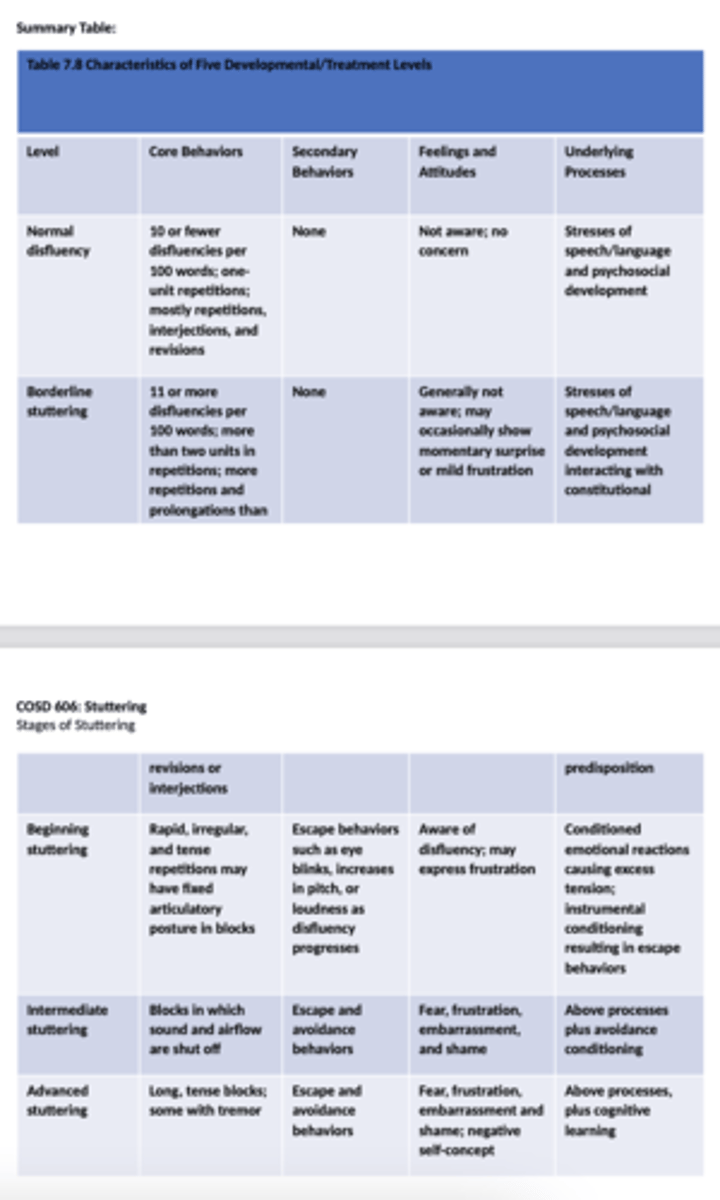
Stages of Stuttering - Fluency
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Developmental/Treatment Level
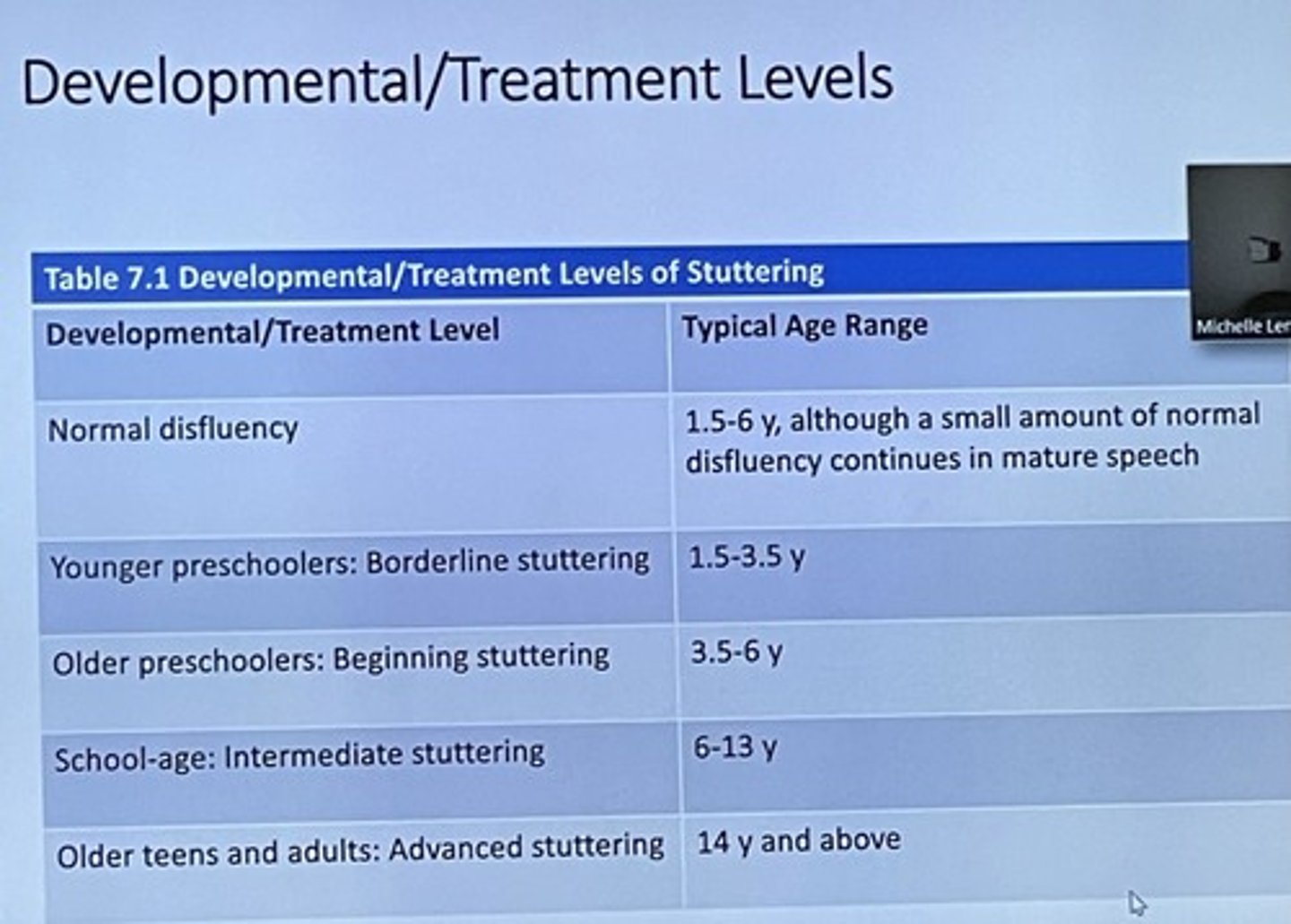
Typical disfluency (stage)
1.5-6 y, although a small amount of normal
disfluency continues in mature speech.
Younger Preschoolers: Borderline Stuttering
1.5-3.5 y
Older preschoolers; beginning stuttering
3.5-6 years
School age; intermediate stuttering
6-13 years
Older teens and adults: advanced stuttering
14 years and above
Caveats about the "Stages"
Exceptions abound
Young children can go back and forth between stages at times.
So why learn? well, pinpointing about what stage someone is in can help guide treatment approach decisions.
Typical Disfluency
Mostly repetition, interjections, and revisions
What is the rate or presentation of normal disfluencies?
< 10 disfluencies per 100 words (Average 6)
One - or two unit repetitions (iteration)
What is the sign of spont. recovery in typical disfluencies?
decreasing SSRs, replaced with revision.
What are the factors that may increase typical disfluencies?
Demands of language acquisition
Speech motor development
Environmental stressor
Pragmatics (interruption)
Excitement (holiday, vacation)
Are there concerns in typical disfluency?
No concern or little awareness.
What are the common types of disfluencies in young preschoolers?
mostly repetition and prolongations
What is the presentation of disfluency in young preschoolers?
increasing frequency of disfluencies to >10 disfluency per 100 words (though still variable)
More SLDs than non-SLDs
Typically, more than two-unit iterations
Low to no tension during stuttering and no additional secondary behaviors
What is the tension
like in young preschoolers?
Low to no tension during stuttering and no additional secondary behaviors
What is the concern or awareness in young preschoolers?
little to no awareness and no concern; may occasionally seem surprised.
What are the factors underlying borderline stuttering?
Speech and language development
Environmental factors
Factors underlying outgrowing borderline stuttering
Speech and language development (factors)
Some langauge and speech skills may be more advanced than others (dissociations)
Inefficiencies in language production processes - Outgrow borderline stuttering may occur
What are the environmental factors?
Communication Stressors
Psychosocial Stressors
When can the outgrow borderline stuttering may occur?
Maturation of speech language system or resources moved to compensate.
Enviro/psychosocial factors.
What are the common types of disfluencies in older preschoolers?
Repetitions - rapid and irregular (increase tense and hurry)
What is the presentation of disfluencies in older preschoolers?
Gradual or sudden onset, variable
Prolongations and blocks may begin
What is the tension like in older preschoolers?
Pitch rises during SLDs (secondary to tension)
What are the secondary behaviors older preschoolers?
escape behaviors begin (blinks, nods, fillers during disfluencies)
No avoidance behaviors yet - no fear of talking.
What are the concerns/awareness for individuals who are older preschoolers?
Awareness and frustration is apparent, but does not have a negative self-image of speech.
What are the factors underlying beginning stuttering
Development less of a factor as language development slows down
Increase muscle tension and tempo - these changes may be attempts to control or escape from stutters.
Effects of learning on stuttering
What are the effects of learning on stuttering?
Classical conditioning: spreads the emotion associated with stuttering to more situations; this means more tension and faster tempo
Operant conditioning: increases frequency of escape behaviors, this means more eye blinks, nods, etc.
What are the common types of disfluency in intermediate stuttering (school age)?
Blocks and prolongations are more common - involuntary but aware of them
Escape behaviors used to try and terminate disfluency
What is tension like in intermediate stuttering (school age)?
What are the secondary behaviors in intermediate stuttering (school age)?
Escape: behaviors used to try and terminate disfluency
Avoidance: words and situtation
Describe the word and situation avoidance in intermediate stuttering (school age)?
Starters, substitution, circumlocutions, postponements, anti-expectancy devices (funny device)
Fear of certain sounds or words, anticipation of sounds and words in speech
Fear of certain sounds or words spreads to fear of certain situations.
What are the factors underlying intermediate stuttering?
- Classical conditioning: creates more and more tension in stuttering in more situations
- Operant conditioning: create a more complex array of escape behavior
- Avoidance conditioning: creates extra sounds and behaviors before the feared word and causes child to avoid more and more words and situations.
What are the core and secondary behaviors classified as in advanced stuttering (adolescents and adults)?
these bx have become ingrained
What are the secondary behaviors in advanced stuttering (adolescents and adults)?
level of secondary behaviors may correlate to level of concern for person
What are the types of disfluency in advanced stuttering (adolescents and adults)?
stuttering can include all types of SLDs with longer durations.
What are the avoidance techniques in advanced stuttering (adolescents and adults)?
avoidance techniques may be fine tuned to minimize display of SLDs.
What are the feelings and attitudes in advanced stuttering (adolescents and adults)?
negative self-concept developed from years of
What's the underlying advanced stuttering?

Characteristics of Advanced Stuttering in Older Teens and Adults
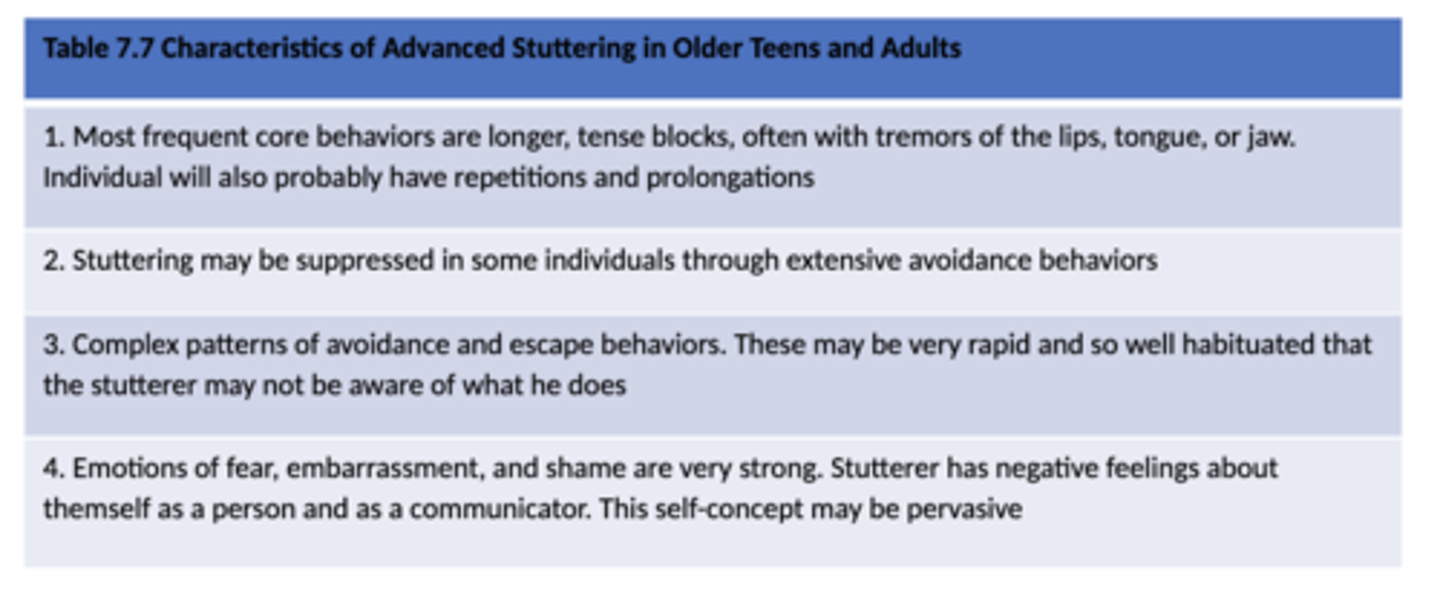
Characteristics of Five Developmental/Treatment Levels