BIOL 1209 Final Exam
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:25 AM on 5/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
1
New cards
Genetic Equilibrium
No change in allele frequency over time. When evolution is not occurring.
2
New cards
Gene Fixation
When you have alleles gained or lost. The total allele frequency level is at 1 or 0. Usually occurs in smaller populations.
3
New cards
Gene Pool
All alleles present in a population at any given time point. Includes dominant, recessive, more fit, less fit, etc.
4
New cards
Gene Flow
the introduction of genetic material (by interbreeding) from one population of a species to another
5
New cards
Fitness
Measures ones ability to survive and have offspring. What natural selection acts upon. Have more offspring = more fit. Have less or no offspring = less fit.
6
New cards
Allele
One representation that could be present in a genotype
7
New cards
Genotype
Genetic representation of expressed alleles
8
New cards
Phenotype
Physical manifestation of the genotype
9
New cards
Hardy-Weinberg
p^2+2pq+q^2=1. Used this to determine null hypothesis in experiment and when evolution is not occurring.
10
New cards
Evolution
The change of allele frequency over time.
11
New cards
Conditions that need to be present for genetic equilibrium
1) Large population size
2) no mutation
3) no gene flow
4) random mating
5) no natural selection
2) no mutation
3) no gene flow
4) random mating
5) no natural selection
12
New cards
Population Ecology
a sub-field of ecology that deals with the dynamics of species populations and how these populations interact with the environment
Measures:
1) birth rates
2) death rates
3) immigration
4) emigration
Measures:
1) birth rates
2) death rates
3) immigration
4) emigration
13
New cards
Community Ecology
study of the organization and functioning of communities (multiple populations)
\
\
14
New cards
Ecosystem Ecology
the integrated study of living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components of ecosystems and their interactions within an ecosystem framework
15
New cards
Things that affect ecology
Biotic factors: competition, predation, migration, birth rates, death rates
Abiotic factors: light, climate, phosphate levels, nitrogen levels, etc
Abiotic factors: light, climate, phosphate levels, nitrogen levels, etc
16
New cards
Population
All individuals that can reproduce together in one area. No inner breeding or mixtures then they are a separate population. Also depends on the breeding seasons. If they have different seasons then that are separate populations.
17
New cards
Food Web
Producers: make their own food from light
Primary consumers: consume producers (herbivores/ omnivores)
Secondary consumers: consume primary consumers (carnivores/ omnivores)
Primary consumers: consume producers (herbivores/ omnivores)
Secondary consumers: consume primary consumers (carnivores/ omnivores)
18
New cards
Decomposer
Decomposes organic material
Ex) Fungi, some protists
Ex) Fungi, some protists
19
New cards
Autotroph
absorptive, make their own food
20
New cards
Heterotroph
Ingestive, consume other organisms to gain nutrients
21
New cards
Chemical tests in ecology
Add a chemical to the sample, color change occurs, indicates the levels of phosphorus, nitrogen, etc
22
New cards
Nitrogen and Phosphorus Cycles
Nitrogen gas being mixed with bacteria
Phosphate stays in lakes once its there, nitrogen cycles more frequently
Natural entrances for nitrogen and phosphate:
nitrogen- soil and air
phosphorus- rocks, pollution
Phosphate stays in lakes once its there, nitrogen cycles more frequently
Natural entrances for nitrogen and phosphate:
nitrogen- soil and air
phosphorus- rocks, pollution
23
New cards
Carrying Capacity
The amount of resources present in environment limits the population growth: food, competitors, etc
24
New cards
Logistic Growth vs Exponential Growth
Logistic: a population's per capita growth rate gets smaller and smaller as population size approaches a maximum imposed by limited resources in the environment
Exponential: the population grows exponentially until it nears the carrying capacity, which is shown by a separate horizontal line. As the population nears the carrying capacity, population growth slows significantly.
Exponential: the population grows exponentially until it nears the carrying capacity, which is shown by a separate horizontal line. As the population nears the carrying capacity, population growth slows significantly.
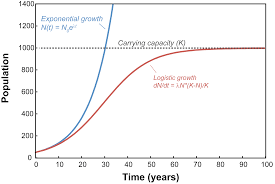
25
New cards
Buncher Funnel
Used in chlorophyll acetate test
\
\

26
New cards
pH meter
used to measure pH level of a sample

27
New cards
Thermometer
used to measure temperature

28
New cards
Secchi Disk
used to measure clarity
29
New cards
replica plate
used to stamp E coli

30
New cards
Domains
Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya
31
New cards
Kingdoms
Eubacteria, Archae, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia
32
New cards
Parts of Phylogenetic Tree
Root: most recent common ancestor
Branch: passing of generational time
Nodes: on individual splits into two based off of genetic difference
Branch: passing of generational time
Nodes: on individual splits into two based off of genetic difference
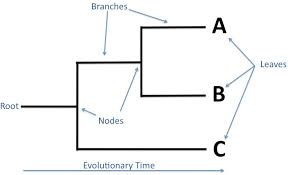
33
New cards
Trends of complexity
Vasculature in plants: as they evolve there is most vasculature (review with practice exercise and know each vasculature system with each organism)
tissue layer in animals: an inner layer (endoderm), an outer layer (ectoderm), and a middle layer (mesoderm). Animals with three tissue layers are called triploblasts.
tissue layer in animals: an inner layer (endoderm), an outer layer (ectoderm), and a middle layer (mesoderm). Animals with three tissue layers are called triploblasts.
34
New cards
homologous
having the same relation, relative position, or structure
35
New cards
analogous
comparable in certain respects, typically in a way which makes clearer the nature of the things compared
36
New cards
Hypothesis
a supposition or proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation
Made of three parts: Independent variable, Dependent Variable, how it is Statistically significant or not
Made of three parts: Independent variable, Dependent Variable, how it is Statistically significant or not
37
New cards
R^2
Correlation coefficient, how closely points on a scatterplot best fit to a line
Higher than .35- more closely related
Lower than .35- less related or random points (outliers)
Higher than .35- more closely related
Lower than .35- less related or random points (outliers)
38
New cards
Standard deviation
the variation in data points. More spread out will equal higher standard deviation, points closer together will equal lower standard deviation
39
New cards
Independent Variable
a variable (often denoted by *x* ) whose variation does not depend on that of another
40
New cards
Dependent Variable
a variable (often denoted by *y* ) whose value depends on that of another
41
New cards
Parts of the Lab Report
Introduction
Methods
Results (graphs, captions, trends paragraph)
Discussion
*know what type of information should go into each section and what tense each section should be written in*
Methods
Results (graphs, captions, trends paragraph)
Discussion
*know what type of information should go into each section and what tense each section should be written in*
42
New cards
APA Citation
**General format for in text citing:** (First Author last name, year).
* One author: (Last name, year)
* Two authors: (Last name 1 & Last name 2, year)
* Three or more authors: (Last name 1 et al., year)
**References**
Author, A. A., Author, B. B., & Author, C. C. (Year). Title of article. *Title of Periodical, volume number*(issue number), pages. **https://doi.org/xx.xxx/yyyy**
\
*be able to decipher if a citation is correct or not for test*
* One author: (Last name, year)
* Two authors: (Last name 1 & Last name 2, year)
* Three or more authors: (Last name 1 et al., year)
**References**
Author, A. A., Author, B. B., & Author, C. C. (Year). Title of article. *Title of Periodical, volume number*(issue number), pages. **https://doi.org/xx.xxx/yyyy**
\
*be able to decipher if a citation is correct or not for test*
43
New cards
Primary resources vs peer reviewed articles
Primary resources- immediate, first-hand accounts of a topic, from people who had a direct connection with it
\
Peer Review- the evaluation of work by one or more people with similar competencies as the producers of the work
\
Peer Review- the evaluation of work by one or more people with similar competencies as the producers of the work
44
New cards
Parts of Microscope
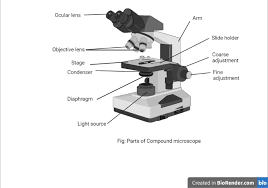
45
New cards
How to make a stock plate
1) apply (pipet) e coli onto plate
2) grows into colonies
3) stamp plates to make replicates
2) grows into colonies
3) stamp plates to make replicates
46
New cards
Pop G
How the different parameters can affect the outcome of the population.
Examples)
smaller population = genetic fixation
make a certain allele more fit then there will be an accumulation of the gene over time
*experiment with Pop G to remember different outcomes*
Examples)
smaller population = genetic fixation
make a certain allele more fit then there will be an accumulation of the gene over time
*experiment with Pop G to remember different outcomes*
47
New cards
Bean Exercise Calculations
\# of beans with certain allele/ #of total beans within that population= % of that allele that was expressed
48
New cards
How PopG and Bean exercise was related
They were related because both are calculating the same thing, but PopG can calculate it more rapidly for multiple generations
49
New cards
General Lab Safety

50
New cards
What technique was used for E Coli stock plates?
Replica plating
51
New cards
What type of environments would you find Archaea?
Extreme environments (Volcanos, extreme salt or acidic environments)
52
New cards
What is the phyla of green algae?
Chlorophyta
53
New cards
What vascular structures in plants can withhold extreme environments?
The cortical bundle is a vascular system which allows the transportation of water and nutrients
54
New cards
Do individuals evolve?
No, only populations
55
New cards
Do dominant alleles have a higher fitness?
No, both alleles have the potential to have a higher fitness. It is dependent on the environment.
56
New cards
Does natural selection act on the genotype?
No, it acts on the phenotype.
57
New cards
Why do we use a computer simulation to test evolution?
It takes too long to physically test it.
58
New cards
A species needs _______ to respond to its environment?
Variation
59
New cards
How could you introduce variation to a population?
Mutation and migration
60
New cards
How are alleles lost?
Small population creates genetic fixation
61
New cards
Why did we use Chlamydomonas for our experiment?
Can reproduce rapidly, photosynthetic, does cost much, easy to measure