Lecture 5: Radiographic Interpretation
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
in regards to radiation physics, which setting on the machine can increase the speed electrons trave from the cathode to anode?
kVp
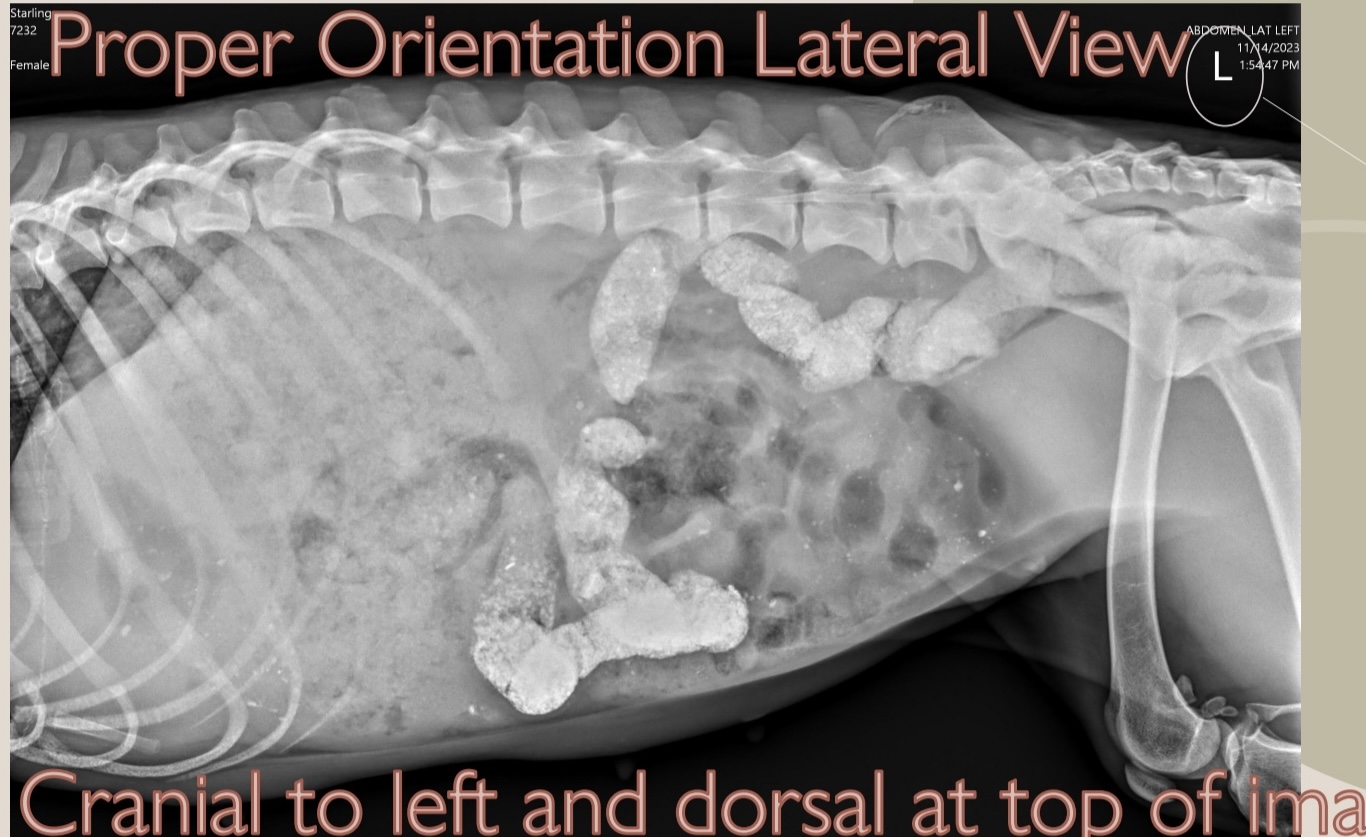
what does the L indicate?
tells the reader this is a left lateral view
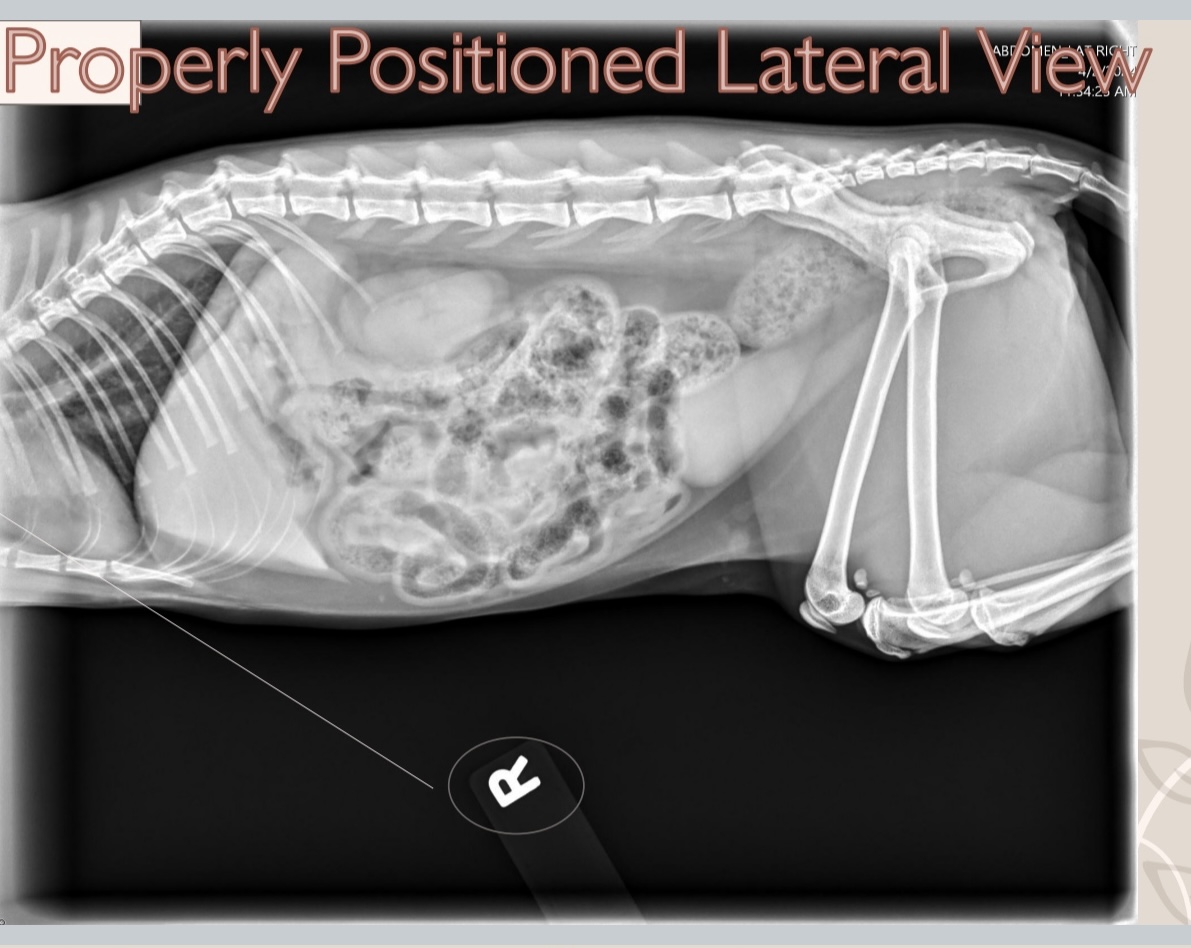
what does the R indicate?
tells the reader this is a right lateral abdomen, it’s also positioned with cranial to the reader’s left
what is the proper orientation for lateral view?
cranial to left and dorsal at top of image
what is properly positioned lateral view?
cranial to left, dorsal at the top of the image, caudal to the right
how should medial-lateral projection be oriented?
with cranial or dorsal to the readers left
ventrodorsal (VD)/dorsoventral (DV) views
positioned with cranial at the top of the image and the patients right on the readers left
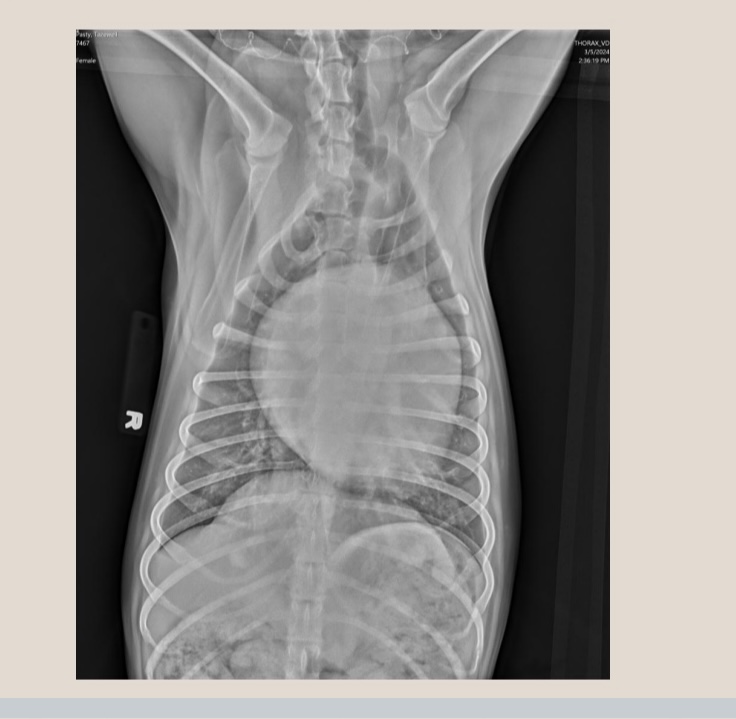
what view is this?
VD/DV
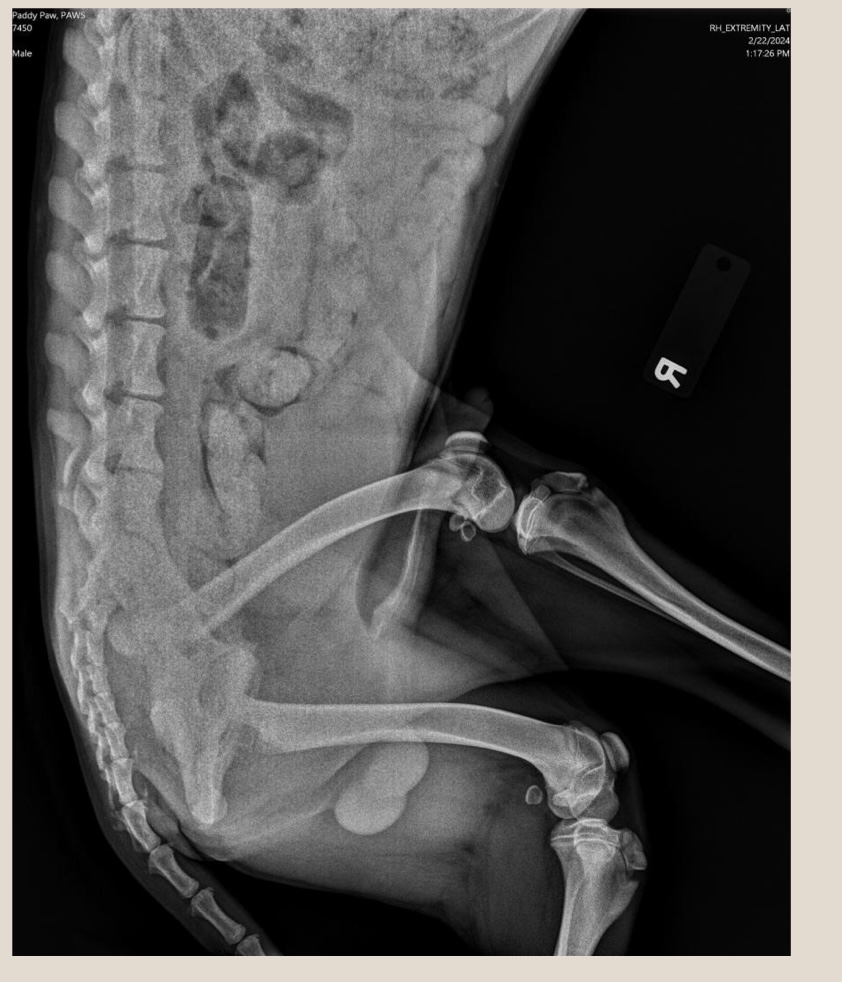
how should this radiograph be adjusted?
rotate to the right and flip cranial and caudal
radiolucent materials will show up
more black
radiopaque materials will show up
more white
what material is the most radiolucent?
air
what material is the most radiopaque?
metal
what is 1
gas/air
what is 2
soft tissue
what is 3
fat
what is 4
bone/mineral
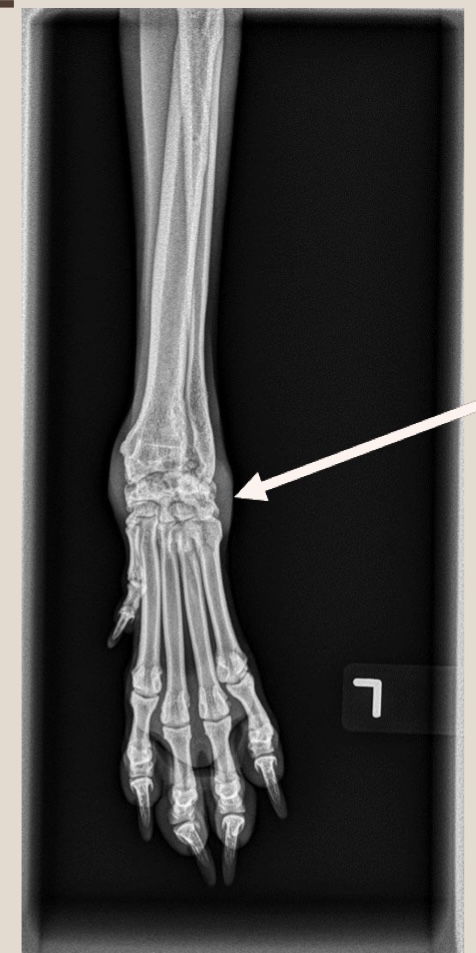
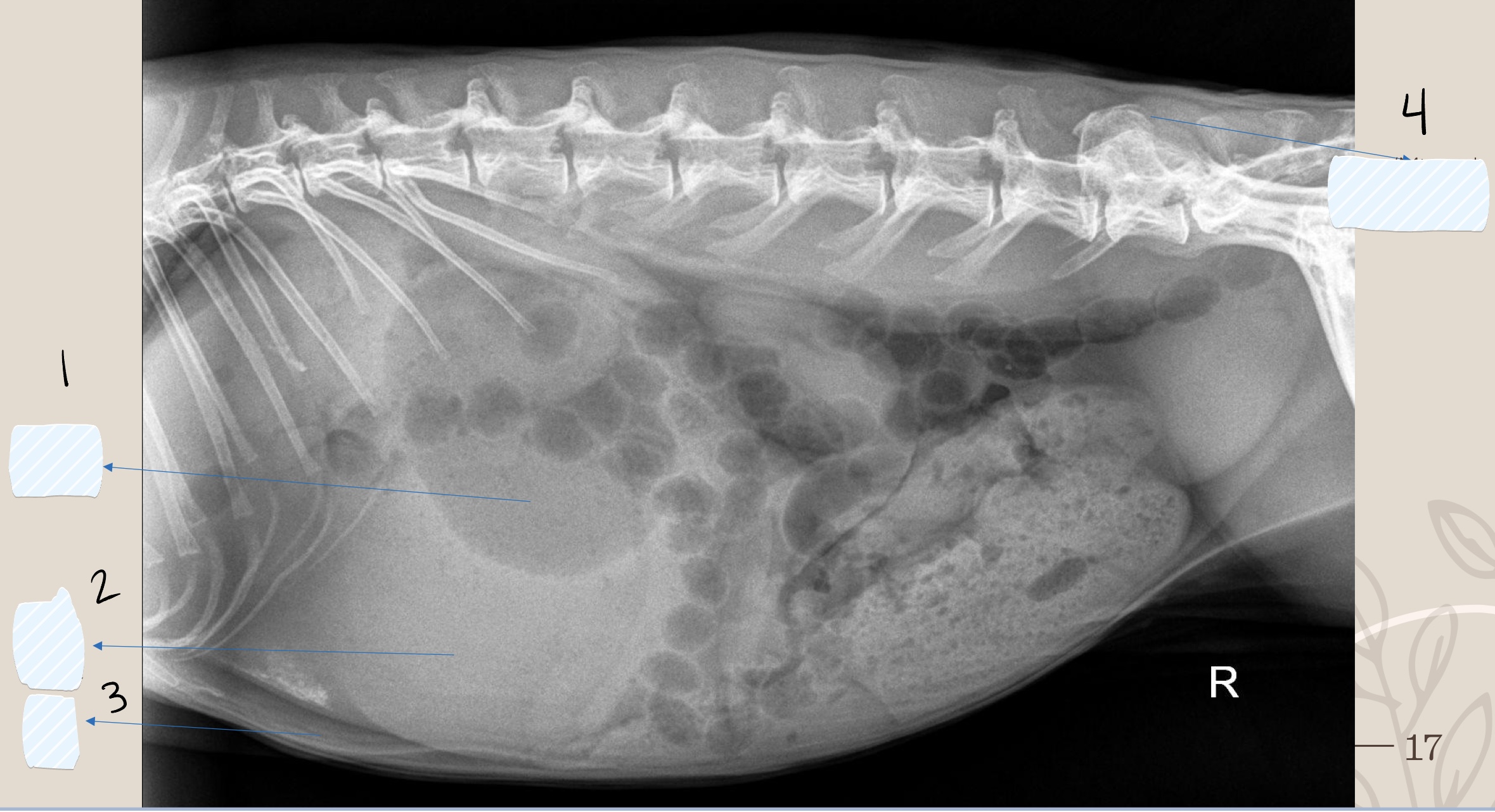
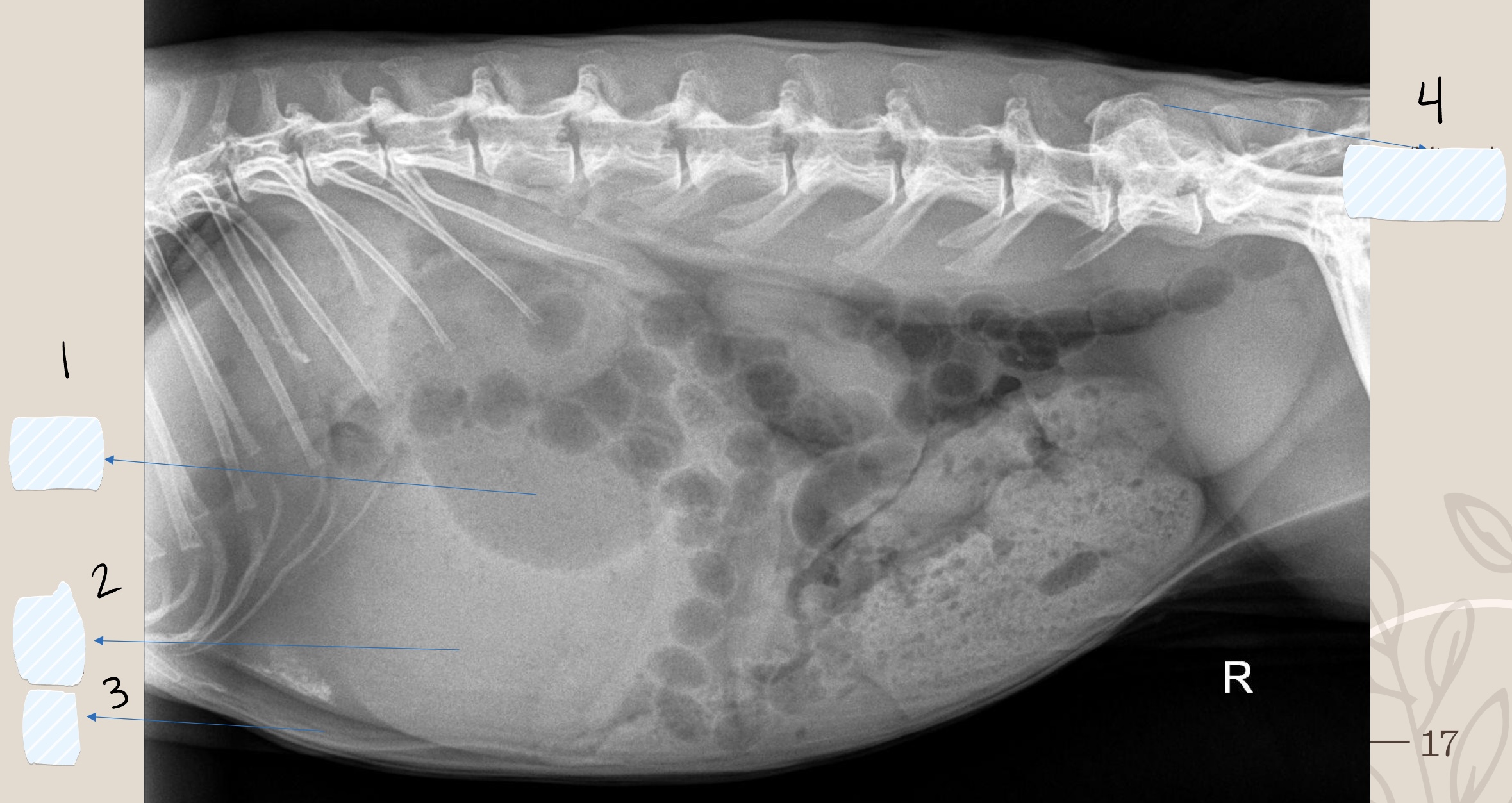
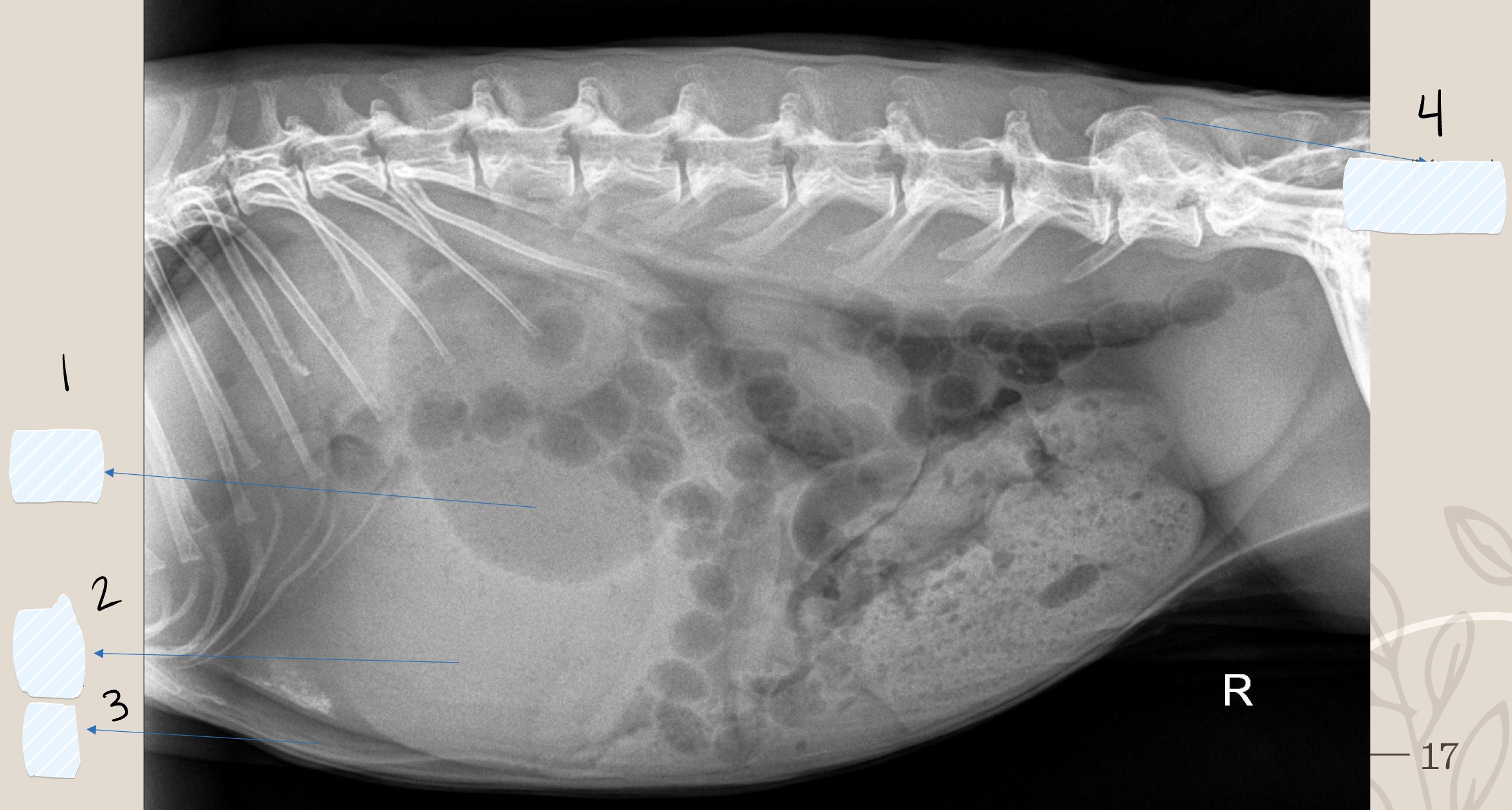
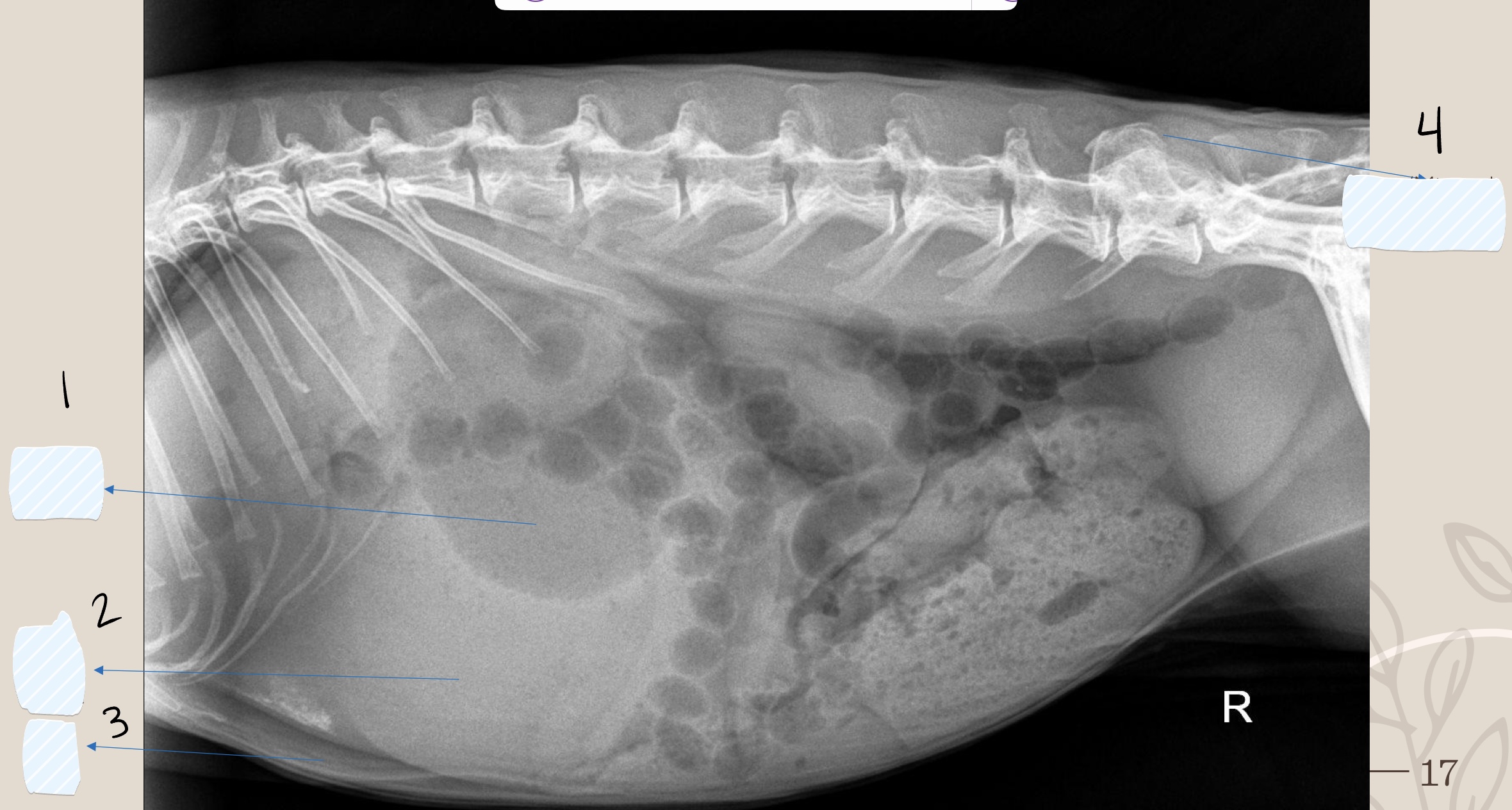
what is the opacity the arrow is pointing at?
soft tissue
what are Roentgen signs?
size, shape, number, location, margination, opacity
magnification occurs due to
the distance between the structure and the receiver → can reduce detail of image
distortion occurs when
the object and receiver are not parallel
summation
opacity created that does not represent a structure that is present within the patient
where is summation common?
the kidneys on lateral radiograph where the intersection of the caudal pole of the right kidney with the cranial pole of the left kidney
border effacement/silhouette sign
two structures in contact with each other that has the same opacity
loss of margin distinction
underexposed images
image is too bright so usually kVp or mAs is too low
overexposed images
image is too dark so usually kVp or mAs is too high
contrast
links directly to the differing of opacities based on varying degrees of x-ray beam absorption
ability of an x-ray beam to penetrate tissue depends on
its energy
the x-ray beams energy directly ties to a
varying kVp and a stable mAs
why does higher kVp give less contrast?
because more x-rays are transmitted through the patient to the plate
lower kVp allows for
higher contrast
detail
spatial resolution or sharpness
detail can be influenced by
exposure factors, matrix of IP, software, monitor, reader’s visual acuity
pixel
picture element
dicom
digital imaging and communications in medicine
pacs
picture archiving and communicating system