of chromosomes during cell division. Defined by specific epigenetic markers. Can be found at any point along the chromosome. Sister chromatids are joined together at the centromere.
Define kinetochore
Large protein complex that connects centromeres to the microtubules.
Describe metaphase
Centromeres align at the spindle equator. Microtubules attaching to each pole - tension between these keeps chromosomes in the centre.
Describe anaphase
Sister chromatid cohesion breaks down. Chromatids become separate chromosomes. Centromeres start moving to opposite poles.
Describe telophase
Chromosomes arrive at the cell poles. Chromosomes recondense - no longer recognisable structures. Daughter nuclei reform.
Describe cytoknesis
Division of the rest of the cell. Cleavage furrow (animals) or cell plate (plants) forms in between the two poles. Constriction to give 2 daughter cells. Can be symmetrical or give 2 unevenly shaped daughter cells.
Define bridge chromosome
A chromosome that erroneously has 2 centromeres being pulled towards both poles at once. Ends up being broken.
Define acentric chromosome
Lacking a centromere, unable to segregate properly.