Biology - Midterm Exam 2022
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/211
Last updated 1:30 PM on 12/8/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
212 Terms
1
New cards
Biology
the scientific study of life
2
New cards
Hypothosis
An educated guess that attempts to explain an observation or answer a question.
3
New cards
The Scientific Method
A series of steps followed to solve problems including collecting data, formulating a hypothesis, testing the hypothesis, and stating conclusions.
4
New cards
independent variable
The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied.
5
New cards
Dependant variable
the variable that relies on the independant variable
6
New cards
Control
In an experiment, the standard that is used for comparison
7
New cards
Proton (positive)
A subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
8
New cards
Neutron (neutral)
A subatomic particle that has no charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
9
New cards
Electron (negative)
A subatomic particle that has a negative charge
10
New cards
valance electrons
the number of electrons in the outermost energy level
11
New cards
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
12
New cards
atomic mass
The average mass of all the isotopes of an element
13
New cards
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
14
New cards
Electronegativity
A measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons
15
New cards
covalent bond
A chemical bond that involves sharing a pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule
16
New cards
ionic bond
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
17
New cards
Polar bonds
a covalent bond in which electrons are shared unequally
18
New cards
nonpolar covalent bond
a covalent bond in which the electrons are shared equally by the two atoms
19
New cards
surface tension
A measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid
20
New cards
specific heat ionization
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree celsius; the heat required to ionize a substance; the amount required to ionize one mole.
21
New cards
pH
a measure of how acidic/basic water is
22
New cards
Acid
A substance that increases the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution.
23
New cards
Base
A substance that decreases the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution.
24
New cards
Eukaryotic cells
Contain a nucleus and other organelles that are bound by membranes.
25
New cards
prokaryotic cell
A type of cell lacking a membrane-enclosed nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles; found only in the domains Bacteria and Archaea.
26
New cards
Organelle
A tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell
27
New cards
Cytosol
Fluid portion of cytoplasm
28
New cards
plasma membrane
A selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells
29
New cards
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
30
New cards
nuclear envelope
layer of two membranes that surrounds the nucleus of a cell
31
New cards
Nucelus
Control center of the cell
32
New cards
Nucleoli
dense masses of RNA and protein that manufacture ribosomes, several of these are located in the nucleus.
33
New cards
Nuclear Pore
a protein-lined channel in the nuclear envelope that regulates the transportation of molecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm
34
New cards
Ribosomes
site of protein synthesis; makes protein
35
New cards
coupled transport
The movement of a substance against its electrochemical gradient (from lower to higher concentration, or from opposite charge to like charge) using the energy provided by the simultaneous movement of a different chemical down its electrochemical gradient.
36
New cards
receptor proteins
Proteins that transmit information in and out of cells. They allow communication between cells.
37
New cards
Ligands (cargo)
A molecule that binds specifically to a receptor site of another molecule.
38
New cards
Receptor - mediated endocytosis
The movement of specific molecules into a cell by the inward budding of membranous vesicles containing proteins with receptor sites specific to the molecules being taken in; enables a cell to acquire bulk quantities of specific substances.
39
New cards
Pinocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which the cell ingests extracellular fluid and its dissolved solutes.
40
New cards
Phagocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which a cell eats large particles or whole cells
41
New cards
Exocytosis
Process by which a cell releases large amounts of material
42
New cards
potential energy
stored energy
43
New cards
Enthalpy
The heat content of a system at constant pressure
44
New cards
Entropy
A measure of disorder or randomness.
45
New cards
free energy
energy that is available to do work
46
New cards
Exergonic
releases energy
47
New cards
Endergonic
requires energy
48
New cards
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
49
New cards
coupled reactions
pairs of chemical reactions in which some of the energy released from the breakdown of one compound is used to create a bond in the formation of another compound
50
New cards
Rate
A ratio that compares two quantities measured in different units
51
New cards
Enzymes
Catalysts for chemical reactions in living things
52
New cards
activation energy
Energy needed to get a reaction started
53
New cards
transition state
a high-energy intermediate state of the reactants during a chemical reaction that must be achieved for the reaction to proceed
54
New cards
Substrate
reactant of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction
55
New cards
Cofactors
nonprotein enzyme helpers
56
New cards
Inhibitor
A substance that slows down or stops a chemical reaction
57
New cards
competative inhibition
when molecules similar to a substrate compete for placement on the active site of an enzyme
58
New cards
noncompetitive inhibitor
A substance that reduces the activity of an enzyme by binding to a location remote from the active site, changing its conformation so that it no longer binds to the substrate.
59
New cards
uncompetative inhibition
results when the inhibitor binds only with the enzyme susbtrate complex (vmax decreased, Km decreased)
60
New cards
feedback inhibition
A method of metabolic control in which the end product of a metabolic pathway acts as an inhibitor of an enzyme within that pathway.
61
New cards
allosteric interactions
the modification of an enzyme's configuration through the binding of an activator or inhibitor at a specific binding site on the enzyme
62
New cards
Chloroplast (will need to draw/ label a diagram)
An organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs
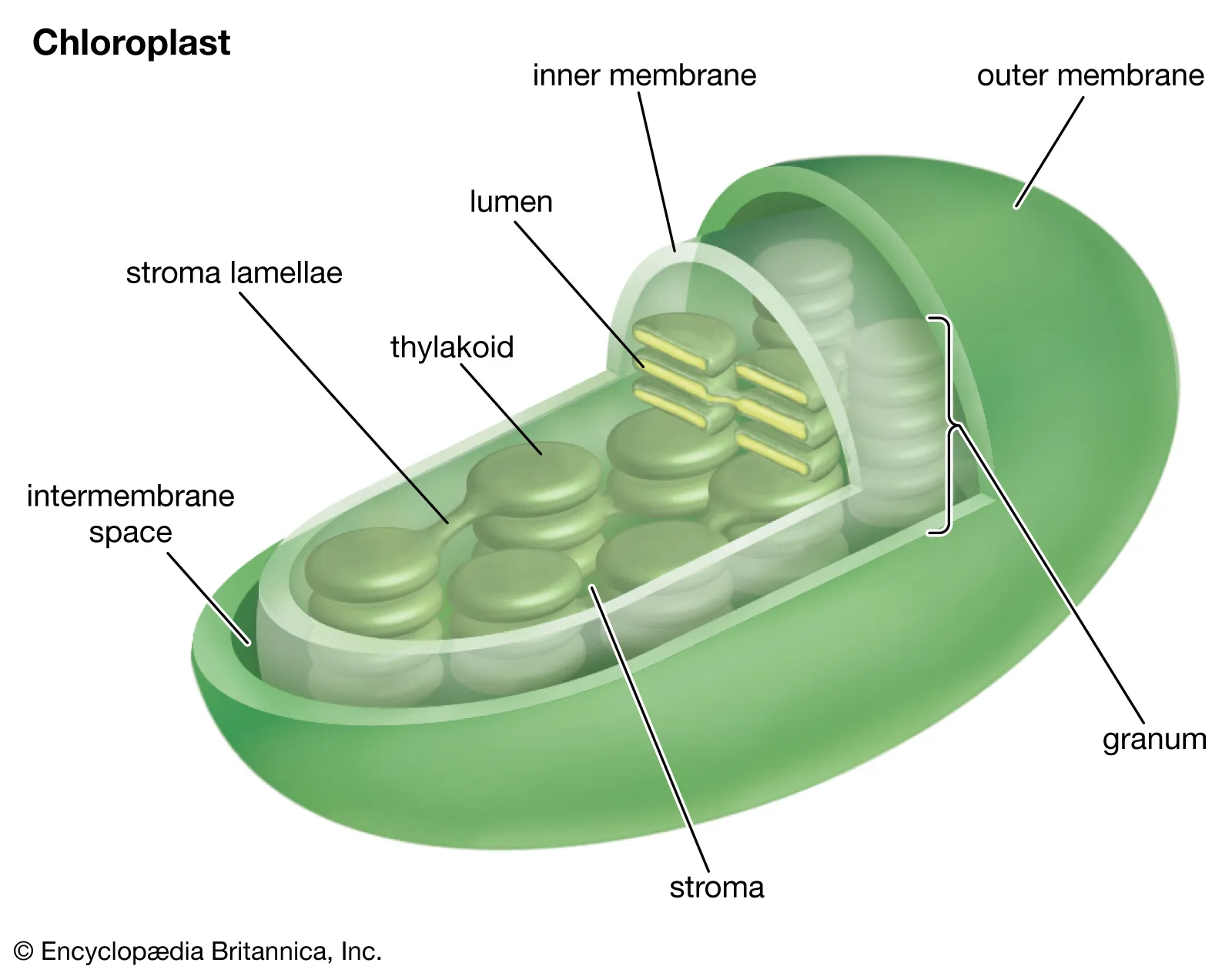
63
New cards
Chlorophyll
A green pigment found in the chloroplasts of plants, algae, and some bacteria
64
New cards
Thylakoid
A flattened membrane sac inside the chloroplast, used to convert light energy into chemical energy.
65
New cards
Granum
stack of thylakoids
66
New cards
Stroma
fluid portion of the chloroplast; outside of the thylakoids
67
New cards
light reactions
reactions of photosynthesis that use energy from light to produce ATP and NADPH
68
New cards
Calvin Cycle
reactions of photosynthesis in which energy from ATP and NADPH is used to build high-energy compounds such as sugars
69
New cards
Photosystem
One of two light-harvesting units of a chloroplast's thylakoid membrane; it uses the P700 reaction-center chlorophyll.
70
New cards
Photosystem II
One of two light-harvesting units of a chloroplast's thylakoid membrane; it uses the P680 reaction-center chlorophyll.
71
New cards
reaction center
The location of the first light driven chemical reaction of photosynthesis.
72
New cards
climate
Overall weather in an area over a long period of time
73
New cards
Microclimate
Climate within a small area that differs significantly from the climate of the surrounding area
74
New cards
Biome
A group of ecosystems that share similar climates and typical organisms
75
New cards
disturbance
an event, caused by physical, chemical, or biological agents, resulting in changes in population size or community composition
76
New cards
Thermocline
a layer in a large body of water, such as a lake, that sharply separates regions differing in temperature, so that the temperature gradient across the layer is abrupt.
77
New cards
turnover
Seasonal changes in warm and cool water layers in lakes.
78
New cards
Distribution
The arrangement of something across Earth's surface.
79
New cards
Density
the degree of compactness of a substance; mass/volume
80
New cards
Dispersion
the pattern of spacing among individuals within the boundaries of the population
81
New cards
survivorship curve
Graph showing the number of survivors in different age groups for a particular species.
82
New cards
exponential growth
Growth pattern in which the individuals in a population reproduce at a constant rate
83
New cards
intrinsic rate of increase
rate at which the population of a species would grow if it had unlimited resources
84
New cards
carrying capacity
Largest number of individuals of a population that a environment can support
85
New cards
logistic growth
Growth pattern in which a population's growth rate slows or stops following a period of exponential growth
86
New cards
life history
Traits that affect an organism's schedule of reproduction and survival.
87
New cards
Semelparous
single reproductive episode before death
88
New cards
Iteroparous
Repeated reproduction throughout lifetime
89
New cards
K-selection
Selection for life history traits that are sensitive to population density; also called density-dependent selection.
90
New cards
r-selection
Selection for life history traits that maximize reproductive success in uncrowded environments; also called density-independent selection.
91
New cards
density dependent
Referring to any characteristic that varies according to an increase in population density.
92
New cards
density-independent
Referring to any characteristic that is not affected by population density.
93
New cards
metapopulation
a group of spatially distinct populations that are connected by occasional movements of individuals between them
94
New cards
age structure
number of males and females of each age in a population
95
New cards
ecological footprint
the impact of a person or community on the environment, expressed as the amount of land required to sustain their use of natural resources.
96
New cards
interspecific interactions
relationships between species in a community
97
New cards
competition
the struggle between organisms to survive in a habitat with limited resources
98
New cards
exploitation
Taking advantage of a weaker group
99
New cards
Predation
An interaction in which one organism kills another for food.
100
New cards
Herbivory
interaction in which one animal (the herbivore) feeds on producers (such as plants)