chapter 10 - muscle tissue
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
3 types of muscle
skeletal - moves & positions the body
smooth - pushes fluids & solids along digestive tract & regulates artery (blood vessel) diameter
cardiac - pushes blood through circulatory system
functions of skeletal muscle
skeletal movement - pulls tendons to move bones
maintain posture & body position
support soft tissues - ex. muscles of the abdominal wall & pelvic cavity
guard entrances & exists - openings of the digestive & urinary tracts
maintain body temp
store nutrients - glucose, lipid & even muscle proteins used during fasing
roots associated with muscle
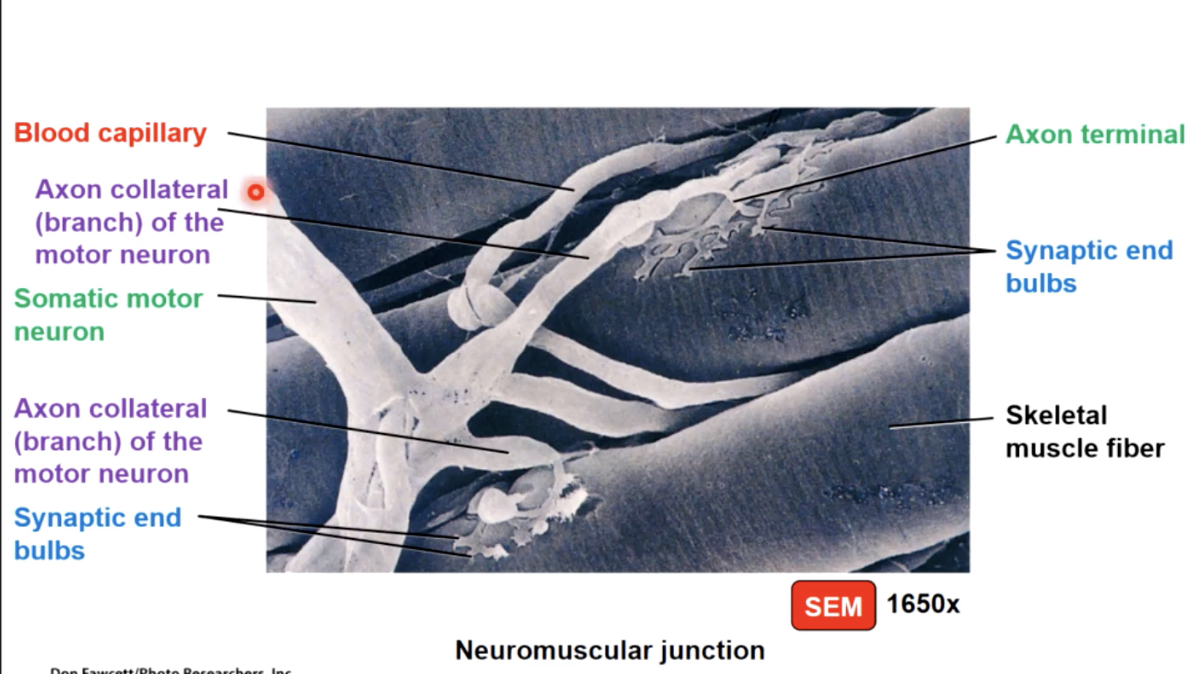
myo, mys = muscle (myoneural junction = muscle nerve junction)
sarco - flesh (Gk)
sarcolemma - cell membrane of a muscle cell
sarcoplasm - cytoplasm of a muscle cell
sarcoplasmic reticulum - modified endoplasmic reticulum of a muscle cell
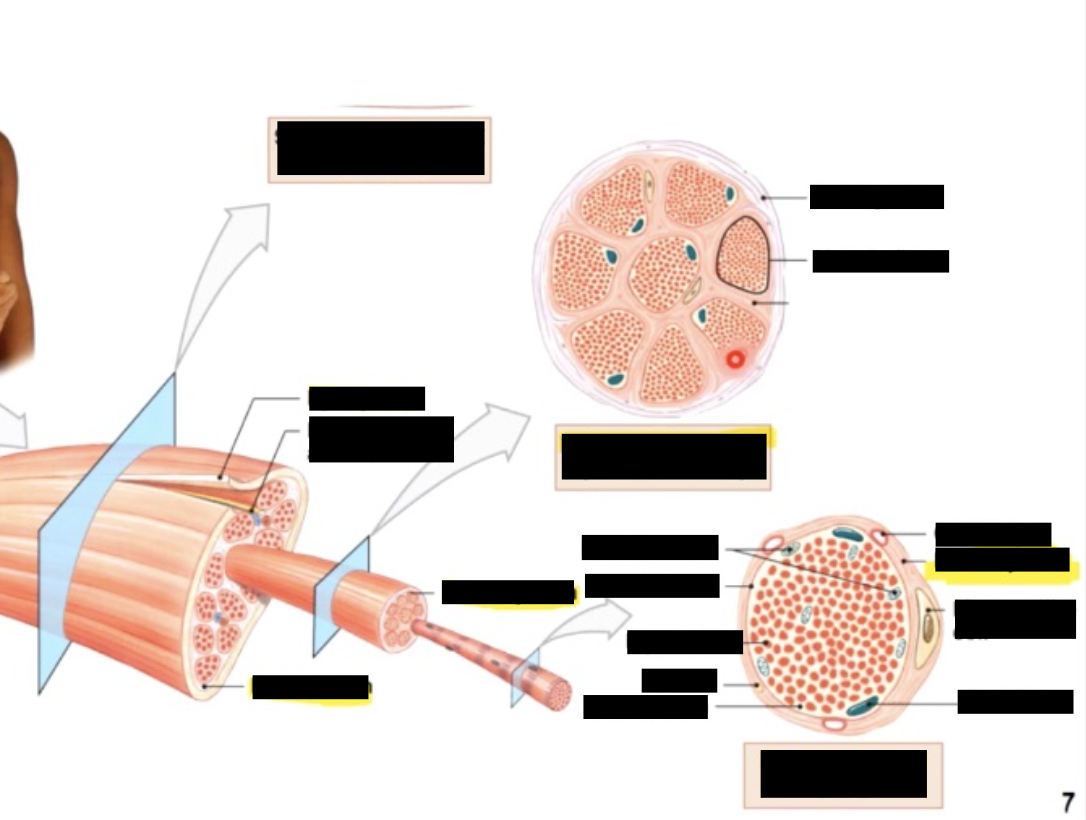
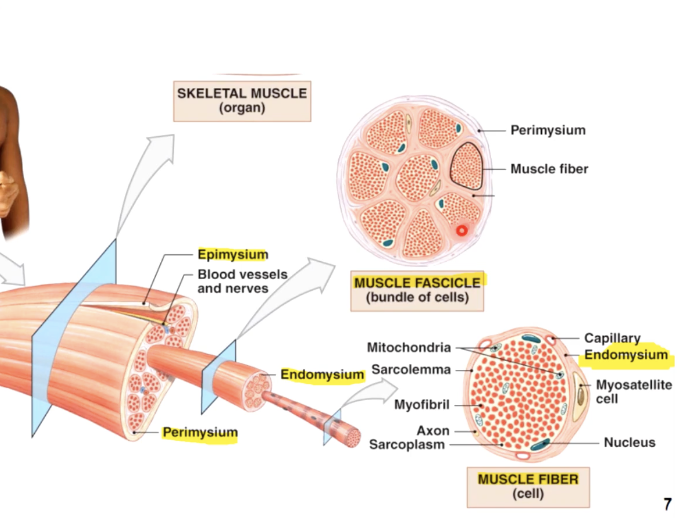
muscle tissue
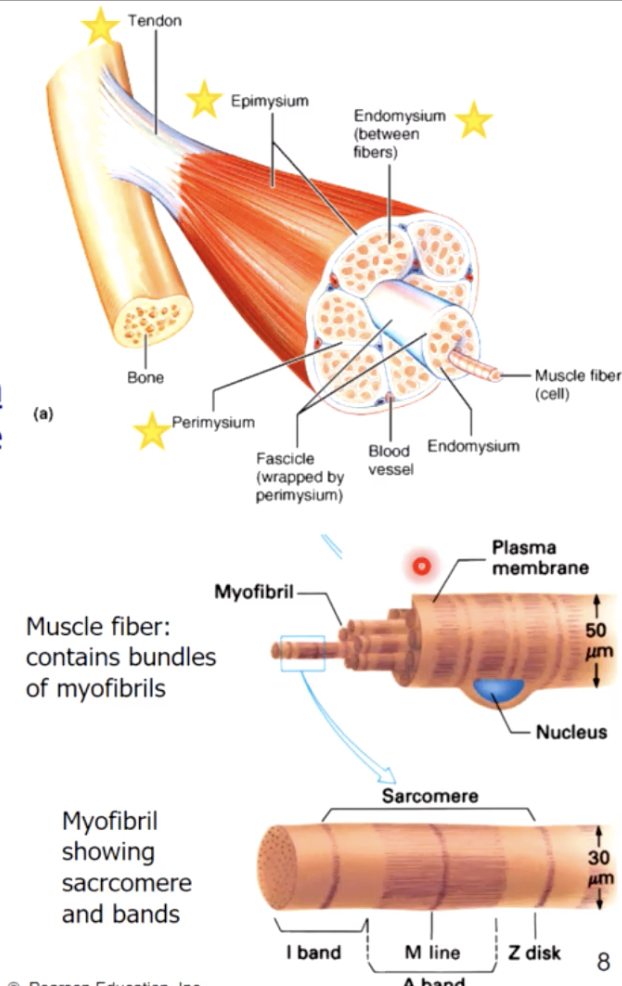
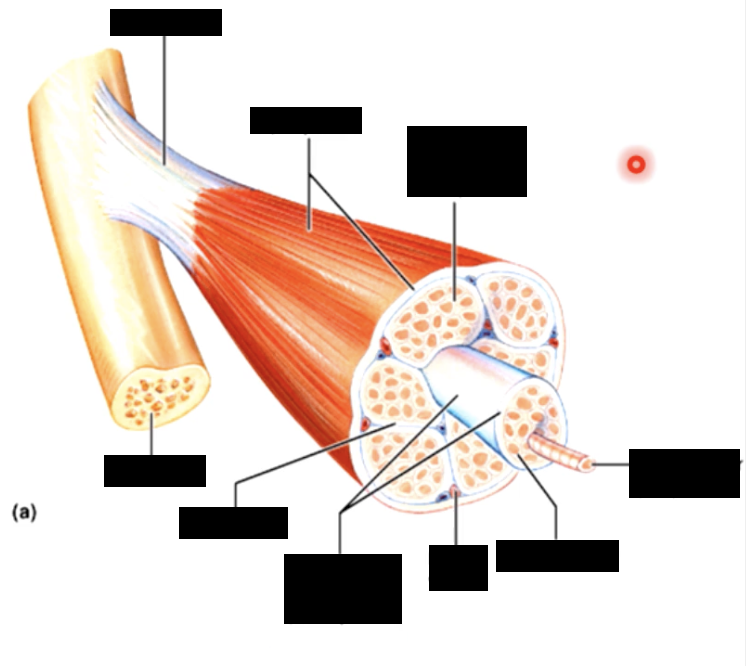
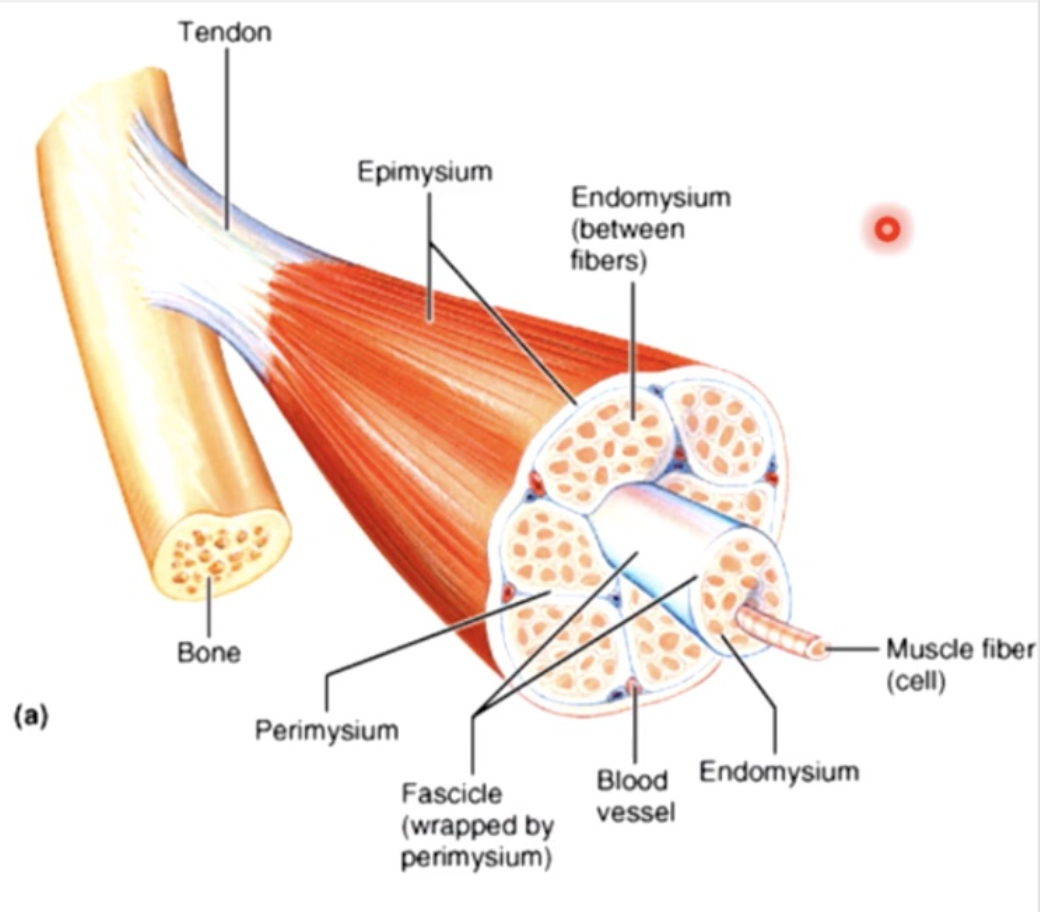
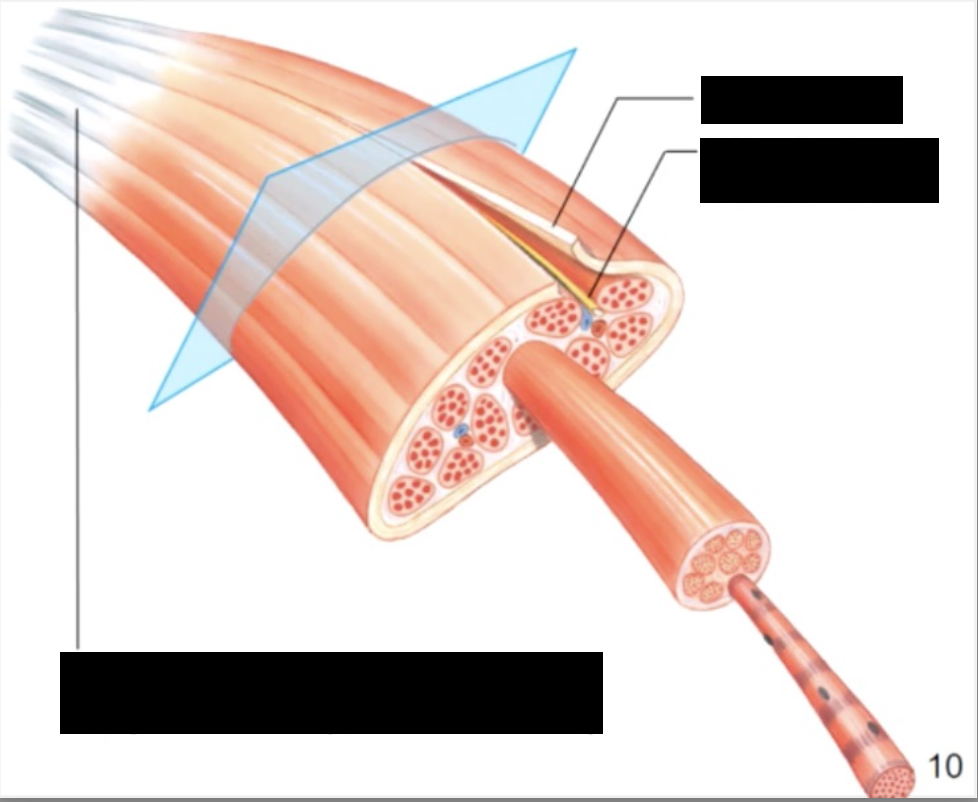
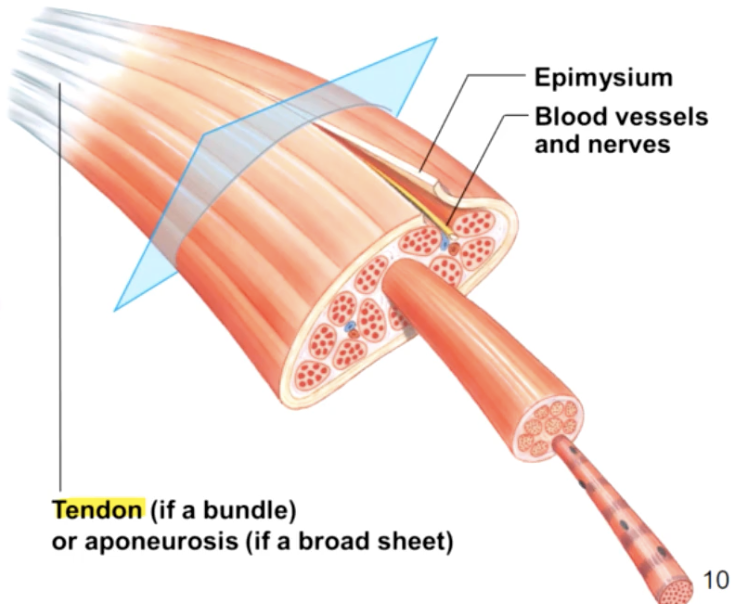
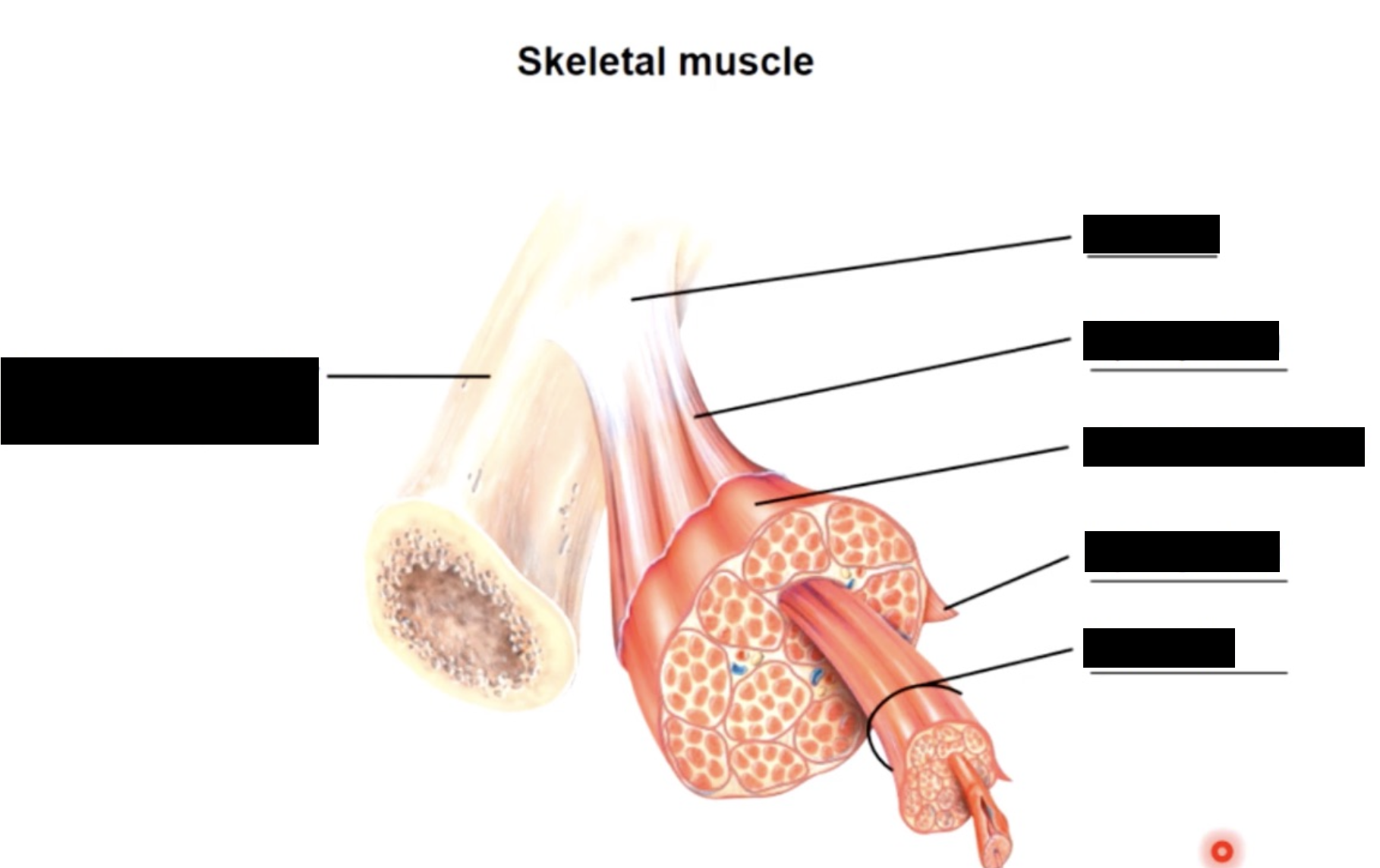
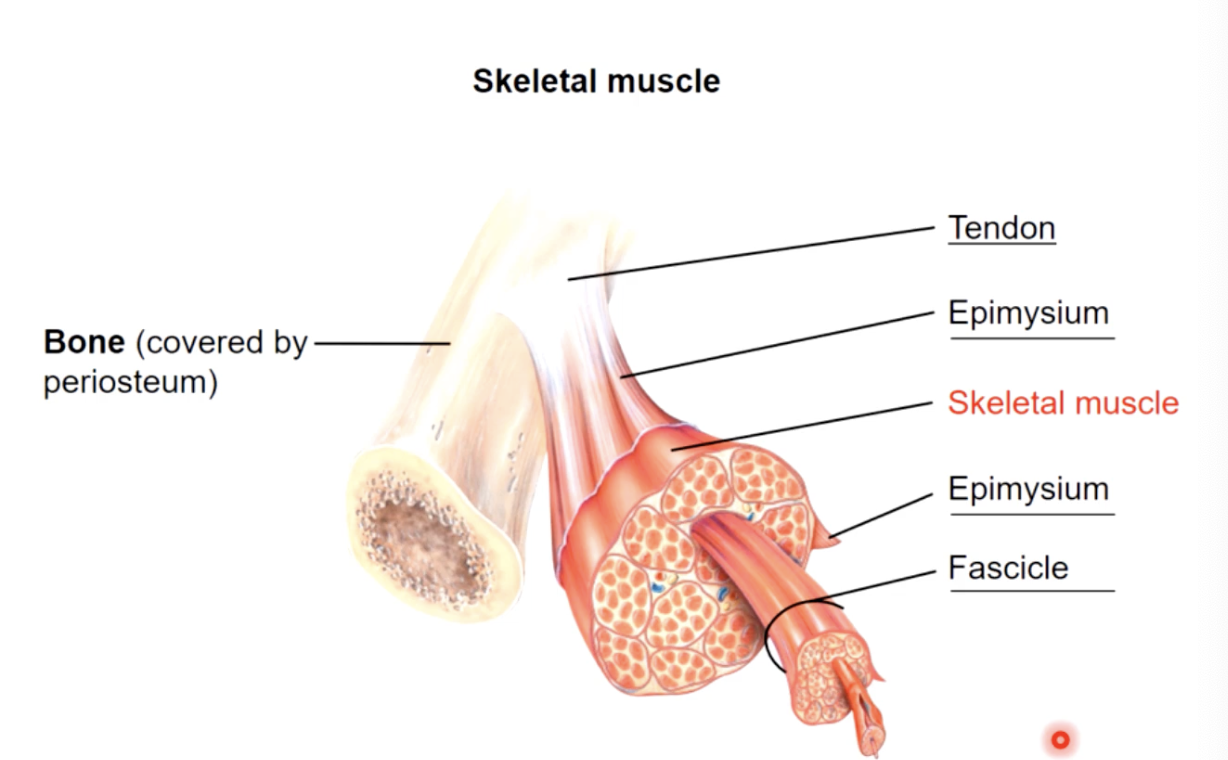
muscle consists of muscle fibres (myofibers) wrapped in a connective tissue called the endomysium
a number of fibres are wrapped together in periosteum to form a fascicle, while fascicles are bundled together to form a muscle, which is wrapped in epimysium or deep fascia
the 3 connective tissue layers come together to form a tendon
Individual fibres are full of contractile organelles called myofibrils, which fill the cell and displace the nuclei to one side
Myofibrils are a systematic arrangement of proteins (myofilaments) which form the contractile unit of the muscle called a sarcomere, which give muscle its striated apperance
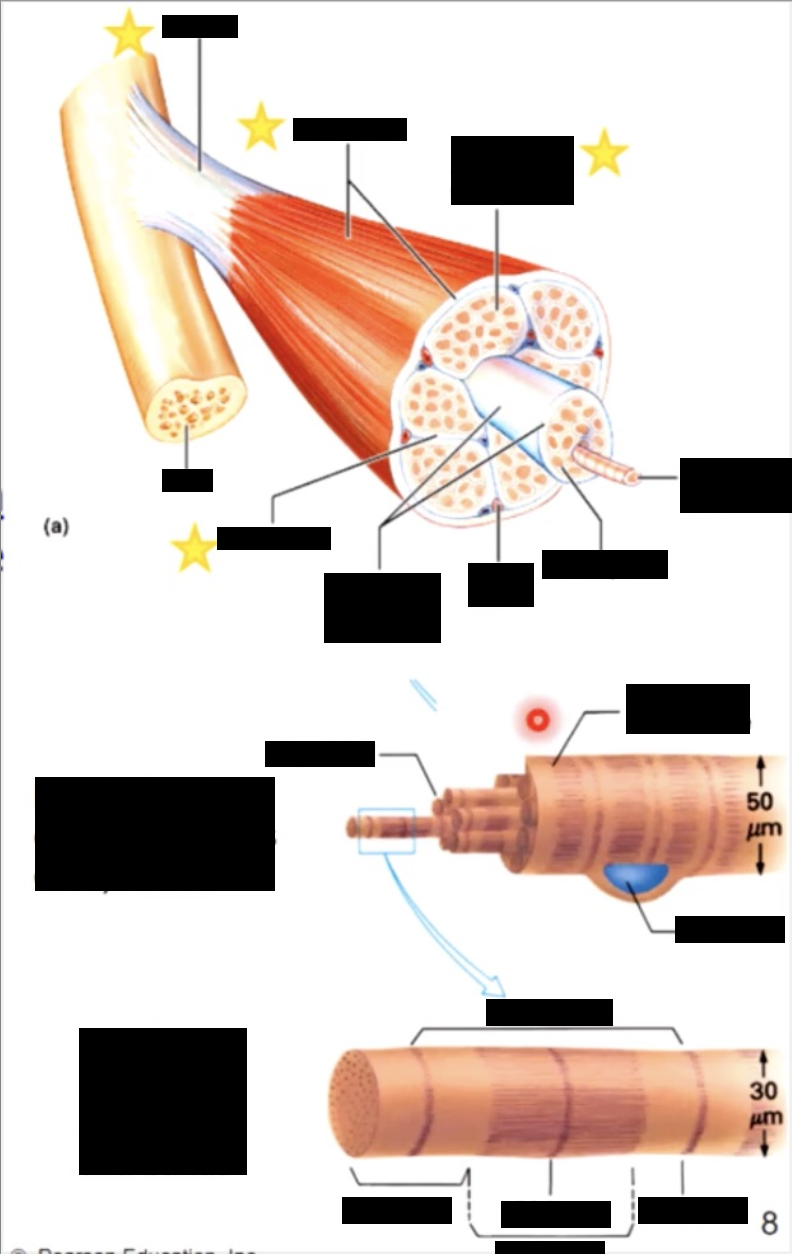
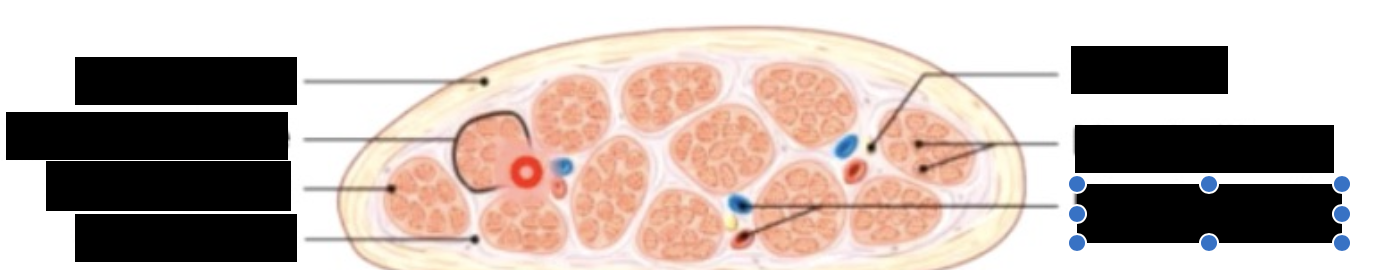
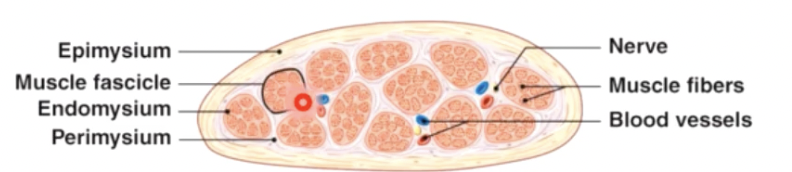
connective tissues around
whole muscle - epimysium
fascicles - perimysium
cells (myofibers) - endomysium
muscle attachments
the collagen fibres of 3 different connective tissue layers come together at the ends of the muscle to form tendons (bundles) or aponeuroses (sheets)
structure - tendons in turn are continuous with matrix of the bone they are attached to
aponeuroses
plural
layers of flat broad tendons with fewer vessels & nerves
structure - typically both tendons and aponeuroses attach muscles to bones
nerve and blood supply
nerve and blood vessels penetrate epimysium together and branch through perimysium and endomysium
each cell is
adjacent to capillaries
Inverted by nerve fibre axons
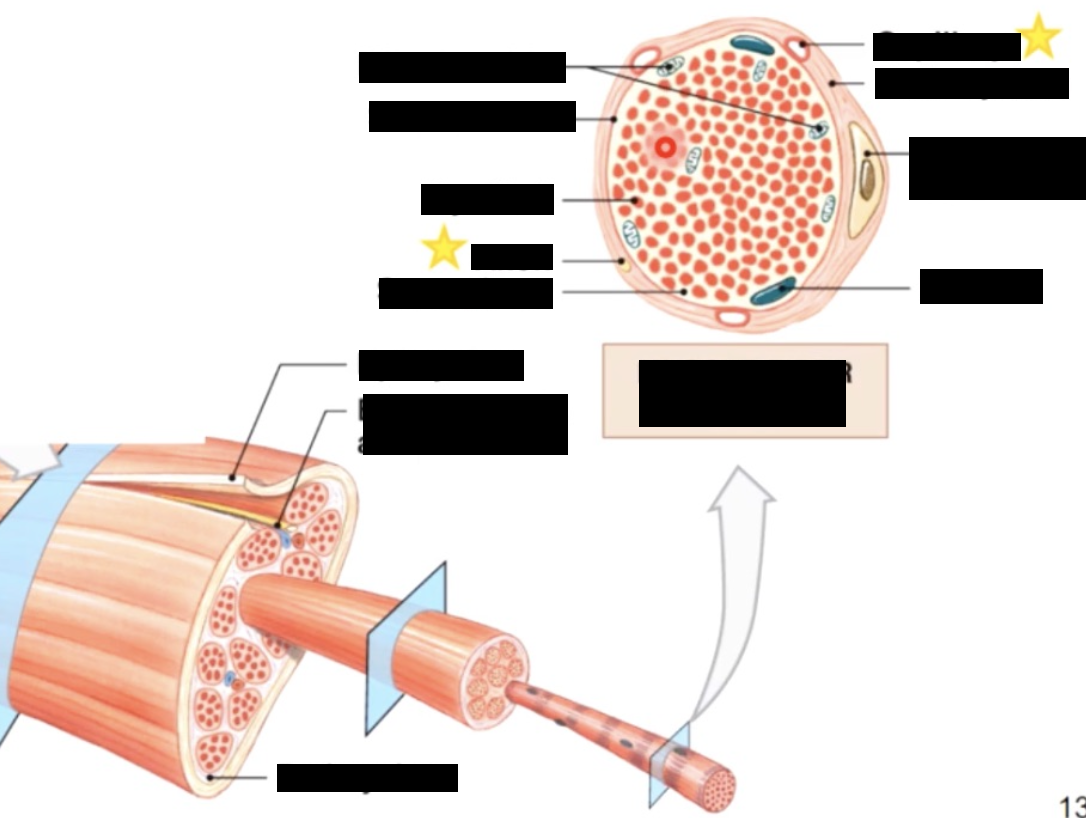
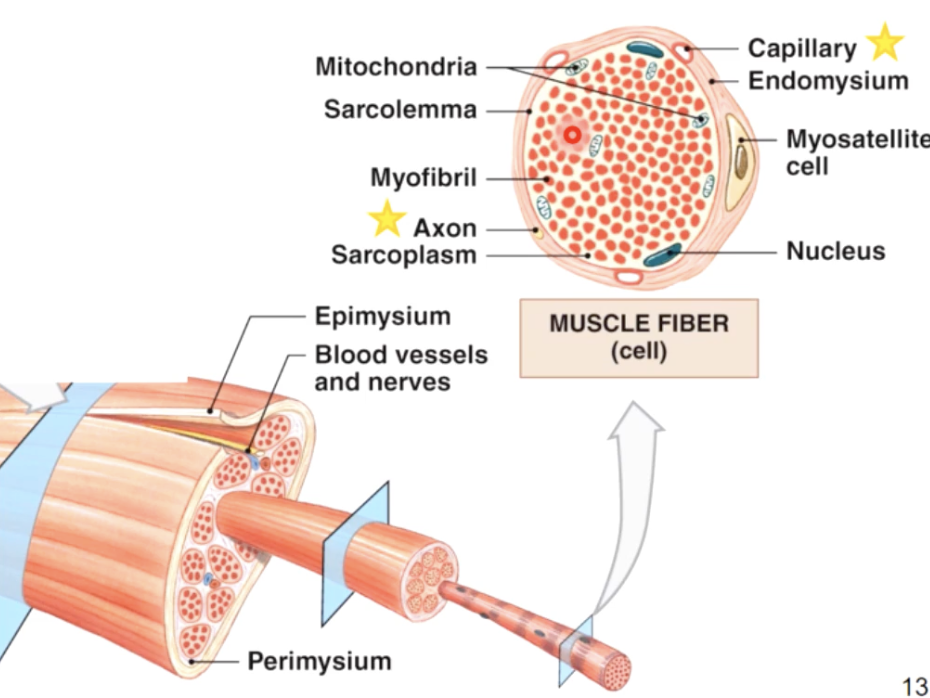
skeletal muscle is made up of..
myofibrils - a bundle of smaller rod like structures
Myofilaments - even smaller structures/proteins make up myofibrils
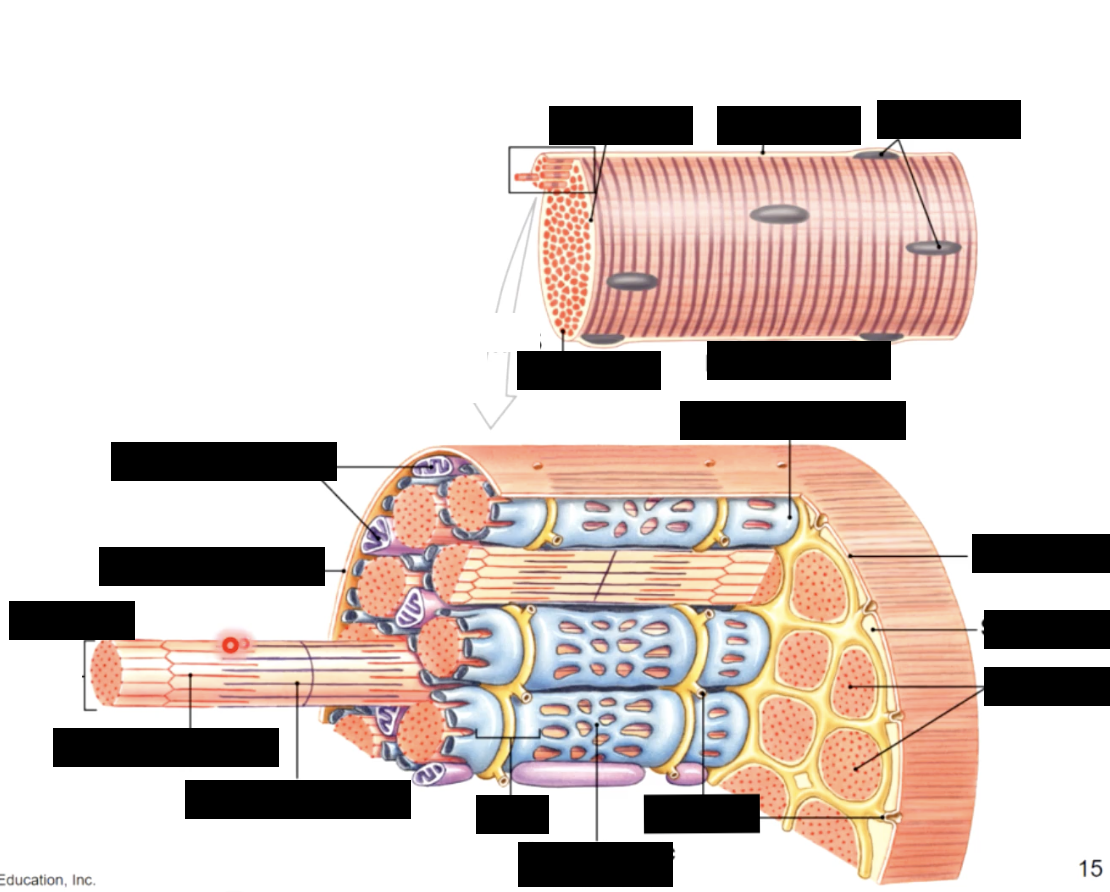
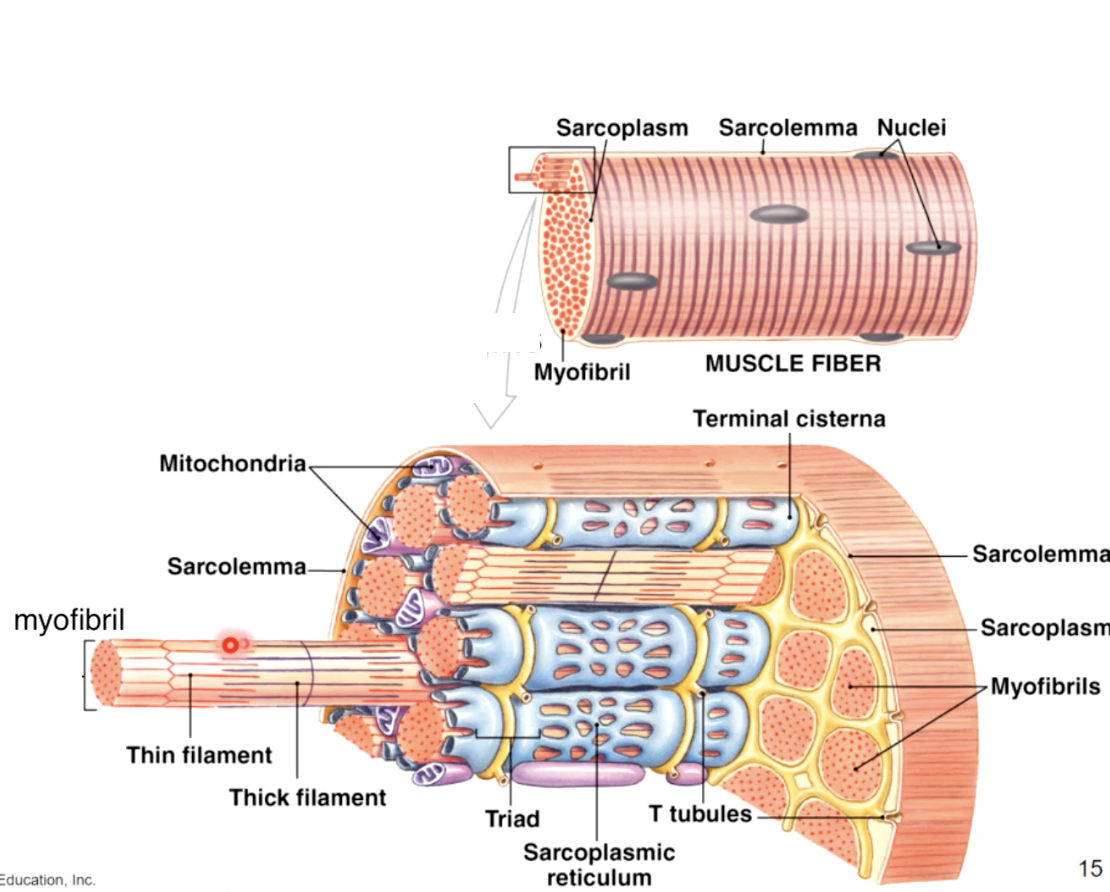
development of skeletal muscle
A few meyoblast cells remain in the tissue as meyosatilite cells
Myoblasts → Fuse together (form multinucleate cells)→ mature into skeletal muscle cells where they start producing proteins and contribute to muscle contraction
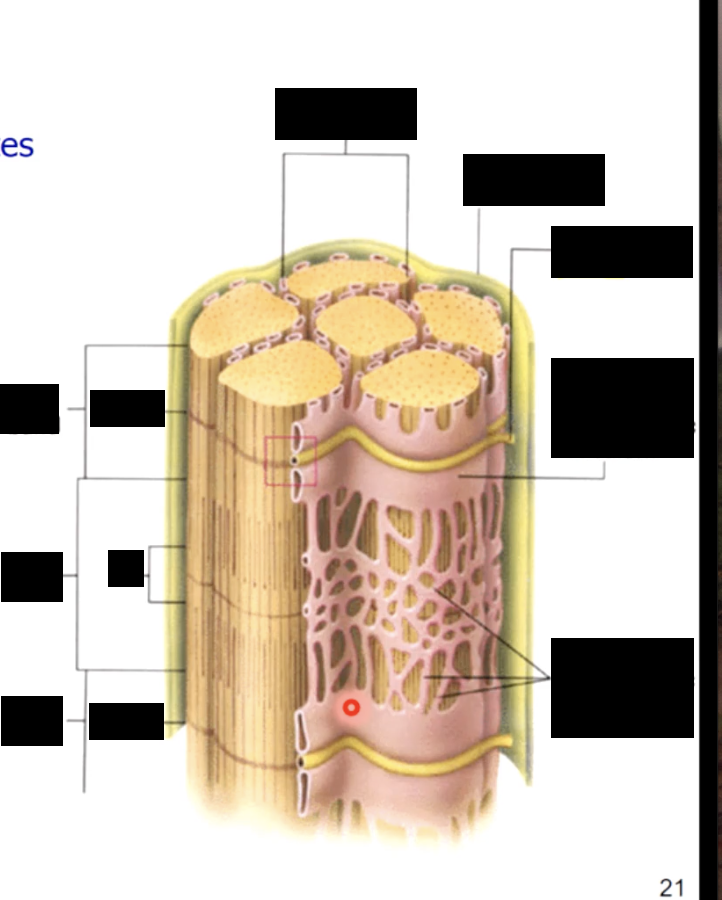
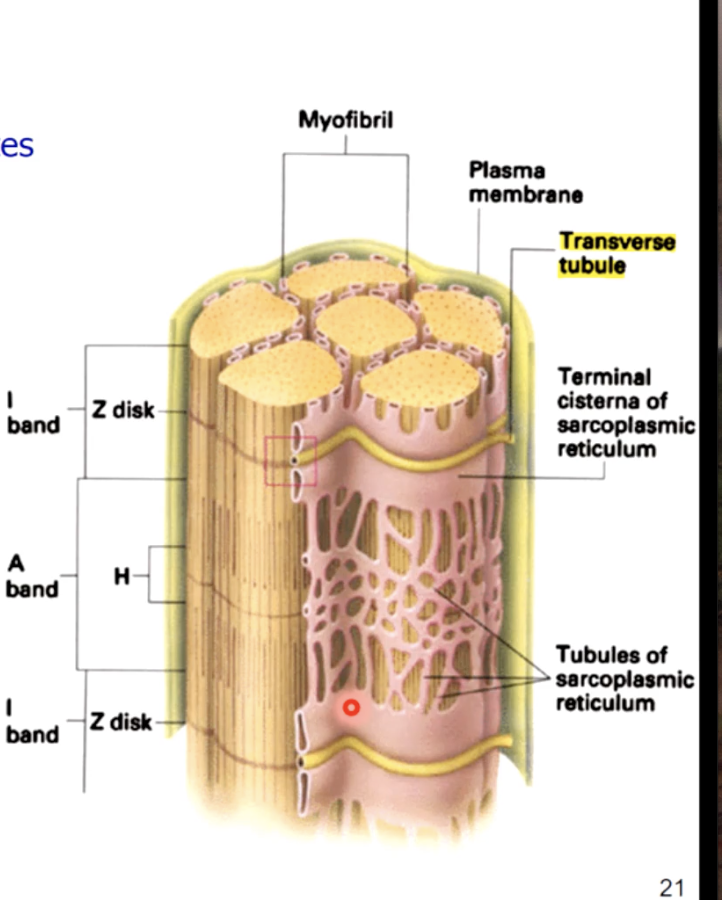
tubules surrounding the myofibrils
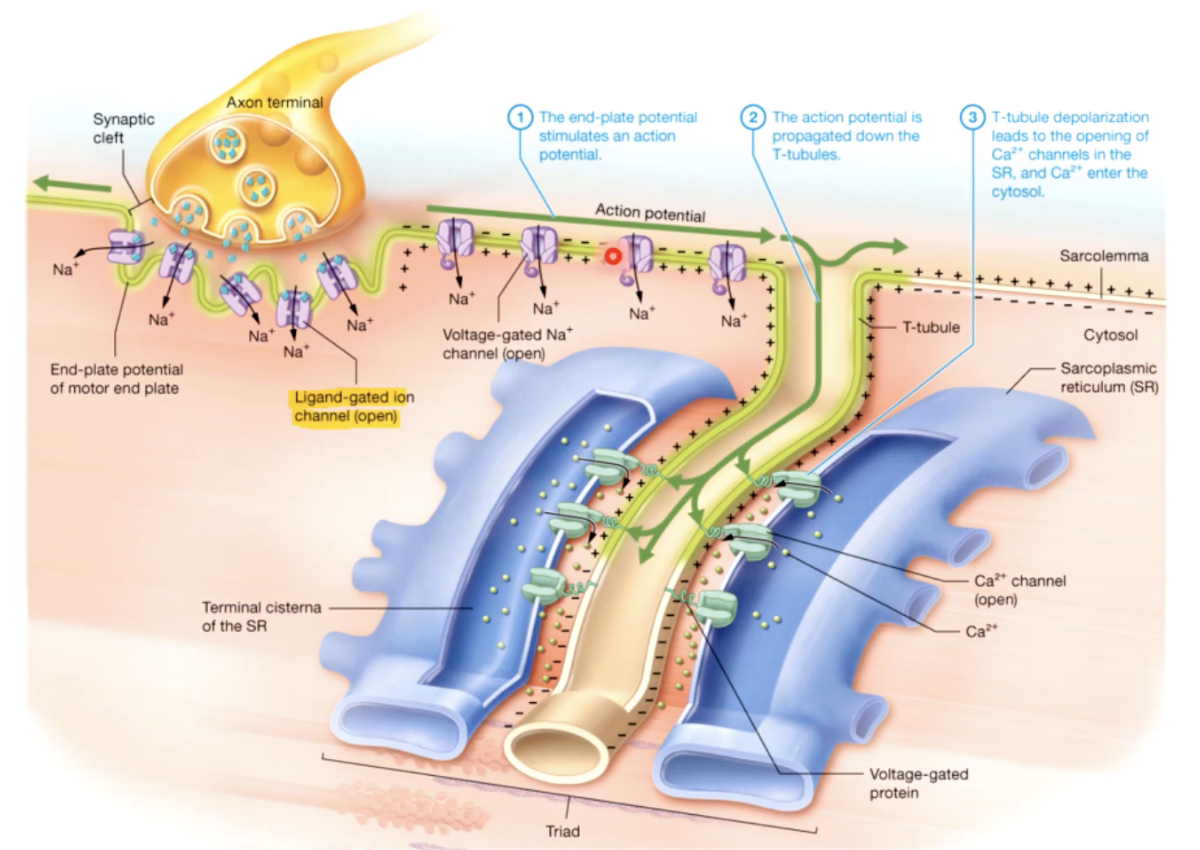
tiny tubules called transverse tubules or T tubules penetrate the sarcolemma and travel deep into the cell surrounding the myofibrils
t tubules - conduct waves of electrical activity from the sarcolemma deep into the cell, providing the signal for the cell to contract
structure of myofibrils
bundles of thick and thin filaments (protein strands)
sarcoplasmic recticulem (basics)
sarcolemma - plasma membrane of the muscle fiber, has an intricate system of penetrating T - tubules that connect to a specialized smooth ER called sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
the SR stores and releases calcium ions which are important for muscle contraction
most SR ca2+ bound to calsequestrin protein
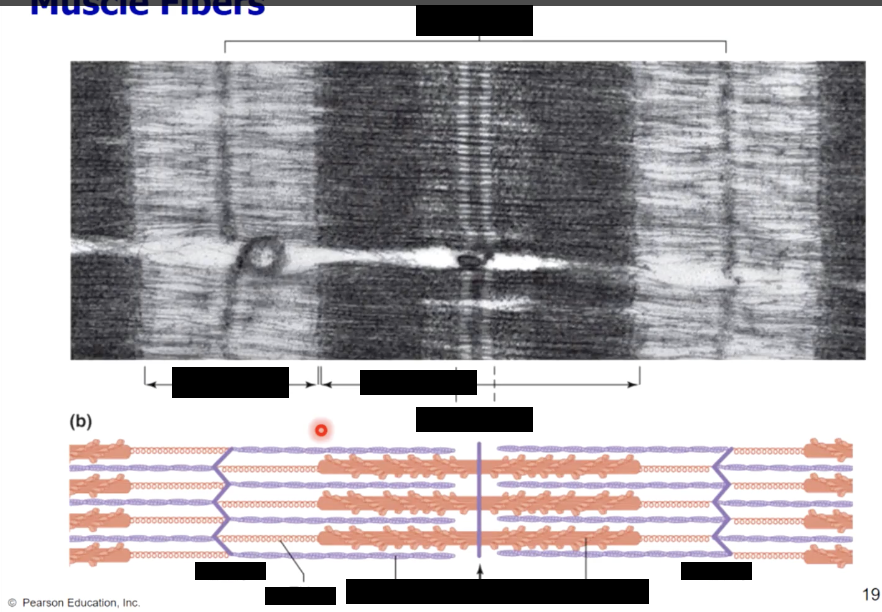
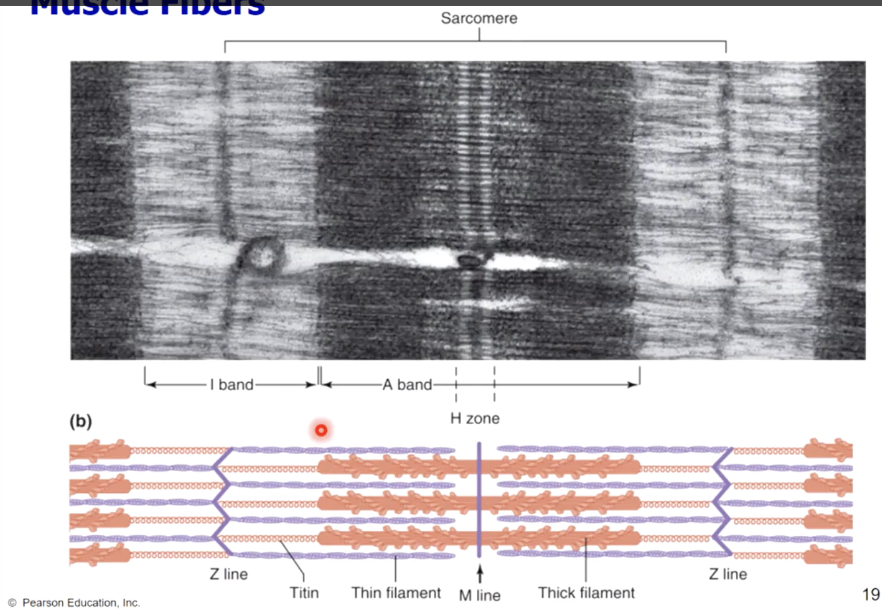
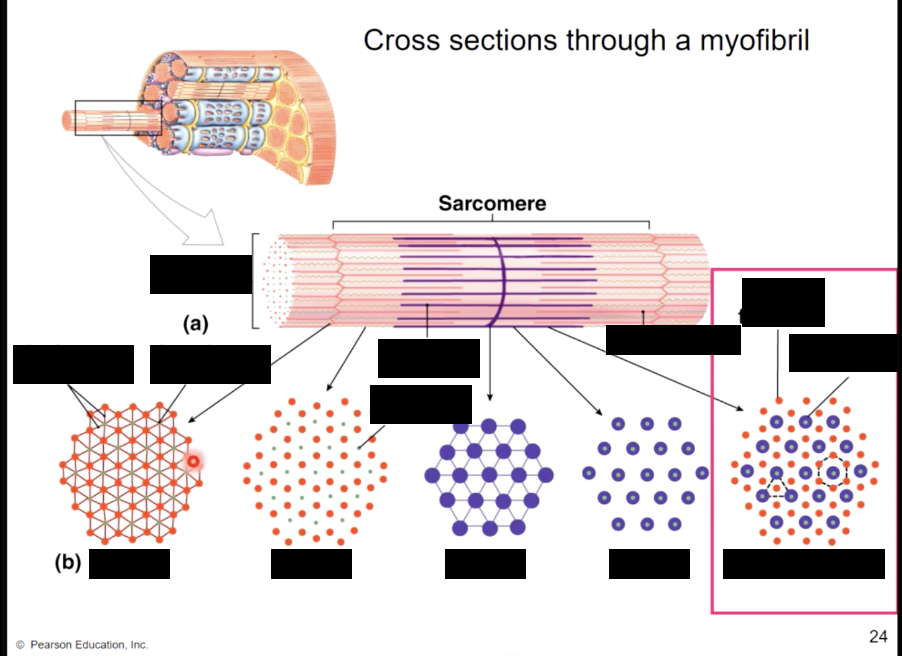
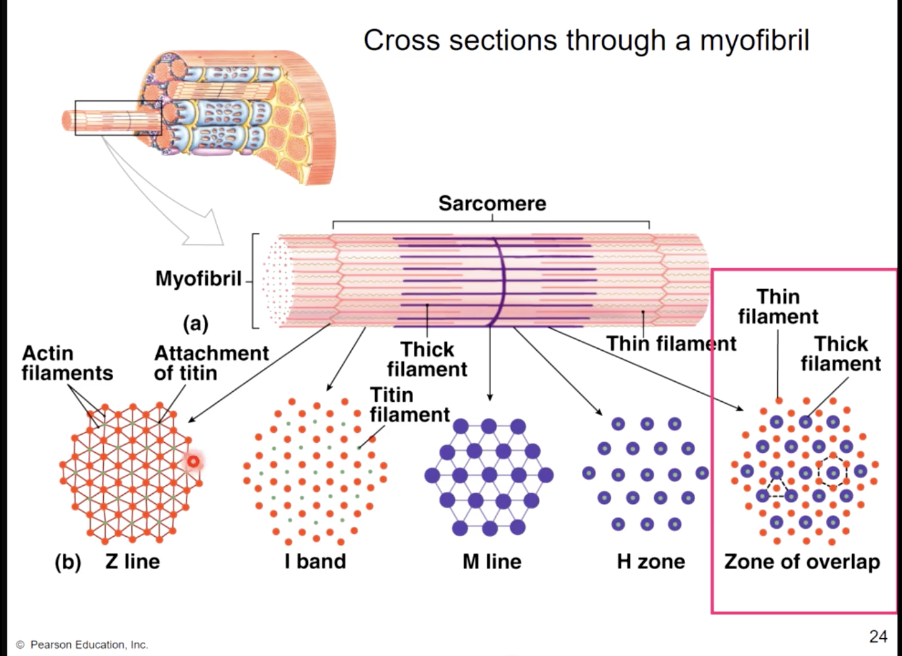
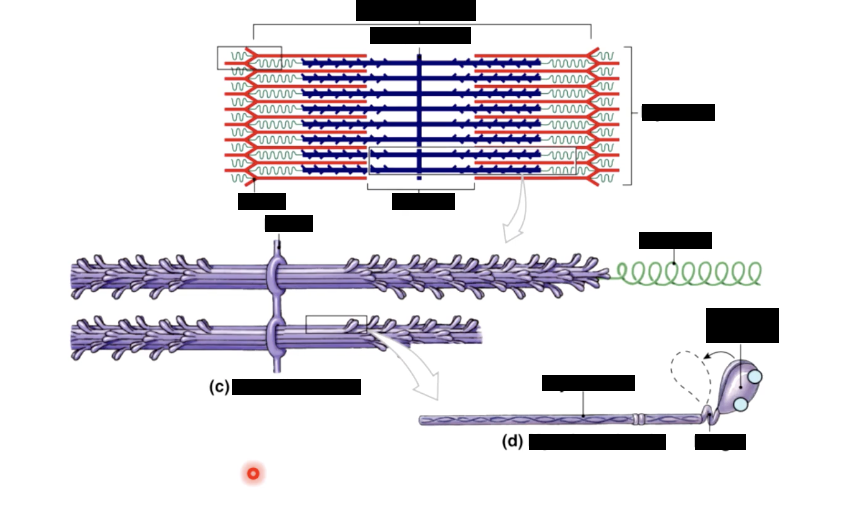
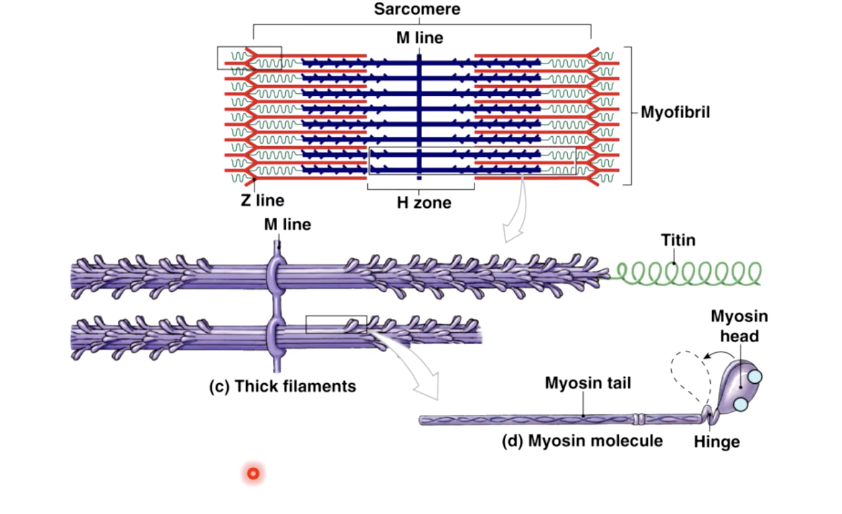
muscle fiber bands/sections
A band - (dark area) corresponds to thick filaments
M line - line of proteins that connect the thick filaments
H zone - lighter region contains no overlap
Zone of overlap - thin filaments protrude between thick filaments
I band - (light area) extends from A band to A band
includes thin filaments, with no overlap with thick filaments
includes Z lines - anchor thin filaments
sarcomere - extends from Z line to Z line
functional unit of the muscle cell
Protein titin anchors thick filaments to Z lines (actin)
sarcoplasmic reticulum (in depth)
form a tubilar network around each myofibril
proteins form enlarged sacs adjacent to the T Tubules = terminal cisternae
sarcoplasmic reticulum contains Ca+ ions (some free and some bound to calsequestrin)
the cell contracts when stored Ca+ ions are released into the sarcoplasm
sliding filament mechanism of contraction
H zone - narrower
I band - narrower
A band - stays the same
Zone of overlap - wider
sarcomeres - contract
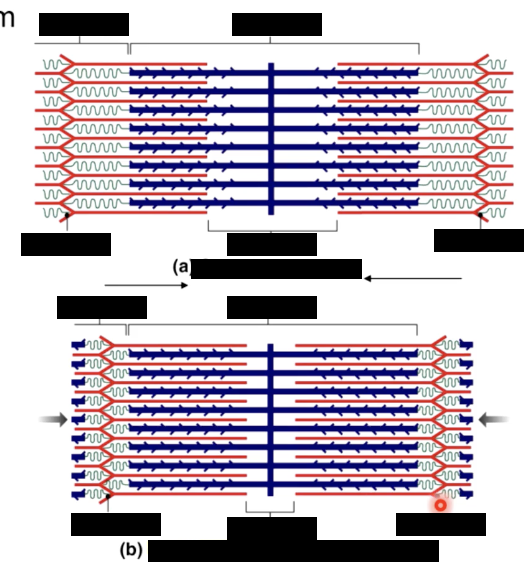
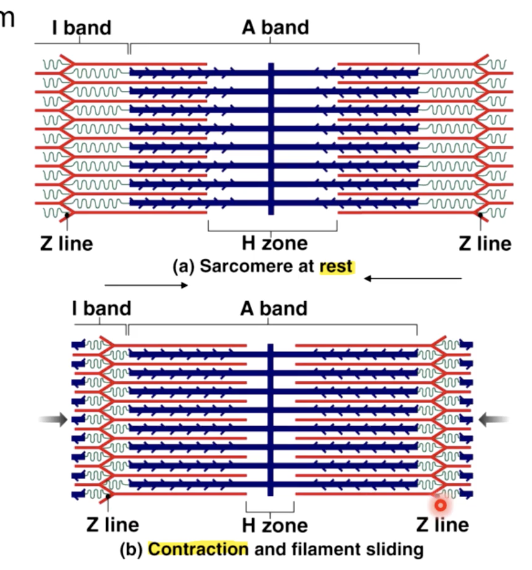
sarcomeres along each myofibril
lie end to end along each
all of the sarcomeres shorten during a contraction, the myofibrils shorten
as all the myofibrils in a muscle cell shorten, the entire muscle fiber (cell shortens & pulls on tendon)
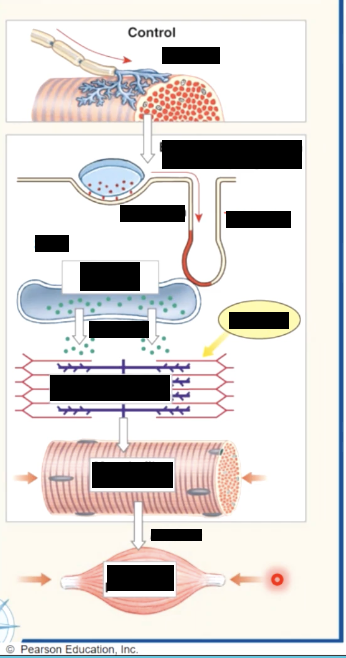
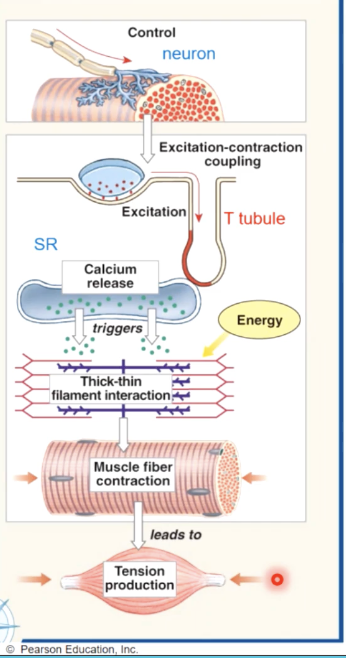
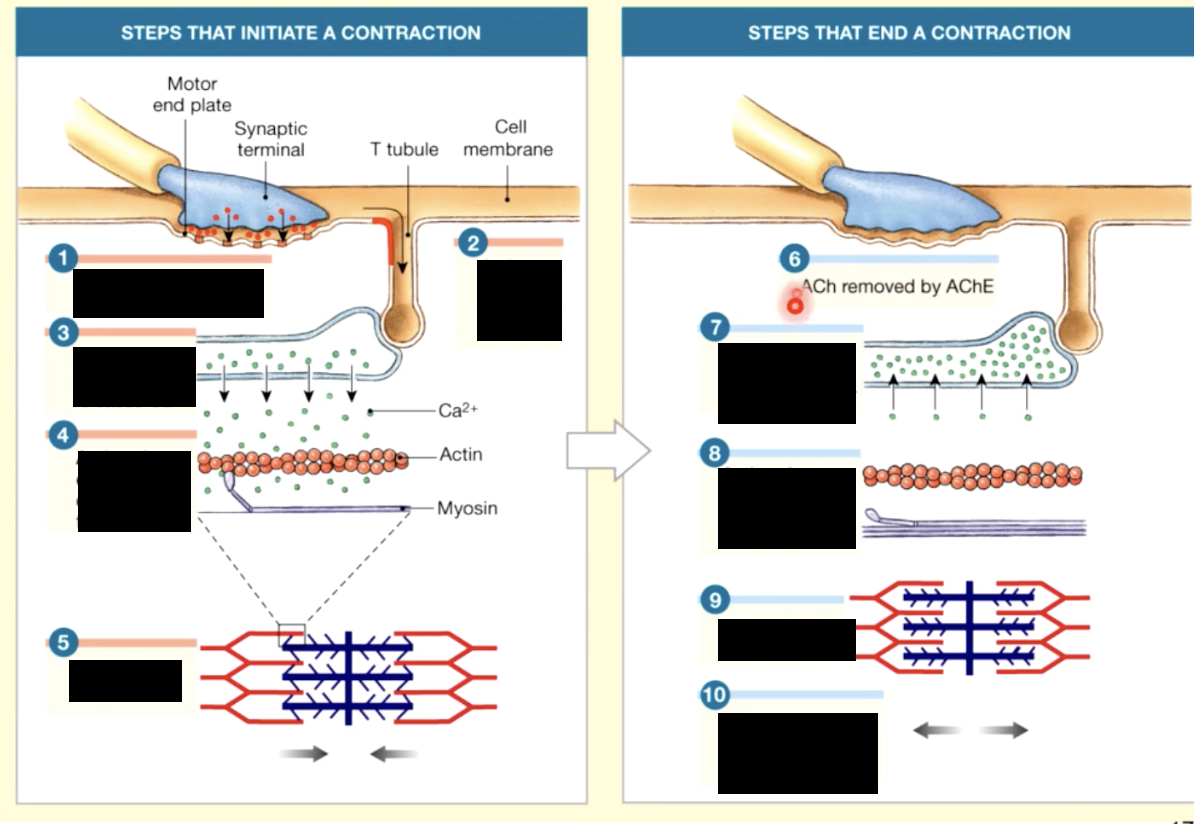
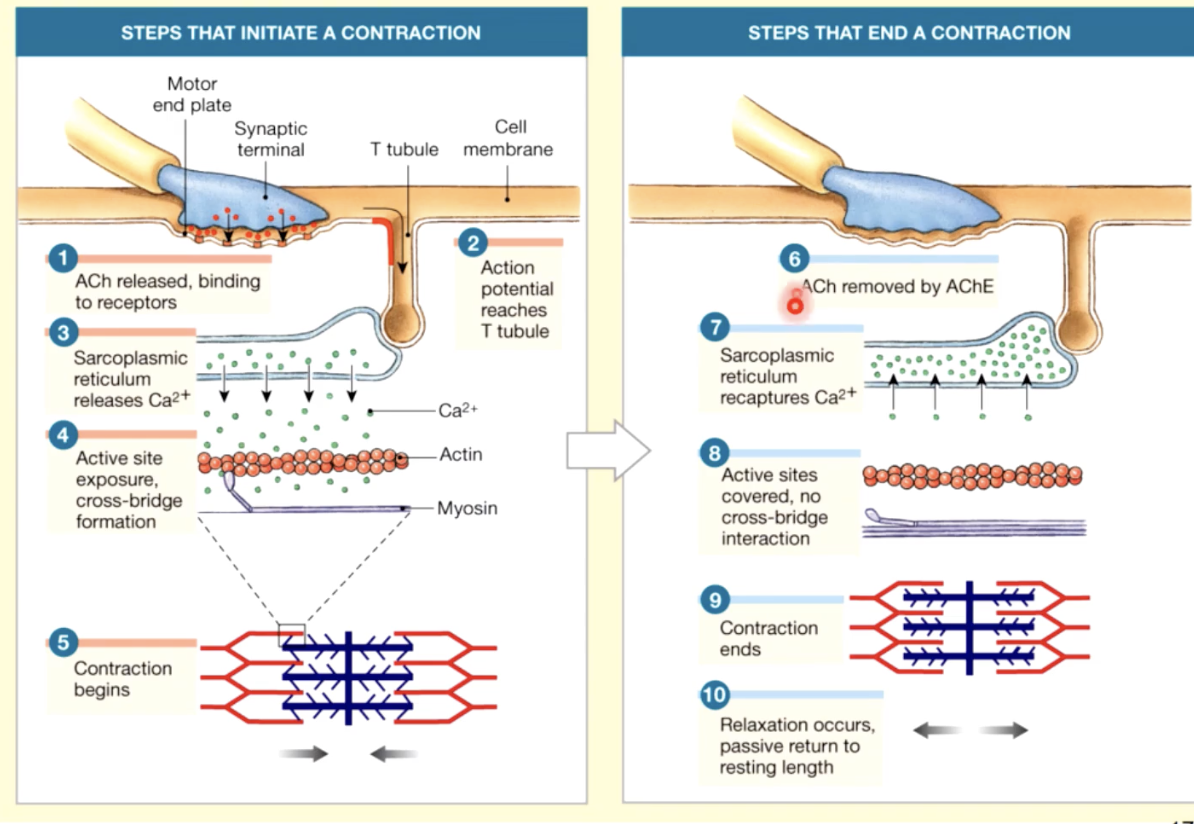
skeletal muscle contraction - overview
1 - skeletal muscle cell contracts only when activated by a neuron
2- electrical activity passes over the sarcolemma, and down the T tubules, triggering the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
3 - Ca+ triggers interactions between thick and thin filaments, causing them to contract muscle fiber
4- as the cell shortens it generates active tension
thick filaments
made of myosin
each myosin molecule consists of 2 tails wrapped into 1 and 2 heads that can swivel
each myosin head has binding sites for - actin and atp
thin filaments consist of __ proteins
actin - globular, strung together like beads on a string each molecule has active binding site for myosis
nebulin - long threadlike protein holding actin in place
tropomyosin - strandlike protein, at rest lies over the active sites on actin molecules
troponin - a globular protein, holds tropomyosin in place
each troponin has a binding site for calcium
when Ca is present in the cytoplasm..
it binds to troponin
this changes the shape of troponin, causing it to allow tropomyosin to slide off the myosin binding the sites of actin
the actin and myosin are now free to interact = cross bridge cycling
contractile proteins
myosin -
largest of the contractile protein
double stranded molecule, produces two heads at one end
myosin is capable of using ATP to generate force and is called a molecular motor
actin -
form the thinner of the contractile filaments and are anchoring strand for myosin
each actin molecule has a binding site for the myosin heads
for contraction to occur the myosin head has to bind to actin
the binding site -
on each actin mol is protected by a long tropomyosin strand
troponin molecules are along tropomyosin strand
when calcium binds to troponin, the tropomyosin strand is pulled aside to reveal the myosin binding site on actin
cross section bridge occurs when..
calcium binds to troponin complex,
tropomyosin is moved from its actin blocking position.
Once the myosin binding site is revealed on the actin molecule, the myosin head can bind and initiate the cross bridge cycle
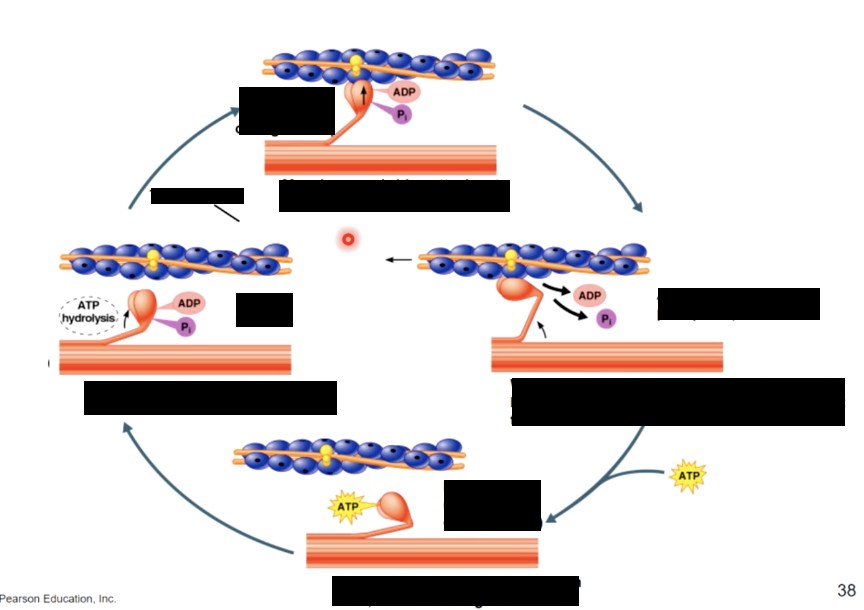
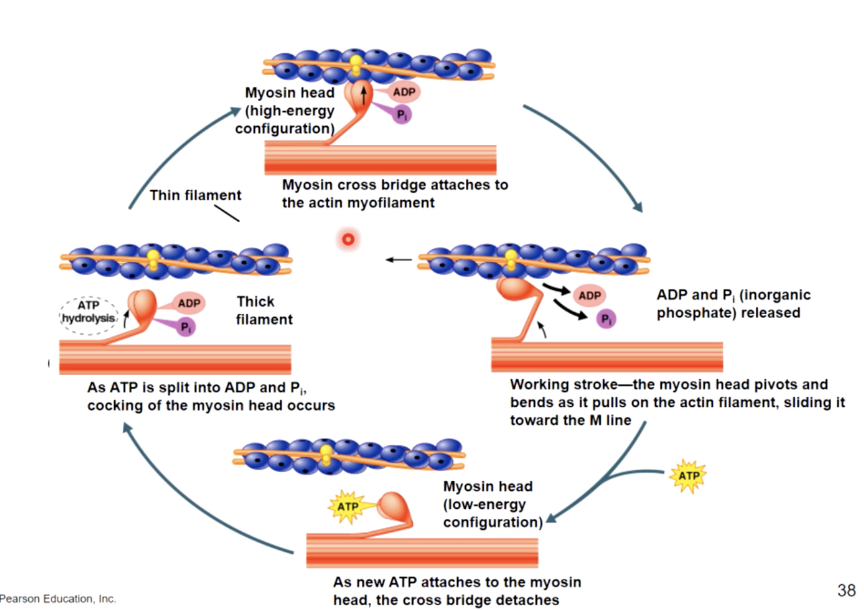
cross bridge cycle
refers to the process of myosin heads binding to actin and the generation force to contract the muscle fibers
begins when myosin is bound to actin after the myosin head is energized by ATP
the myosisn head changes shape, pulling on the actin filament and releasing ADP. The results in the shortening of the sarcomere
the head remains bound to the actin filament until another ATP binds to it, allowing myosin to release the actin
once released the myosin head is energized when ATP is broken down into ADP and Pi which again provides the energy for subsequent binding and pulling
sarcomere and the cross bridge
when calcium is released into the cytosol, actin & myosin are allowed to interact,
resulting in the myosin heads pulling the actin fibers,
generating tension: if sufficient this force shortens the sarcomere & the muscle fiber
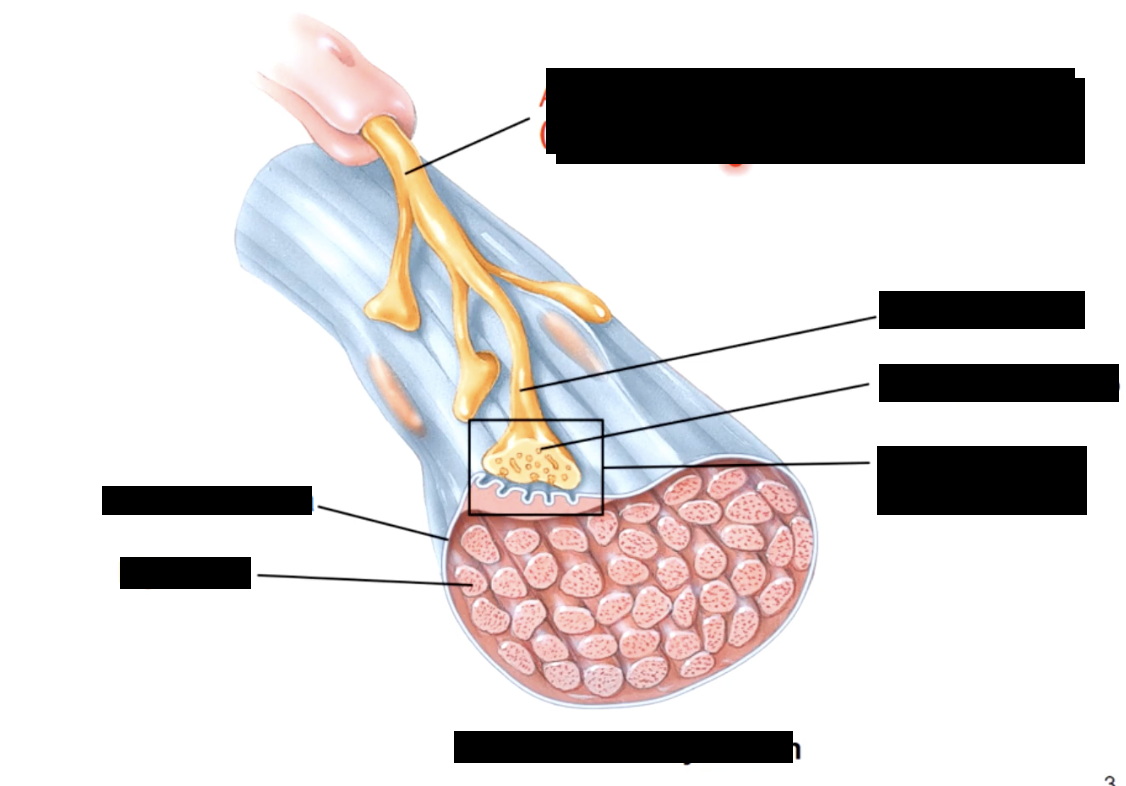
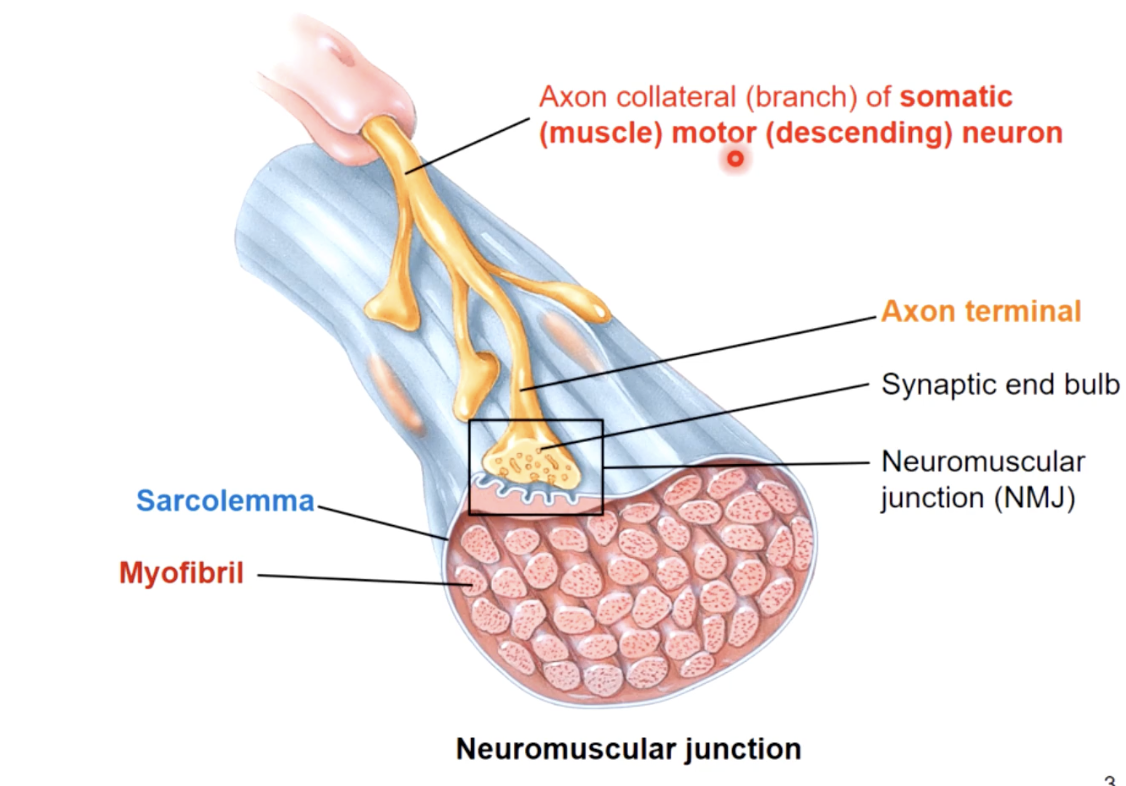
each skeletal muscle cell is controlled by..
a single nerve cell
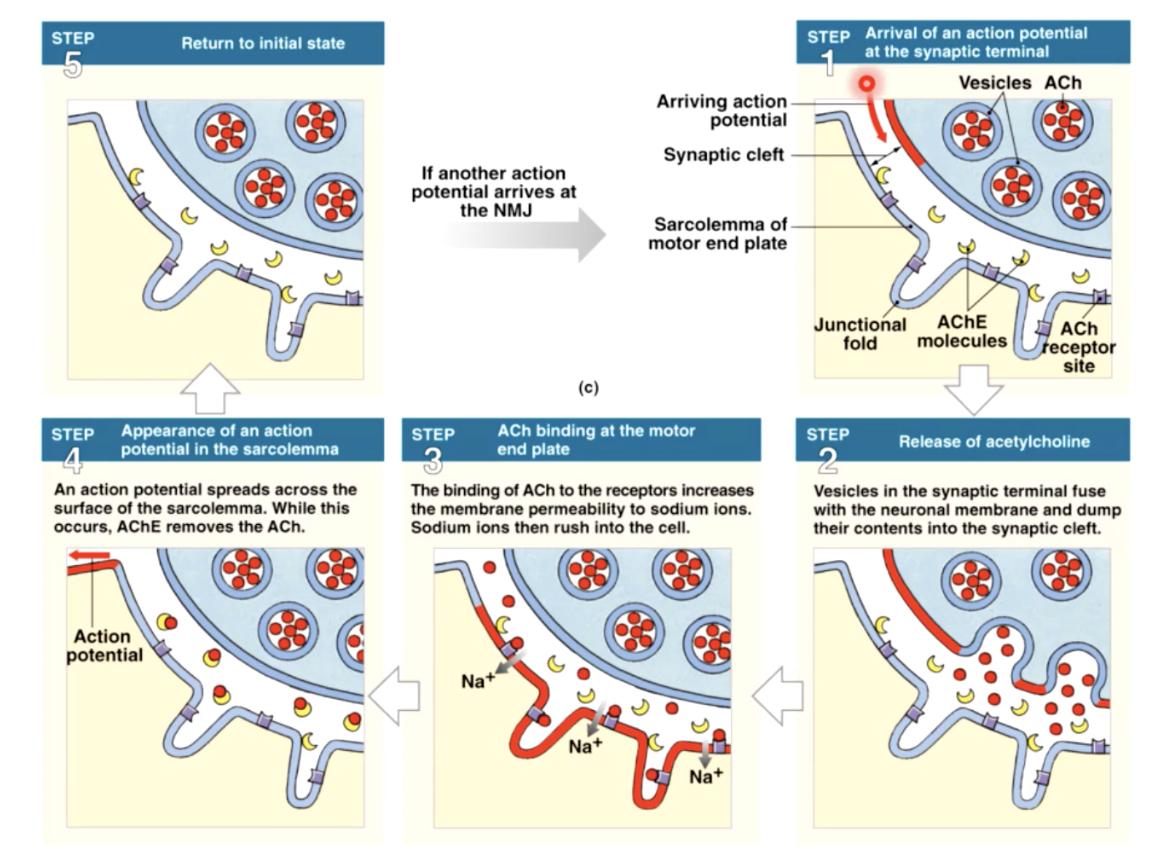
excitation contraction coupling
1. when an electrical stimulus triggers the release of calcium by the sarcoplasmic recticulem, initiating the mechanism of muscle contraction by the sarcomere
2.as the thick and thin filaments interact, the sarcomeres shorten, pulling the ends of the muscle fiber closer together
2.during the contraction, the entire skeletal shortens and produces a pull, or tension, on the tendons on either end
ACh acetylcholine
chemical message - neurotransmitter
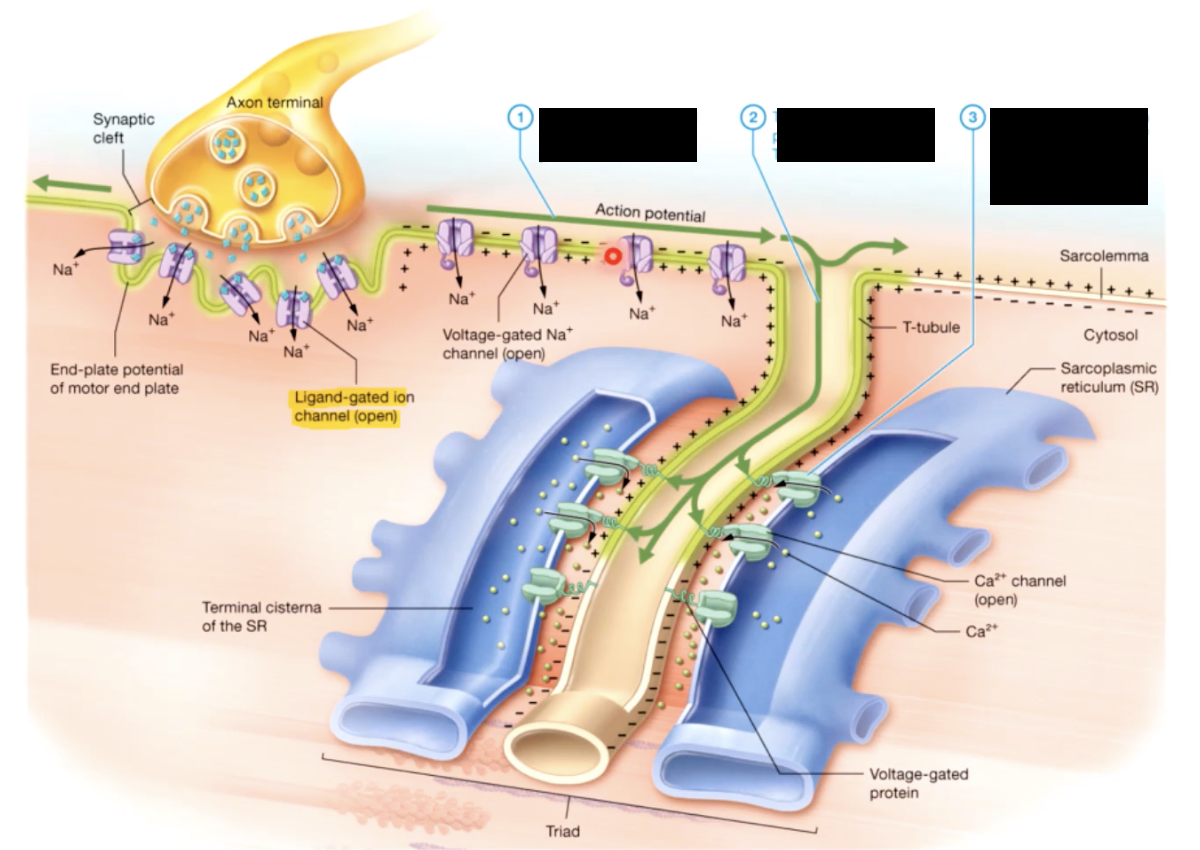
EXCITATION CONTRACTION COUPLING
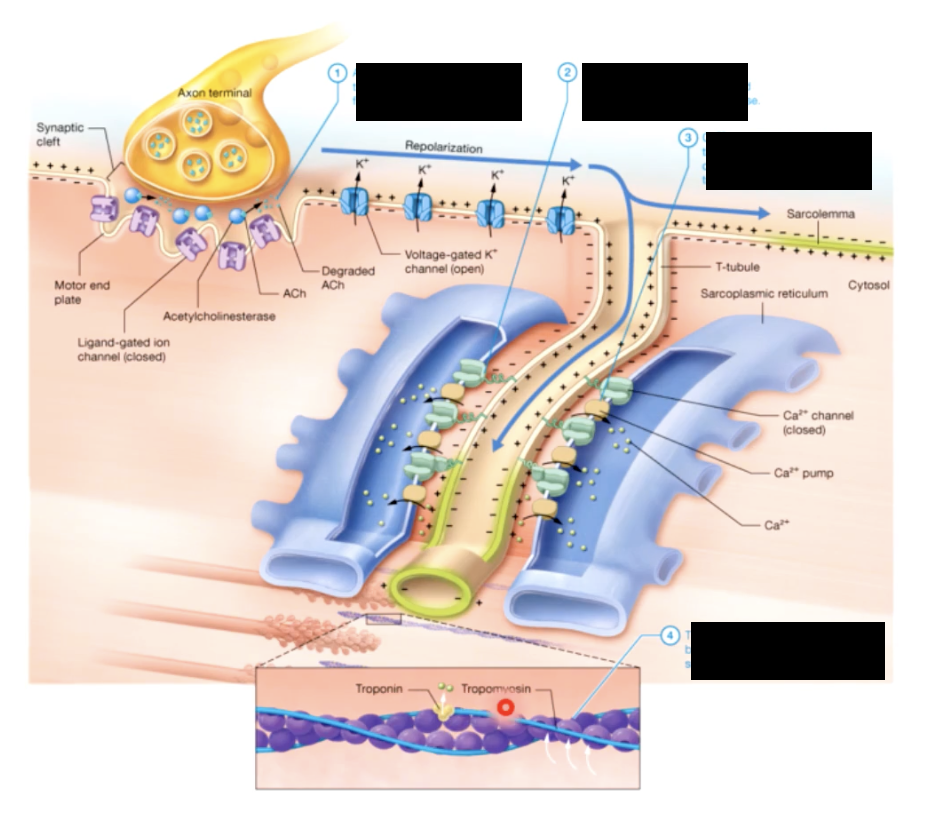
RELAXATION PHASE
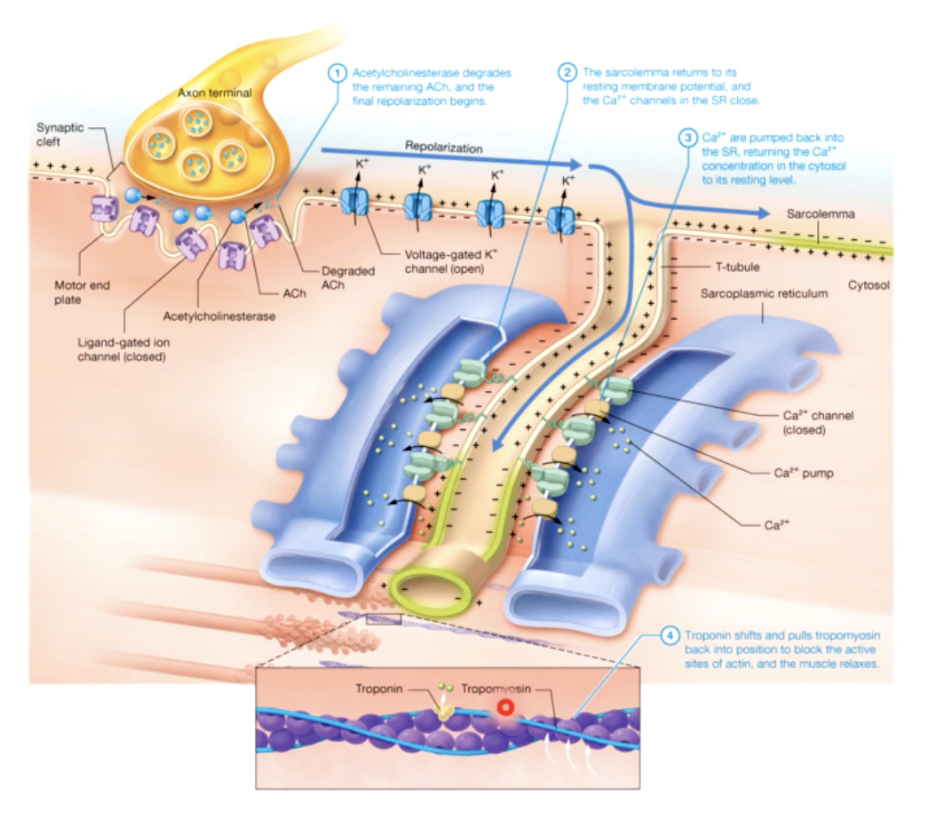
muscle twitch
a single stimulus contraction relaxation
response of a muscle to a stimulus (action potential)
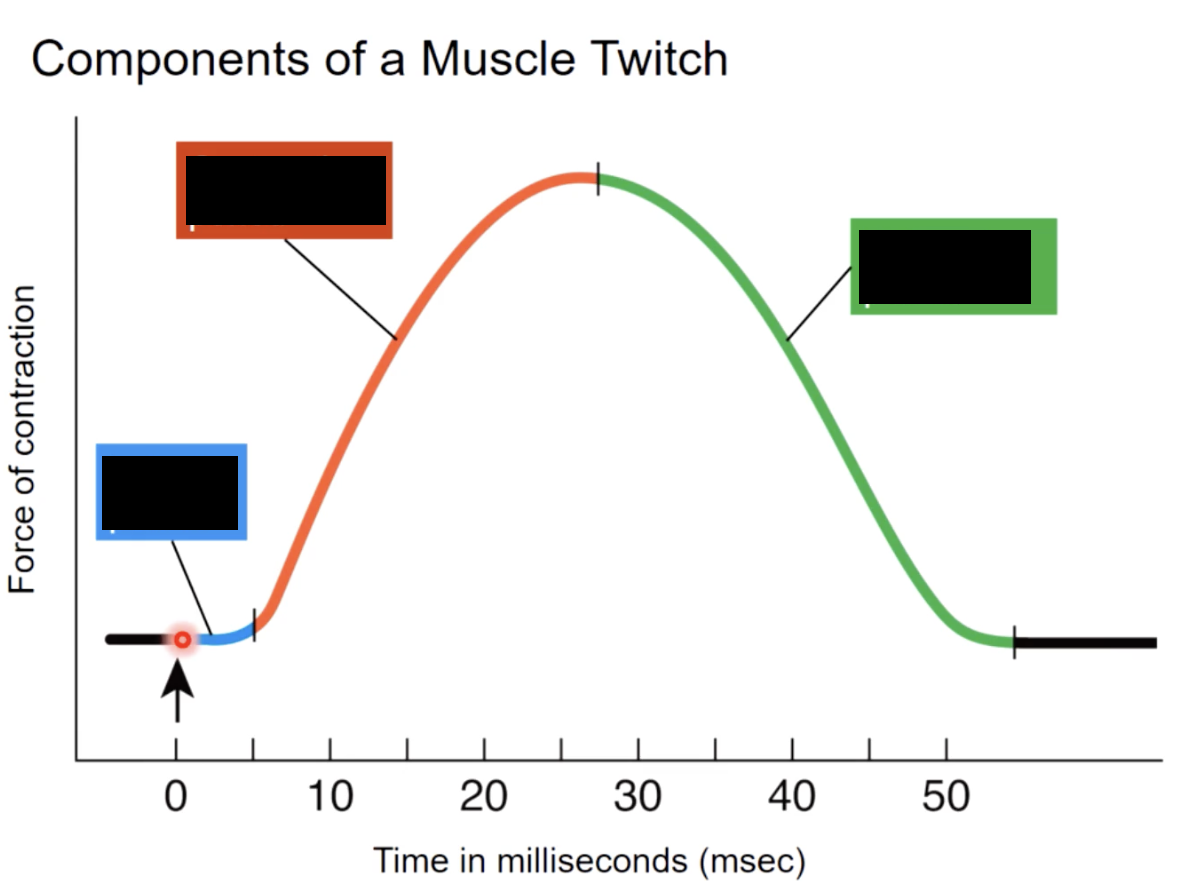
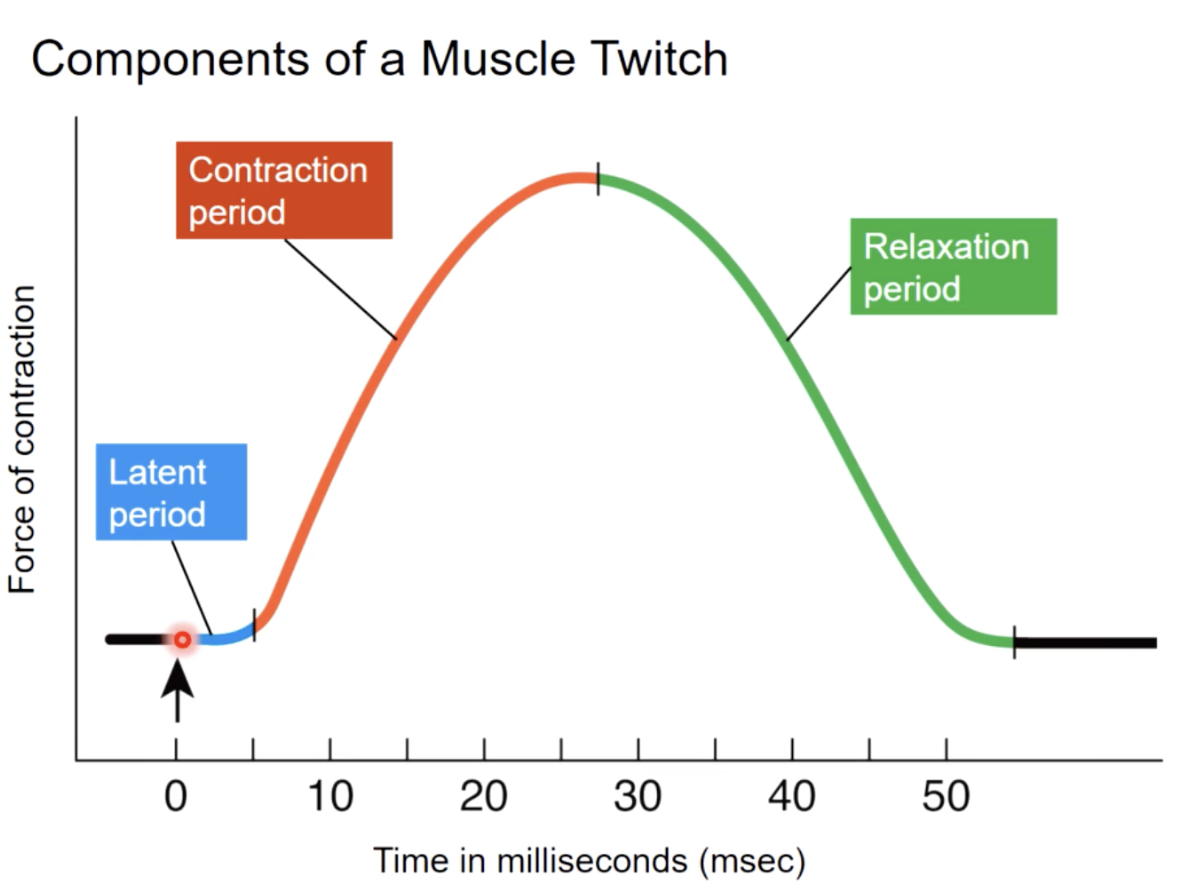
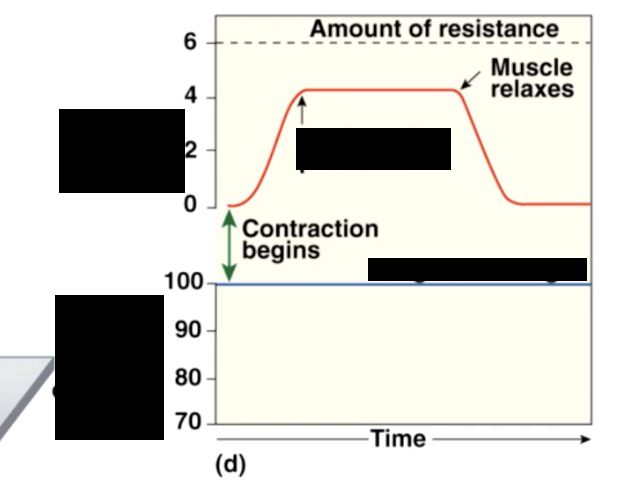
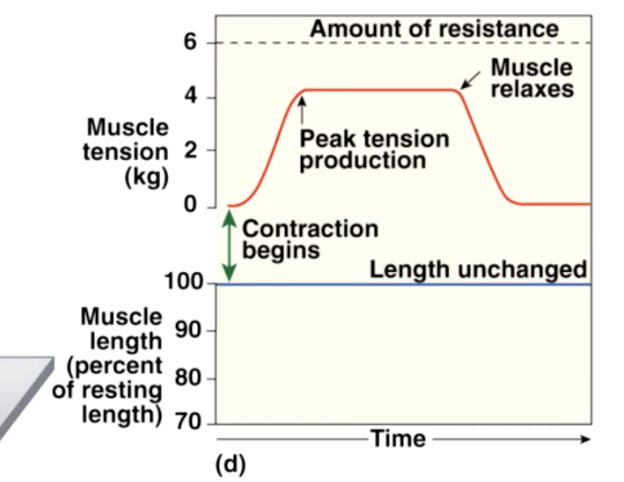
tension
active (shortening) force exerted by a muscle when it contracts
to generate useful contractions we must be able to vary the amount of tension generated when a. muscle contracts
typically a contraction is held for longer than a single twitch
factors that influence the amount of tension developed by each muscle cell
1- length of the cell at the time of contraction
2- frequency of stimulation
how does the length of muscle influence the amount of tension developed by each muscle cell
it’s the degree of stretch when the body is in a resting position : degree of overlap between thick and thin filaments
we can alter the degree of stretch by holding the muscle so that muscle fibers are stretched to a length that is close to “ideal” before they are stimulated to contract
effects of over stretching/compressing the cell
overstretching - reduces the zone overlap and # of cross bridge interactions
over compressing - reduces the zone of overlap and # of cross bridge interactions
in both cases the amount of tension possible is reduced
how does the frequency of stimulation influence the amount of tension developed by each muscle cell
increased frequency of stimulation —> increased tension
1) treppe
subsequent twitches have increased tension
cause - gradual increase in Ca + ions in sarcoplasm, becasue SR ion pumps dont. have time to capture the Ca ions in between stimuli
2) wave stimulation
muscle cell stimulated a seccond time before relaxation phase is complete
result - wave stimulation; muscle is never allowed to relax completely, and tension rises until it is roughly 4x the maximum produced by the treppe
stimulus frequency >50/second
3) Complete/Unfused tetanus
cell stimulated repeatedly and periods of relaxation are very brief and muscle reaches a submaximal tension
4) complete/fused tetanus
cell stimulated a high frequency no relaxation between stimuli and all cross bridges form, so muscle reaches max tension
cause of 3 AND 4 - Ca levels rise in sarcoplasm as SR ion pumps dont have time to recapture Ca between stimulation
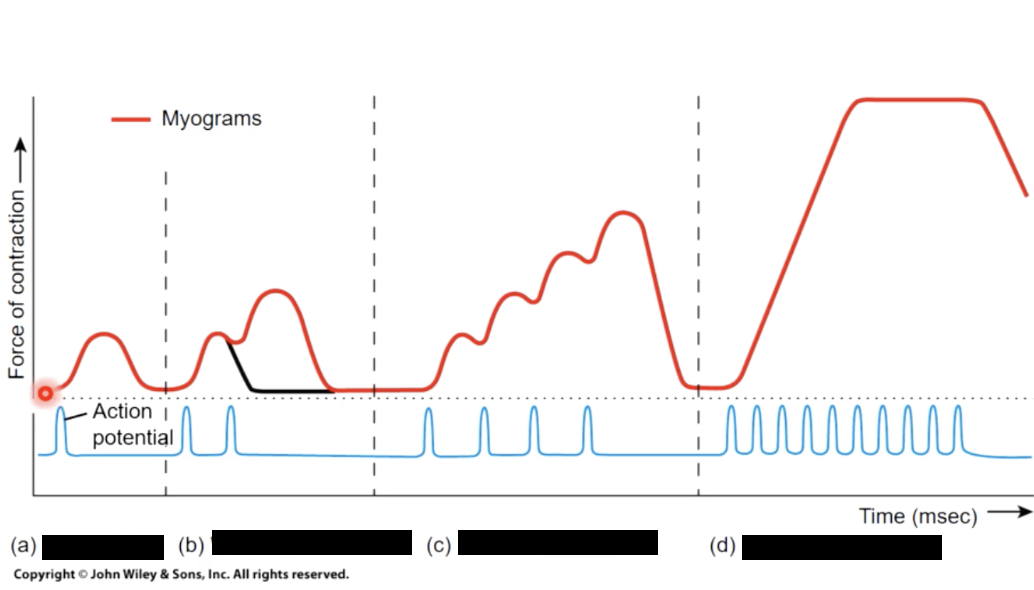
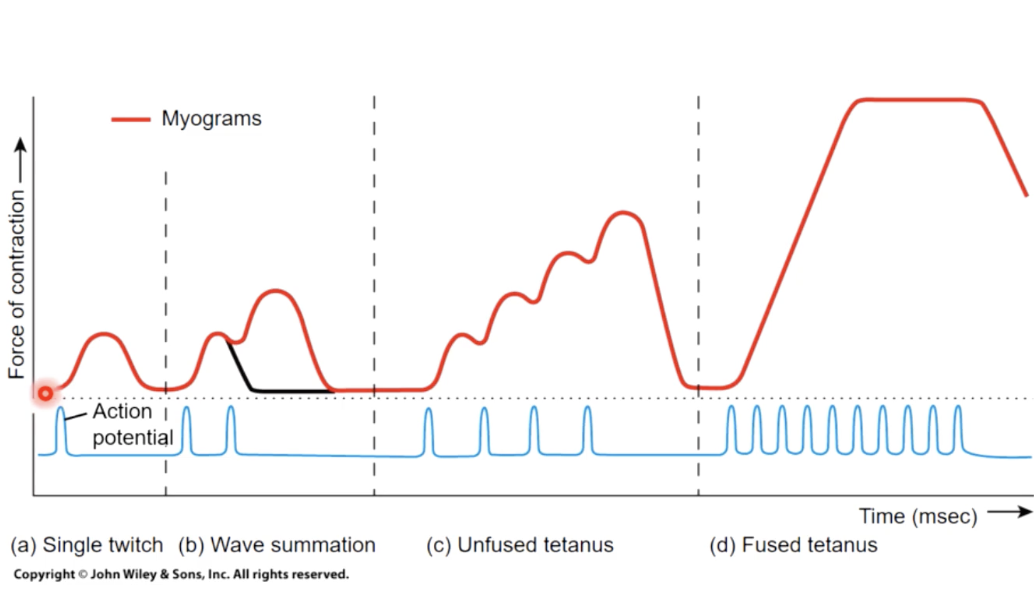
tension produced by the muscle depends on
1 - tension generated by individual muscle cells activated depends on
a) tendons resting length when stimulated
b) degree of overlap between thick and thin filaments
c) frequency of stimulation
2 - number of cells in stimulated muscle
3 - number of contractile proteins (myofibrils) in each stimulated muscle cell (differences between slow, intermediate and fast twitch muscle fibers
motor unit
all the muscle fibers controlled by a single motor neuron
number of cell varies from a few to 1000s
how would the nervous system increase muscle tension
the nervous system can activate more motor units - recruitment
sequence of recruitment
a) smallest motor unit containing fewest an slowest muscle fibers
b) larger motor units containing faster and more powerful muscle
c) peak tension production when all motor units are in a state of complete tetanus
asynchronous motor unit
at slightly less than maximal tension because motor units are activated on a rotating basis
func - limited energy reserves make it necessary for motor units to rest and recover.
This is done on a rotating basis to allow for simultaneous recovery and sustained contraction
*asynchronous motor unit summation
muscle tone
slight level of contraction in muscles that are at rest
caused by - in any skeletal muscle, some motor units are always active
func - does not generate active movement, but tenses and firms the muscle to maintain/stabilize bone positions and also absorb sudden bumps/shocks
heightened muscle tone
accelerates the recruitment process, because some motor units are already stimulated
Isotonic Muscle Contractions
muscle length changes
a) concentric contractions
peak muscle tension exceeds resistance —> muscle shortens
b) eccentric contractions
peak muscle tension less than load —> muscle elongates
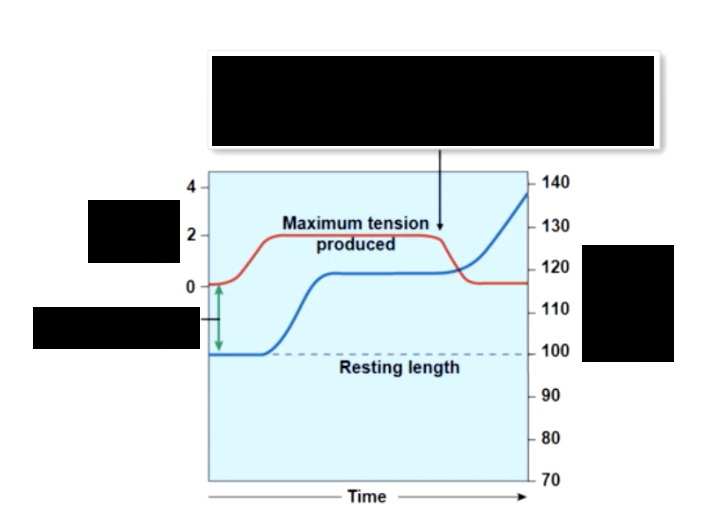
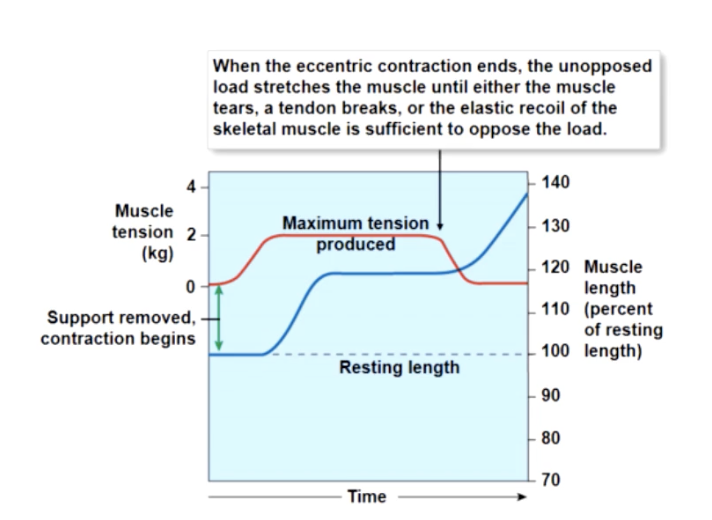
isometric contrations
tension does not overcome resistance
no change in length of muscle
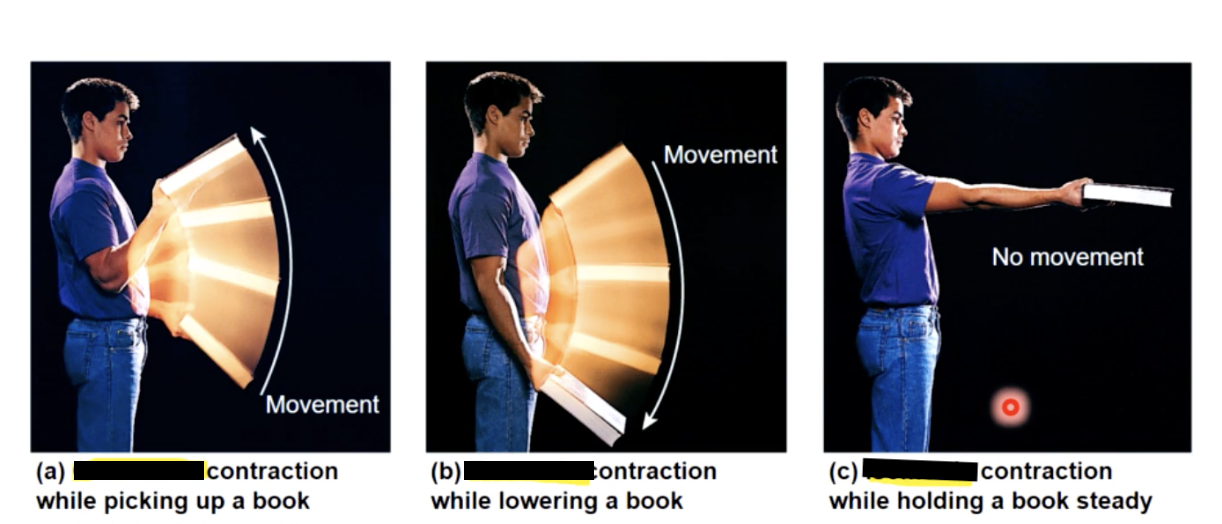
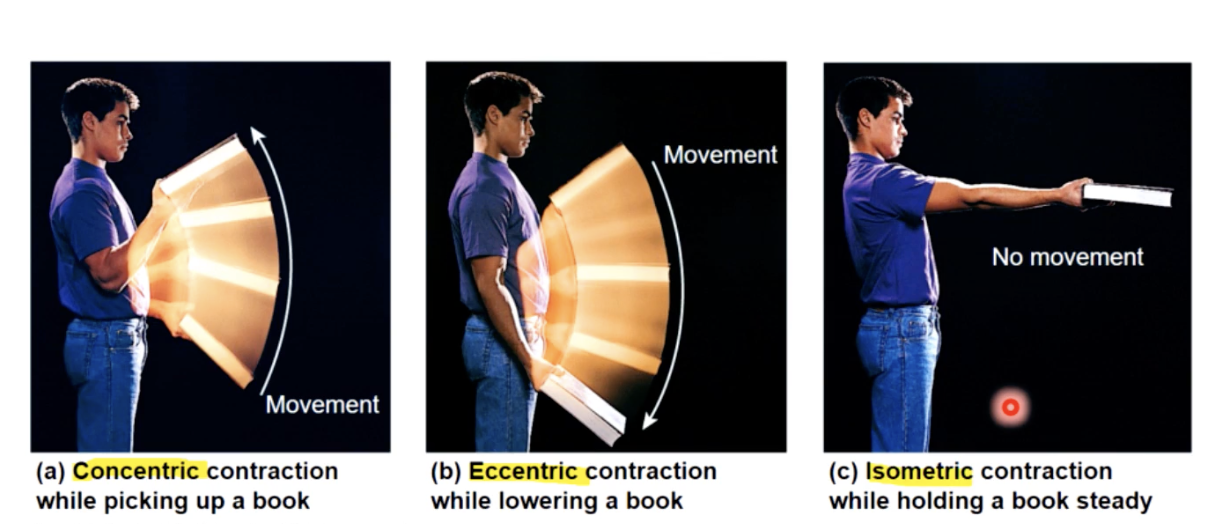
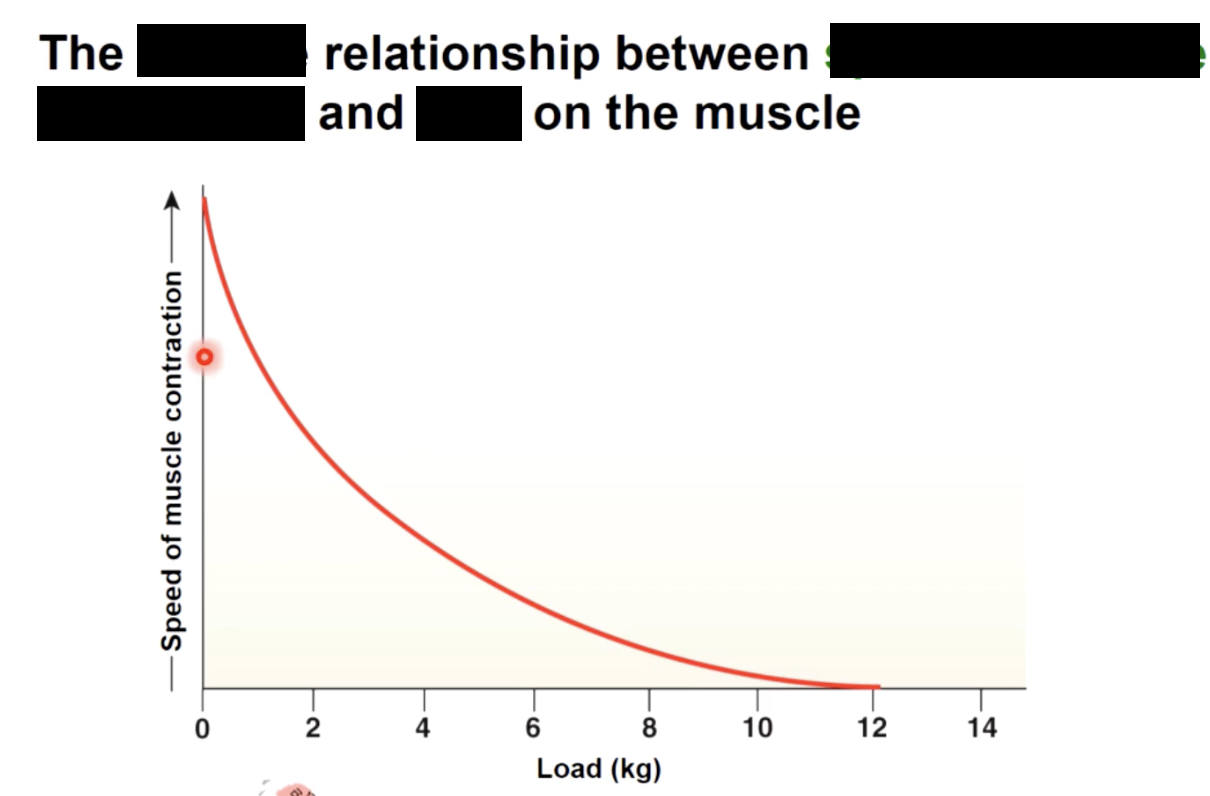
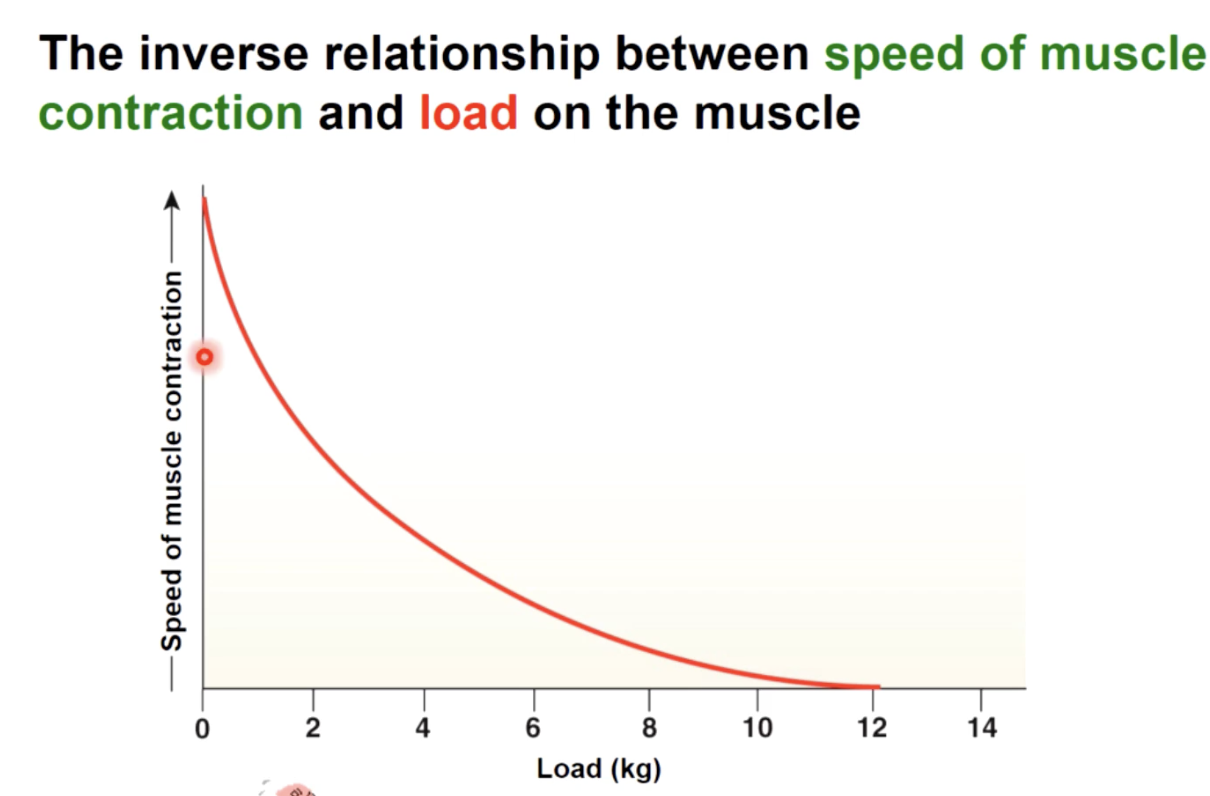
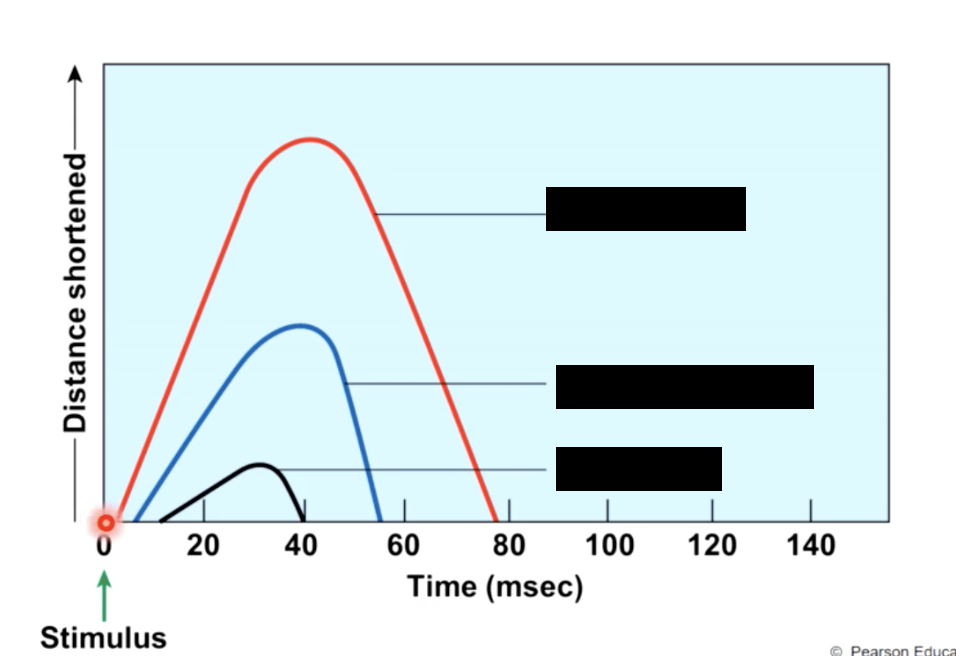
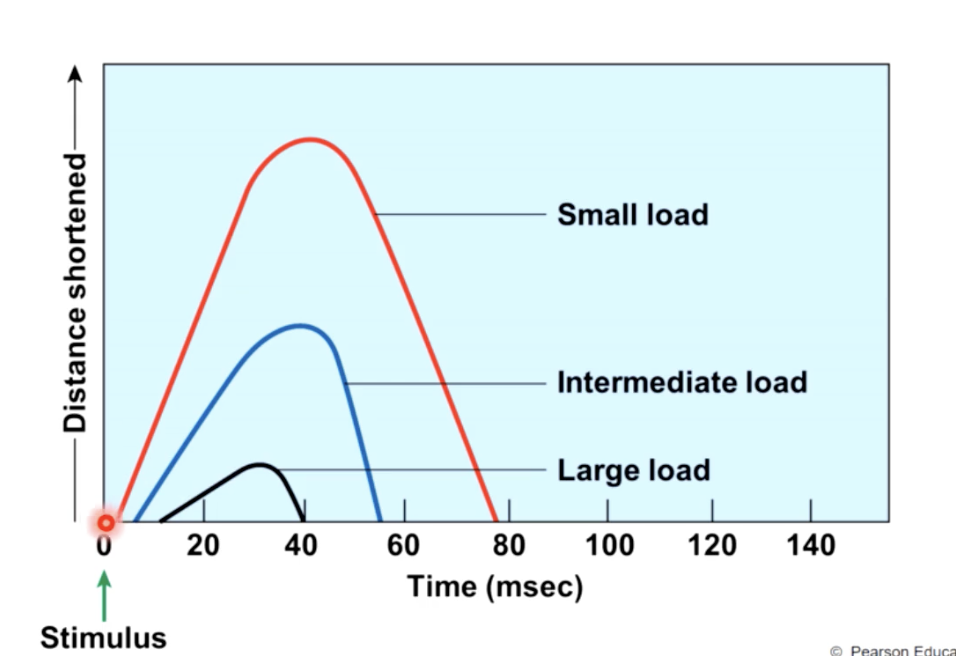
as load increases
the slower the start of contraction, the slower the speed of contraction and the more tension produces.
A concentric contraction occurs and the muscle will shorten
muscle relaxation
muscles cannot lengthen actively
a) ELASTIC FORCES
Some of the energy spent stretching tendons and organelles is recovered as they recoil
b) Opposing muscle contractions
contraction of opposing muscles, return a muscle to resting length quicker than elastic forces can
c) gravity
may assist (relaxing biceps, involves pulling forearm downward)
some active tension will be required however, to controlthe rate of movement & prevent damage to joints
polio
attacks neurons in the spinal cord and brain.
what happens?-motor neurons die and can no longer stimulate myofibers resulting in muscular atrophy (reduction in muscle size) and flaccid paralysis
Tetanus
suppresses the inhibition of motor neuron activity
what happens - a bacterium, clostridium tetani releases a toxin, tetanospasm, that block inhibitory neurotransmitters glycine and GABA - causing inappropriate activation of motor neurons and thus sustained muscle contractions, “spastic paralysis”
Botulism and Myasthenia gravis
affect neuromuscular communication
what happens. - in botulism, a bacterium clostridium botulinum releases a toxin that blocks the release of neurotransmitter ACh receptors resulting in muscle weakness in many regions of the body
without adequate ATP
calcium ions remain in cytosol and cross bridges cannot detach, causing muscle fibers to lock in contracted state.
This happens when muscle cells are deprived of O2 and nutrients causing sustained contraction
(the cause of rigor mortis after death - which lasts a few days until decomposition begins)
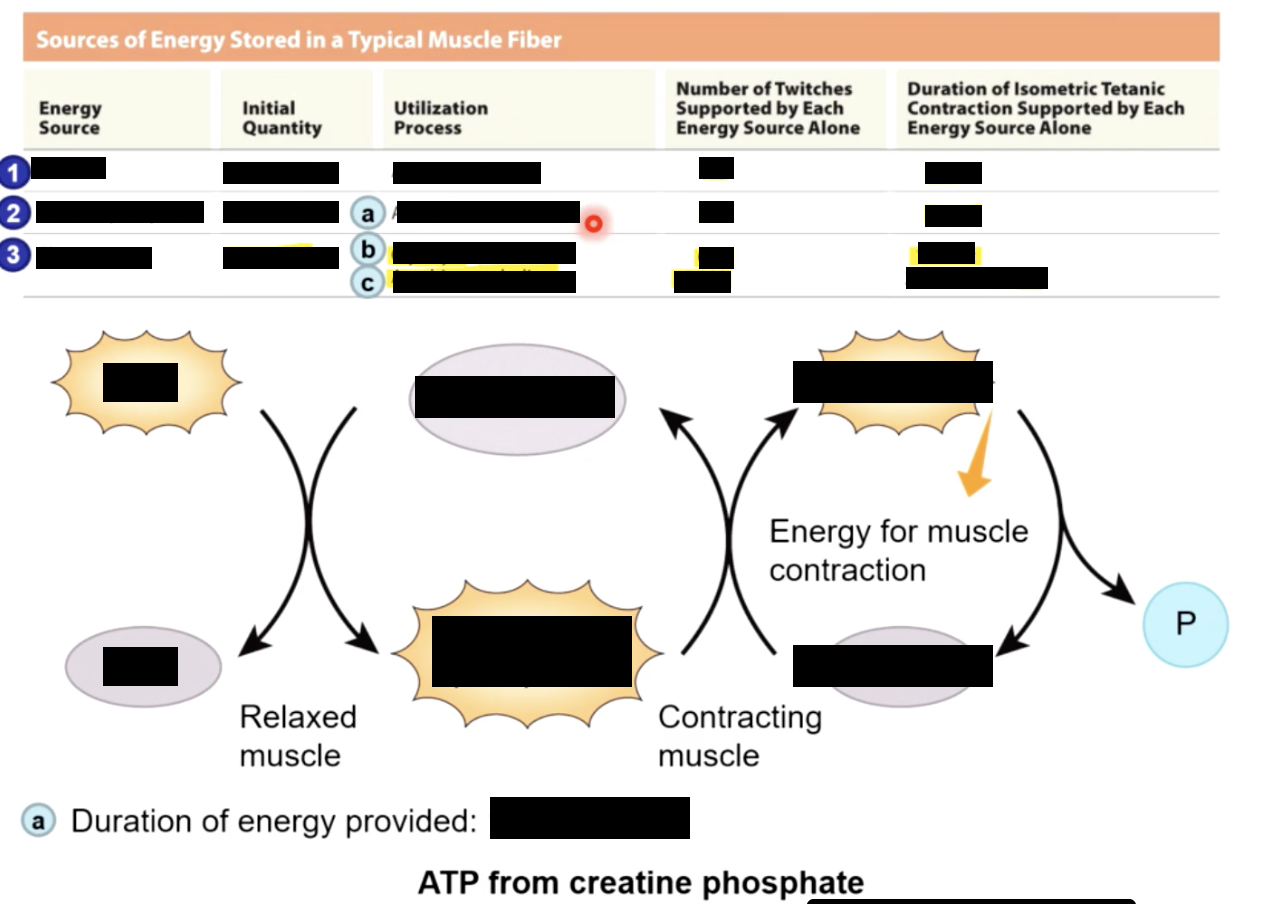
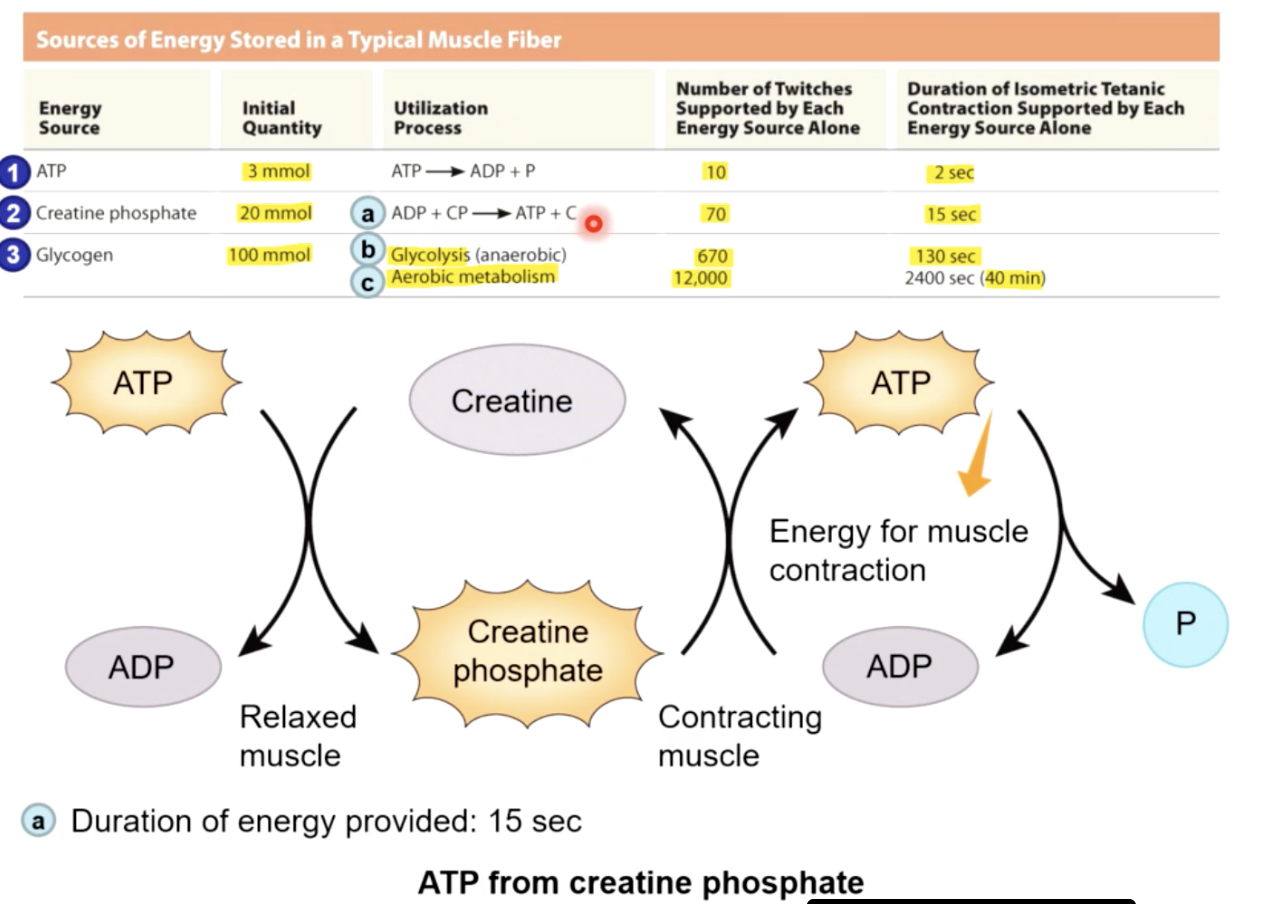
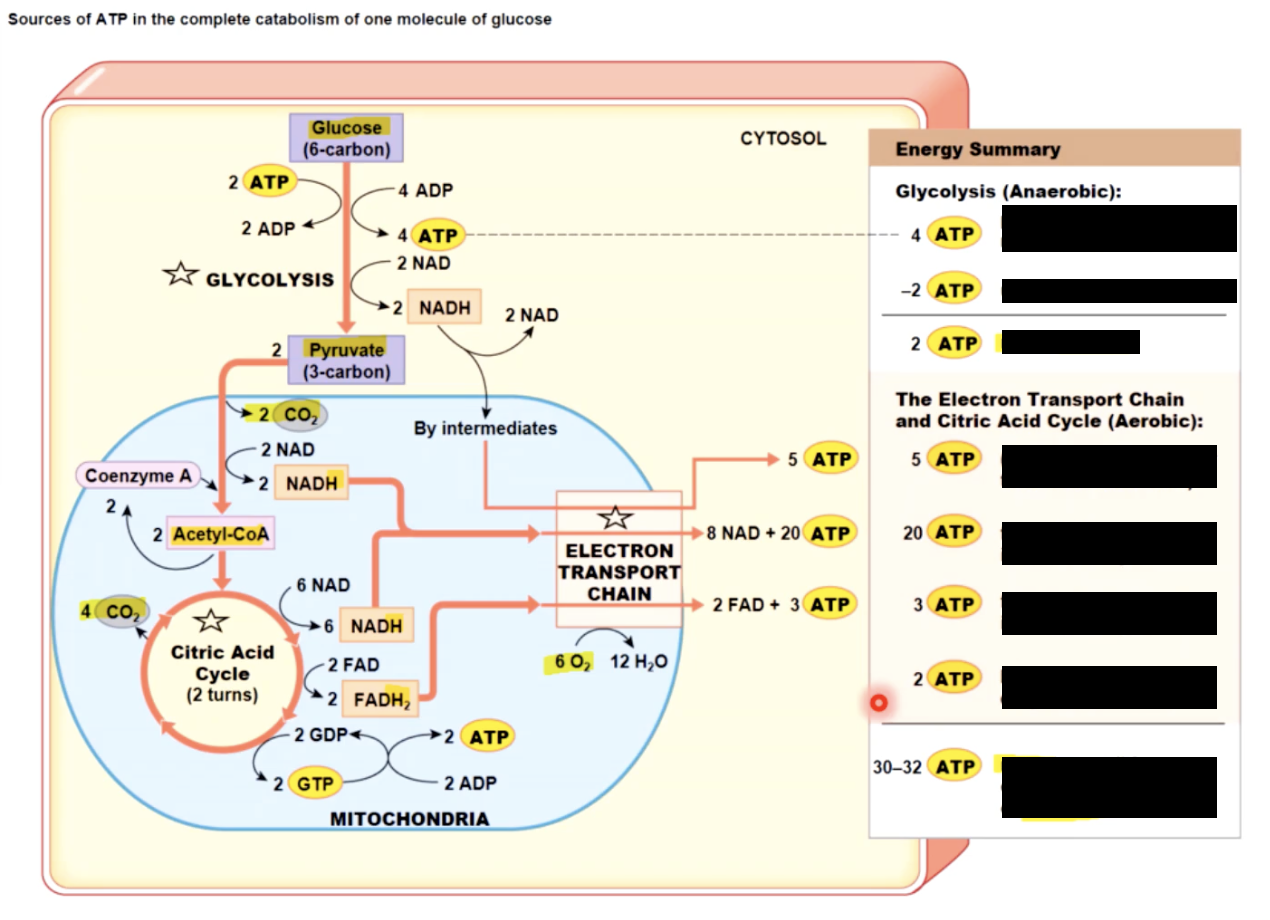
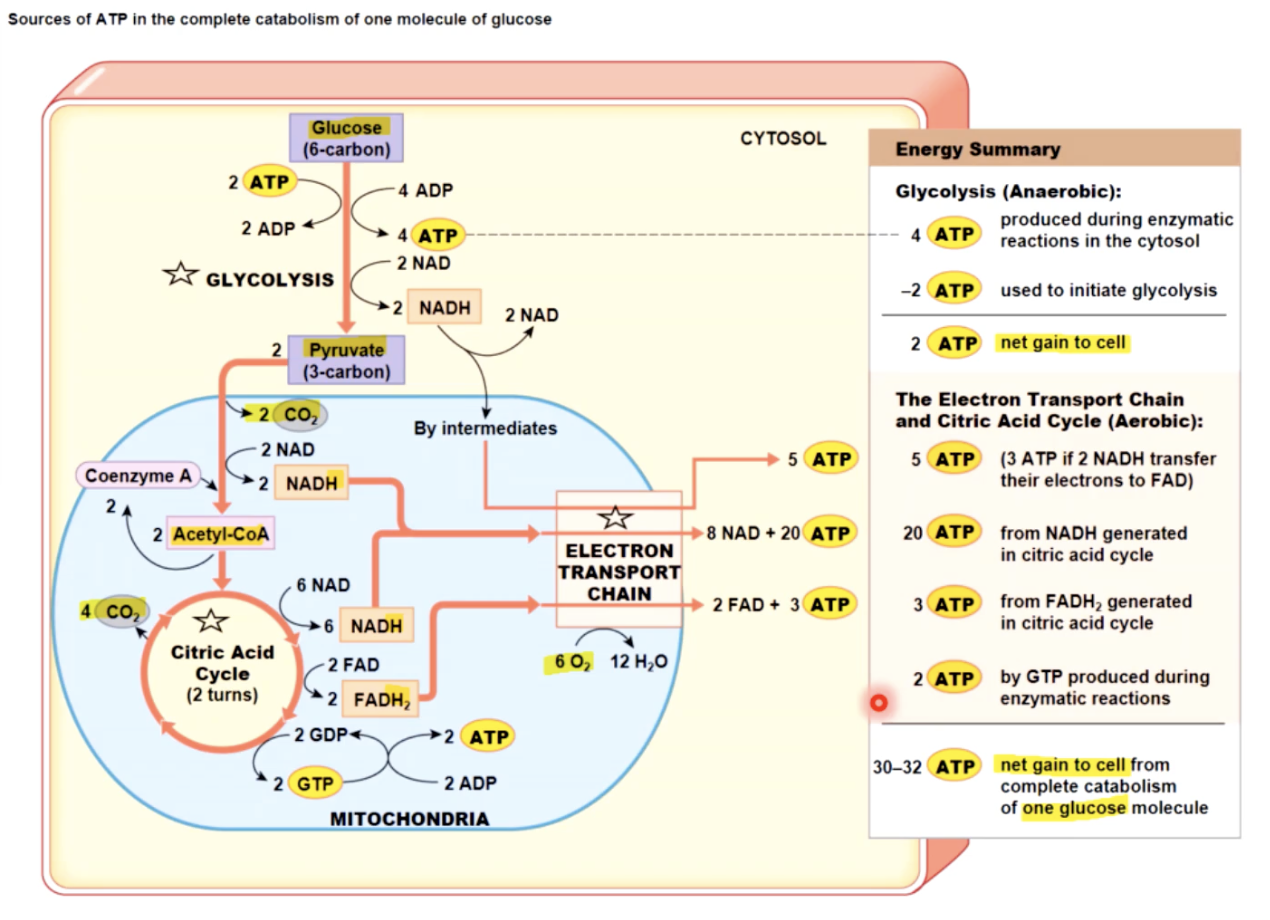
Muscle’s energy
sources of ATP
1- STORED in muscle fiberes before contraction begins as: 3mmol ATP, 20mmol CP (creatine phosphate) and 100mmol glycogen
2 - GENERATED in 3 ways in muscle cell:
Generated ATP in Muscle Cell (3 ways)
1) direct phosphorylation ADP by creatine phosphate:
CP + ADP ←→ Creatine + ATP
←→ - CPK (Creatine PhosphoKinase)
at rest - skeletal fiber produces more ATP & CP than it needs
as ATP is used - more atp is made through:
2) aerobic metabolism & 3) anaerobic metabolism
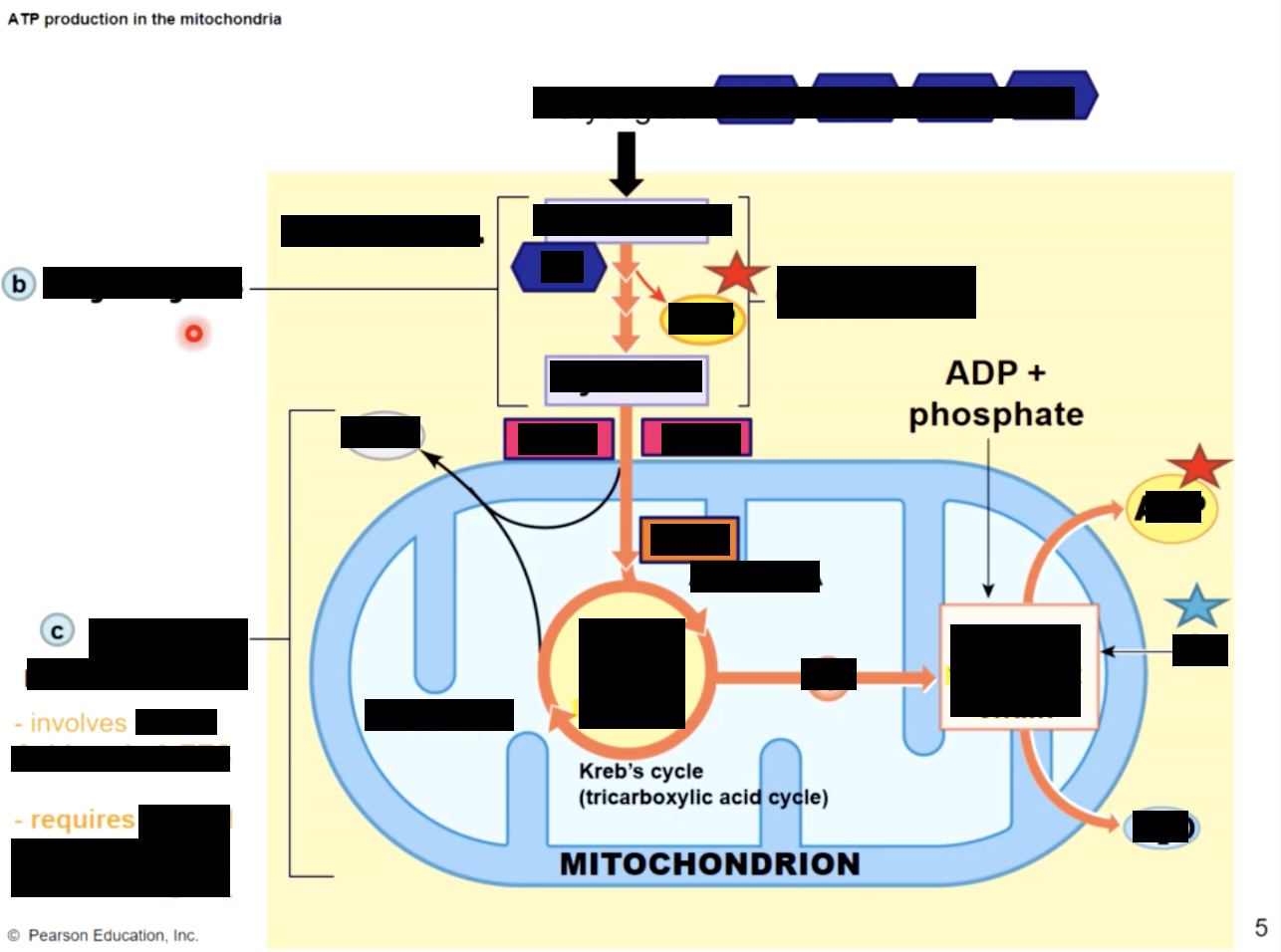
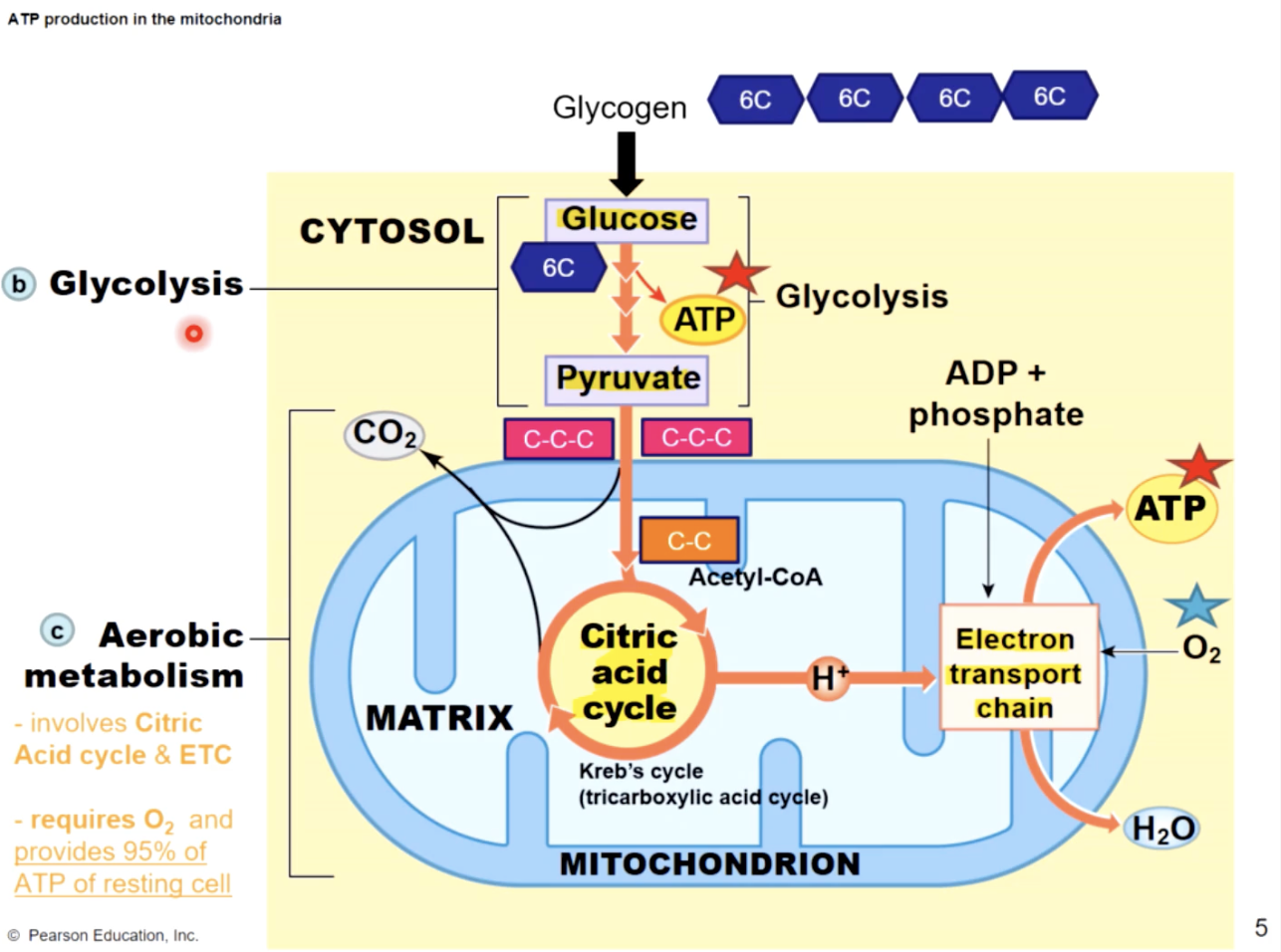

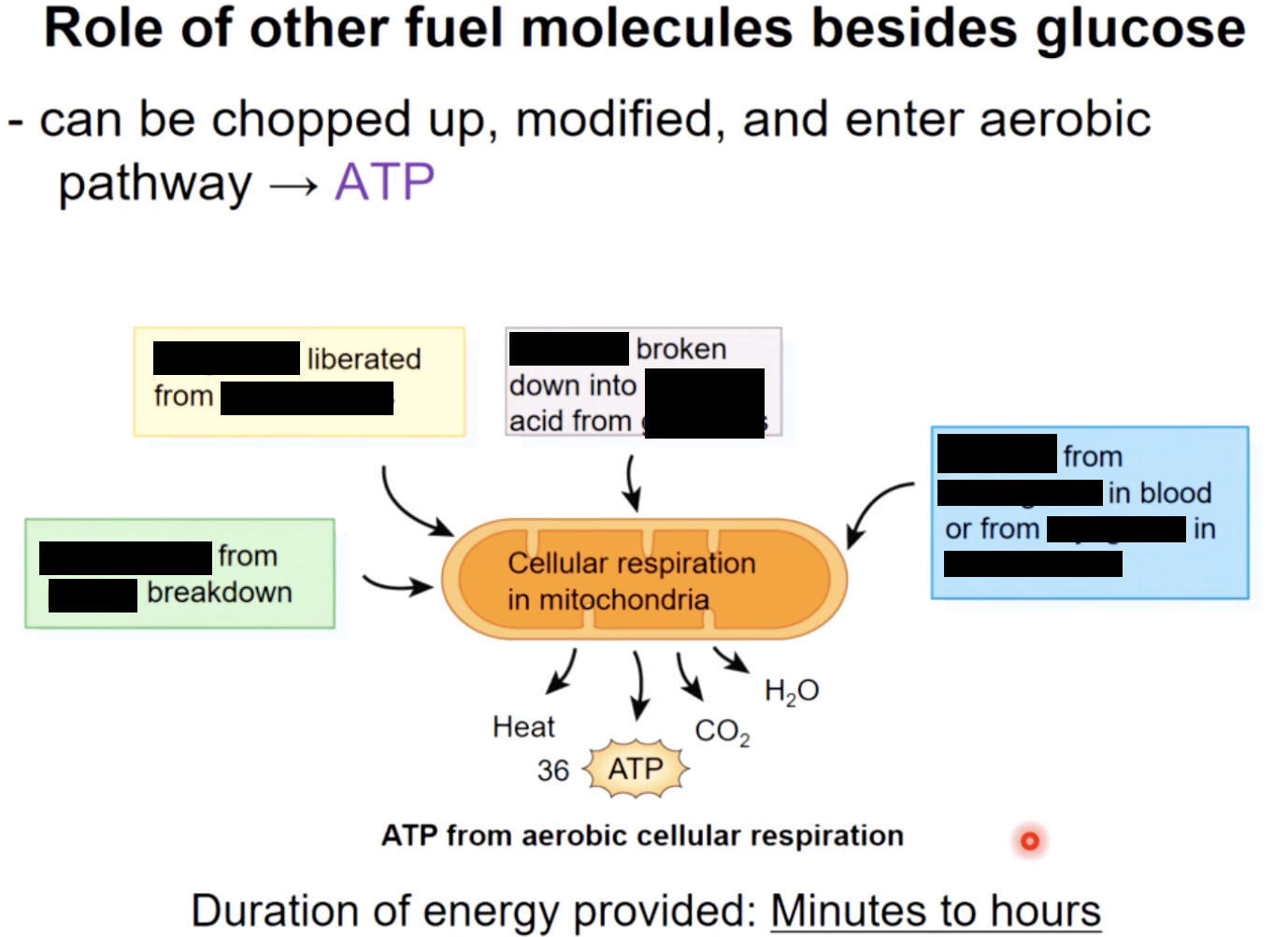
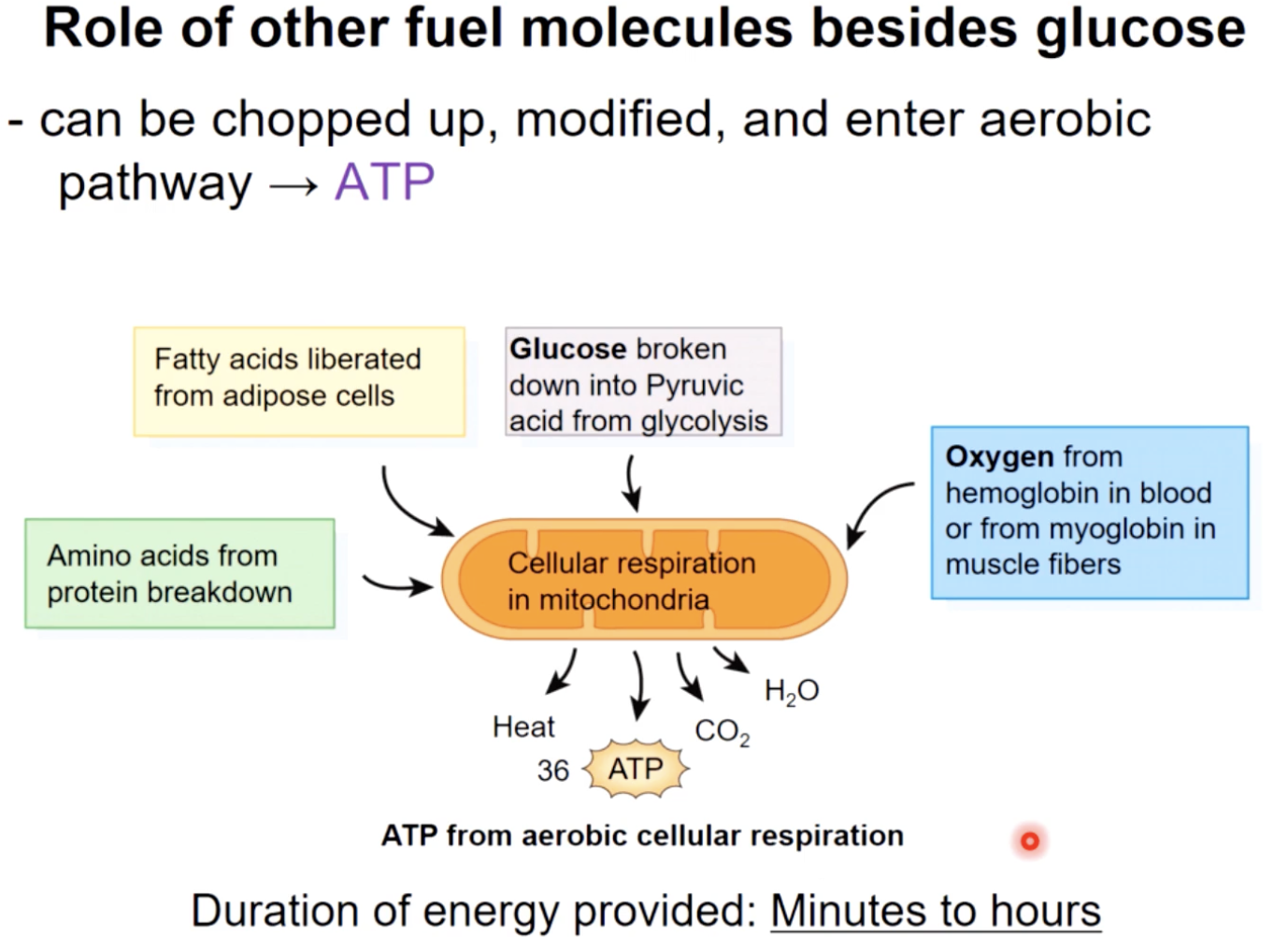
what to do in the absence of O2
anaerobic respiration : glycolysis followed by lactic acid production (can’t do krebs or ETC without O2
anaerobic respiration has limits-
lowered pH will disable key enzymes necessary for contraction and decrease Ca+ binding to troponin
debleation of metabolic reserves within muscle fibers
damage to sarcolemma and SR
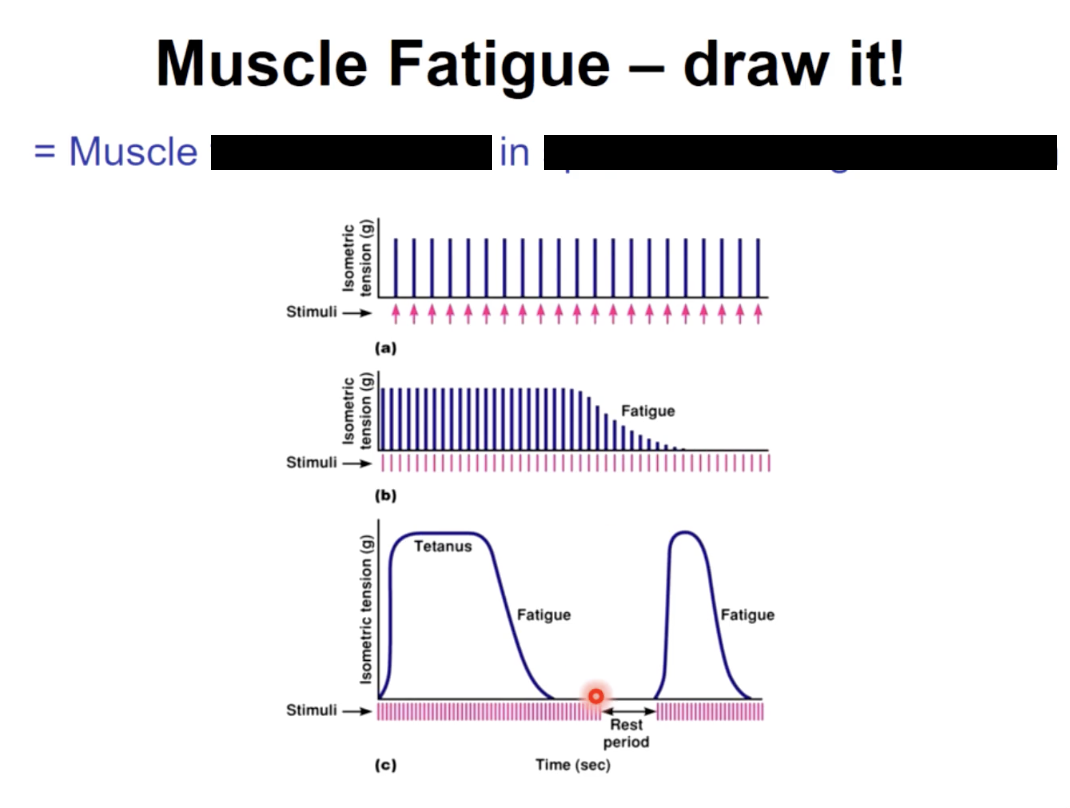
Muscle fatigue
advantages of aerobic respiration over anaerobic
1 - produces 32 ATP/glucose molecule instead of just 2
2- no lactic acid produced
limiting factors of aerobic respiration
-availblability of O2 that can diffuse into muscle fiber
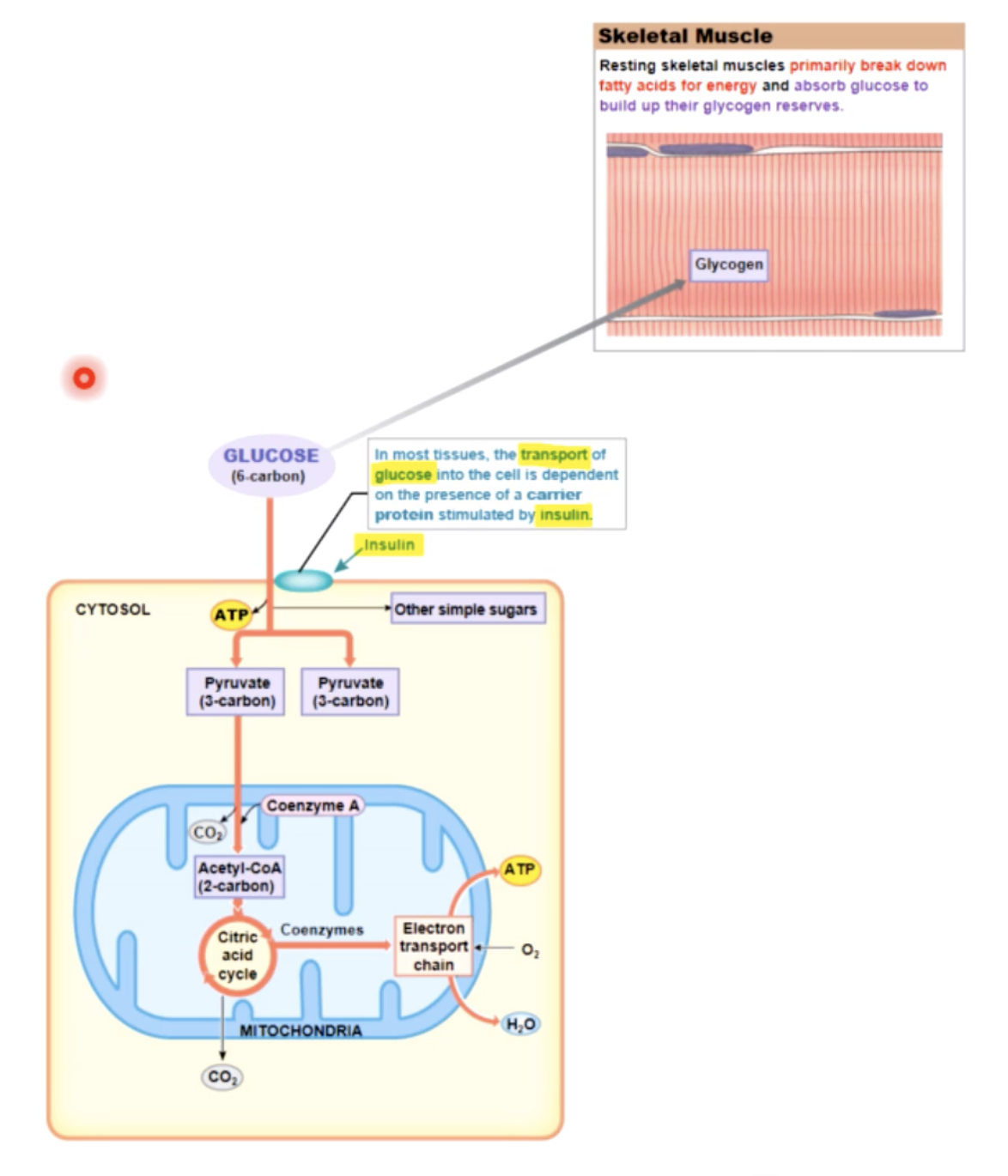
energy use of muscular activity - at rest
mostly fatty acids (& some glucose) used as fuel to generate ATP (aerobic resp) ATP used to build reserves of CP and glycogen
resting - fatty acids are catabolized; the ATP produced is used to build energy reserves of ATP,CP, and glycogen
energy use of muscular activity - moderate activity
glucose and fatty acids used as fuel in aerobic respiration —> 32 molecules of ATP/molecule of glucose
energy use of muscular activity - peak activity
most (2/3) ATP produced through glycolysis (anaerobic resp)
some ATP via CP catalysis to creatine
buildup of H+ ions leads to fatigue once sarcoplasm buffer system reaches its limit (enzymes become less functional)
when blood pH drops = metabolic acidosis (or lactic acidosis)
peak - most ATP is produced through glycolysis, with lactic acid as a by product.
Mitochondrial activity now provides only about one-third of the ATP consumed
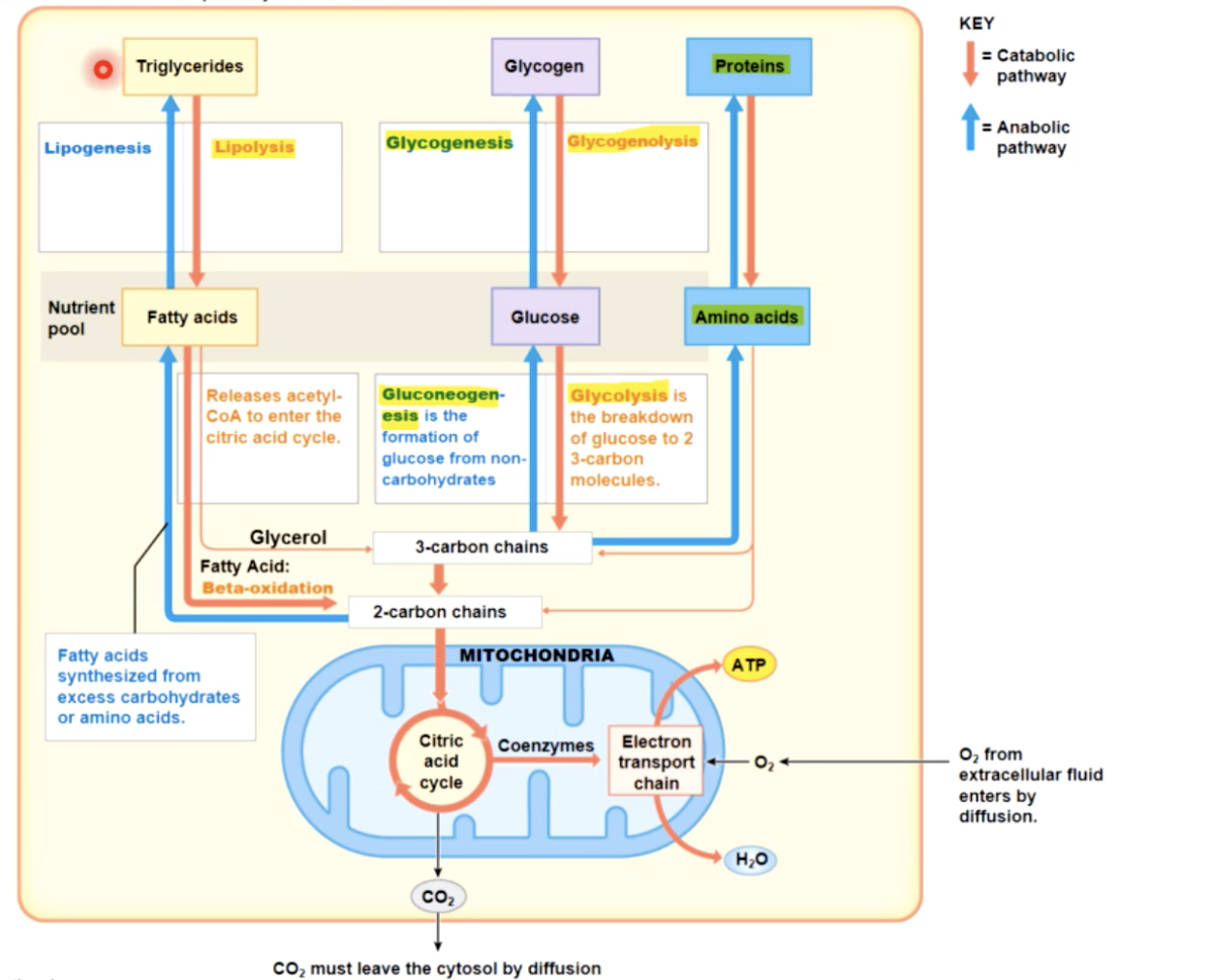
glycolysis
enables a skeletal muscle to continue contracting even when insufficient oxygen is available
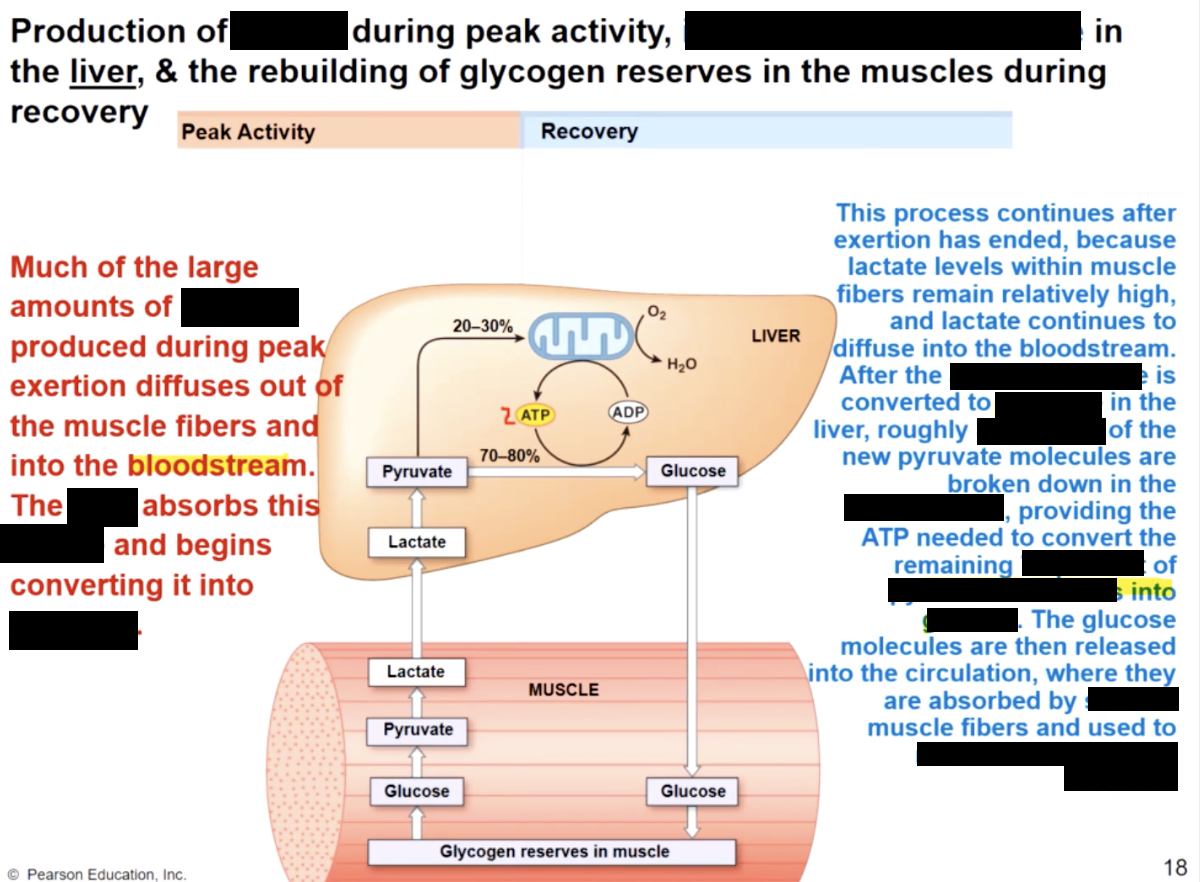
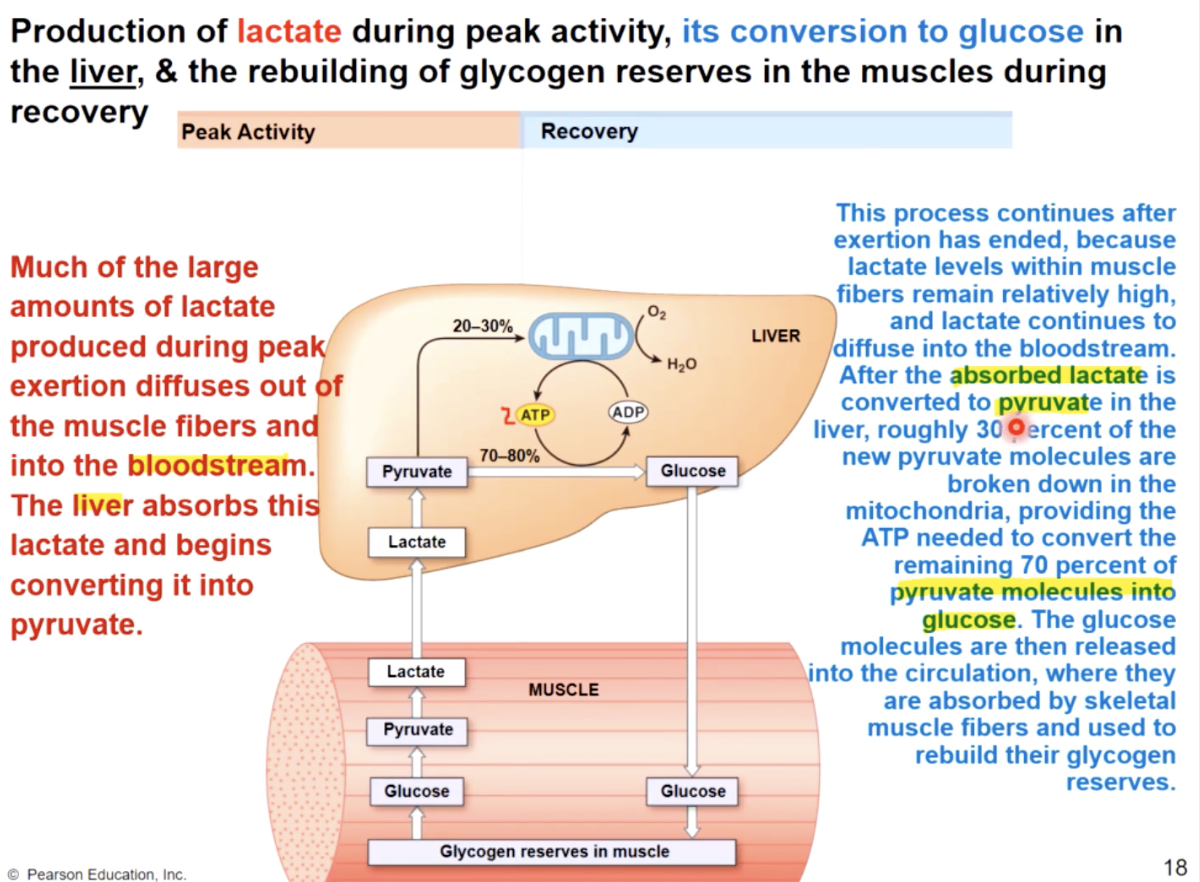
post exercise recovery processes
remove lactic acid from muscle & convert to pyruvic acid in liver;
remove ATP, CP, & glycogen reserves in muscle
the oxygen debt
the above processes all require ATP
generated by aerobic respiration
requires O2 above resting rates
O2 debt
the amount of O2 required to restore normal, pre exersion conditions (restore ATP,CP and glycogen reserves) and convert lactic acid to pyruvic acid or glucose
what happens at rest
85% of heat needed to maintain body temp, is produced by skeletal muscles
during aerobic respiration, 58% of released energy warms sarcoplasmm, interstitial fluid and circulating blood
as a consequence - during exercize, body temperature starts to rise, and anaerobic respiration releases 70% of energy as heat. Heat loss is accelerated at the skin level to compensate
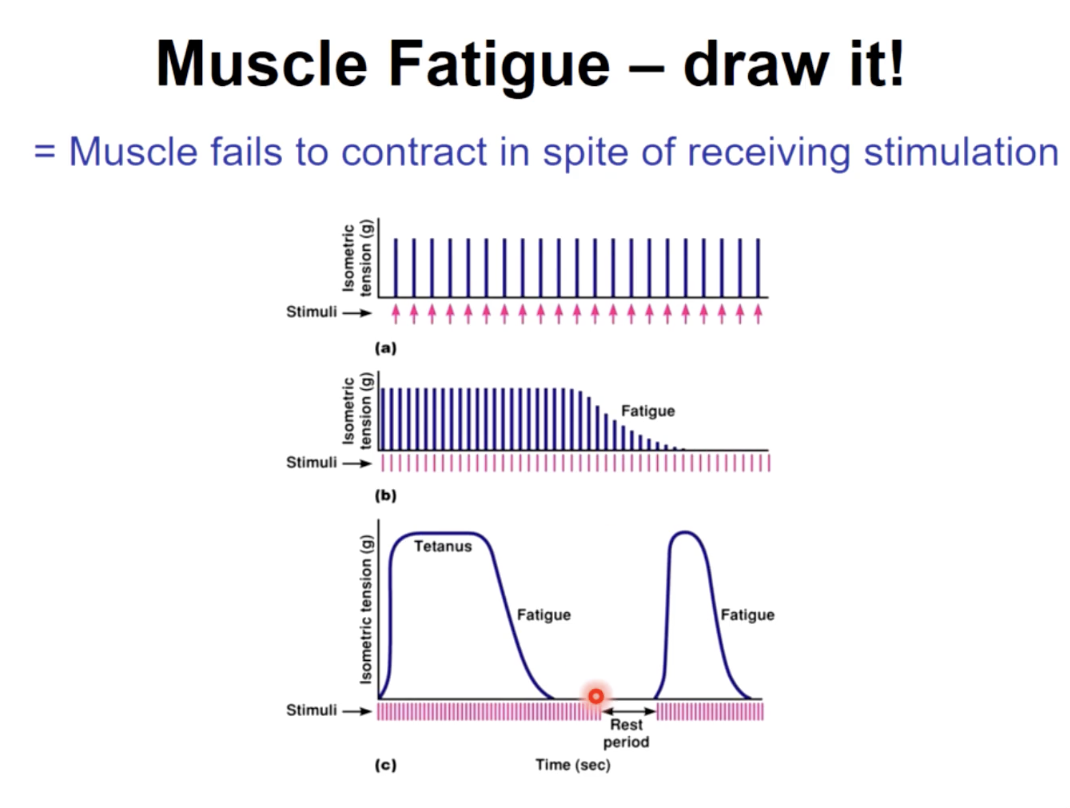
psychological fatigue
the desire to discontinue the activity due to the effect of low blood pH & feelings of pain on the brain
causes of actual muscle fatigue & soreness
not well understood
depletion of glycogen, lipid and amino acid reserves
accumulation of lactic acid and other metabolites
causes of muscle soreness (DOMS)
small damage that will be repaired
classification of skeletal muscle
based on 2 criteria
1 - speed of contraction : fast, intermediate, slow
result of differences in number of myofibrils, glycogen reserves & number of mitochondria between fast & slow fibers
2- major pathways used to form ATP
anaerobic or aerobic respiration
based on these 2 factors there are 3 types of skeletal muscle cells
3 types of skeletal muscle cells
slow oxidative (slow fibers) = tyoe I
fast oxidative (intermediate fibers) = type IIa
fast oxidative (intermediate fibers) = type IIb