Chapters 8-12
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This world ain't worth living
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Each muscle is an organ, comprised of skeletal muscle tissue, several connective tissue coverings, nervous tissue to cause it to contract, and blood to nourish it.
Skeletal muscle
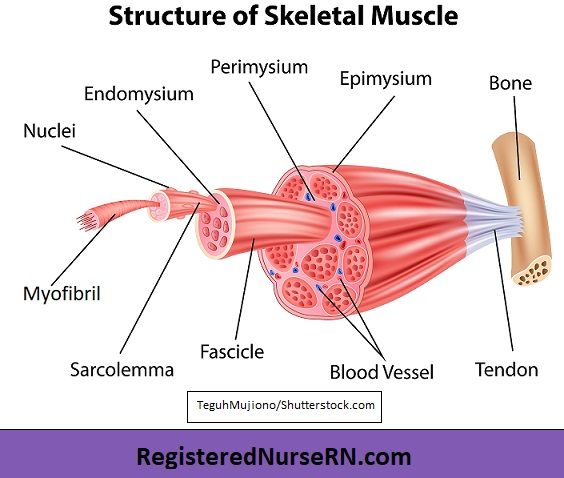
The muscle has several dense connective coverings. Layers of dense connective tissue— fascia, surround and separate each muscle.
This connective tissue extends beyond the ends of the muscle and gives rise to cord-like tendons that are fused to the periosteum of bones.
Sometimes muscles are connected to each other by broad sheets of connective tissue called aponeuroses.
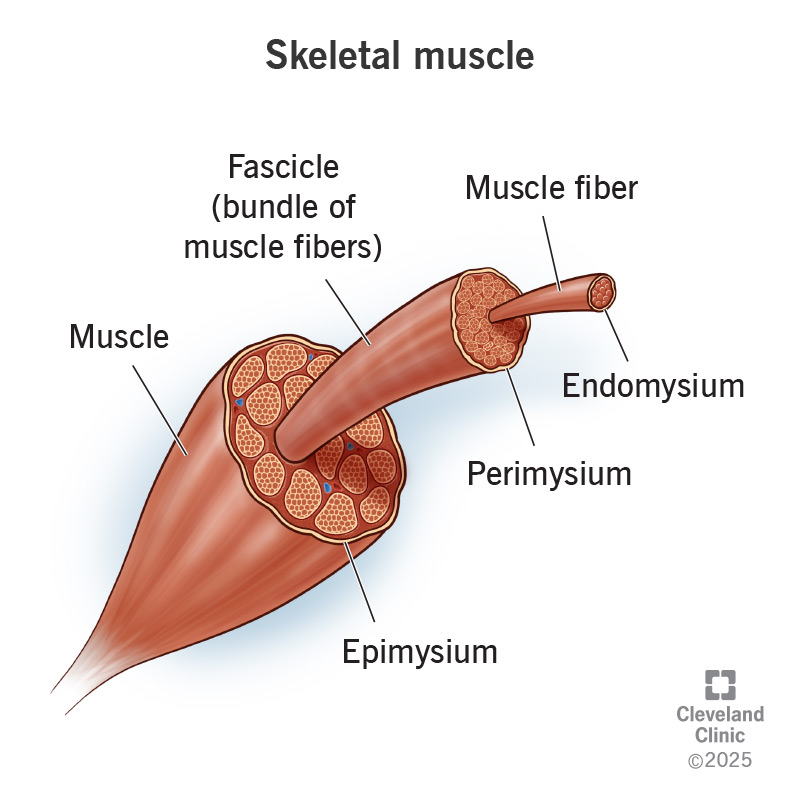
Under the outer layer another layer of connective tissue around each whole muscle is called the epimysium.
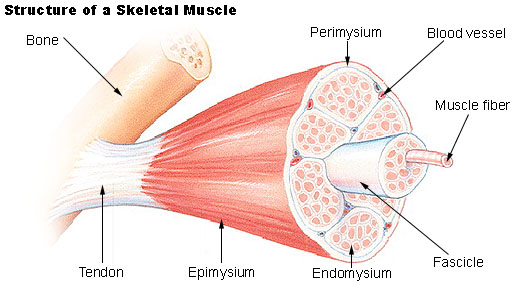
The perimysium surrounds individual bundles of fibers called fascicles within each muscle.
Each muscle cell (fiber) is covered by a connective tissue layer called endomysium.
The muscle fiber membrane is called the sarcolemma. The fiber contains the cytoplasm, called sarcoplasm.
Within the sarcoplasm are many parallel myofibrils, composed of smaller filaments called myofilaments.
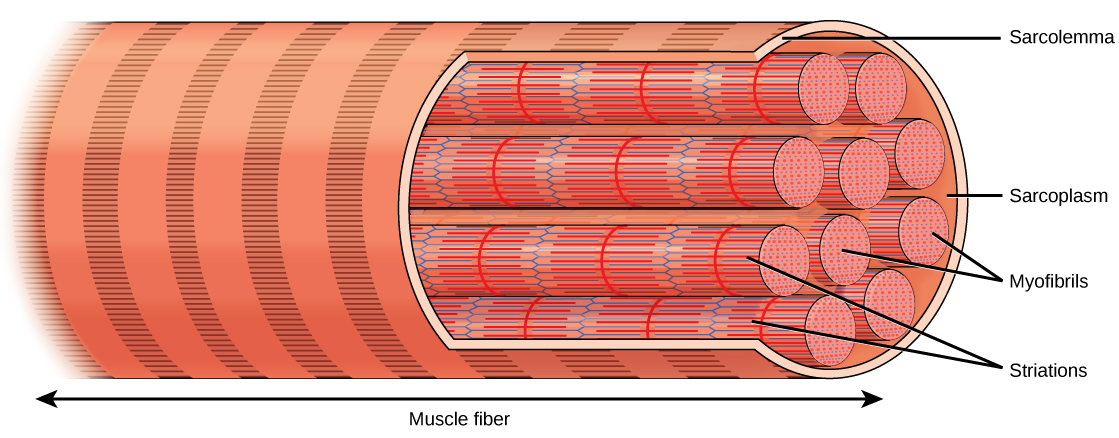
The muscle fiber membrane is called the sarcolemma. The fiber contains the cytoplasm, called sarcoplasm.
Within the sarcoplasm are many parallel myofibrils, composed of smaller filaments called myofilaments.
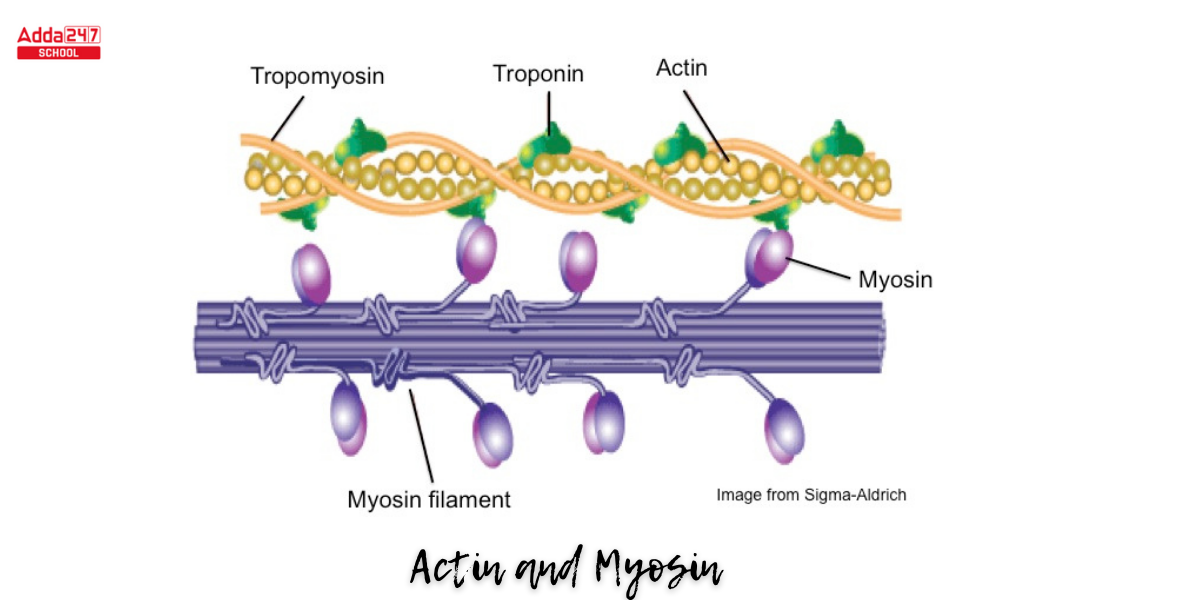
Thick filaments composed of the protein myosin.
Thin filaments mostly made of the protein actin.
The 2 types of protein filaments that make up the myofibrils
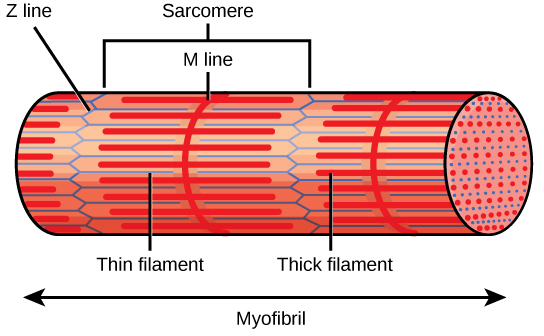
Striations in skeletal muscle are due to a pattern of overlapping thin and thick filaments, called sarcomeres.
A sarcomere is defined as a functional unit extending from one Z line to the next (in the center of the light band). The dark stripes are called A bands and the light stripes are called I bands.
T tubules = transverse tubules. Where are they located? Surface indentations of the sarcolemma. They open to the outside of the fiber
Associated with tubular structure Sarcoplasmic reticulum. They store and release calcium ions for muscle contraction.
The site where the motor neuron and muscle fiber interact, so that the motor neuron can control the muscle fiber.
Neuromuscular Junction
The muscle fiber membrane contains a motor end plate in which the sarcolemma is tightly folded and where nuclei and mitochondria are abundant.
Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter released from the end of the motor neuron.
Muscle contraction involves several components that result in the shortening of sarcomeres, and the pulling of the muscle against its attachments.
The protein myosin consists of two twisted strands with globular cross-bridges projected outward along the strands.
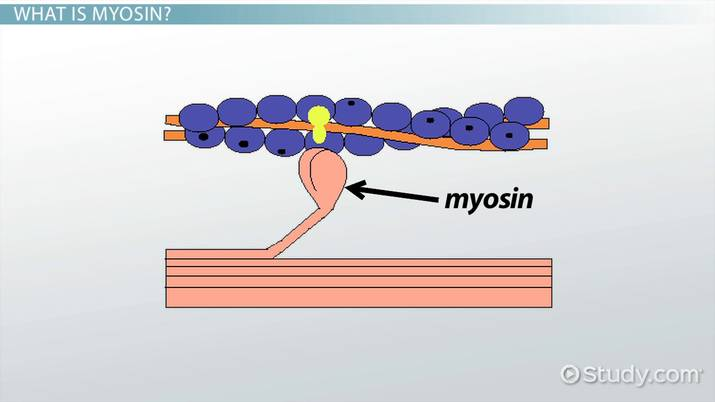
Actin is a globular protein with myosin binding sites. What two proteins are associated with it?
Troponin and tropomyosin.
The sliding filament theory of muscle contraction: If allowed to, the myosin will attach to the binding site on the actin filament and pull on the actin filament before releasing (targets every site). What prevents this from happening continuously?
It requires calcium ions and ATP to be present in order to occur.
Energy from the conversion of ATP to ADP is what?
Provided to the cross-bridges from the enzyme ATPase, causing them to be in a “cocked” position again.
1) The motor neuron must release the neurotransmitter acetylcholine from its synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft in order to initiate a muscle contraction. Protein receptors in the motor end plate detect the neurotransmitters.
A muscle impulse spreads over the surface of the sarcolemma and into the transverse (T) tubules where it reaches the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
2) Upon receipt of the muscle impulse, the sarcoplasmic reticulum releases its stored calcium ions into the sarcoplasm of the muscle fiber.
The high concentration of calcium in the sarcoplasm interacts with the troponin and tropomyosin molecules, which move aside, exposing the myosin binding sites on the actin filaments.
3) Myosin heads now bind and pull on the actin filaments, causing the sarcomeres to shorten. After the nerve impulse has been received, the enzyme acetylcholinesterase rapidly decomposes the acetylcholine.
Then calcium is returned to the sarcoplasmic reticulum, and the linkages between myosin and actin are broken.
Energy for contraction comes from molecules of ATP. This chemical is in limited supply and must often be regenerated.
ATP - Adenosine Triphosphate
As ATP decomposes, the energy from creatine phosphate can be transferred to ADP molecules, converting them back to ATP.
Creatine phosphate
The early anaerobic phase of cellular respiration yields few molecules of ATP, so muscle has a high requirement for oxygen, which enables the complete breakdown of glucose in the mitochondria.
Cellular respiration
Oxygen is carried in the blood, bound to the pigment hemoglobin.
In muscle tissue, oxygen is stored by combining with a similar pigment called myoglobin.
May develop during strenuous exercise, and lactic acid accumulates as an end product of anaerobic respiration. This acid diffuses out of muscle cells and is carried in the bloodstream to the liver.
Oxygen deficiency
Refers to the amount of oxygen that liver cells require to convert the accumulated lactic acid into glucose, plus the amount that muscle cells need to resynthesize ATP and creatine phosphate to their original concentrations.
Oxygen debt. May take several hours to repay
When a muscle loses its ability to contract during strenuous exercise, it is referred to as fatigue. This usually arises from the accumulation of lactic acid in the muscle causing a lowered pH.
A muscle cramp occurs due to a lack of sufficient ATP required to return calcium ions back to the sarcoplasmic reticulum so muscle fibers can relax.
Why does muscle contraction produce so much heat?
More than half of the energy produced by cellular respiration becomes heat.
A muscle fiber remains unresponsive to stimulation unless the stimulus is of a certain strength is called the threshold stimulus.
When a muscle fiber contracts, it contracts to its full extent; it cannot contract partially. The all-or-none response.
The contractile response of a single muscle fiber to a muscle impulse.
Muscle twitch. A twitch consists of a period of contraction followed by a period of relaxation.
A motor neuron and the muscle fibers it controls make up a ____; when stimulated to do so, the muscle fibers of the ____ contract all at once.
Motor unit