Geometry
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What are vectors in R^n, common norms/distances, and what is the scalar product used for?
A vector is just a point/arrow in
R^n, written as coordinates:
x = (x1, x2, ..., xn)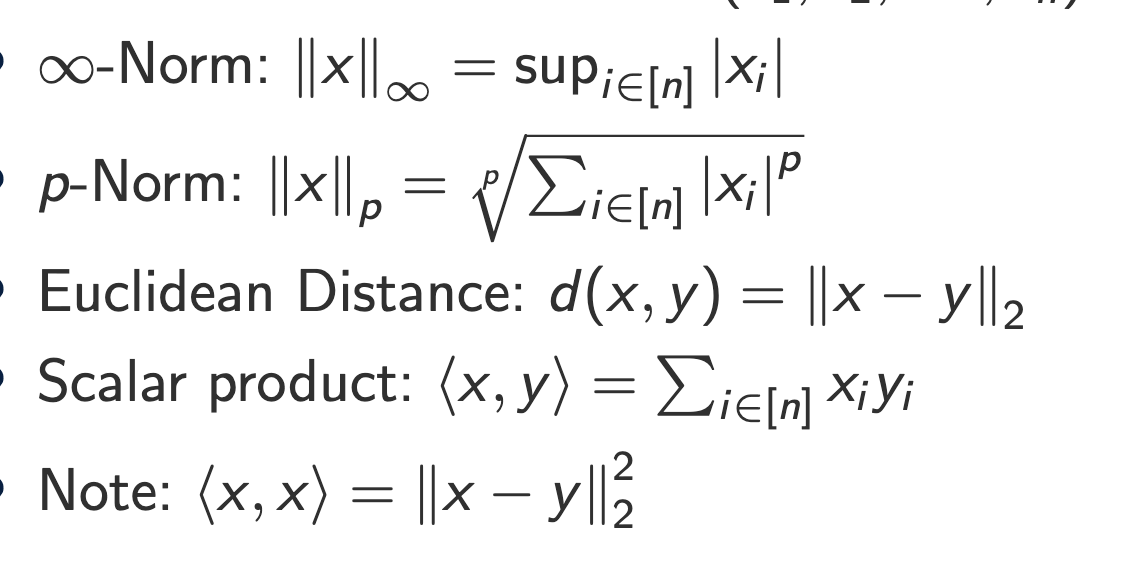
Infinity norm (max absolute coordinate):
Example: x=(2,-5,1) ⇒ ||x||∞ = 5.
p-norm (general norm)
Example with p=2: x=(3,4) ⇒ ||x||2 = sqrt(3^2+4^2)=5.
Euclidean distance between two points
x,y:
d(x,y) = ||x-y||2Example: x=(1,2), y=(4,6) ⇒ x-y=(-3,-4) ⇒ distance =5
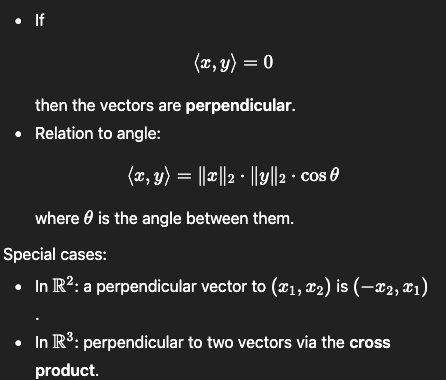
How do you test perpendicularity and how can you construct perpendicular vectors in R^2 and R^3?
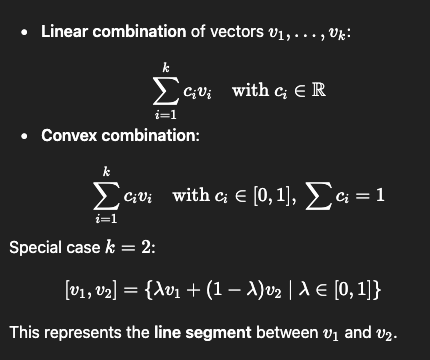
What are linear and convex combinations?

What does the determinant tell us geometrically?

When do two vectors lie on the same line through the origin?
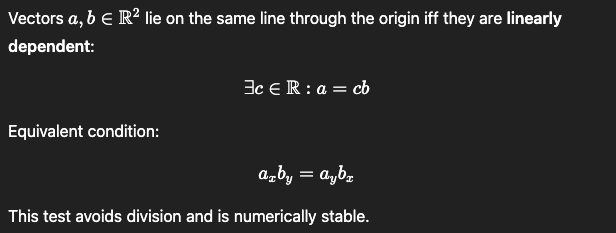
first Vectorx * second Vectory = first Vectory * second Vectorx
How do you test whether a point lies on a given line?
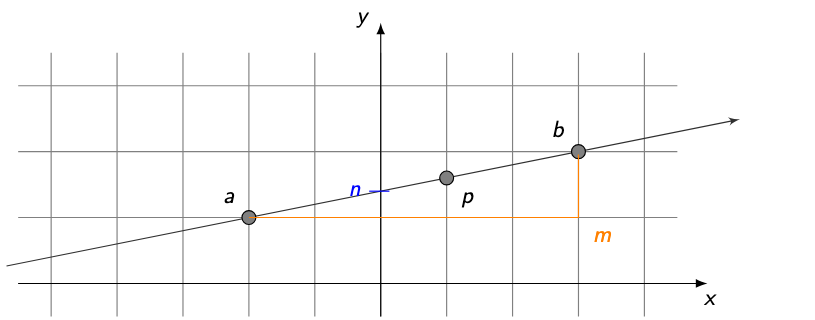
A point p lies on the line through a and b if vectors:
p − a and b − a
are linearly dependent. (first Vectorx * second Vectory = first Vectory * second Vectorx)
In 2D, the condition is:
(px − ax)(by − ay) = (py − ay)(bx − ax)
Interpretation:
Both vectors point in the same direction →
pis on the line
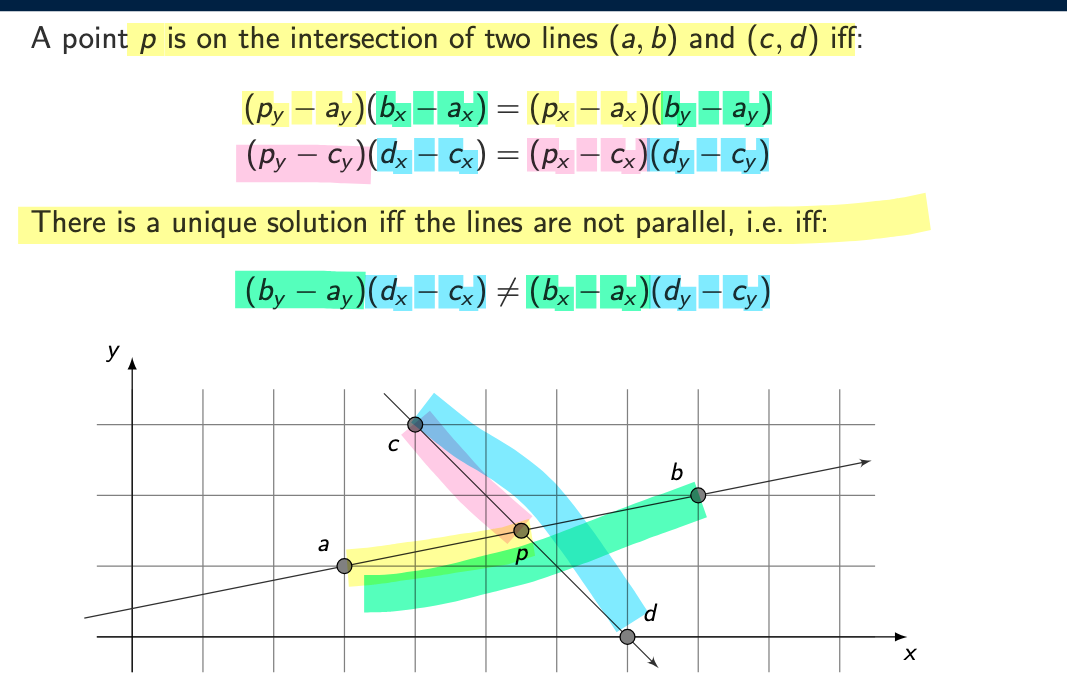
When do two lines intersect, and when is the intersection unique?
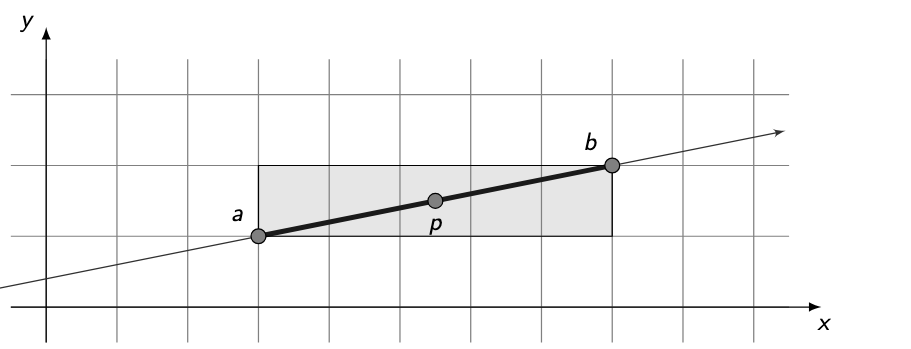
How do you check if a point is on a line segment?
Two steps:
Check if the point is on the infinite line
Check if it lies between the endpoints
Condition:
px is between ax and bx
py is between ay and by
Both x and y must be within bounds.
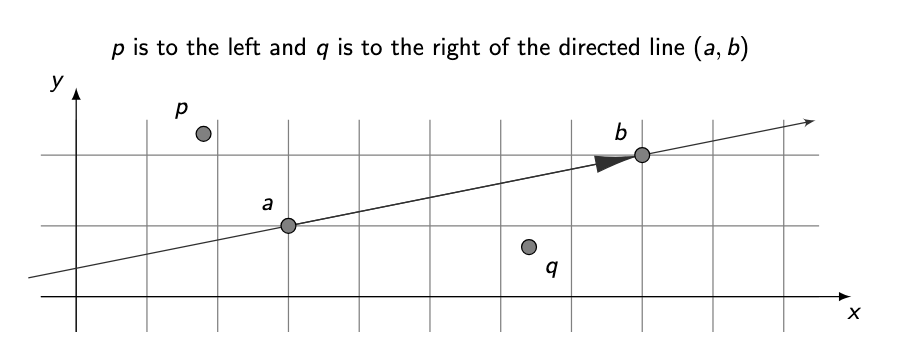
How do we decide if a point is left, right, or on a directed line?
We use the counter-clockwise (CCW) function:
CCW(a, b, p) = (py − ay)(bx − ax) − (px − ax)(by − ay)
Interpretation:
CCW = 0→ point is on the lineCCW > 0→ point is left of the lineCCW < 0→ point is right of the line
det(CCW) / 2 = area of triangle (a, b, p)
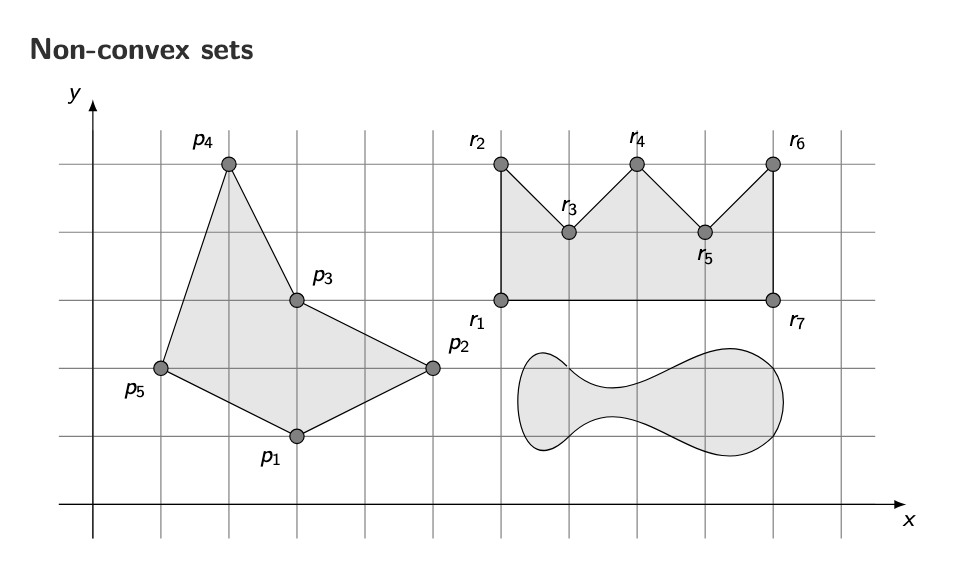
What is a polygon, and what does “simple polygon” mean?
A polygon is a closed shape made of straight line segments.
A polygon is simple if:
Edges do not intersect somewhere in the middle,( except at shared endpoints.)
What is the point-in-polygon problem?
Given a polygon and a point
q, isqinside or outside the polygon?
This is a very common geometry problem, for example in graphics and collision detection.
We solve it using the ray casting algorithm.
Idea:
From point
q, cast a ray (half-line) in any directionCount how many times the ray intersects polygon edges
Decision rule:
Odd number of intersections → point is inside
Even number of intersections → point is outside
Why it works:
Every time we cross the boundary, we switch between inside and outside
Important:
Direction does not matter, as long as it doesn’t go exactly through vertices
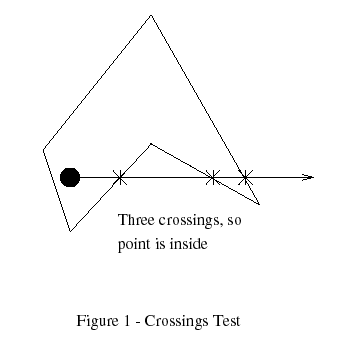
What special cases must be handled in the ray casting algorithm?
wo important issues:
Ray hits a vertex
Hard to define if it counts as 1 or 2 intersections
Simple solution: change ray direction
Floating-point precision
Point may be very close to an edge
Use tolerances (
epsilon) in comparisons
How can we compute the area of a polygon?
We compute the area by splitting the polygon into triangles.
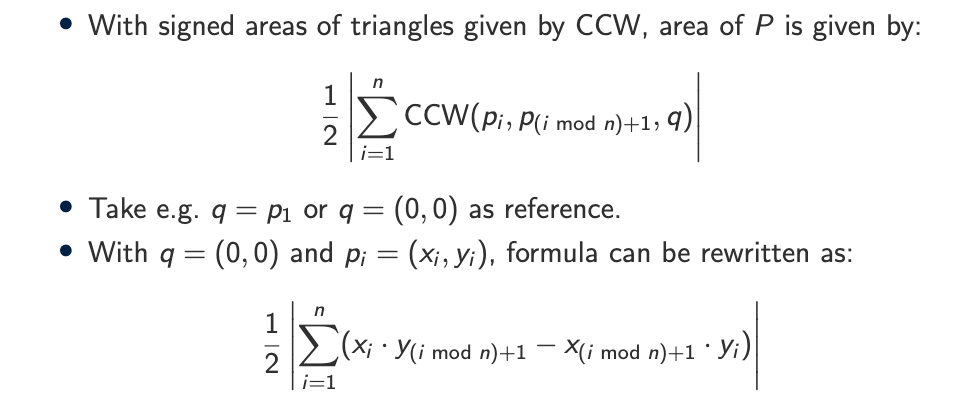
Key facts:
Works only if vertices are in order
If order is counter-clockwise, area is positive
If clockwise, area is negative (signed area)
What is the center of mass in geometry? What is the center of mass of a triangle or polygon?
The center of mass (COM) is the average position of all points in a shape.
Intuition:
If the object were made of uniform material,
the center of mass is where it would balance perfectly.
For geometry problems, we compute it using averaging or area-weighted formulas.
For a finite set of points:
COM = (sum of all points) / (number of points)
For a shape with area:
COM = (integral of x over the shape) / (area of the shape)
If a shape is split into parts:
COM = weighted average of the parts’ COMs
Weight = area of each part.
For a triangle with vertices
a, b, c:
COM = (a + b + c) / 3
For a simple polygon:
Uses a formula based on the shoelace terms
Requires vertices in counter-clockwise order
Depends on the polygon’s area
For oral exams:
👉 Say that polygon COM is computed by area-weighted averaging of edges.
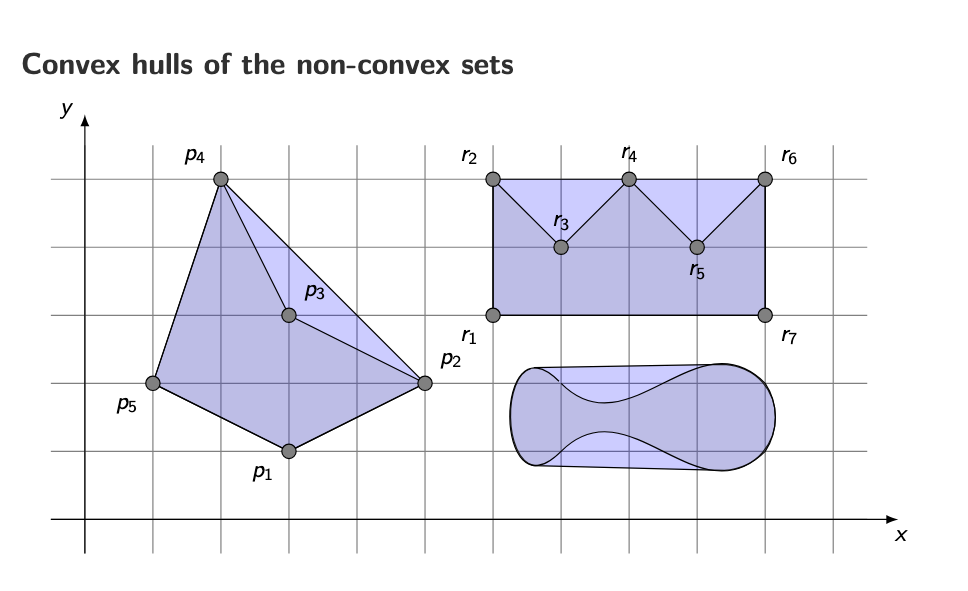
What does it mean for a set to be convex? What is the convex hull of a set of points? When is a polygon convex?
A set is convex if:
For any two points in the set,
the entire line segment between them is also inside the set.
Formally:
x, y ∈ P ⇒ [x, y] ⊆ PThe convex hull is:
The smallest convex set that contains all points.
Intuition:
Imagine stretching a rubber band around the points
When released, it forms the convex hull
Important facts:
The convex hull of points is a polygon
Only outer points become hull vertices
Inner points are ignored
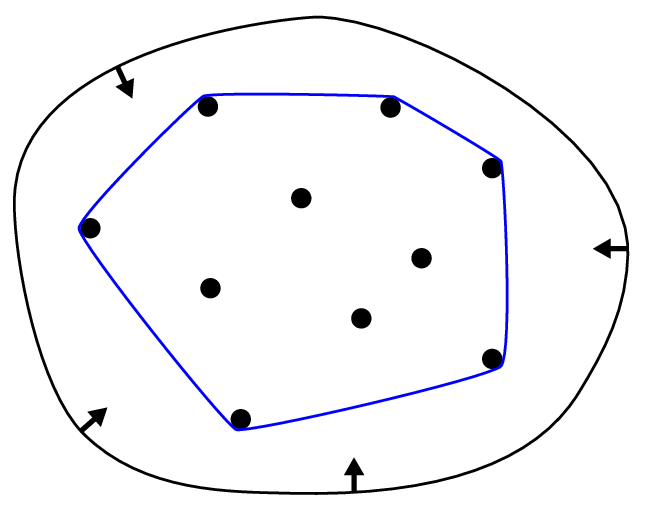
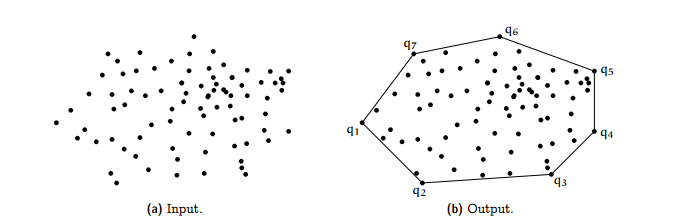
A polygon is convex if and only if:
All interior angles are ≤ 180°
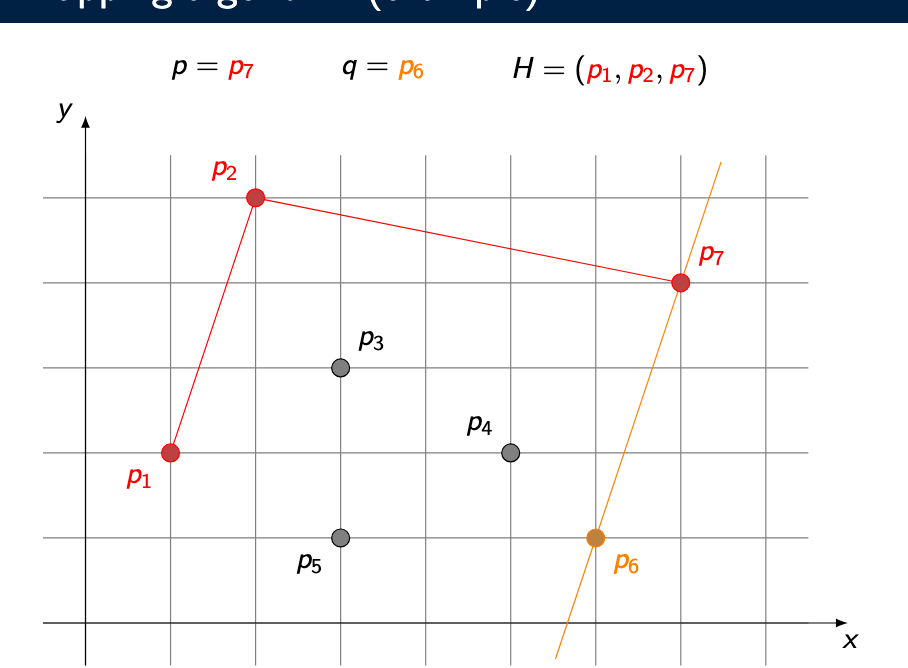
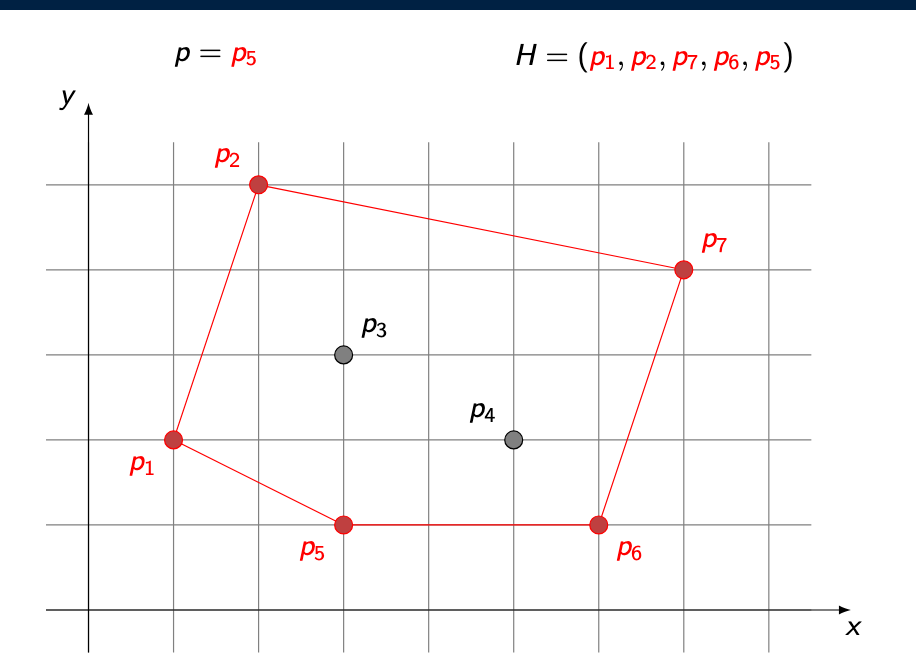
What are the key observations used to find a convex hull? GIFT WRAPPING ALGORITHM
Important ideas:
The lexicographically smallest point is always on the convex hull
(smallestx, then smallesty)An edge
(p, q)is a hull edge iff all other points lie on the same sideOrientation is tested using CCW
Steps:
Pick smallest point
pTry all other points
qChoose
qsuch that all other points lie on the same side of(p, q)Add
qto the hullRepeat until we return to the start
What is the time complexity of the gift-wrapping algorithm?
Naive implementation:
O(n³)
Improved version:
O(n²)
Precise bound:
O(nh)
where:
n= number of pointsh= number of hull vertices
Good when:
The hull has few points
What is Graham’s scan used for?
Graham’s scan is an algorithm to compute the convex hull of a finite set of points.
Main idea:
Pick a starting point on the hull, with smallest x and smallest y
All points are sorted by the angle they form with the starting point
p.Reference direction:
Usually the positive y-axis or x-axis
Start with first two points in the stack
Move through sorted points:
If the path makes a left turn, pop the middle point
Continue until a right turn is formed
Push the current point
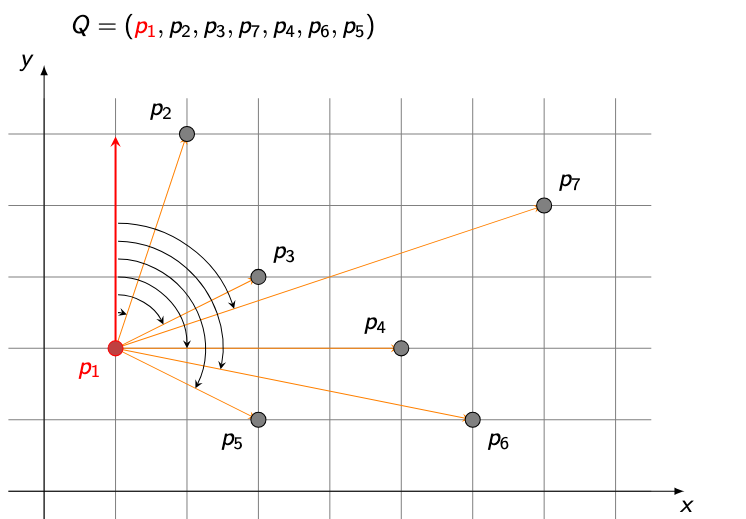
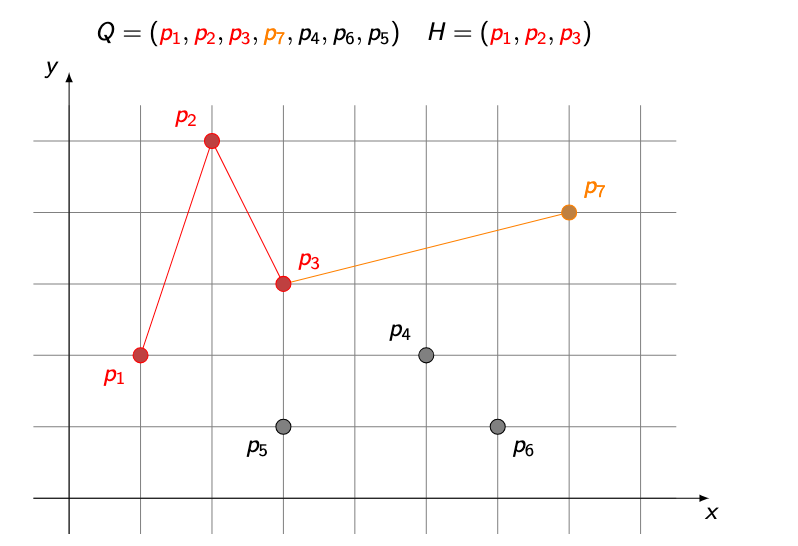
TURN is left (angle at p3 is left) → pop p3, add p7
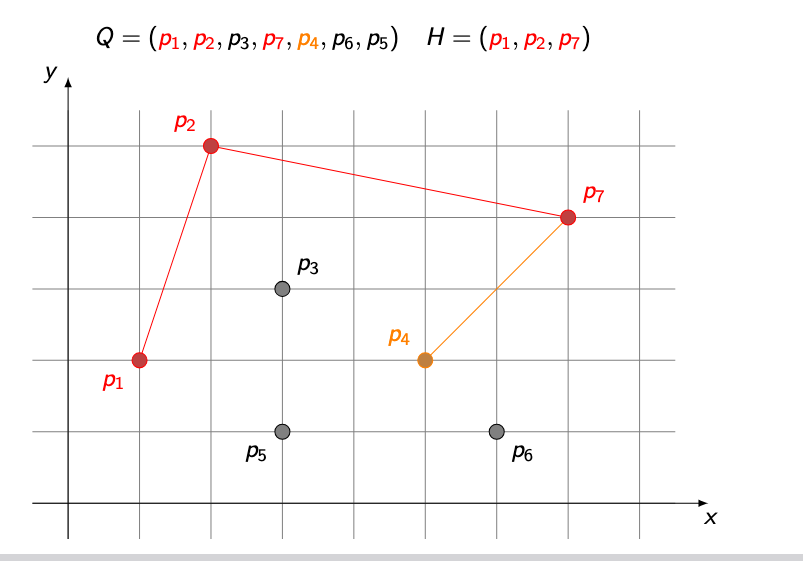
TURN is RIGHT (angle at p7 is right) → continue, add p4
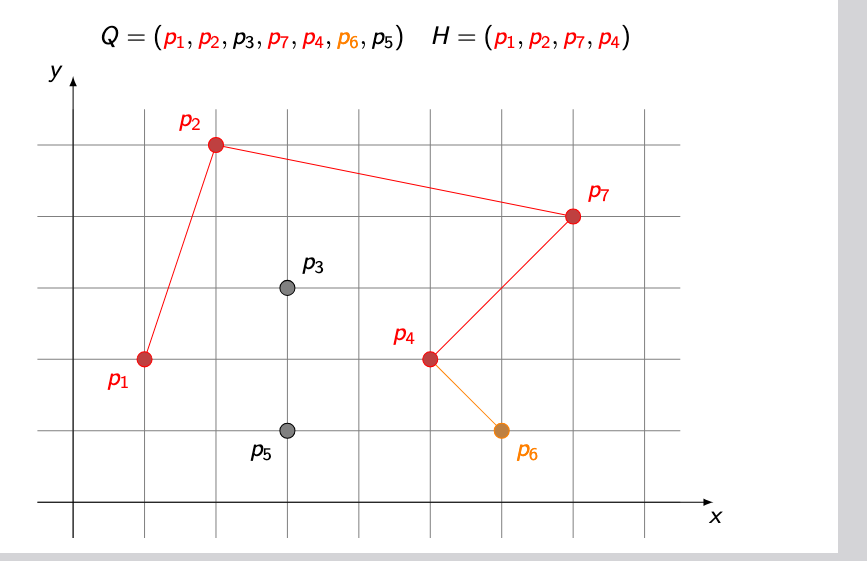
TURN is LEFT (angle at p4 is left) → pop p4 and add p6
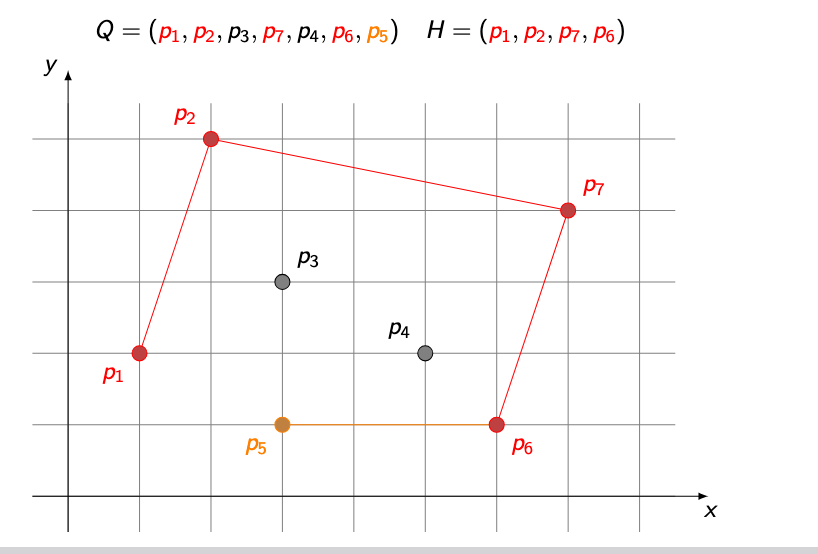
TURN is RIGHT (angle at p6 is right) → continue, add p5
DONE.
It is faster than gift-wrapping for large inputs.

What is the time complexity of Graham’s scan?

What other convex hull algorithms exist, and how do they compare?
