7. Hygiene requirements to drinking water quality
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What three categories of indicators are monitored in drinking water?
Chemical, microbiological, and radiological indices.
Name four general qualities potable water must have.
1) Free of harmful microorganisms,
2) No excessive harmful chemicals,
3) Acceptable pH,
4) Pleasant taste/odor and clear appearance.
Why is disinfection (e.g., chlorination, UV) essential for drinking water?
To inactivate or destroy pathogenic microorganisms.
What causes turbidity and why must it be minimal?
Suspended particles or sediments; high turbidity indicates inadequate treatment or pipe disturbance.
Give two common causes of color in drinking water.
Humic substances (organic matter) and dissolved metals (iron, manganese).
An unusual odor or taste in water often signals what?
Possible chemical contamination or excess chlorine.
Ammonia
Guideline value is ≤ 0.5 mg/L.
It is an indicator of sewage or animal waste contamination.
Nitrite (NO₂⁻)
Guideline value is ≤ 0.5 mg/L.
High levels pose a risk of infant methemoglobinemia (blue baby syndrome).
Nitrate (NO₃⁻):
Guideline value is ≤ 50 mg/L.
Similar to nitrite, high levels can lead to methemoglobinemia in infants.
Chlorides:
Guideline value is ≤ 250 mg/L.
High chloride levels can affect the taste of water and may indicate seawater or wastewater intrusion.
Sulfate
Guideline value is ≤ 250 mg/L.
Excess sulfate gives water a bitter taste and can have a laxative effect.
Phosphate:
Guideline value is ≤ 0.5 mg/L.
It serves as an indicator of organic pollution, often from agricultural or domestic sources.
Which two ions determine water hardness?
Calcium and magnesium.
List four toxic metals that are tightly regulated in drinking water.
Lead, cadmium, chromium, selenium
(plus arsenic, mercury as additional examples).
What is the allowable level for total coliforms and E. coli in 100 mL of drinking water?
0/100 mL
(none detectable).
What is the permissible count for Enterococci in drinking water?
None detectable in 100 mL.
Presence of Clostridium perfringens spores in water indicates what?
Possible fecal contamination;
must be 0/100 mL.
What is the standard volume used to detect Pseudomonas aeruginosa in bottled waters?
250 mL sample—must be free of the organism.
Radiological Indices
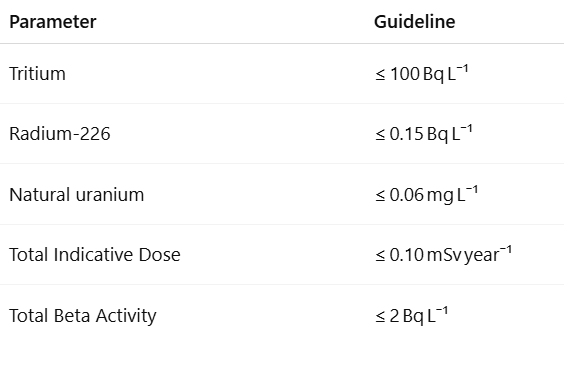
Why are calcium and magnesium desirable in drinking water?
Support bone health and may benefit cardiovascular function.
What dual role does fluoride play in water?
Prevents dental caries at optimal levels; excess causes fluorosis.
Which trace element is vital for antioxidant defenses and immunity?
Selenium.
Excess sodium in drinking water is a concern mainly for whom and why?
People with hypertension; high sodium may elevate blood pressure further.
Name three heavy metals in water that are carcinogenic.
Beryllium, cadmium, arsenic (also chromium VI).
How can inadequate iodine in local water supplies manifest in populations?
Endemic goiter and cretinism.
Which mineral in drinking water is critical for insulin synthesis and carbohydrate metabolism?
Zinc.