NUCL32O Exam 2 - Defects
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
(1/3)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What are 0D defects, what are the three main types, and what are the subtypes?
point defects:
vacancies
interstitials
self-interstitial
impurity interstitial
substitutional
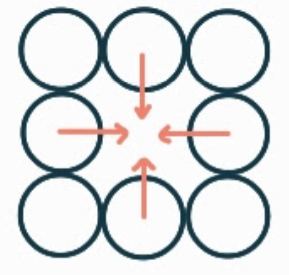
What is the name, dimension and definition of this defect?
vacancy, 0D, it is when an atom is missing where there should be one.
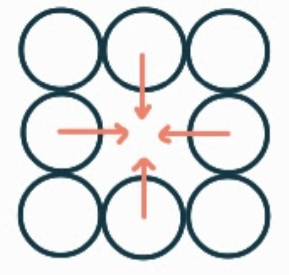
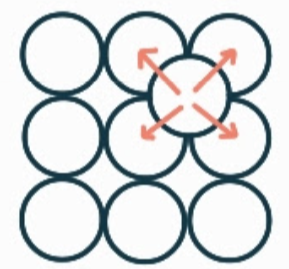
What is the name, dimension and definition of this defect?
self-interstitial, 0D, it is an extra of the correct type of atom where there should be none.
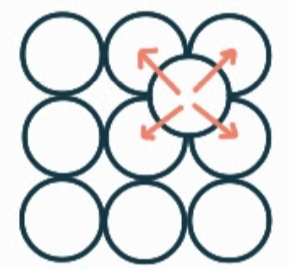
What is the name, dimension and definition of this defect?
interstitial impurity, 0D, it is an extra of a different type of atom where there should be none.
What is the name, dimension and definition of this defect?
substitutional impurity, 0D, a wrong type of an atom where there should be a different, correct atom type.
What are 1D defects and what are the three main types?
linear defects:
edge dislocation
screw dislocation
mixed dislocation
What is the name, dimension and definition of this defect?
edge dislocation, 1D, extra half-plane of atoms inserted in a crystal structure
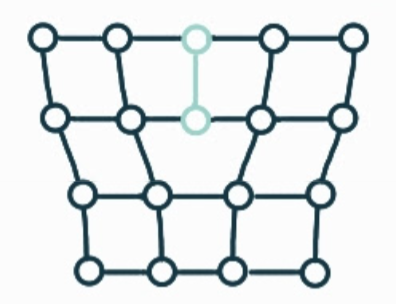
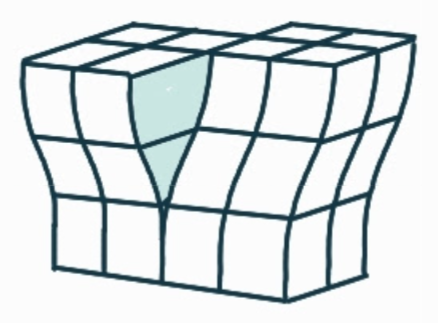
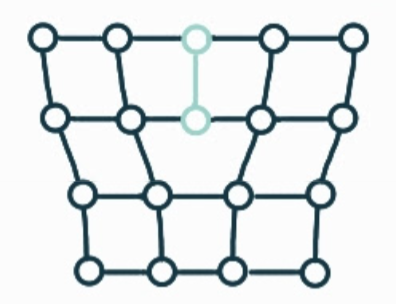
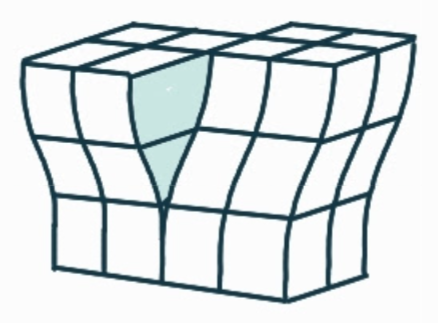
What is the name, dimension and definition of this defect?
screw dislocation, 1D, spiral planar ramp resulting from shear deformation
What is the name, dimension and definition of this defect?
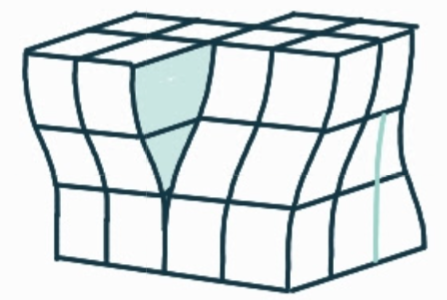
mixed dislocation, 1D, a combination of edge and screw dislocations in the same region; the effects of both overlap creating a region for which the burgers vector is neither parallel or perpendicular to the direction of the burgers circuit
What are 2D defects and what are the two main types?
planar (interfacial) defects:
grain boundaries
surfaces

What is the name, dimension and definition of this defect?
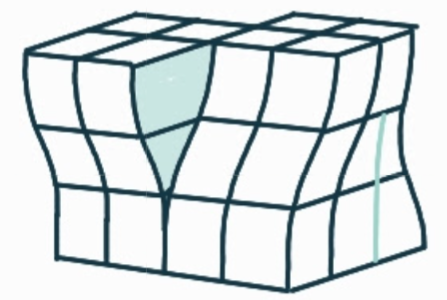
grain boundaries, 2D, the interface between two different types of grain, or the same grain but in different grain directions

What is the name, dimension and definition of this defect?
surfaces, 2D, an open surface defined by having spaces of free surface bonds
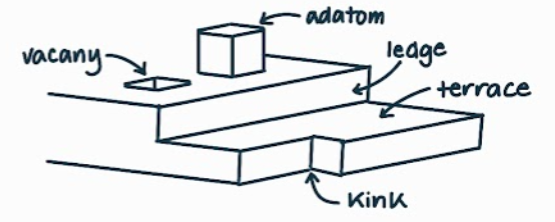
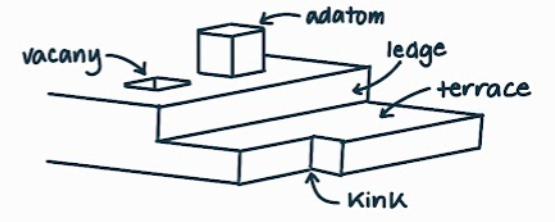
What are the different features a surface defect can have? What are their definitions?
step - like a stair step
terrace - the horizontal surface created by a step
vacancy - like a hole taken out of a flat surface
kink - where a ledge goes in or out, not straight
ledge - the vertical surface created by a step
adatom - the opposite of a vacancy coming out of a flat surface
What are 3D defects and what are some of the types?
pores
cracks
foreign inclusions
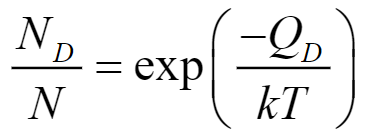
What is this equation and its variables?
ND - number of defects
N - number of lattice cites
QD - activation energy (energy required to create defect) [J, eV]
k - 1.38×10-23 J/atomK or 8.62×10-5 eV/atomK
T - temperature [K]
![<p>ND - number of defects</p><p>N - number of lattice cites</p><p>QD - activation energy (energy required to create defect) [J, eV]</p><p>k - 1.38×10<sup>-23</sup> J/atomK or 8.62×10<sup>-5</sup> eV/atomK</p><p>T - temperature [K]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9b0a4614-3587-4c1e-9d75-8762af57c9f7.png)
What is the definition of impurity?
atoms that are that are different from the host
True or false, solids can be 100% pure?
False, it can only be 99.9999%
Are impurities intentional, unintentional, or both?
both
What is the definition of an alloy?
a deliberate mixture of metals
What is the definition of a solid solution?
a host (a solvent or matrix) which dissolves the minor component (solute), it is homogenous, maintains crystal structure, and contains randomly dispersed impurities
What is the definition of solubility?
the ability to dissolve
What is the definition of a solvent in an alloy?
the element or compound present in a greater amount
What is the definition of a solute in an alloy?
the element or compound present in a lesser amount
What is the definition of the second phase of a solid solution?
when if as atoms of solute are added, precipitates form
What are the factors for high solubility?
atomic size factor - to form a solute the atomic sizes need to be within ~15%
crystal structure - to form a solute their crystal structures need to be the same
electronegativity - to form a solute their electronegativities need to be comparable
valency - a solution can handle more solute when the solute valency is higher than the solvent valency
What is the equation for weight percent?
Cwt - weight percentage
m1 - mass 1
m2 - mass 2
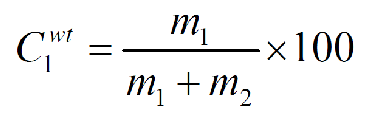
What is the equation for atom percent?
Cat - atom percentage
nm1 - moles of m1
nm2 - moles of m2
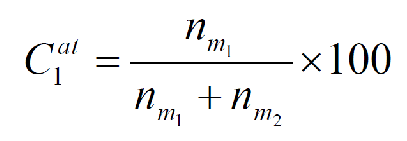
What is the equation from atom percent to weight percent?
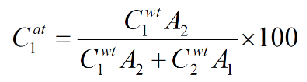
What is the equation from weight percent to atom percent?
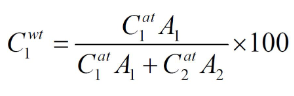
What makes a grain boundary high or low angled?
the angle between the directions of two different grains bounding each other
How do grain boundaries impact dislocations?
Grain boundaries can stop dislocations from being able to move. The higher the angle the harder it is for the dislocation to continue due to the misorientation between grains.
What is the definition of a tilt boundary?
when the grains of two regions don’t mirror each other perfectly as they meet
What is the definition of a twin boundary?
when the grains of two regions mirror each other perfectly as they meet
What is the definition of a slip plane?
The highest packed plane for a structure, through which it is therefore easiest for dislocations to move.