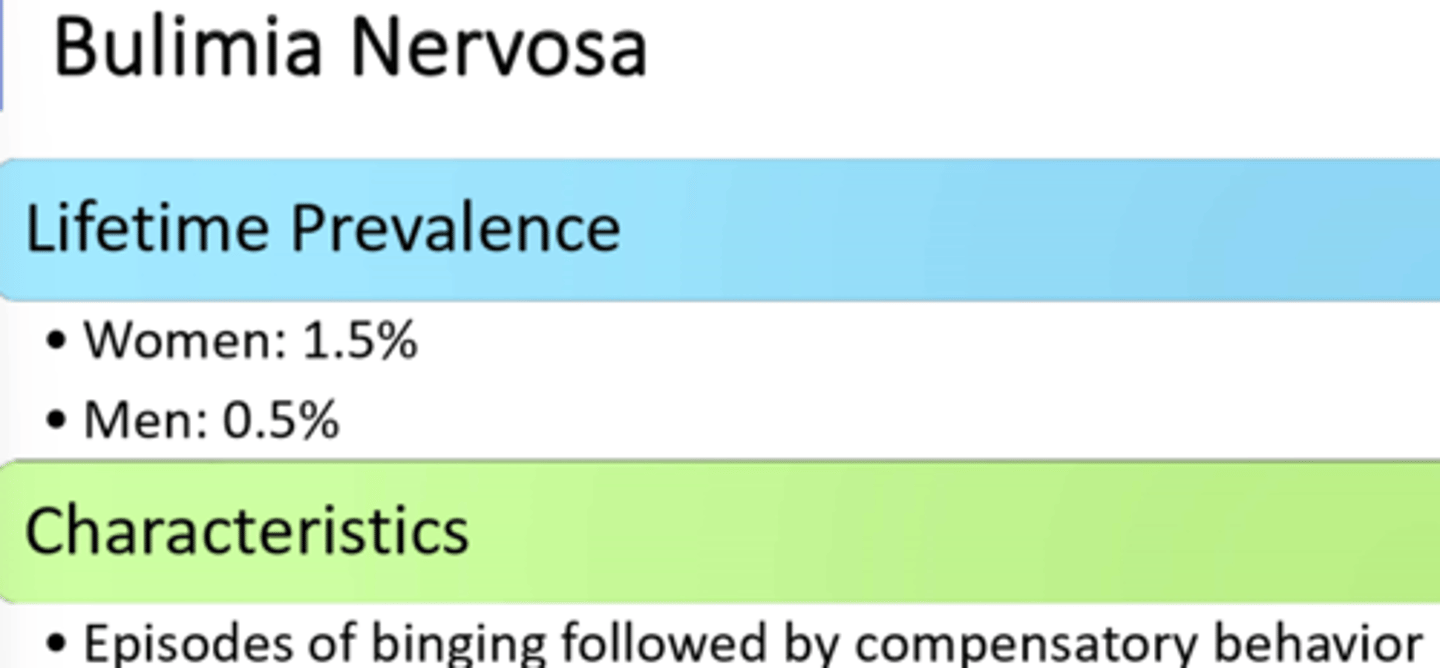
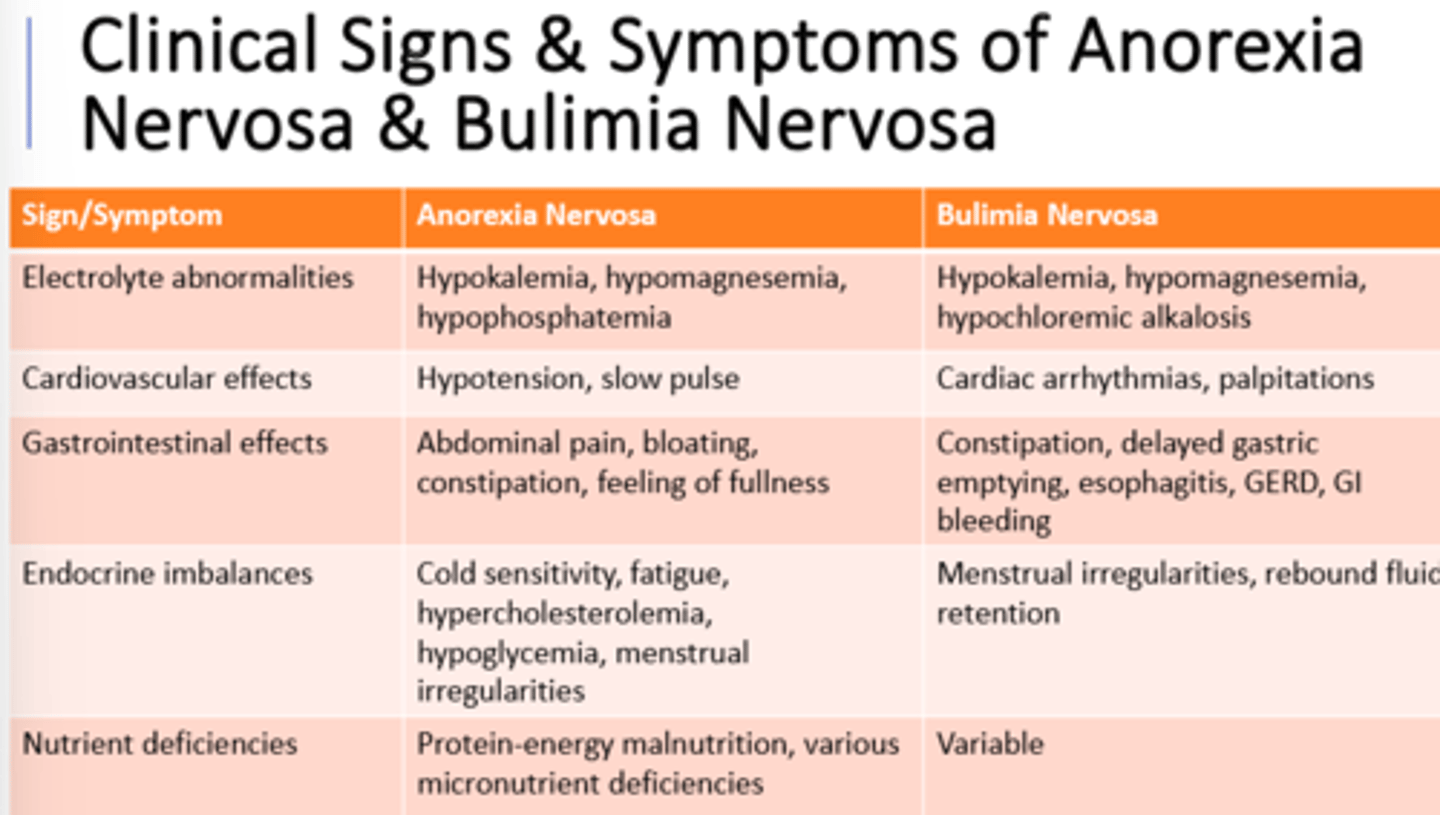
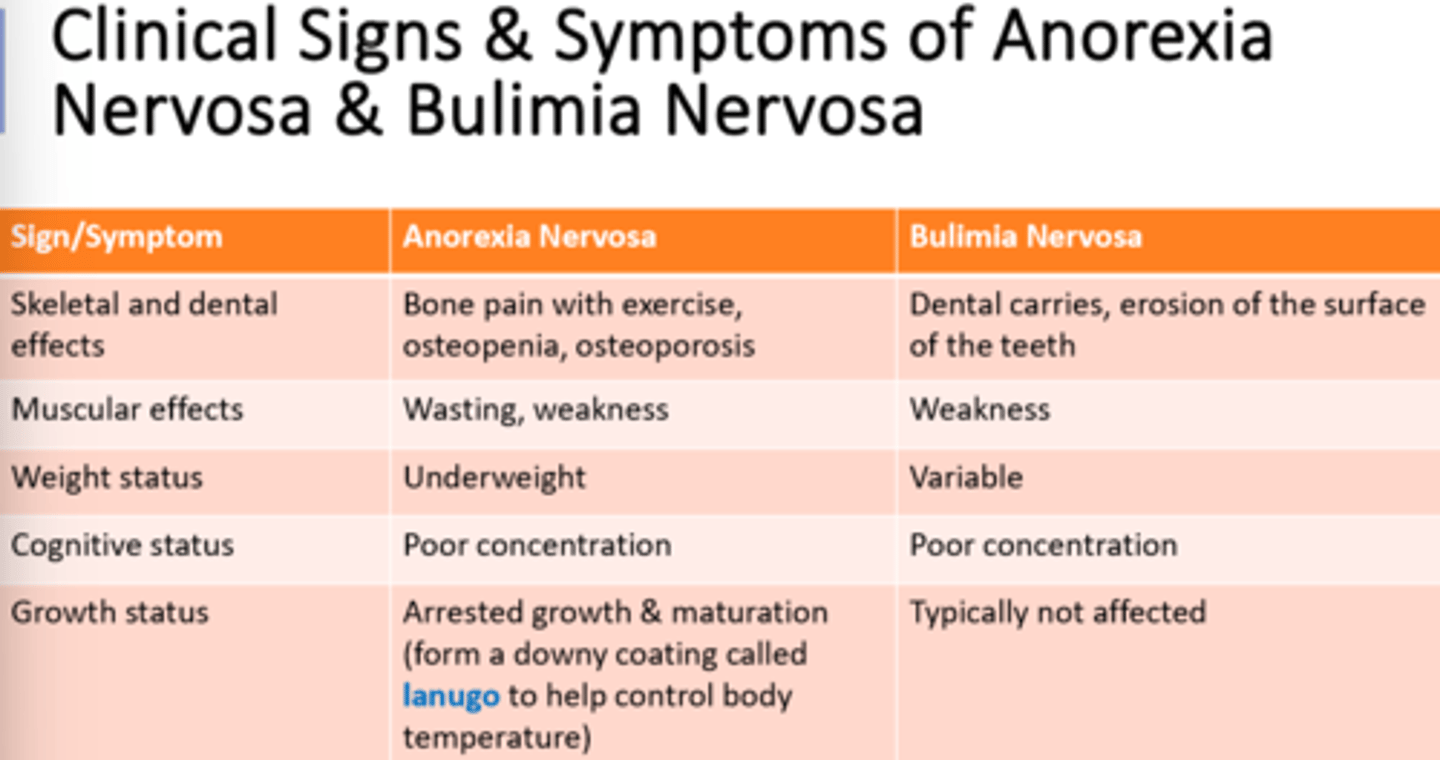
KingChiro - Weight Management (QUIZ 2)
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
<16.0 = Severe thinness
16 - 16.9 = Moderate thinness
17 - 18.49 = Mild thinness
18.5 - 24.9 = Normal range
> or = 25 = Overweight
25 - 29.9 = Pre-obese
30 - 34.9 = Obese Class 1
34 - 39.9 = Obese Class 2
> or = 40 = Obese Class 3
***Give all of the BMI categories, and which number BMIs are related to it
eating disorder
A BMI of less than 16 would be a red flag for
kg/m^2
What is the measurement of BMI
<120/<80 = Normal
120-129/<80 = Elevated
130-139/80-89 = Stage 1 HTN
>140/>90 = Stage 2 HTN
>180/>120 = Hypertensive Crisis
Describe the different categories of blood pressure and the systolic and diastolic numbers with them
1) Waist Circumference
2) Neck Circumference
3) Waist-to-Hip Ratio
4) Waist-to-Height Ratio
What are other predictors of body weight than BMI that should be analyzed along side BMI
Men = < or = 40 inches
Women = < or = 35 inches
**What are the healthy Waist Circumference for both men and women?
Men < or = 0.95
Women < or = 0.80
**What are the healthy Waist-to-Hip Ratios for both men and women?
between ileum and ribs
Where do you measure wait circumference
Underweight = <0.35
Slim = 0.35-0.43
**Healthy = 0.43-.53
Overweight = 0.53-0.58
Obese = 0.58-0.63
Very Obese = >0.63
**What are the healthy Waist-to-Height Ratios for MEN?
Underweight = <0.35
Slim = 0.35-0.42
**Healthy = 0.42-0.49
Overweight = 0.49-0.54
Obese = 0.54-0.58
Very Obese = >0.58
**What are the healthy Waist-to-Height Ratios for WOMEN?
bookmark: stuff below?
Transtheoretical Model of Change
a model that has been applied to understanding how change occurs in discrete health behaviors and can be useful in providing a general framework for considering how other change processes occur in a person's behavior
Not ready to change = 1-3
Unsure about change = 4-7
Ready to change = 8-10
When asking the person to rate how ready they are to change, when would each of the ratings lead you to believe?
1. Precontemplation
2. Contemplation
3. Preparation
4. Action
5. Maintenance
What are the stages of the Transtheoretical Model of Change
Precontemplation
Stage of the Transtheoretical Model where they are not intending to make changes within the next 6 months
contemplation stage
Stage of the Transtheoretical Model where they are considering a change within the next 6 months
preparation stage
Stage of the Transtheoretical Model where the person intends to take action in the immediate future
Action
Stage of the Transtheoretical Model where they are currently making changes and motivated to continue
Maintenance stage
Stage of the Transtheoretical Model where they are maintaining behavioral change that they started
Fat Mass
Lean Body Mass/Fat Free Mass
What are the two types things that contribute to body composition
Essential fat and Storage fat
What is found within "Fat Mass"
Muscle, Bone, Fluid
What is found within the category of Lean Body Mass/Fat-Free Mass
bookmark: stuff above?
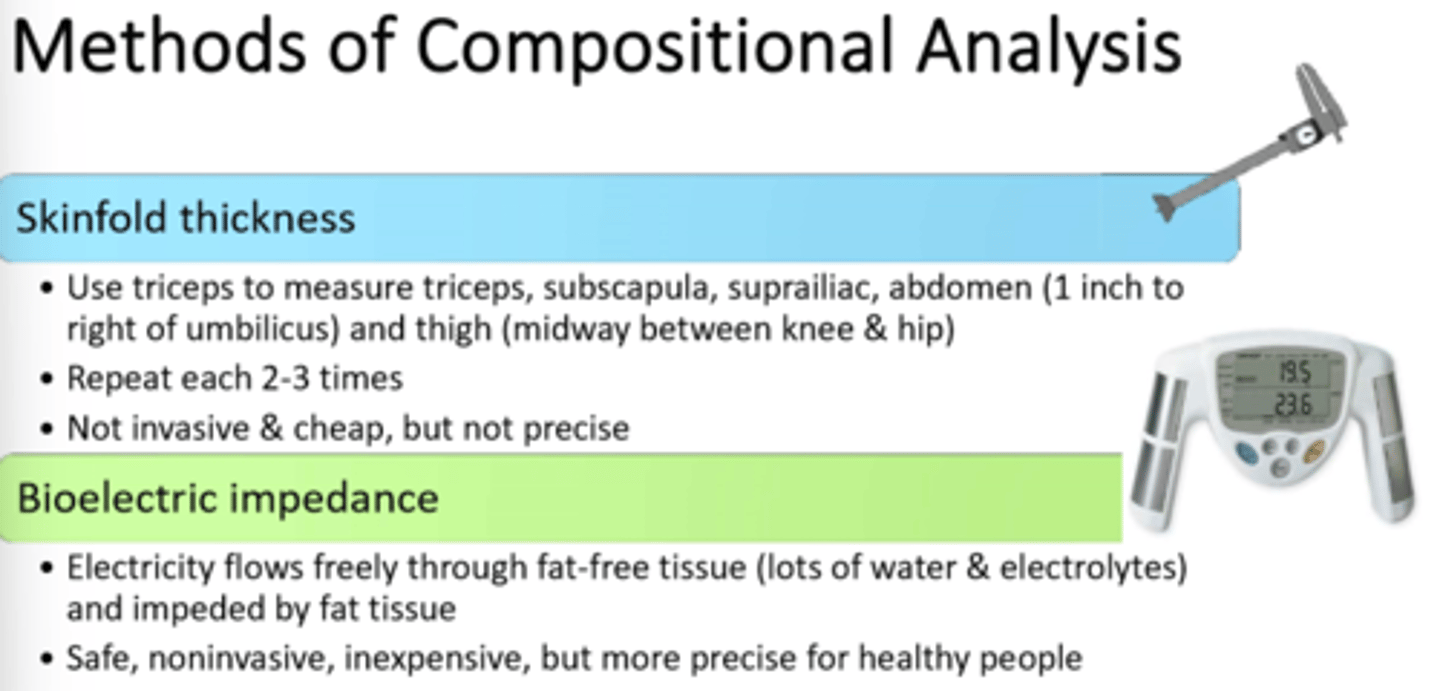
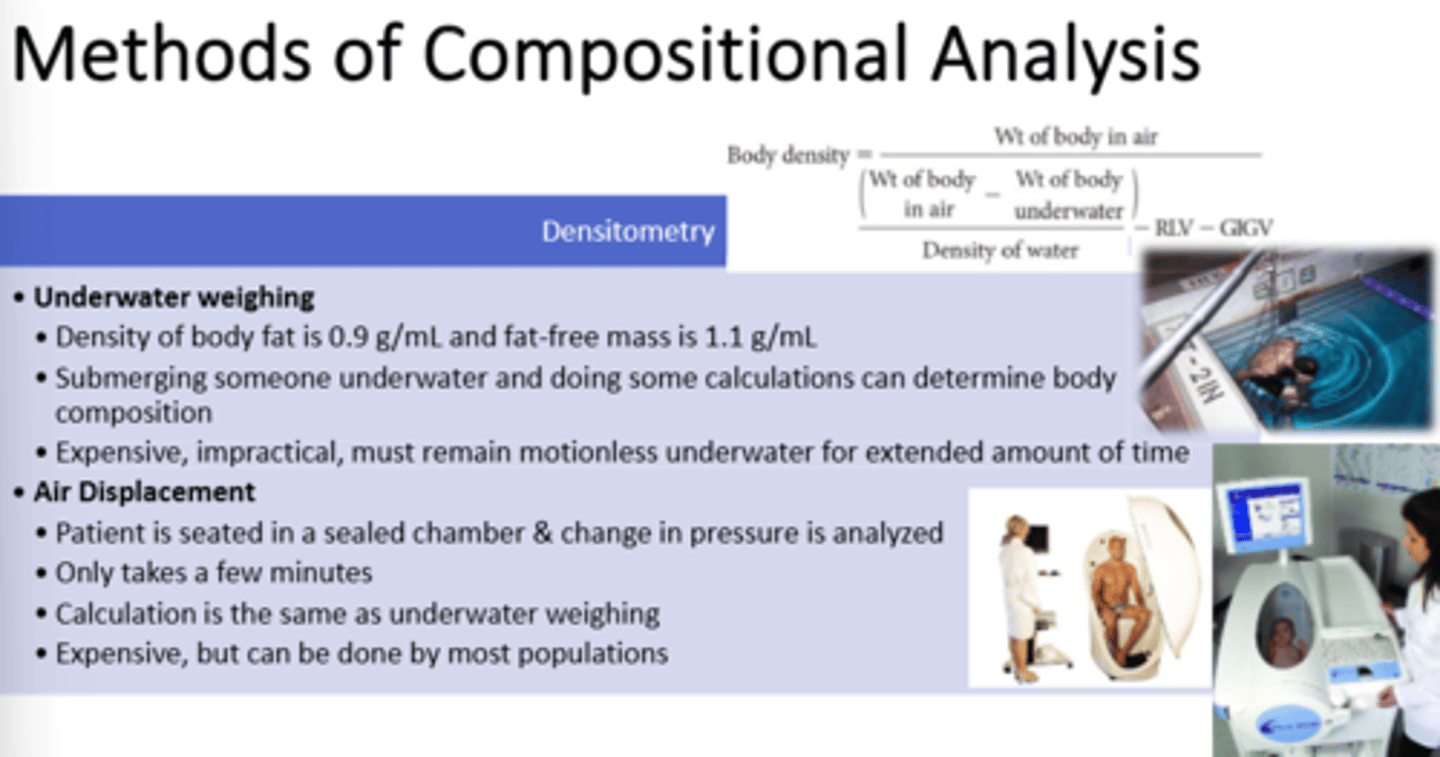
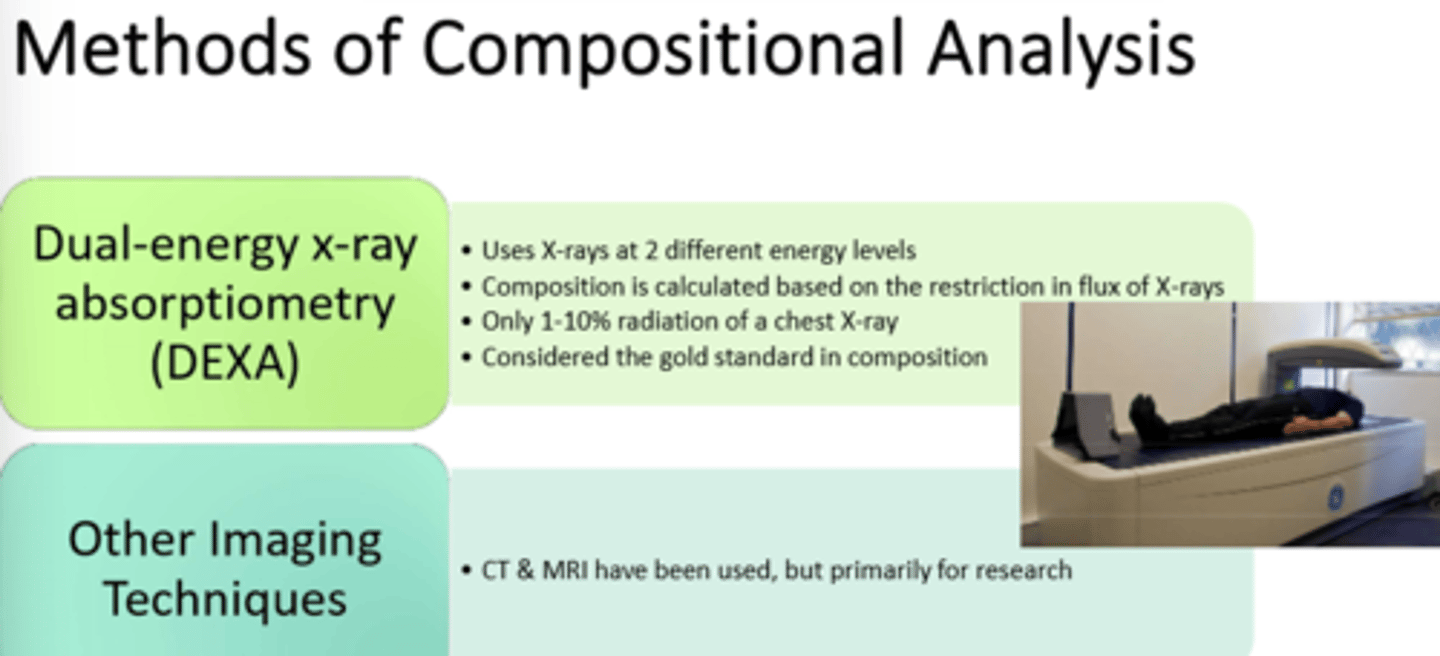
1) Calipers
2) Hydrostatic Weighing
3) Bioelectric Impedance
4) Air Displacement
5) Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry, DEXA --gold standard!!
What are ways we can measure Body Composition? Which one is our current gold standard?
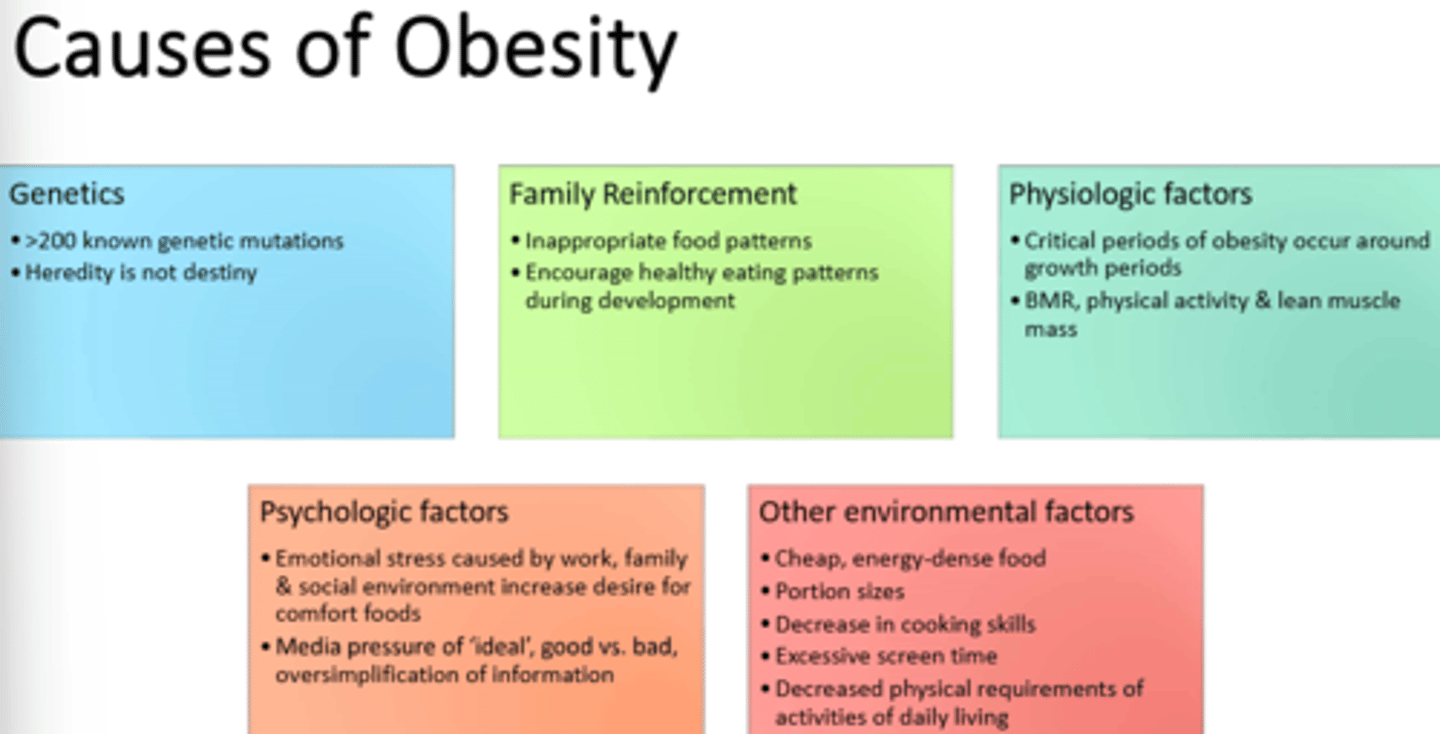
1) Sedentary Lifestyle
2) Genetics
3) Family Reinforcement
4) Physiologic Factors
5) Psychological Factors
6) Other environmental --food, portion sizes, screen time, etc
What are the 6 main causes of obesity
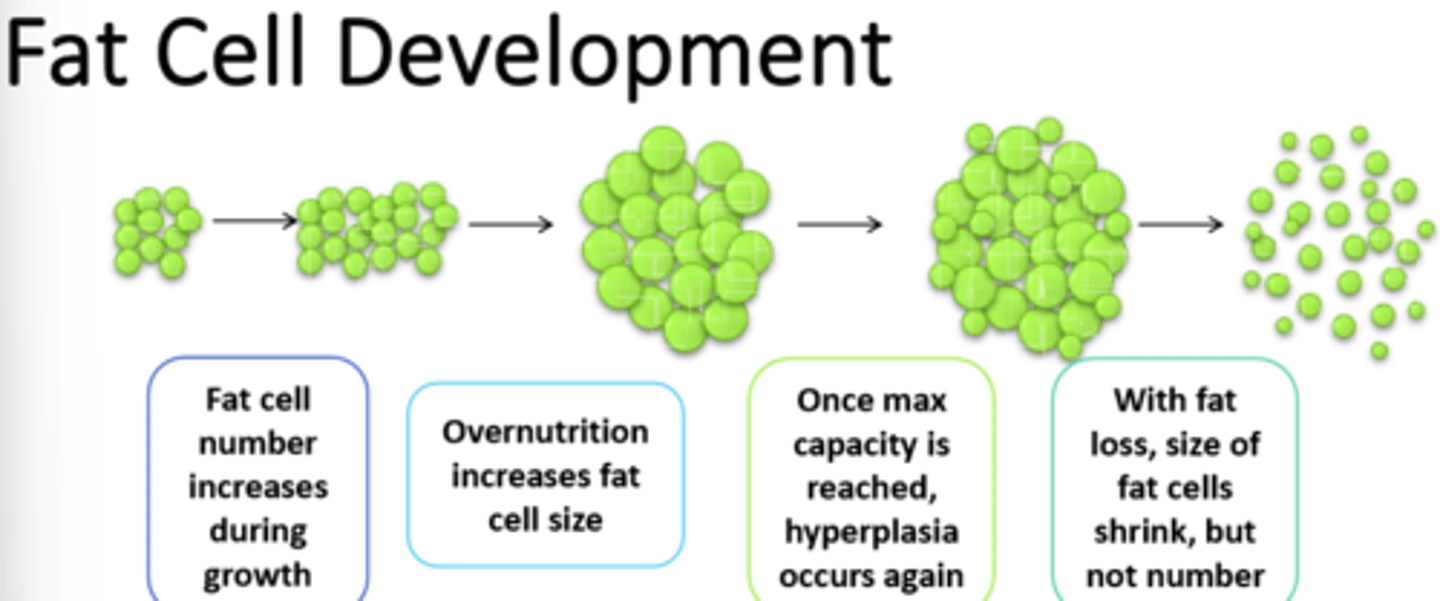
1) Taste, satiety, and portions
2) Obesogens (Endo disruptors)
3) Viruses
4) Gut microflora
What are some minor contributors to obesity?`
Leptin
hormone that signals the hypothalamus and brain stem to reduce appetite
Ghrelin
hormone secreted by empty stomach; sends "I'm hungry" signals to the brain
1) White --coupled
2) Brown --uncoupled
What are the two type of adipose tissue? Which one is coupled --oxidation heat is ATP generation coupled with heat release-- and which one is uncoupled?
infants
more in women than men
people in colder temps
people with lower BMIs
Brown adipose is found in higher concentrations in which types of people?
Beiging
Cold weather or intro of a cold stimulus may cause subcutaneous WAT to express BAT genes
Android; men
body shape described as "apple-shaped" with excess body fat distributed primarily on the upper body and trunk. Who commonly shows this type?
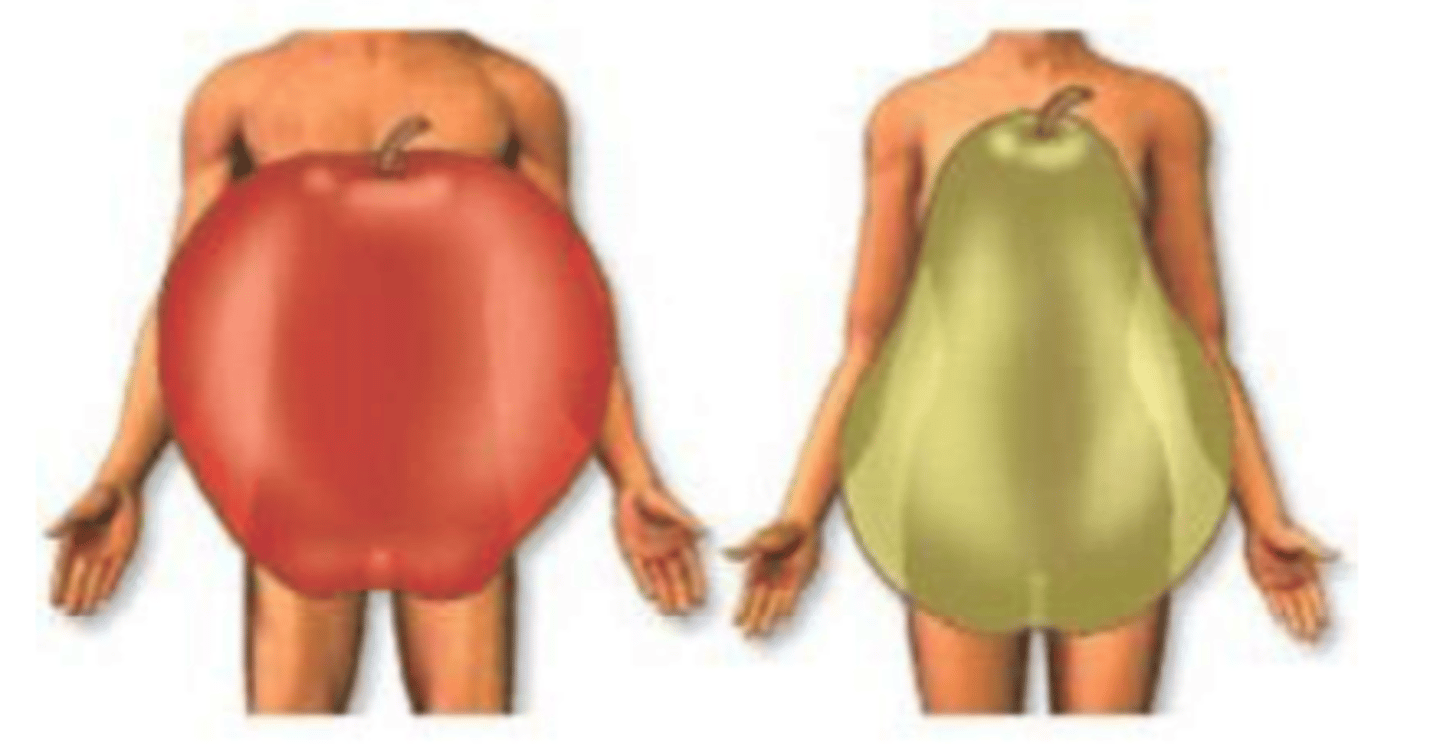
Gynoid; females
Body shape described as "pear-shaped" where excess body fat is distributed primarily on the lower body (hips and thighs). Who commonly shows this type?
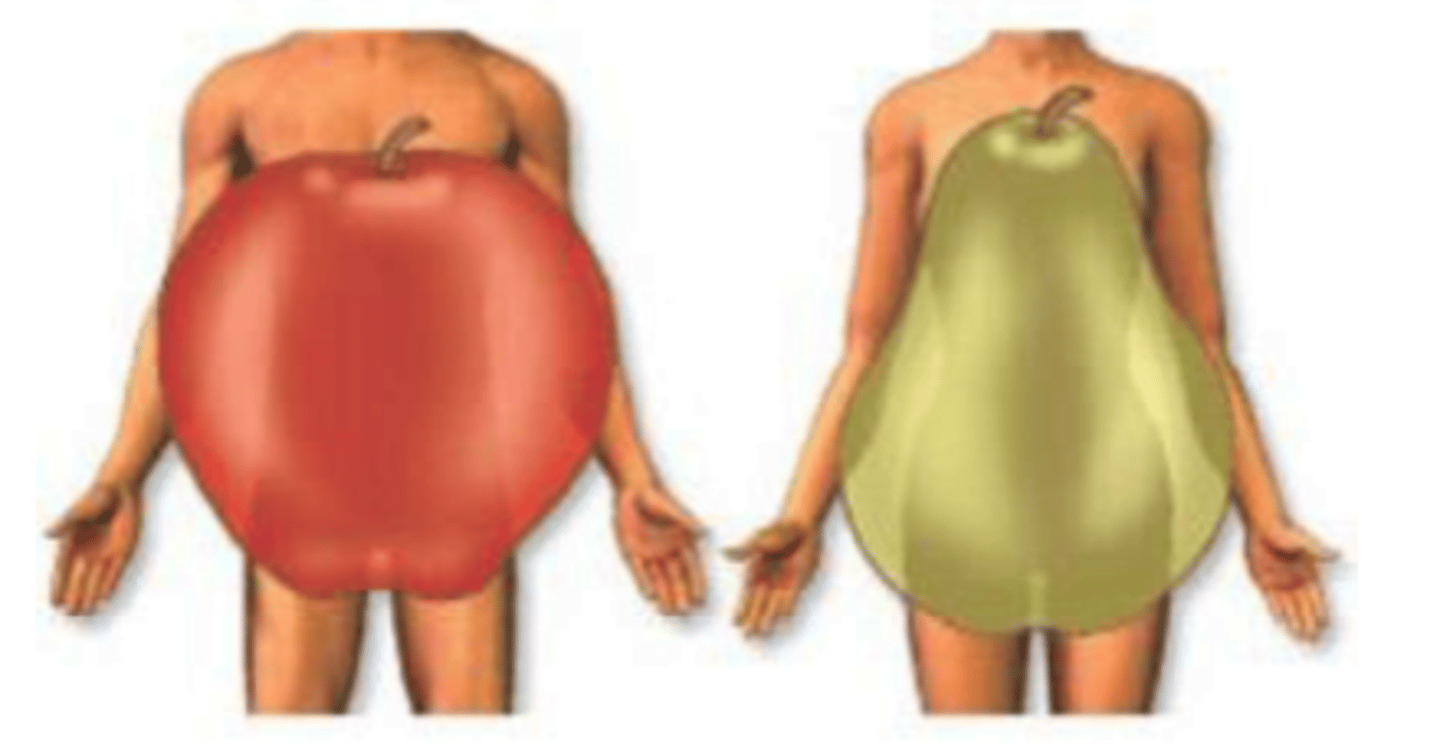
Android; more visceral adipose compared to subcutaneous
What body shape type --in regards to fat distribution-- is associated with more health risk? Why?
1) Visceral fat
fat stored around organs, main cause of central obesity, and VERY METABOLICALLY ACTIVE
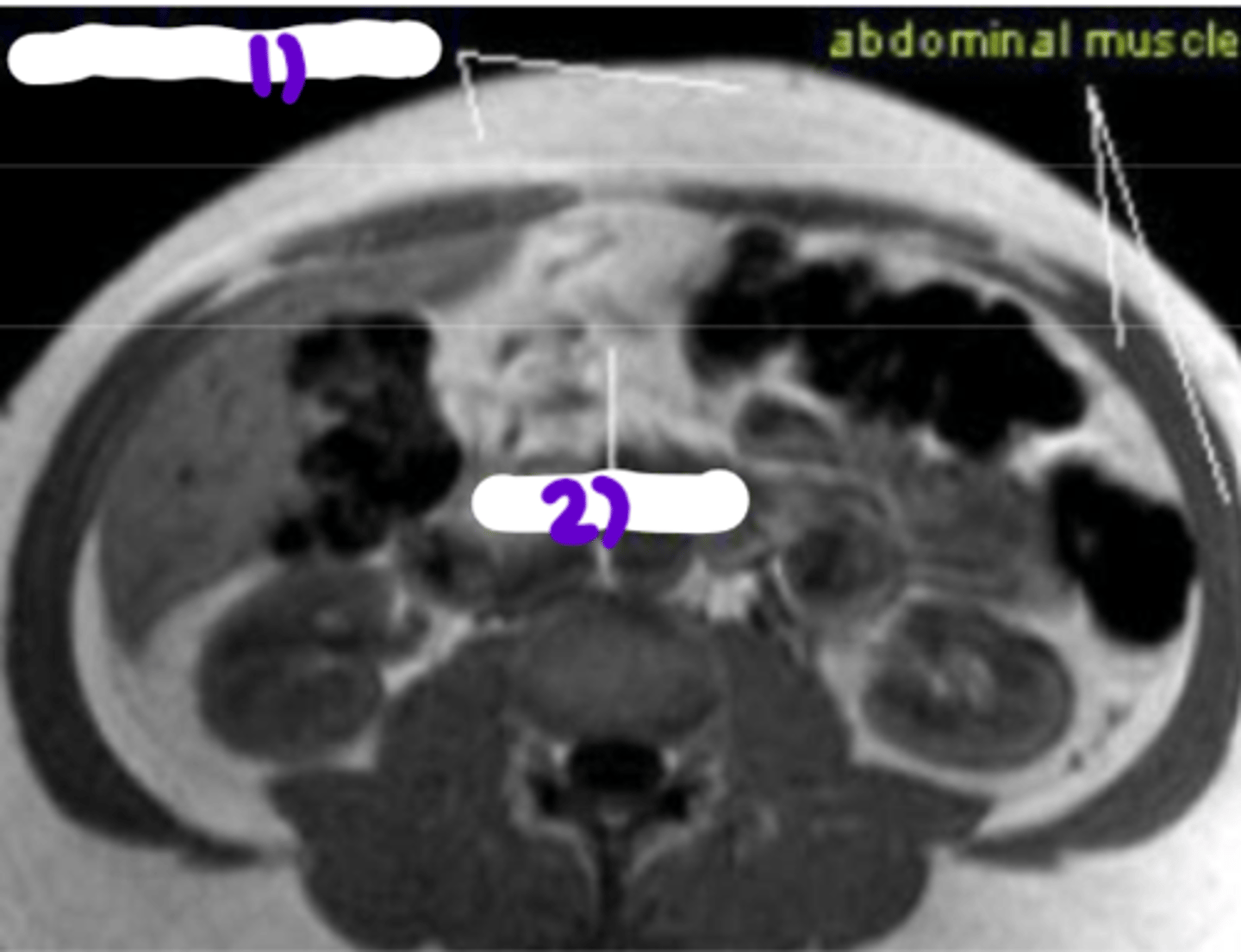
2) Subcutaneous fat
fat stored around the hips, thigs, or exterior of abdomen muscle
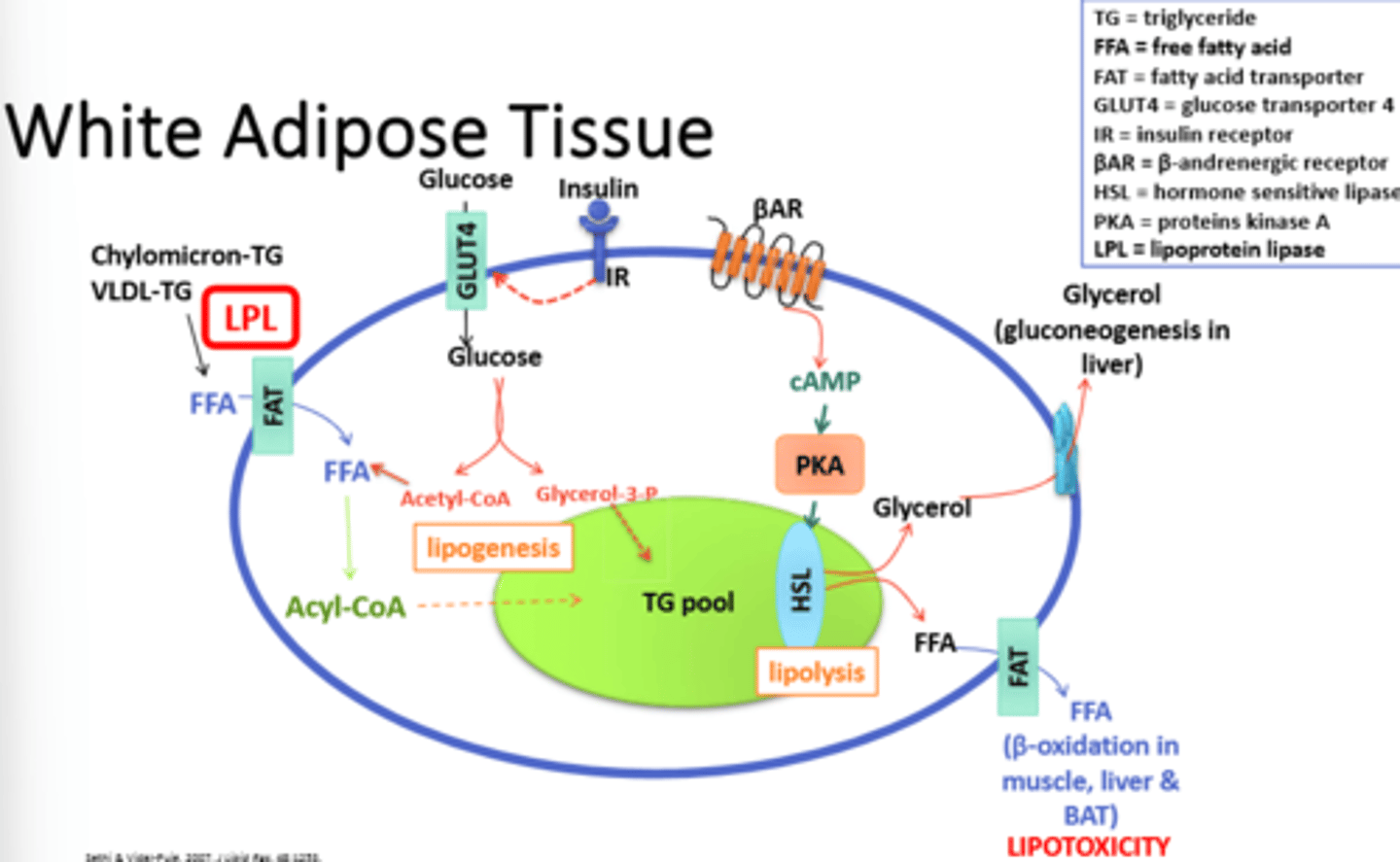
lipotoxicity
Visceral adipose tissue is very metabolically active, which increases what?
Lipoprotein lipase, LPL
which enzyme when in higher quantities increases lipotoxicity
increase
Does lipoprotein lipase activity increase or decrease after weight loss
1) major determinant in obesity development
2) more active in obese than lean individuals
3) activity makes fat storage more efficient
Describe key things about lipoprotein lipase
easier
Is visceral adipose tissue, VAT, easier or harder to lose than subcutaneous fate
Visceral adipose tissue, VAT
Exercise with or without weight loss leads to reduction of _____
Males = abdomen
Females = breasts, hips, and thighs
Where is Lipoprotein Lipase usually found to be more active in males? What about females?
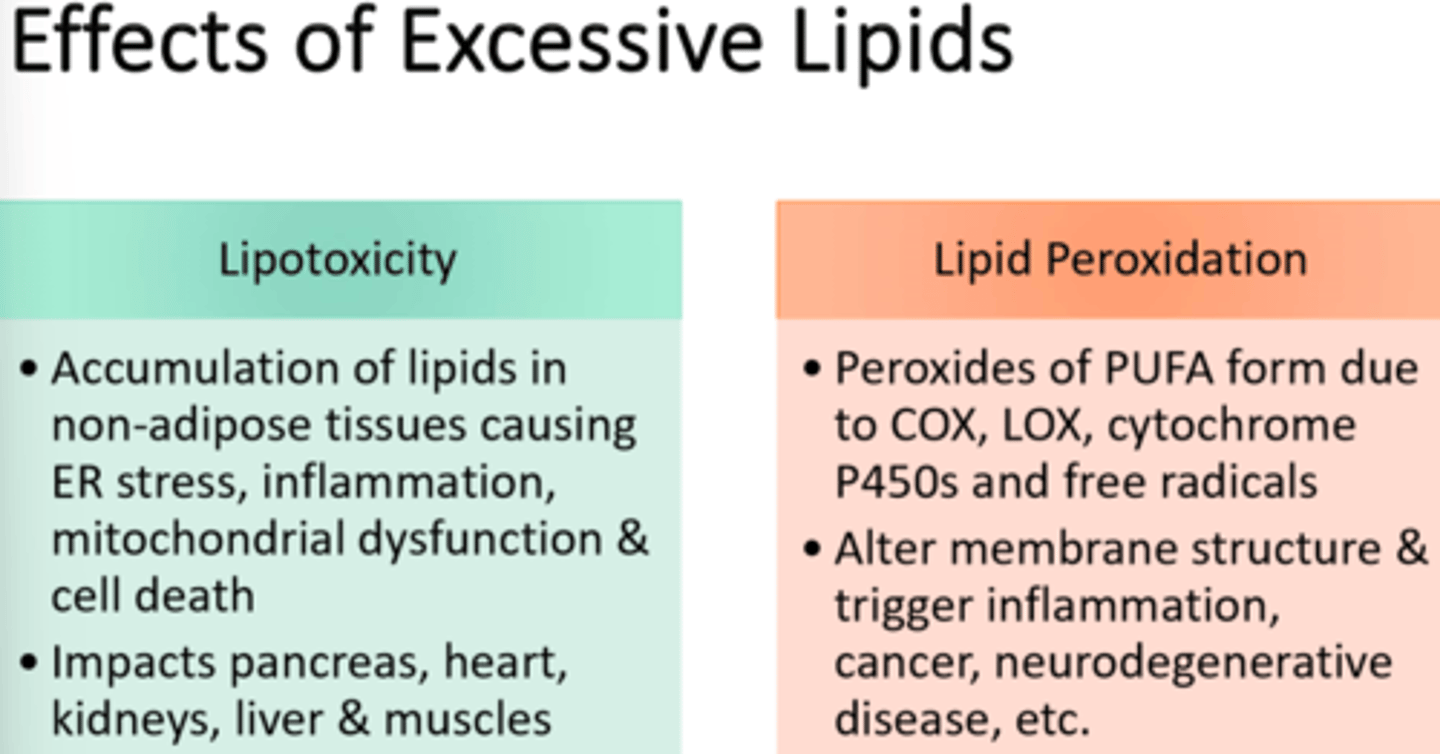
Adipotoxicity and Lipotoxicity
What are the two ways the body responds to nutritional overload?
Adipotoxicity
negative effects of storage of excess fat in adipose tissue
Lipotoxicity
Negative effects of storage excess fat in non-adipose tissue
TNF-Alpha
IL-6
Leptin
Adiponectin
Resistin
What type of adipokines secreted more during Adipotoxicity
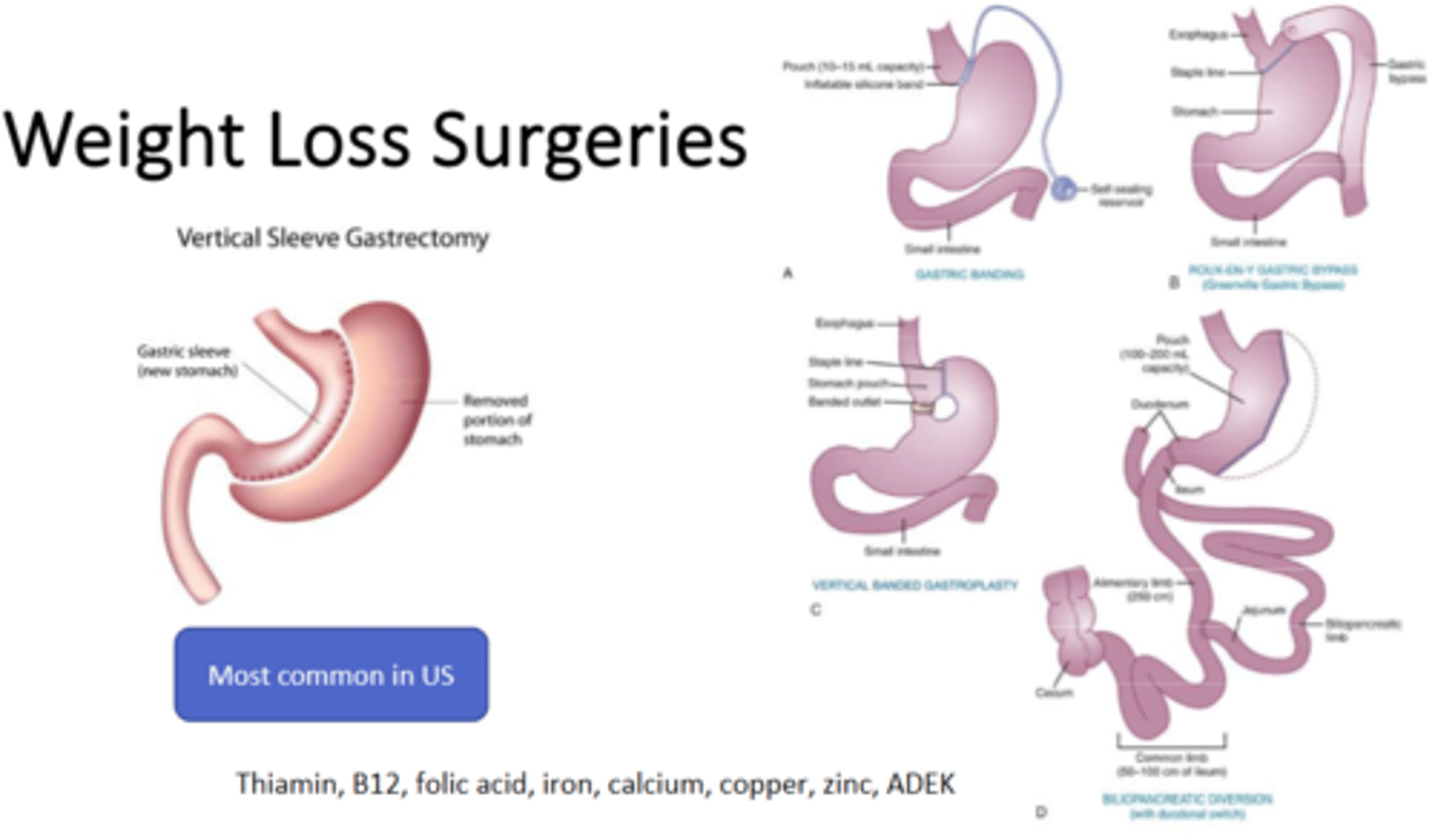
Roux-en-y Gastric Bypass
Gastric Banding
What are the two types of surgery we discussed to help lose weight
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass
bariatric surgery that involves stapling the stomach to decrease its size and then shortening the jejunum and connecting it to the small stomach pouch, causing the base of the duodenum leading from the nonfunctioning portion of the stomach to form a Y configuration, which decreases the pathway of food through the intestine, thus reducing absorption of calories and fats
dumping syndrome
This is a side effect of the Roux-en-y surgery
gastric banding surgery
restricts the size of the stomach with an adjustable band
Iron
Calcium
Vitamin D
Vitamin B12
What are the common bariatric surgery deficiencies
Antecedent (Trigger)
Behavior
Consequence
What are the ABCs of behavior modification
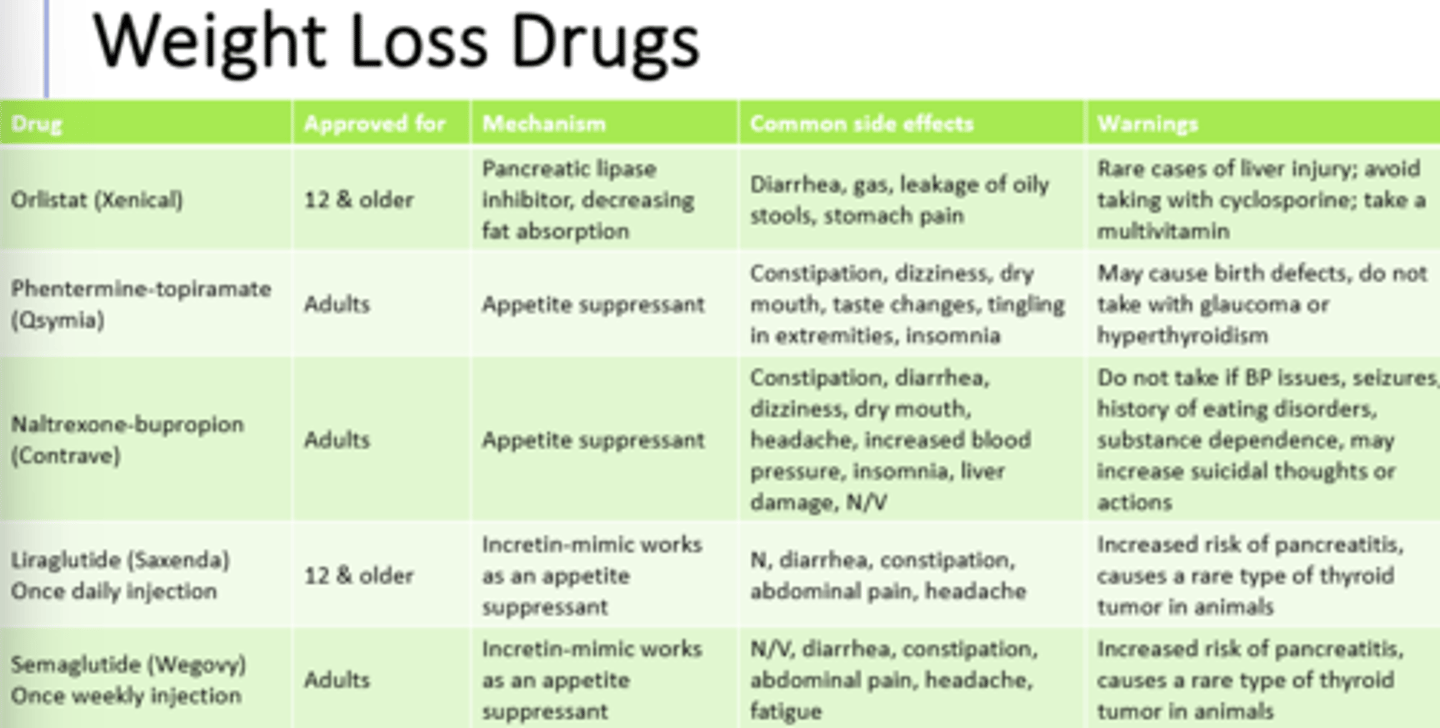
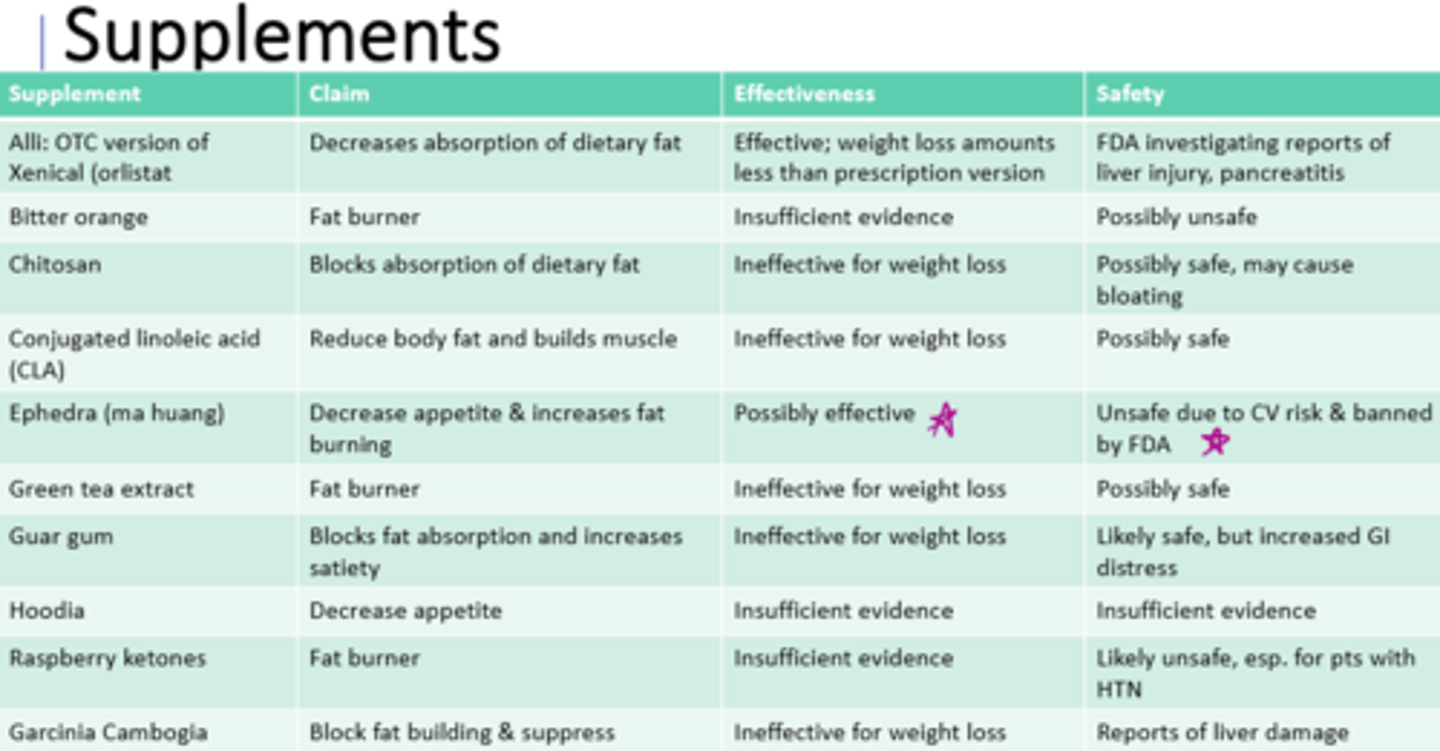
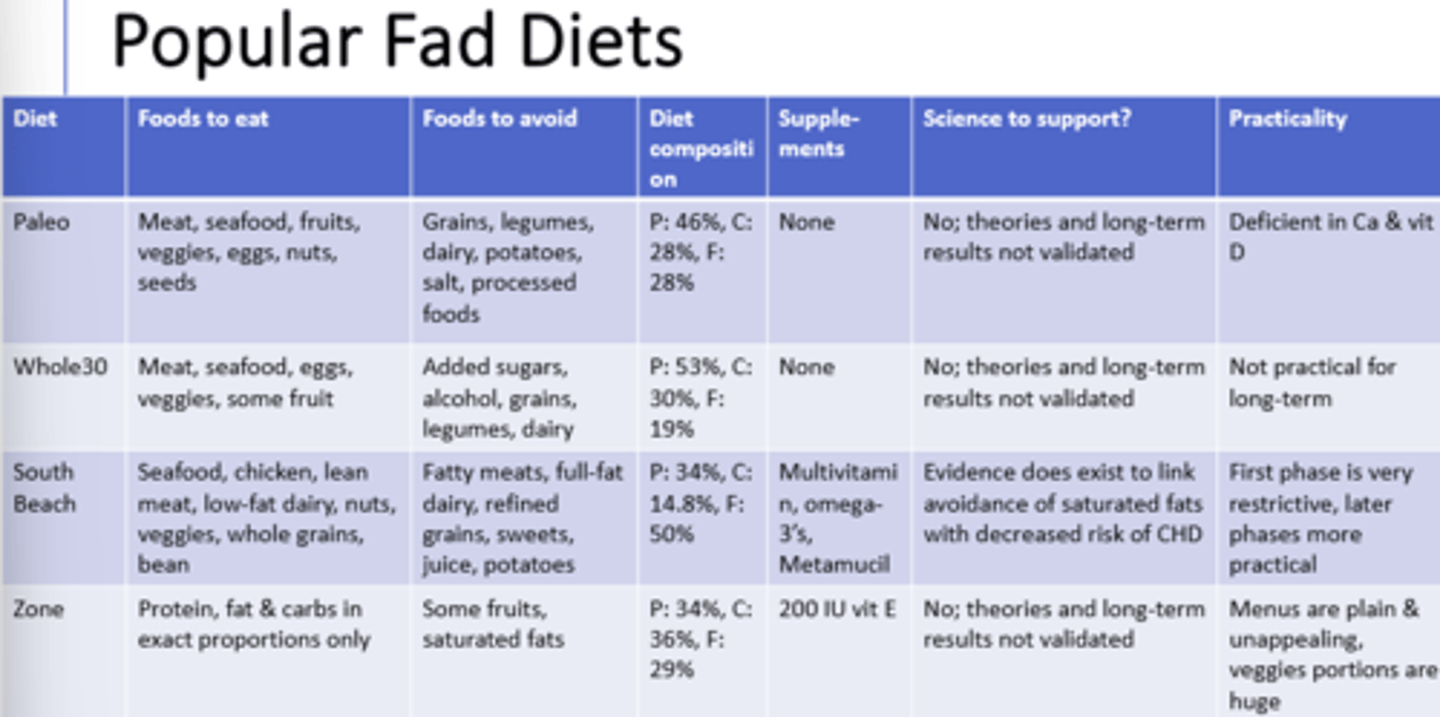
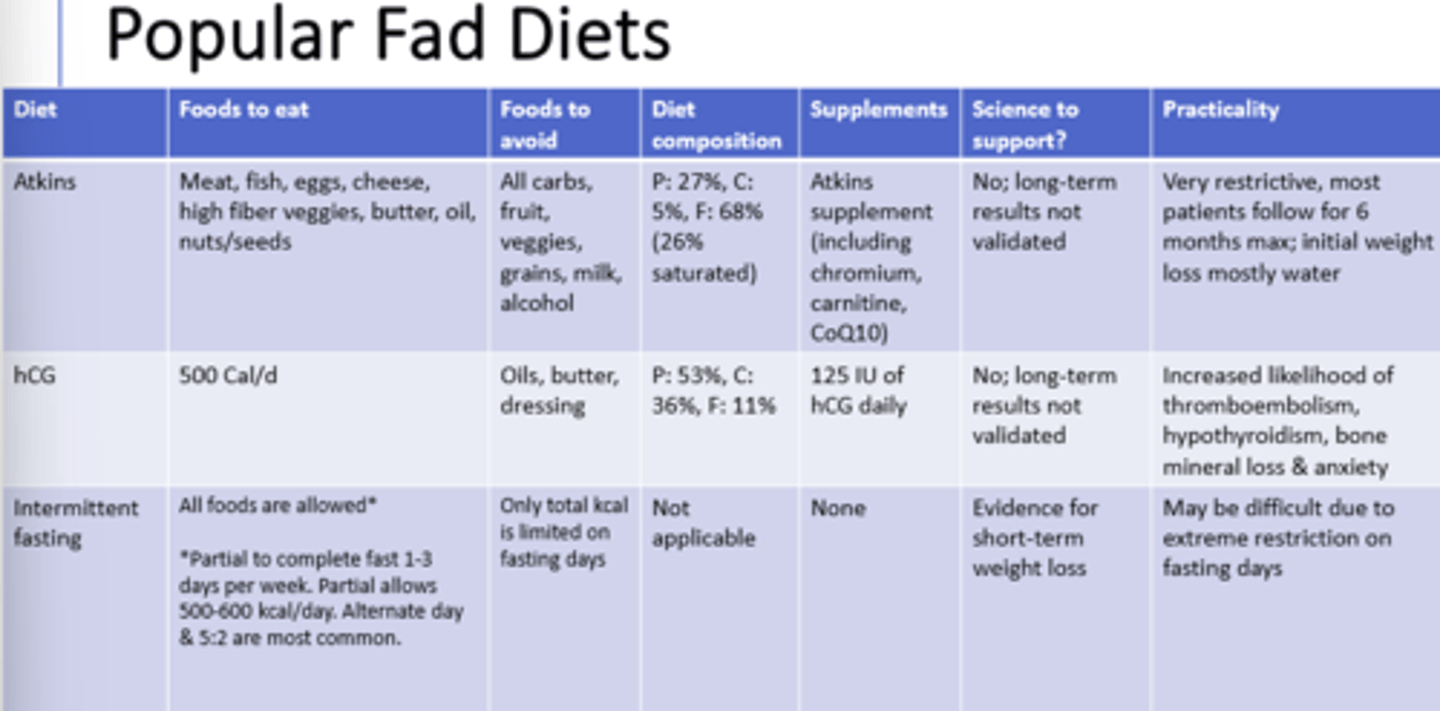
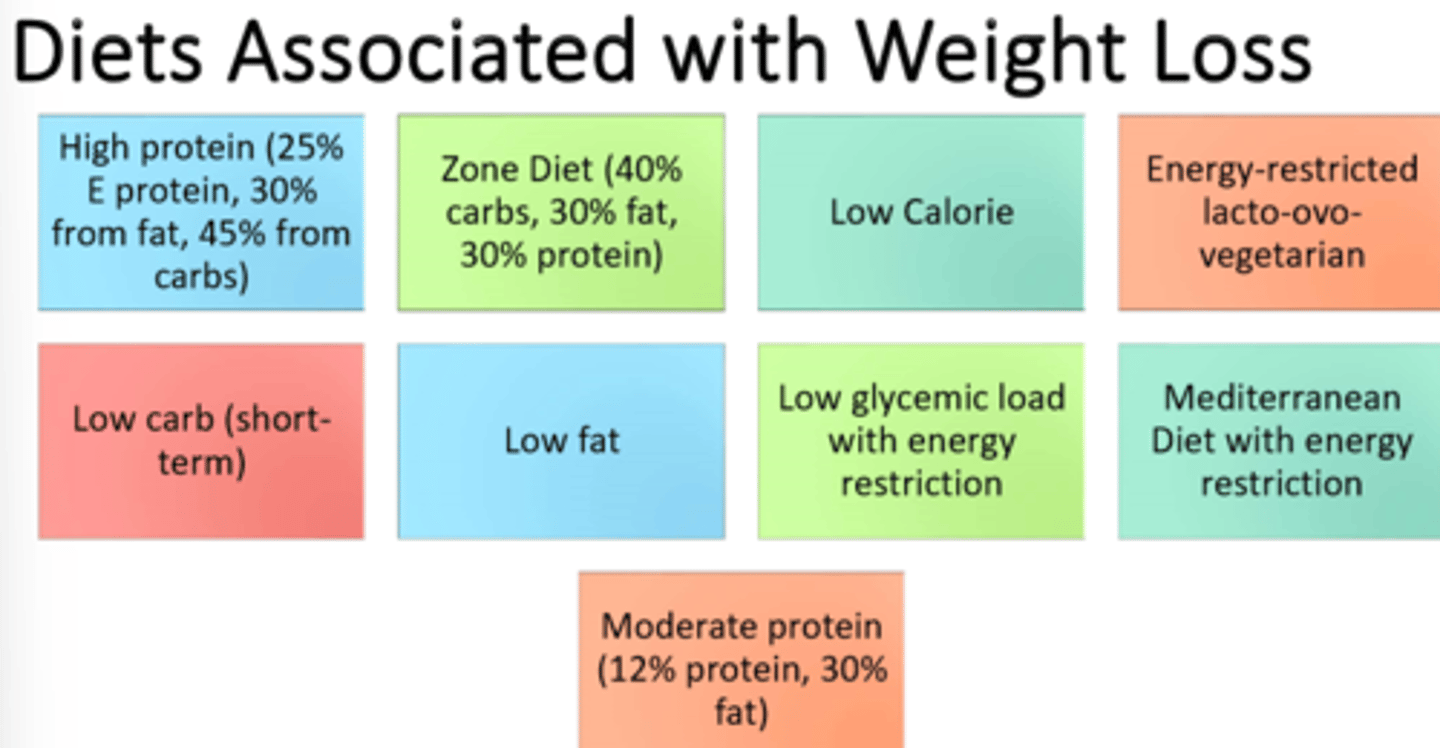

1) dietary modifications --swaps to decrease energy intake
2) changing food behavior --manage cues
3) activity --increase activity each week
What are three examples of sound weight management
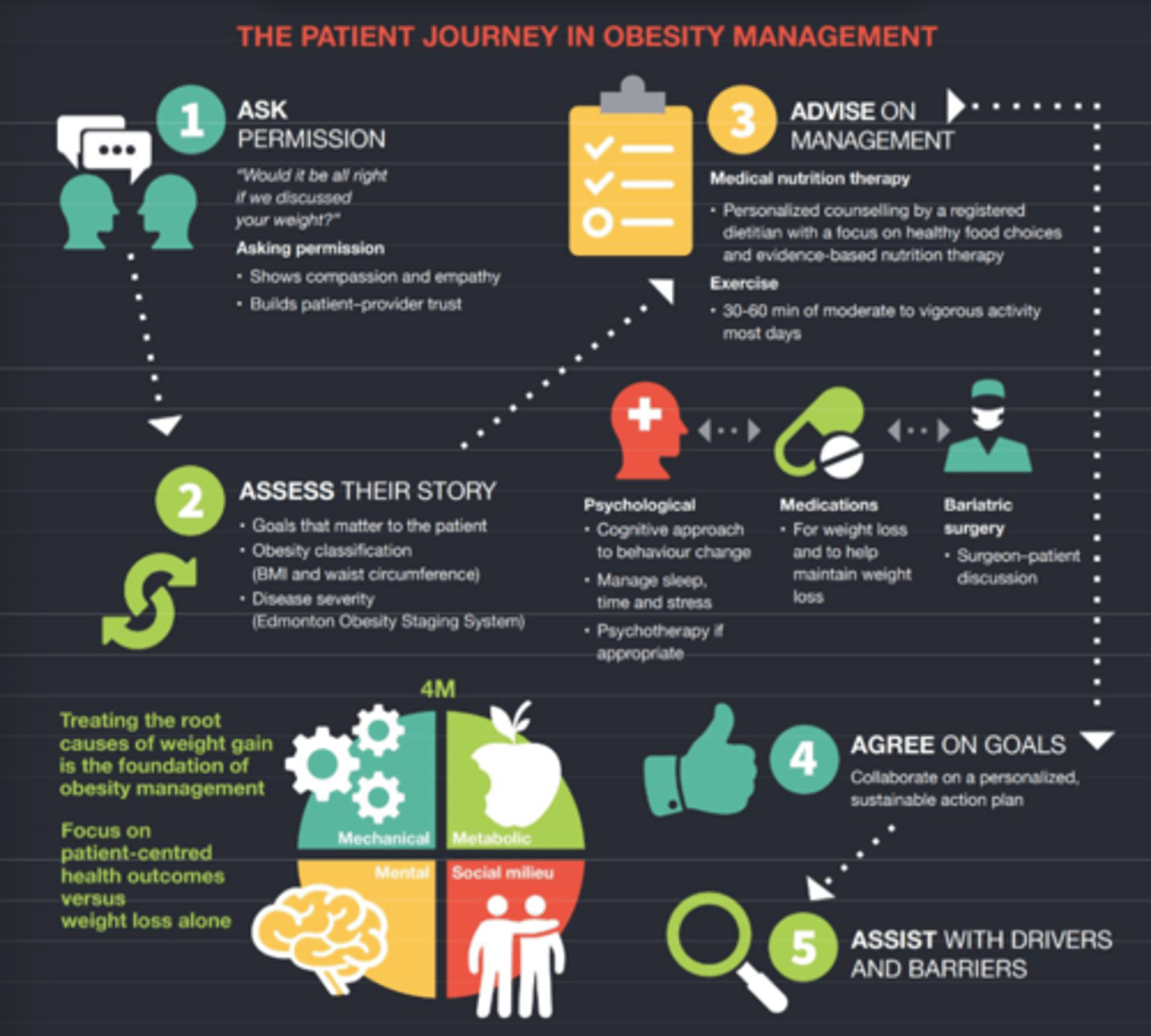
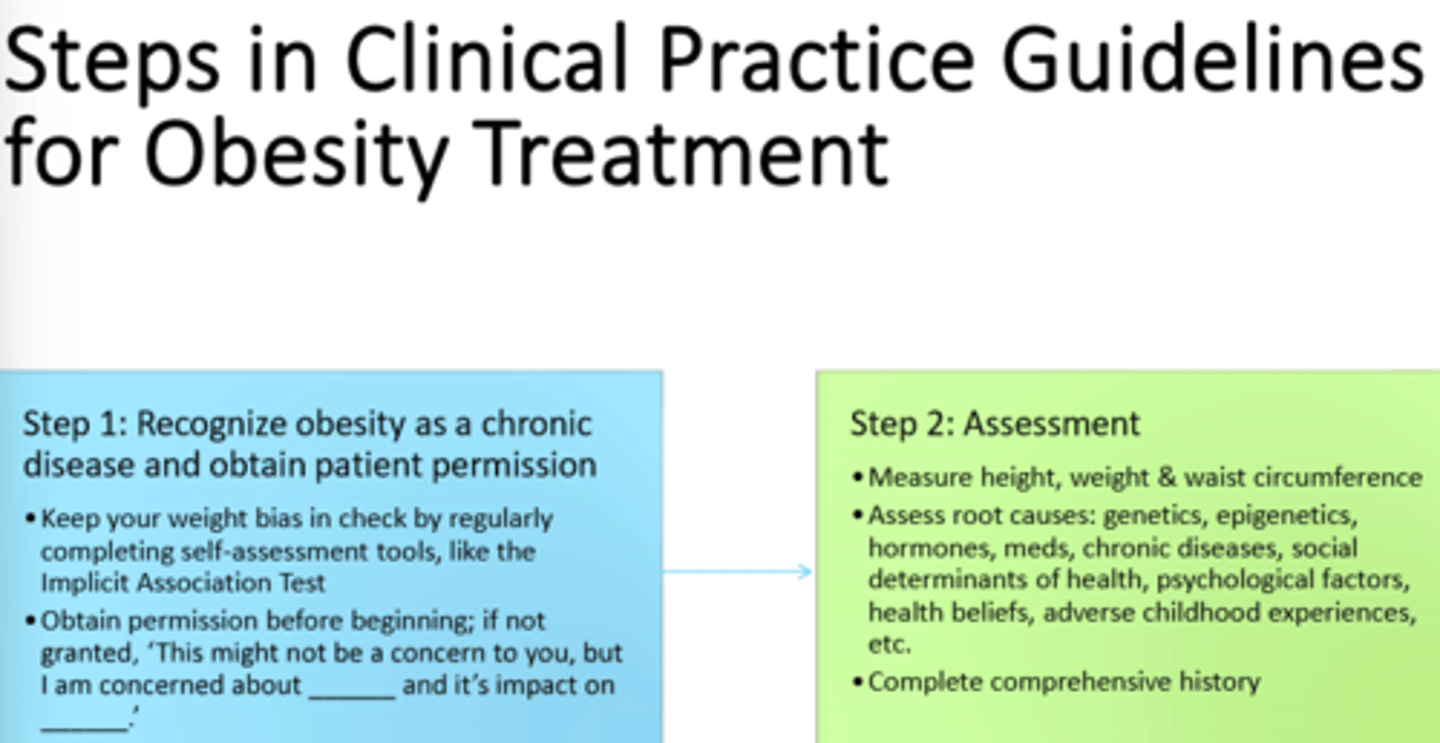


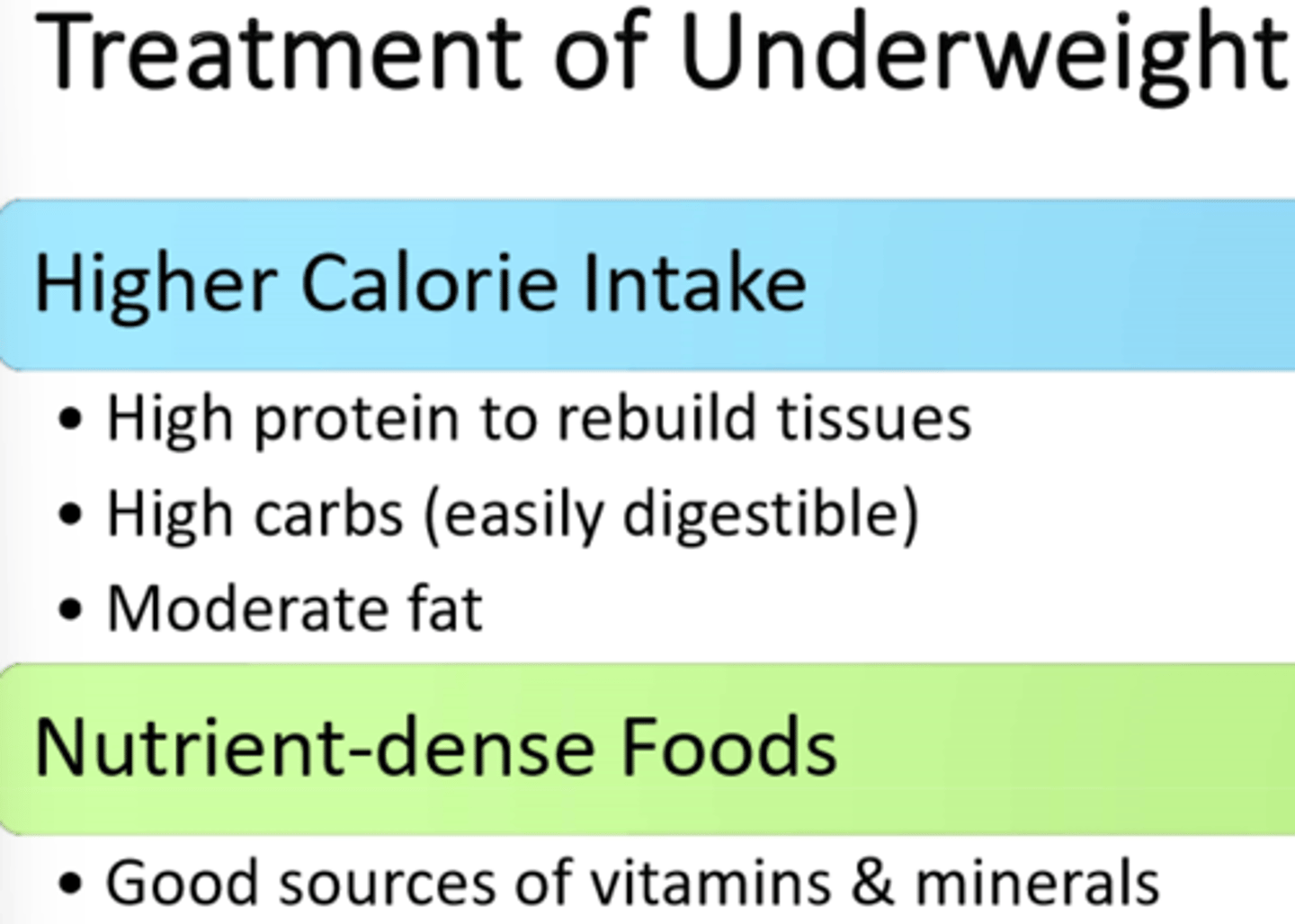
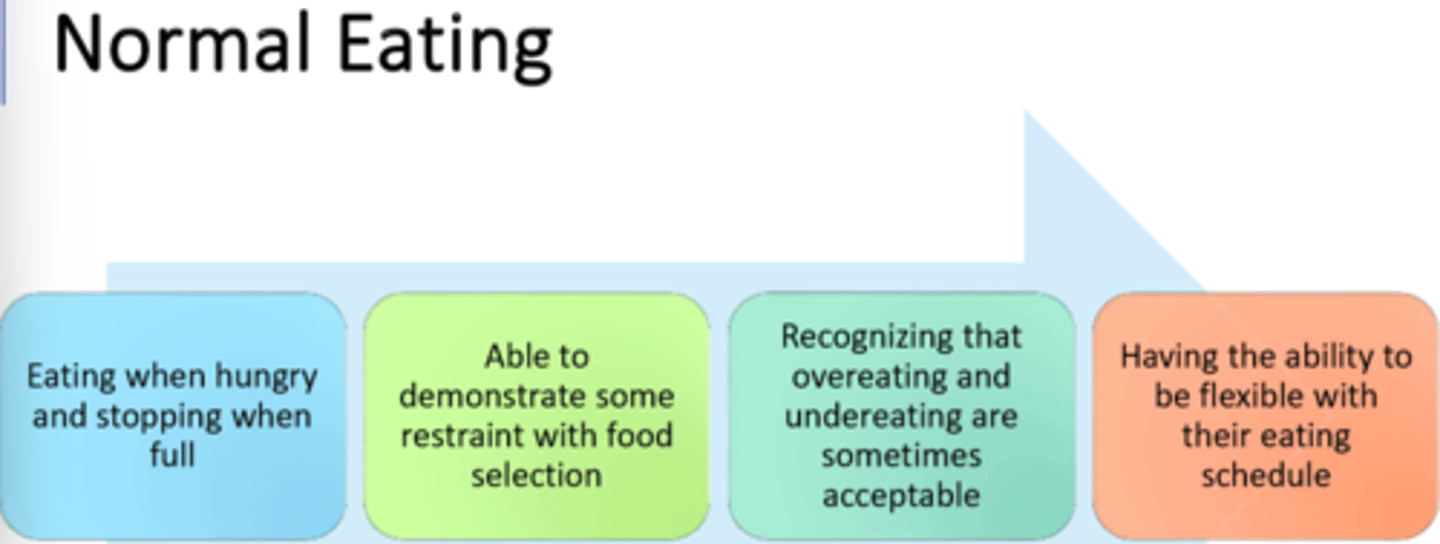

1) Sick
2) Control
3) One
4) Fat
5) Food
***SCOFF is an acronym for screening for eating disorders. What does it stand for?

women
Who is anorexia nervosa more common in

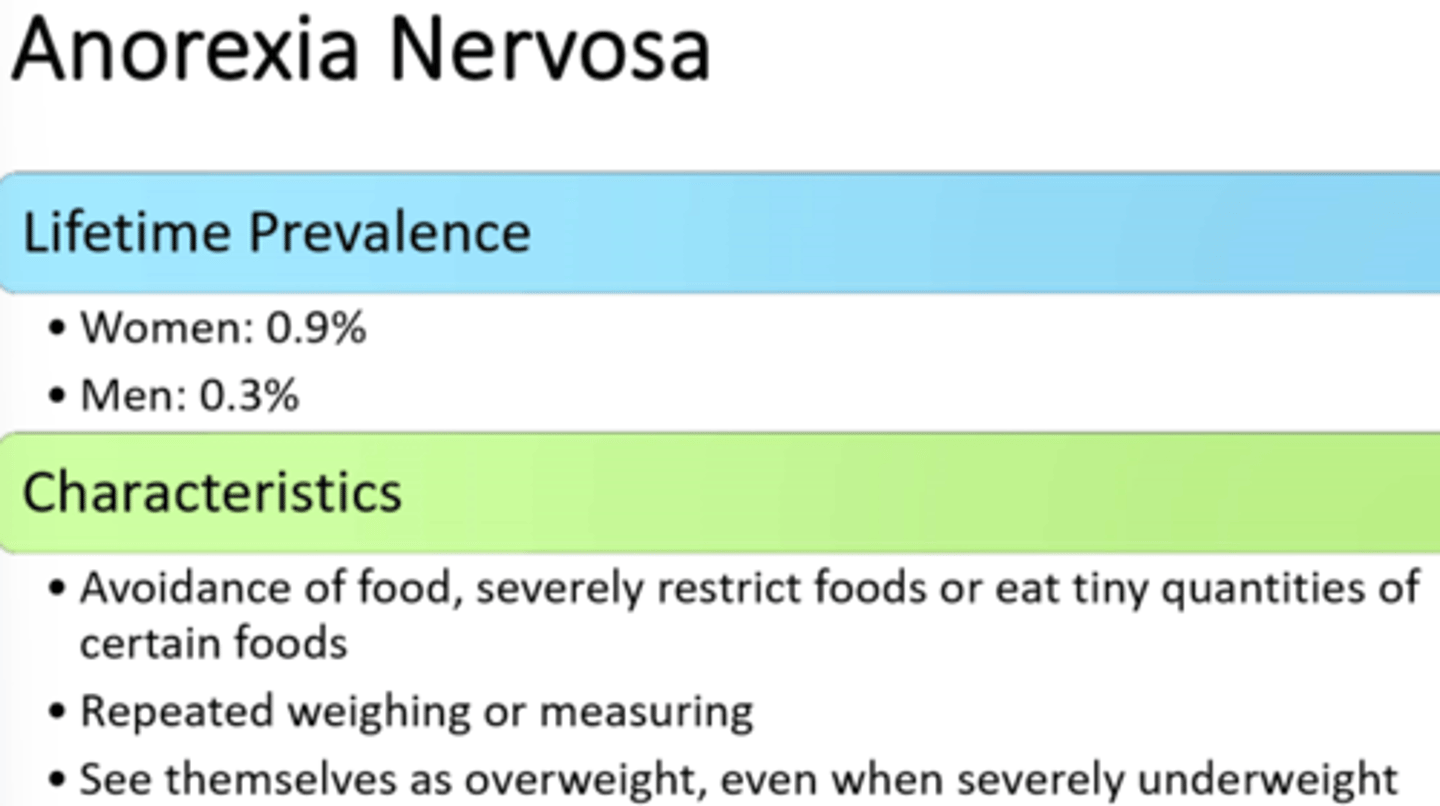

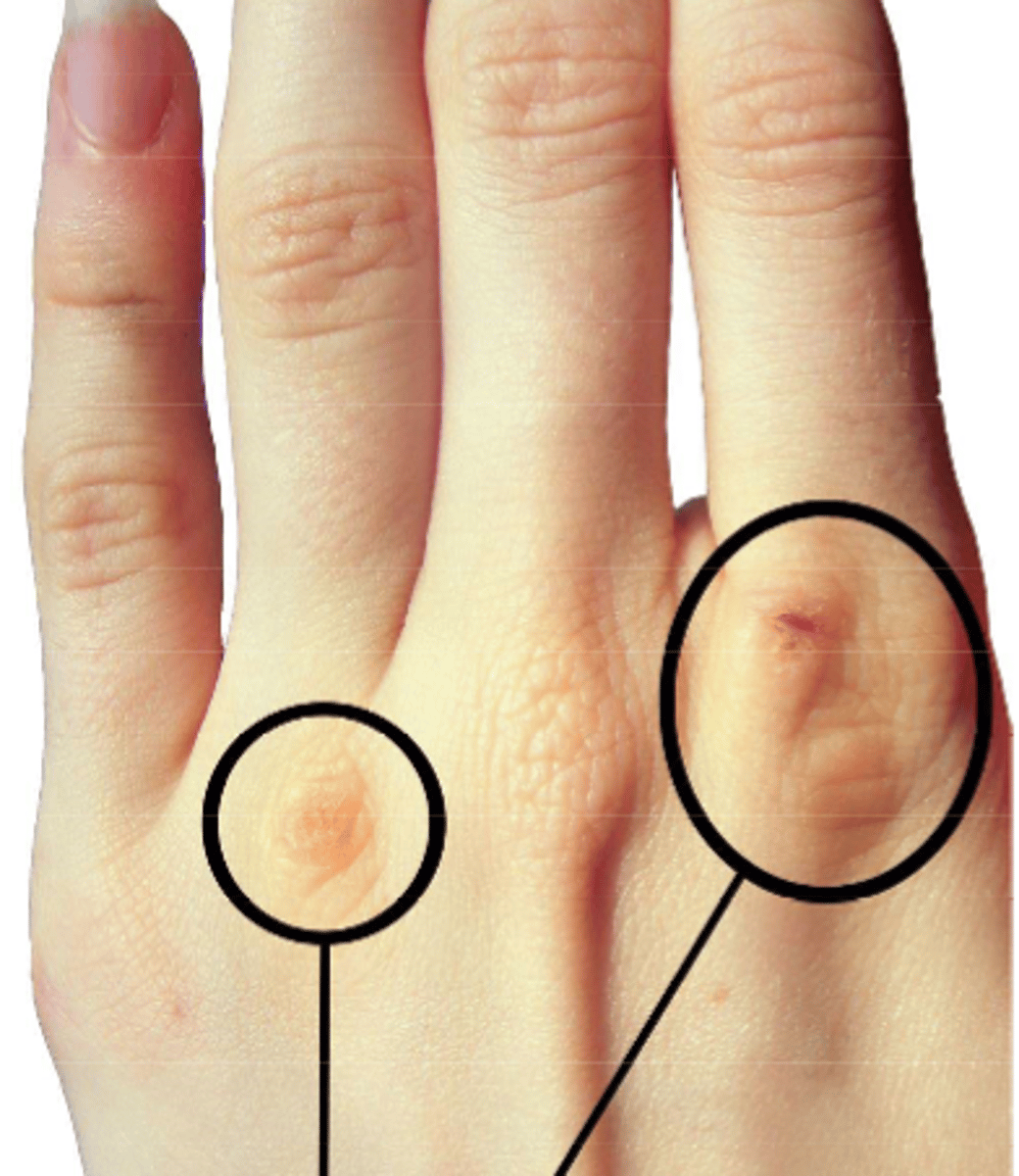
Russel's sign
this is associated with people who force themselves to throw up. What is this called?

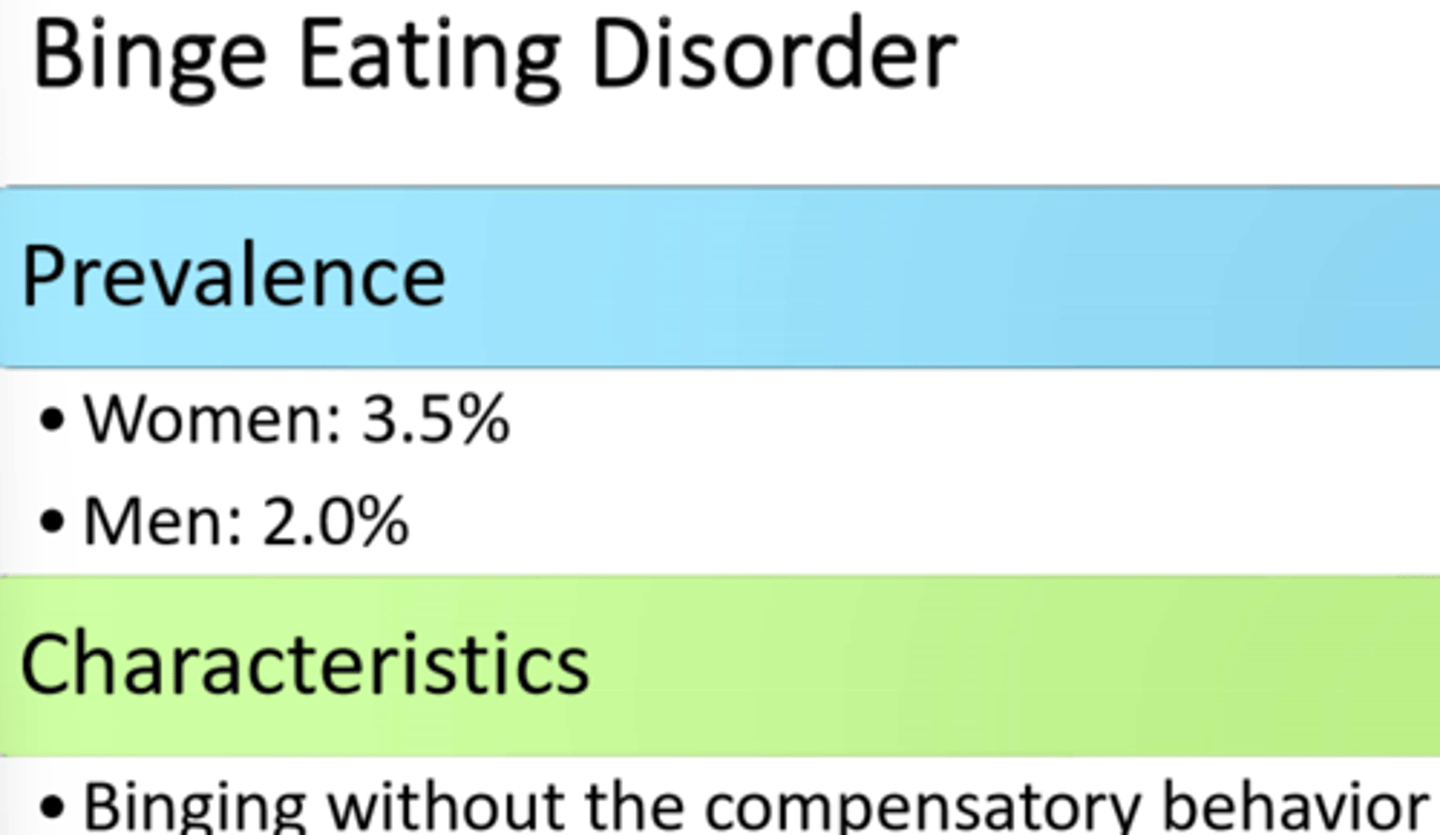
bookmark: binge eating disorder