maps
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Thematic map
A map that shows a specific them or type of data (like population, climate, income)
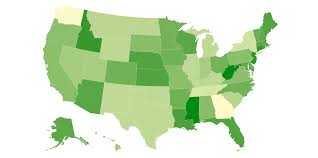
Choropleth map
Uses colors or shading to show data levels in different areas(ex: darker = more population)
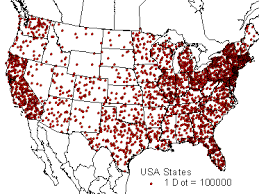
Dot distribution map
Uses dots to represent how often something happens. More dots = more of that thing (farms, people, etc)
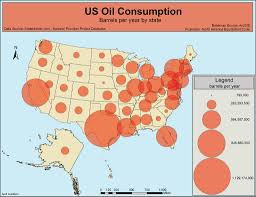
Graduated symbol map
Uses different-sized symbols (like circles) to show amount. Bigger symbol = more of the variable
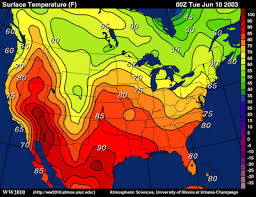
Isoline map
Uses lines to connect equal values (like temperature and elevation) common in weather maps
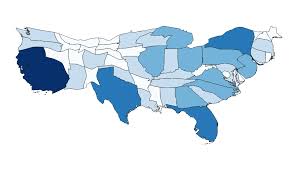
Cartogram
Disorts the size of places to show data. For example, a country with more people looks larger than one with less
Map projections
all map projections distort some part of the Earths surface.
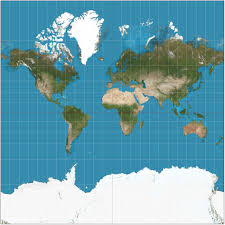
Mercator
Good for navigation (preserves direction)
Disorts size
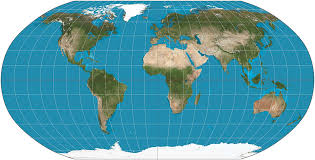
Robinson
Tries to balance disortions of size, shape, distance, and direction. Looks realistic, good for general use
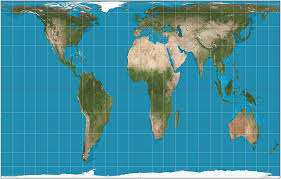
Peters
Keeps area (size) accurate, especially for countries near the equator. Distorts shapes — makes continents look stretched or squished
HM: Edge city
A large center of business, shopping, and entertainment that develops on the outskirts of a major city, usually near highways or at transportation intersections.
HM: First agricultural revolution
Around 10,000 years ago. Humans began farming and domesticating animals instead of hunting and gathering. Result: permanent settlements, population growth, early civilizations
HM: Second agricultural revolution
Around 1700-1800s(during the industrial revolution). New tools, machines and farming methods(like the seed drill and crop rotation) introduced. Result: increased food production, supported urbanization, and industrial growth
HM: Green (Third agricultural) revolution
Around 1950s-1970s. Use of high-yield seeds, chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and irrigation. Result: boosted food production (especially in developing countries) but also raised concerns about sustainability and environmental harm.