Ch3 product design and process selection
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
product design
compaies decide on the unique characteristics and fetaures of their product
process selection
companies develop the process necessary to produce the designed product
what do product design and process selection affect
the product quality, cost, manufacturability and customer satisfaction
1) idea development
customers, competitors, suppliers
market research
benchmarking
reverse engineering
early supplier involvement
R&D
2) product screening
operation : study the impact on the resources needed
marketing : study the sales potential of the firm
finance : study the requirements and their return
break-even analysis
compute the amount of goods a company would need to sell to cover its fixed and variable costs
3) preliminary design and testing
technical specifications are developed
prototypes are built
prototypes are revised based on test results
4) final design
final specifications are translated into manufacturing instructions
design for manufcature (DFM)
guidelines to follow in order to produce a product easely and profitably
minimize parts
design parts for different products
use modular design
avoir tools
simplify operations
on what is design for manufacture based
→ simplification : limited number of parts and features
→ standardization : common and interchangeable parts
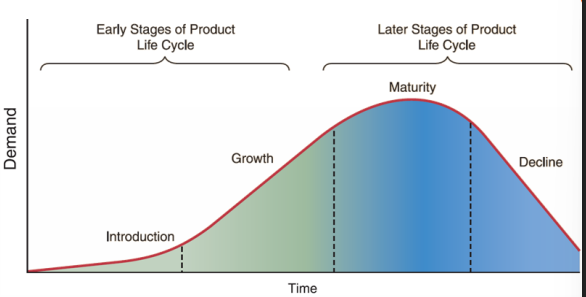
product life cycle
stages that products pass through in their lifetime, characterized by changing product demands over time
→ the expected lenght of the life cycle determines the profitability relative to initial invesments
concurrent engineering
simultaneously design of products and process in multifunctions teams, instead of traditional over the wall approach
more efficient
cheaper
faster
team aproach
remanufacturing
using components of old products in the production of new ones
envionmental benefits
costs benefits
types of processes :
intermittent operations
repetitive operations
types of processes : intermittent operations
→ variety of products in lower volumes
products have different processing requirements
products do not follow a stanard route through the facility
labor intensive (skilled workers)
volume directly tied to number of orders
project process and batch process
types of processes : repetitive operations
→ one or a few products in high volumes
products are standardized
resources are organized in a line flow
capital intensive (faclities, automation technology)
volume based on forecasts of demand
line porcesses
continuous processes
what does a process flowchart do
shows the sequence of steps from inputs to outputs
process flow chart analysis
how to imrpove the design of the process
examples of design consideration
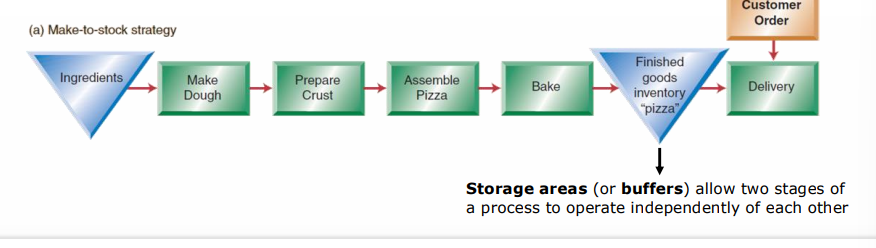
make to stock strategy
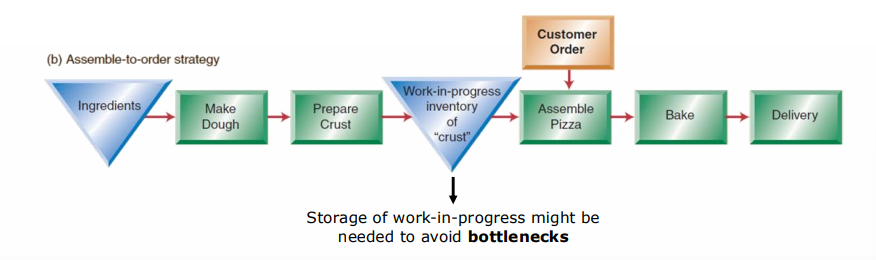
assemble to order startegy
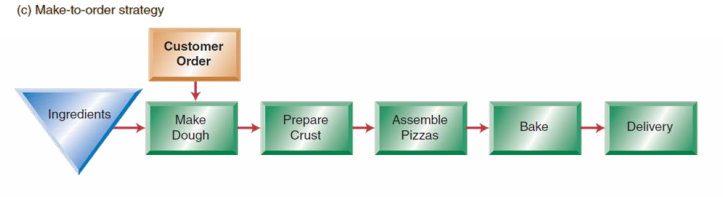
make to order strategy
make to stock strategy
standardized products for immediate sale
storage areas (or bufffers) allow two stages of process to operate independently of each other
assemble to order strategy
standard components which are combined to customer specifications
storage of work-in-progress might be needed to avoid bottelnecks
make to order strategy
products to custiomer specifications, produced after the order is received
process performance metrics : throughput time
average amount of time product takes to move through the system
process performance metrics : process velocity
= throughput time / value-added
a measure of wasted time in the system
process performance metrics : productivity
output / input
a measure of how well a company uses its resources
process performance metrics : utilization
= time a resource used / time a resource available
the proportion of time a resource is actually used
process performance metrics : efficiency
= actual output / standard output
measures performance relative to a standard
techology decisions
technological advancements enable the development of new processes and fatser, better and cheaper production
information technology
automation
E-manufcaturing
design
specifies what customers should experience
shoudl meet or exceed customer expectations
→ need for quality management to ensure consistency and reliability
design : service package / bundle
= tangible aspects + sensual benefits + psychological benefits
three approaches to differ service design
replacing people by technology :
reduces the uncertaintu of the service
cuts costs
gettting the customer involved
allows faster and cheaper service
control by the customer increases satisfaction
providing high customer attention
personal relationship with customers at higher cost