Organic Chemistry GCSE aqa triple higher
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
What is a hydrocarbon
compound formed from only carbon and hydrogen atoms
general formula of alkanes
C(n)H(2n+2)
What is a homologous series?
a group of organic compounds that react in a similar way
Why are alkanes staurated compounds?
each carbon has four single convalent bonds
What are the first four alkanes?
methane; ethane; propane; butane
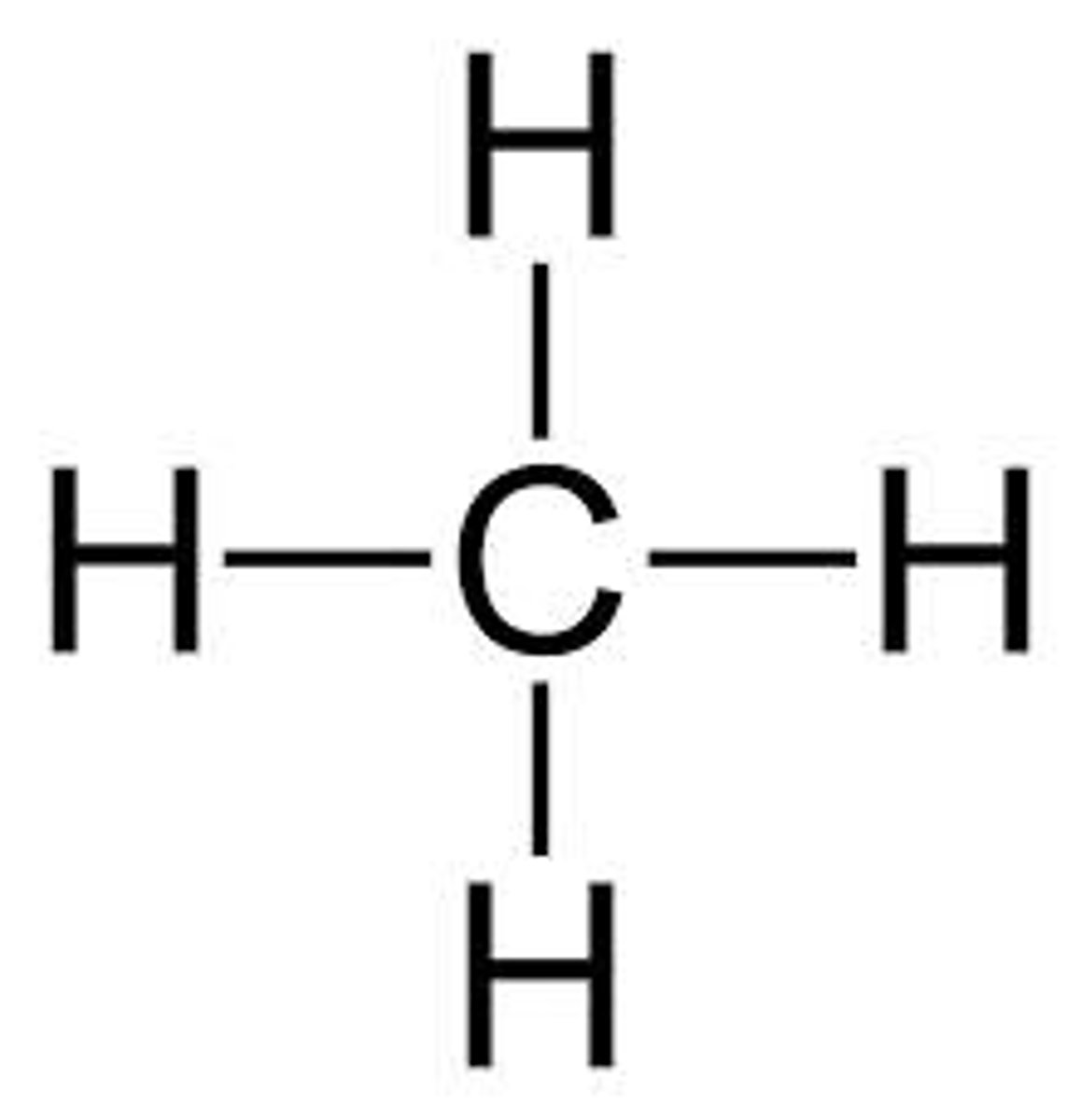
What is this the displayed formula for?
methane
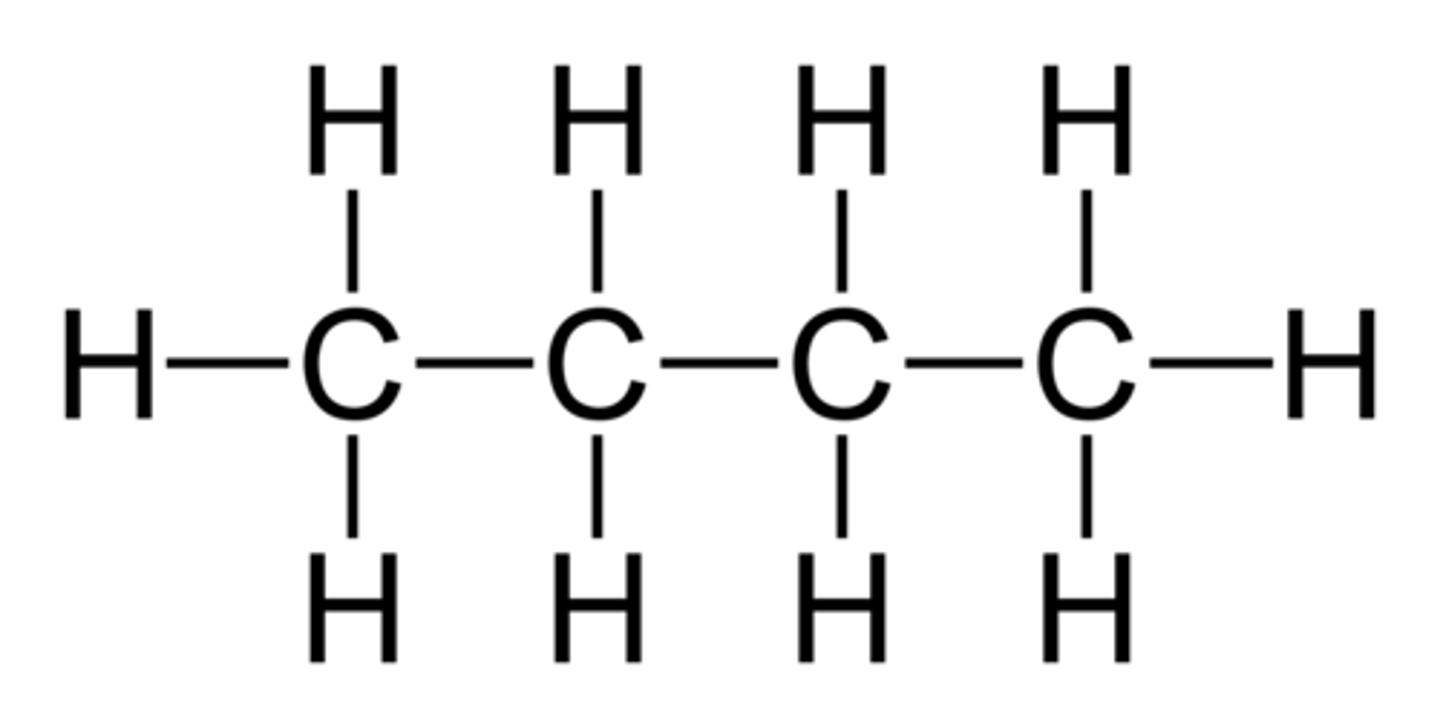
What is this the displayed formula for?
butane
What does a shorter carbon chain in a hydrocarbon mean?
less viscous; more volatile; more flammable
What does it mean if a substance is more volatile?
lower boiling point
Complete combustion of any hydrocarbon in oxygen releases lots of energy. What is the equation to show the complete combustion of any hydrocarbon in oxygen
hydrocarbon + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
What are the waste products of the complete combustion of any hydrocarbon in oxygen
carbon dioxide; water vapour
What two things from the complete combustion of any hydrocarbon in oxygen are oxidised?
carbon; hydrogen
Why are hydrocarbons used as fuels?
release large amount of energy when they combust completely
List the hydrocarbons fractions in fractional distillation from the top to the bottom
LPG; gasoline (petrol); naptha; kerosine; diesel; lubricating oil; fuel oil; bitumen
What hydrocarbon fraction has the longest carbon chain?
bitumen
What fuels from crude oil power most modern transport?
diesel oil; kerosene; heavy oil fuel; LPG
What are organic compounds?
compounds containing carbon atoms
Why are short-chain hydrocarbons in high demand?
more flammable- make good fuels
What is the process wherein longer alkane molecules are turned into smaller ones?
cracking
Cracking is a thermal decomposition reaction. What is thermal decomposition?
breaking molecules down by heating them
give steps of catalytic cracking
1 Heat long-chain hydrocarbon to vaporise them
2 Vapour is passed over hot powered aluminium oxide catalyst
3 Long-chain molecules split apart on the surface of the specks of the catalysts
give steps of steam cracking
1 Heat long-chain hydrocarbons to voprise them
3 Mix them with steam
4 Heat them to a v high temperature
Alkanes are a group of organic compounds that react in a similar way? What does mean they are?
a homologous series
What is a substance more of if they have a lower boiling point?
more volatile
What are most of the hydrocarbons that makeup crude oil?
alkanes
With what method are the different compounds in crude oil separated?
fractional distillation
Describe the fractional distillation of crude oil
1 oil heated (about 370 °)until most of it is gas; gas enter a fractionating column, and the liquid is drained off
2 in the fractionating column, there's a temperature gradient (it's hot at the bottom and gets cooler as you go up)
3 longer hydrocarbons have high boiling points- they condense back into liquids and drain out of the column early on, near the bottom. Shorter hydrocarbons have lower boiling points- condense and drain out later, near the top of the column where it's cooler
4 crude oil mixture separated into different fractions; each fraction contains a mixture of hydrocarbons that all contain a similar number of carbon atoms, so have similar boiling points
Describe the temperature gradient of a fractionating column
it's hot at the bottom and gets cooler as you go up
Why do longer hydrocarbons condense back into liquids and drain out of the column early on, near the bottom?
high boiling points and fractionating column is hottest at the bottom, getting cooler as you go up
Where in the fractionating column do longer hydrocarbons condense back into liquids and drain out of the column?
bottom; it's hottest at the bottom, getting cooler as you go up and longer hydrocarbons have high boiling points
Why do the fractions of fractional distillation of crude oil have similar boiling points?
each fraction contains a mixture of hydrocarbons that all contain a similar number of carbon atoms,
Petrol drains further up a fractionating column than diesel. What does this suggest about the boiling points of the hydrocarbons which make up petrol compared to those in diesel?
hydrocarbons that make up petrol have lower boiling point than those in diesel
What does the petrochemical industry use some of the hydrocarbons from crude oil?
feedstock to make new compounds in things like polymers, solvents, lubricants, and detergents
Who uses what as feedstock to make new compounds in things like polymers, solvents, lubricants, and detergents?
petrochemical industry; some of the hydrocarbons from crude oil
What does the petrochemical industry use some o the hydrocarbons from crude oil as feed stock to make new compounds in?
polymers, solvents, lubricants, detergents
Why are all the products from crude oil oil examples of organic compounds?
they're all compounds containing carbon atoms
Why is there a large variety of products from crude oil?
carbon atoms can bond together to form different homologous series, and each homologous series contain similar compounds with many properties in common
As well as alkanes, cracking also produces another type of hydrocarbon called what?
alkenes
What are alkenes used as?
starting material when making lots of other compounds and can be used to make polymers
Pentane, C₅H₁₂, can be cracked into ethene, C₂H₄, ad one other hydrocarbon.Give the formula of the other hydrocarbon.
C₃H₈
hydrocarbons that have a double bond between two of the carbon atoms in their chain
alkenes
Why are alkenes far more reactive than alkanes?
the C=C double bond can open to make a single bond, allowing the two carbon atoms to bond with other atoms
list the first four alkenes
ethene, propene, butene, pentene
general formula for alkenes
C(n)H(2n)
What are the products when alkenes combust completely in a large amount of oxygen?
water, carbon dioxide
What is needed for alkenes to combust completely?
a large amount of oxygen
Why do alkenes tend to undergo incomplete combustion?
isn't enough oxygen in the air
What are the products when alkenes undergo incomplete combustion?
carbon, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, water
word equation of alkene undergoing incomplete combustion
alkene + oxygen → carbon + carbon monoxide + carbon dioxide + water (+energy)
What does incomplete combustion of alkene result in?
smoky yellow flame, less energy
Two products which are produced during incomplete combustion of alkene which aren't produced during complete combustion
carbon, carbon monoxide
functional group
a group of atoms in a molecule that determine how that molecule typically reatcs
What is meant by 'alkenes via addition reactions'?
C=C will open up to leave a single bond and a new atom is added to each carbon
Why do alkene react in similar ways?
they have the functional group C=C
hydrogenation
addition of hydrogen
addition of hydrogen
hydrogenation
How do you get alkene to react with hydrogen?
in the presence of a catalyst
How does hydrogen react with an alkene, in the presence of a catalyst?
hydrogen reacts with the doiuble-bonded carbons to open up the double bond and form the equivalent, saturated, 'alkane'
What is needed to form alcohol from an alkene?
steam
Describe how alcohol is formed from an alkene
alkene reacts with steam, water is added across the double bond and an alcohol is formed
How can ethanol be made?
mixing ethene with steam, then passing it over a catalyst
Industrially, how is ethene converted to ethanol?
ethene react with steam, water is added across the double bond: reaction has taken place
reaction mixture is passed from reactor into a condenser
ethanol and water have a higher boiling point than ethene- both condense whilst any unreacted ethene is recycled back into the reactor
alcohol then purified from the mixture by fractional distillation
Describe the addition reaction between halogens (e.g. bromine, chlorine, iodine) and alkenes
molecules formed are saturated, with C+C carbons each becoming bonded to a halogen atom
What do bromine and ethene react to give?
dibromoethane
Why does dibromoethane have the di bit?
there are two bromine atoms
How can the addition of bromine to a double bond be used to test for alkenes?
when orange bromine water is added to a saturated compound (alkanes are saturated compounds) no reactions will happen and it'll stay bright orange.
if orange bromine water is added to an alkene, the bromine will add across the double bond,making a colourless dribromo-compound; the bromine water is decolourised
Sate what colour change occurs when butene reacts with bromine water
after being shaken, orange bromine water goes from bright orange to colourless
long molecules formed when lots of small molecules called monomers join together
polymers
polymers
long molecules formed when lots of small molecules called monomers join together
small molecules that would join together to make polymers
monomers
monomers
small molecules that would join together to make polymers
reactions where monomers join together to form polymers, which usually needs high pressure and a catalyst
polymerisation
polymerisation
reactions where monomers join together to form polymers, which usually needs high pressure and a catalyst
What does polymerisation usually need?
high pressure and a catalyst
Plastics are made up of polymers. What are they usually _based and what are their monomers often?
carbon based, their monomers are often alkenes
What type of bond do monomers that make up addition polymers have?
double covalent bond
Describe addition polymerisation
where lots of unsaturated monomer molecules (alkenes) open up their double bonds and join together to form polymer chains
In addition polymerisation, what do lots of unstaurated monomer molecules (alkenes) open up their double bonds and join together to form?
polymer chains
What is the only product when monomers react in addition polymerisation?
the polymer
Why does an addition polymer contain exactly the same type and number of atoms as the monomers that formed it?
when monomers react in addition polymerisation, the only product is the polymer
How do the type and number of atoms differ in an addition polymer from the monomers that formed it?
they don't; the only product when monomers react in addition polymerisation is the polymer
How do you draw the displayed formula of an addition polymer from the displayed formula of its monomer?
draw the two alkene carbons; replace the double bond with a single bond; add an extra single bond to each of the carbons; fill in the rest of the groups in the same way they surround the double bond in the monomer; put a pair of brackets around the repeating bit;put an n after it to show there are lots of monomers
What part of the displayed formula of an addition polymer shows there are lots of monomers?
the n after the brackets around the repeating
How do you get the displayed formula of the monomer from the displayed formula of the polymer?
draw out the repeating bit of the polymer; get rid of the two bonds going through the brackets; put a double bond between the carbons
How do we show that there can be any number of monomers with the displayed formula of a monomer?
the n before the bracktes
How do we get the name of the polymer?
poly(type of monomer); eg propene becomes poly(propene)
general formula for an alcohol
C(n)H(2n+1)OH
C(n)H(2n+1)OH
general formula for an alcohol
What is the functional group of alcools?
OH
To show an alcohol, would it be CH₃OH or CH₄OH?
CH₄OH
word equation of alcohol undergoing complete combustion
alcohol + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
What four alcohols are soluble in water?
methanol, ethanol,propanol, butanol
What four alcohols are soluble in water, the solution having a neutral pH?
methanol, ethanol,propanol, butanol
What four alcohols react with sodium to give hydrogen as one of the products if this reaction?
methanol, ethanol,propanol, butanol
What do methanol, ethanol,propanol, butanol, akk react with to have hydrogen as one of the products?
sodium
What is one of the products when methanol, ethanol,propanol, butanol, react with sodium?
hydrogen
How can alcohols be oxidised, producing a carboxylic acid?
reacting with oxygen
What's the product after an alcohol is oxdised by reacting with oxygen?
a carboxylic acid
What carboxylic acid is produced when methanol is oxidised?
methanoic acid
What carboxylic acid is produced when ethanol is oxidised?
ethanoic acid