stress and coping: types, causes, effects and practicak strategies
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Define stress?
It is the body’s response to a perceived challenge or threat
Define Folkman and Lazarus’s (1984) cumulative nature to stress.
Minor stresses (i.e. moving houses, changing jobs) —> can add up to major stresses (i.e. death of loved ones or divorce).
How is stress influenced by individual cognitive processes i.e. how is it subjective?
going on a date for some people may be exciting whereas it may be terrifying for others
Appraisals are subjective and influence the effect of the event
What are the three parts of stress that help define it?
Stressor (i.e. the stimulus)
Stress Response (physiological and psychological)
Coping
What is the “Stress as a Stimulus” Model?
It views stress as an external event or change, such as losing a job or getting married, which may cause stress regardless of its desirability (Holmes & Rahe, 1967).
What is Life Change Units (LCUs)?
A measure used to quantify the impact of major life events, regardless of whether the event is possible (stress) or negative (distress).
What are the daily hassles and uplifts?
Daily Hassles - minor stressors (e.g. deadlines)
Uplifts - positive events (e.g. good conversations) that can counterbalance stress (Kanner et al., 1987).
What do different LCU scores indicate about illness risk?
11-150: Low to moderate risk
150-299: moderate to high risk
300-600: high to very high risk
What is the ‘stress as a transaction’ model?
it sees stress as a result of interactions between the person and their environment, including personal characteristics , resources and appraisals.
Transactional Model of stress
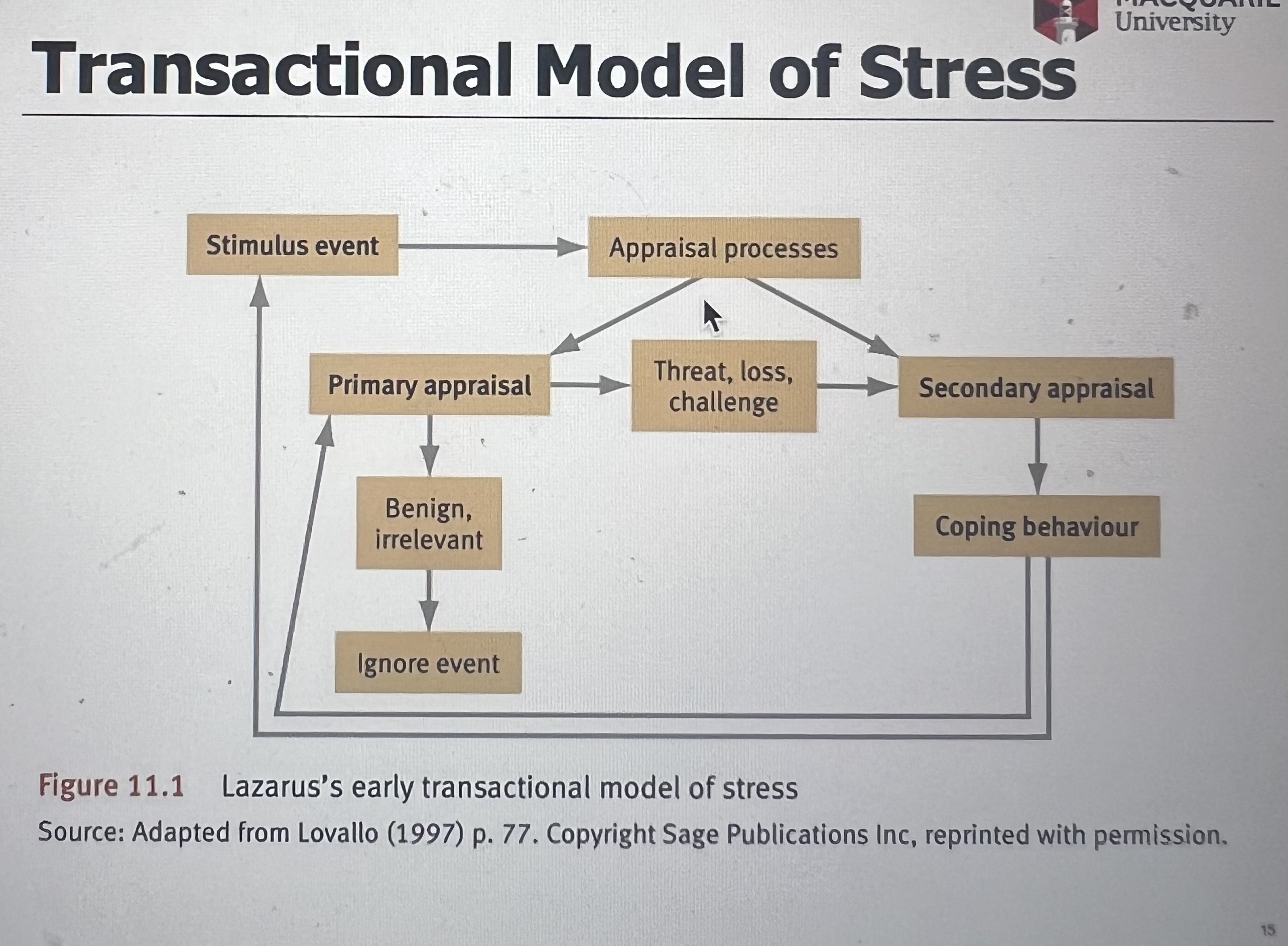
What is primary appraisal in the Transactional Model of Stress?
it is the evaluation of the significance of a stressor as a threat, a challenge, or benign.
What is a secondary appraisal in the Transactional Model of stress?
it involves evaluating one’s internal (e.g. determination) and external (e.g. social support) resources to cope with the stressor.
Give an example of perceived threat with no perceived resources.
“There is no way I can possibly deal with this — I simply know I will fail”
Give an example of a perceived challenge with possible internal resources
“Maybe I can manage this if I revise really hard.”
Give an example of benign appraisal.
“This isn’t a problem — I know the material really well.”
What are the three types of stress?
Acute stress - short-term response to immediate threat (e.g. sudden fright)
Intermittent stress - varies in duration (e.g. being at university)
Chronic Stress - Long-term, often from modern life (e.g. financial issues)
Which type of stress is linked to the fight-flight-freeze-fawn response?
Acute stress
Which type of stress is common in modern life and has negative health effects?
Chronic Stress
Which type of stress is associated with ‘physiological toughening’
Intermittent stress
Yerkes Dodson Law (1908)- what does it suggest about the relationship between arousal and performance?
Performance improves with increased arousal up to an optimal point, beyond that, excessive arousal can impair performance.

What factors can increase an individual’s appraisal of an event as stressful?
Events perceived as risky, imminent, unexpected, unpredictable, ambiguous, undesirable, life-changing, or those with low perceived control.
How are emotional responses linked to stress appraisals?
Negative appraisals can lead to emotions like guilt or sadness, while positive emotions during stress can promote adaptability and problem-solving.
What are the four primary physiological responses to acute stress?
fight, flight, freeze and fawn - automatic reactions to perceived threats.
What are the stages of Hand Selye’s General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS)?
Alarm: immediate reaction to stress
Resistance: adaption to ongoing stress
Exhaustion: Depletion of resources leading to decreased stress tolerance
What behavioural responses might individuals exhibit when coping with stress?
responses can include;
learned helplessness
Aggression
Indulgence in substances
Use of defense mechanisms
Constructive coping strategies
What is learned helplessness in the context of stress?
A condition where individuals feel unable to control or change a stressful situation, leading to passive behaviour and potential depression.
How do primary and secondary appraisals differ in stress evaluation?
primary appraisal assesses the significance of the stressor (threat, challenge, or benign), while secondary appraisal evaluates coping resources and options
What is the ‘Fawn’ response in stress reactions?
a stress response where an individual attempts to appease or please the threat to avoid conflict or harm.
Why can positive emotions during stress be beneficial?
they can enhance creativity, flexibility in problem-solving, and reduce adverse physiological effects of stress.
Which personality traits are associated with an increased risk of coronary Heart disease (CHD)?
Traits:
competitiveness
Time urgency
Anger and hostility
Characteristics of the TYPE A personality
How does stress impact the immune system?
Stress hormones like corticosteroids can be exacerbated by stress
What psychosomatic conditions can be exacerbated by stress?
Stress can worsen conditions such as hypertension, asthma, eczema and migraine headaches
What is “choking under pressure”, and how is it related to stress?
it refers to performance decline due to stress-induced self-consciousness and disrupted attention, often occurring in high-stakes situations.
What psychological effects can result from chronic stress?
mood disorders
Anxiety
Substance addiction
Cognitive impairments - impacts on CNS
How does stress influence cancer progression?
promotes tumour development and metastasis by affecting immune response and increasing glucocorticoid levels
What is the relationship between stress and bowel diseases?
can exacerbate symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and may influence inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) although the exact mechanisms differ.
What are compassion fatigue and burnout, and what are their effects?
compassion fatigue is emotional exhaustion from caring for others = burnout; decreased concentration L, isolation and impaired immune function.
How can stress contribute to depression?
Prolonged burnout from unmanaged stress ca lead to depression w/ variations observed across different genders and occupations.
Can stress have positive effects?
yes, stress can:
promote personal growth
Enhance coping abilities
Increase self-efficacy
What are the 5 forms of social support that help buffer stress?
emotional
Belongingness
Informational
Esteem/relational
Networking support
How does optimism? Influence stress management?
optimism is linked to better psychological and physical wellbeing and promotes adaptive coping strategies
What role does conscientiousness play in stress resilience?
associated with an internal locus of control and high self-efficacy = better health habits that protect against stress
How does age affect coping strategies for stress?
as people age —> use more effective coping mechanisms: emotion-focused coping for uncontrollable stressors, and report fewer stressors due to proactive problem prevention.
What is gender minority stress model?
It’s a framework explaining that transgender and gender non-conforming individuals face unique stressors like discrimination and safety concerns, and often use strategic avoidance and seek in-group support to manage stress
What is emotion-focused coping?
A strategy aimed at relieving the emotional impact of stress without changing the stressor itself; e.g. via relaxation or reframing thoughts
What is problem-focus coping?
A strategy involving efforts to change the source of stress, like seeking information, planning and taking direct action.
What are some CBT techniques for stress management?
cognitive restructuring
Relaxation training
Time management
Problem-solving skills
Behavioural activation
Developing coping strategies
How does humour contribute to stress management?
a good sense of humour can buffer the effects of stress and promote wellness by providing perspective and emotional relief.
Why is understanding stress important in professional settings?
it helps identify at-risk individuals
Understand the manifestation of stress differences
Promotes healthy coping mechanisms to prevent issues like compassion fatigue and burnout